Physics II Lesson 4: Film Interference and Spectroscopy Part I
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Give an example of when Thin Film Interference might occur in real life.
It might occur when you have a thin film of oil on top of water like when it rains on a road and then a little oil gets on top of the water. Another example would be when you blow a bubble with the thin film of soap around the bubble.
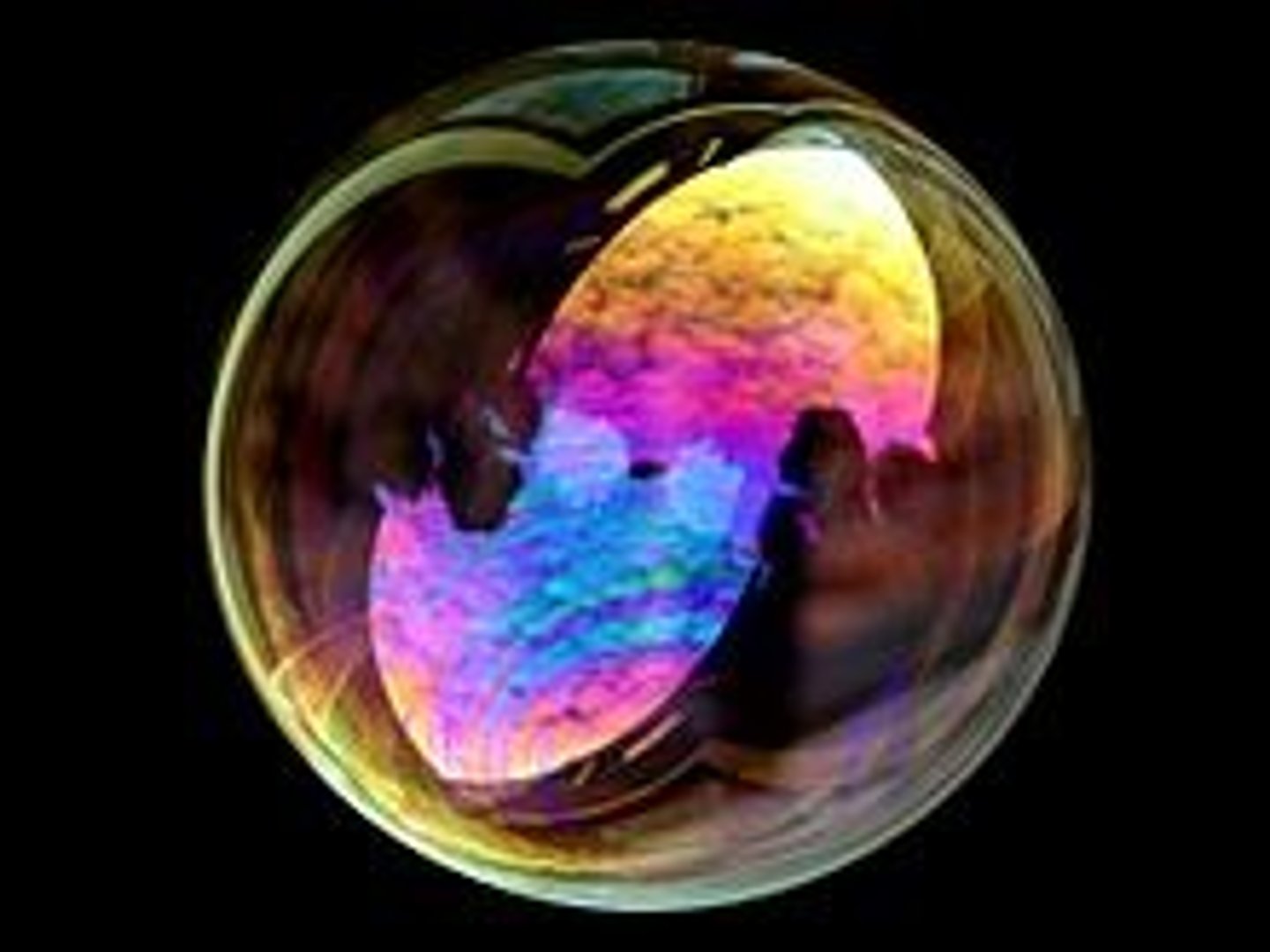

True or False? The speed of light is always constant no matter what medium it is travelling through.
False. The speed of light is variable depending upon the medium it is travelling through.
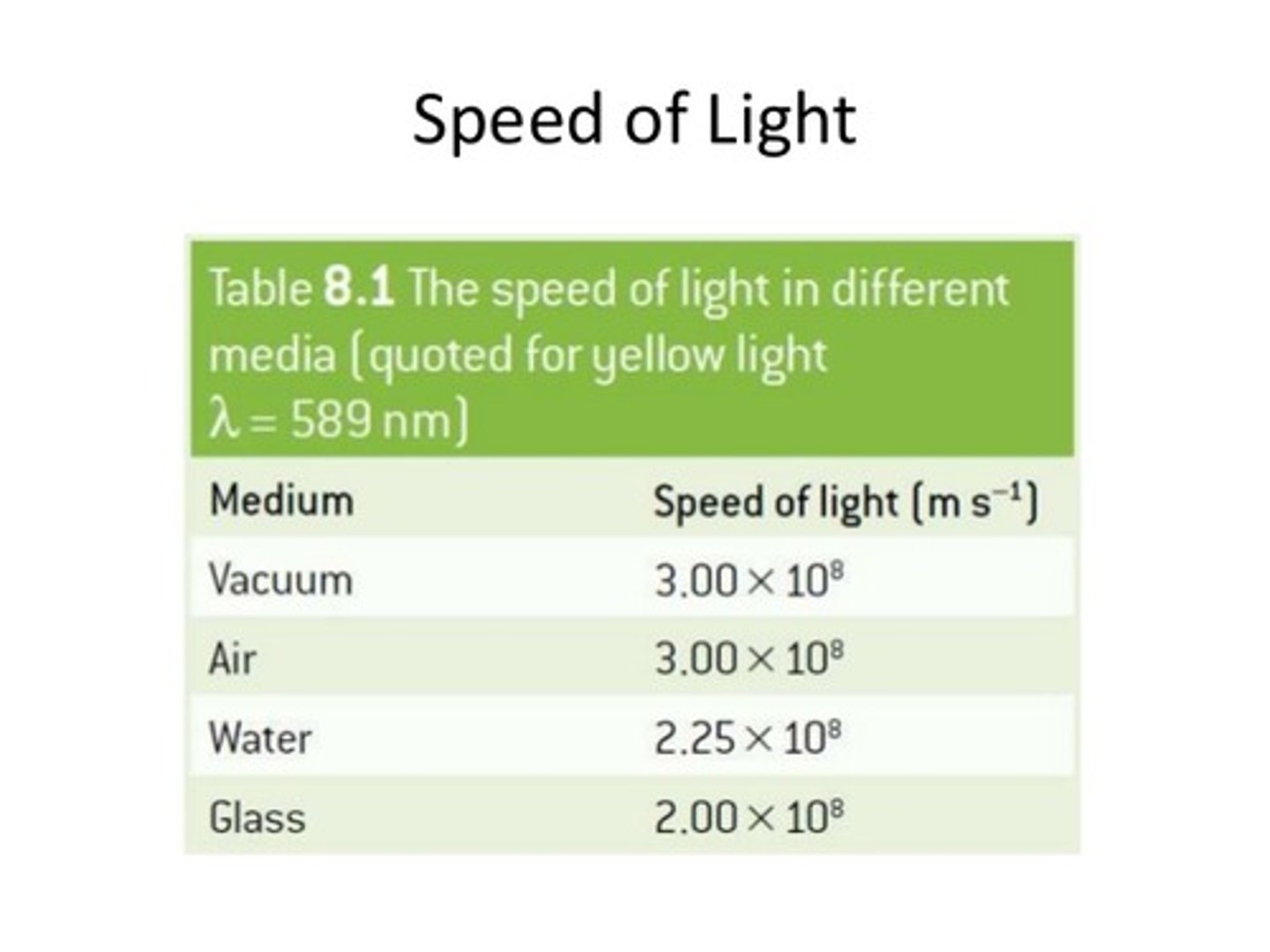
CRB True or false? The more densely the molecules are packed in the medium that light travels through, the faster the speed.
False. The more densely the molecules are packed in the medium that light travels through, the slower the speed.
This is why the speed of light in a vacuum is 3 x 10^8 m/s, whereas in Water, it is only 2.25 x 10^8 m/s!
What will Thin Film Interference look like when you see it/What visual phenomenon will you see? Why does this occur?
You will see a rainbow. This is due to the constructive and destructive interference that occurs due to reflection off the top interface and the second interface.
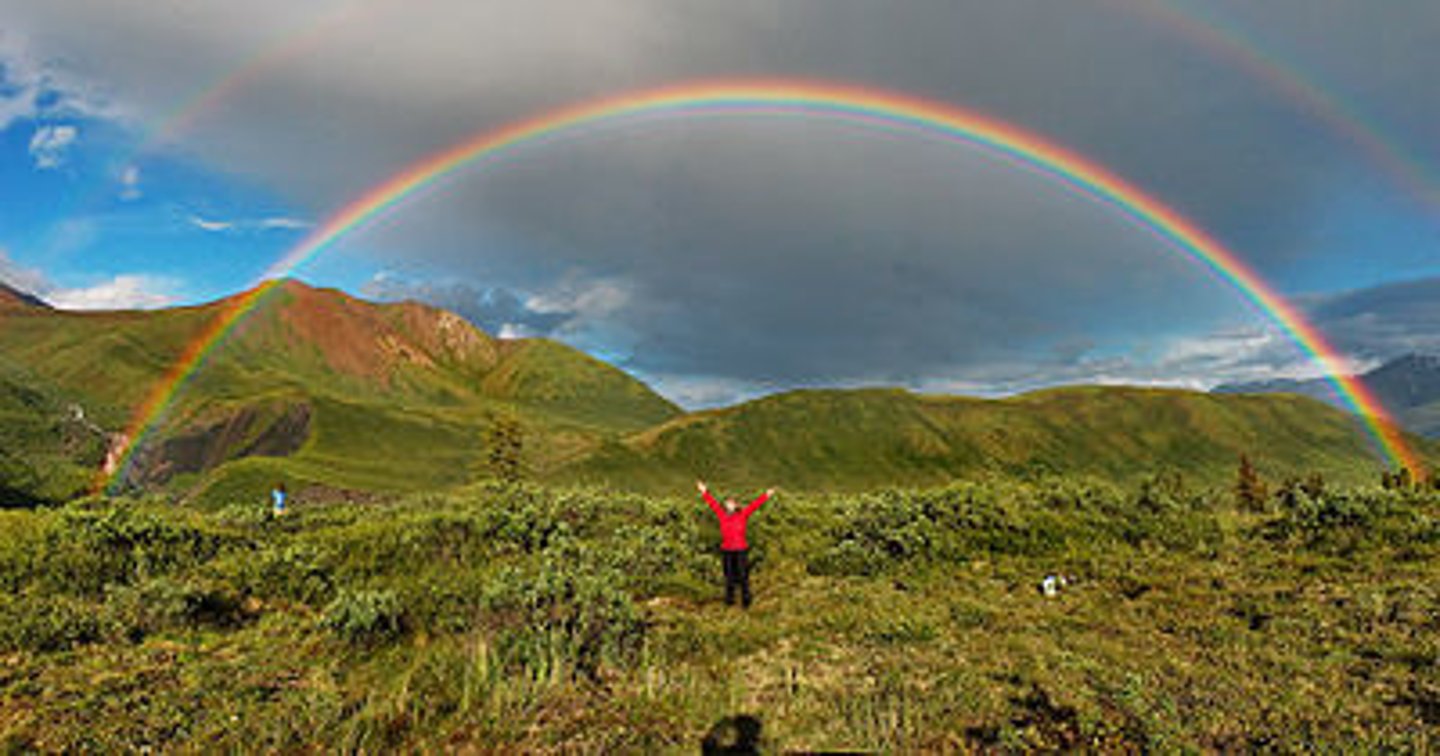

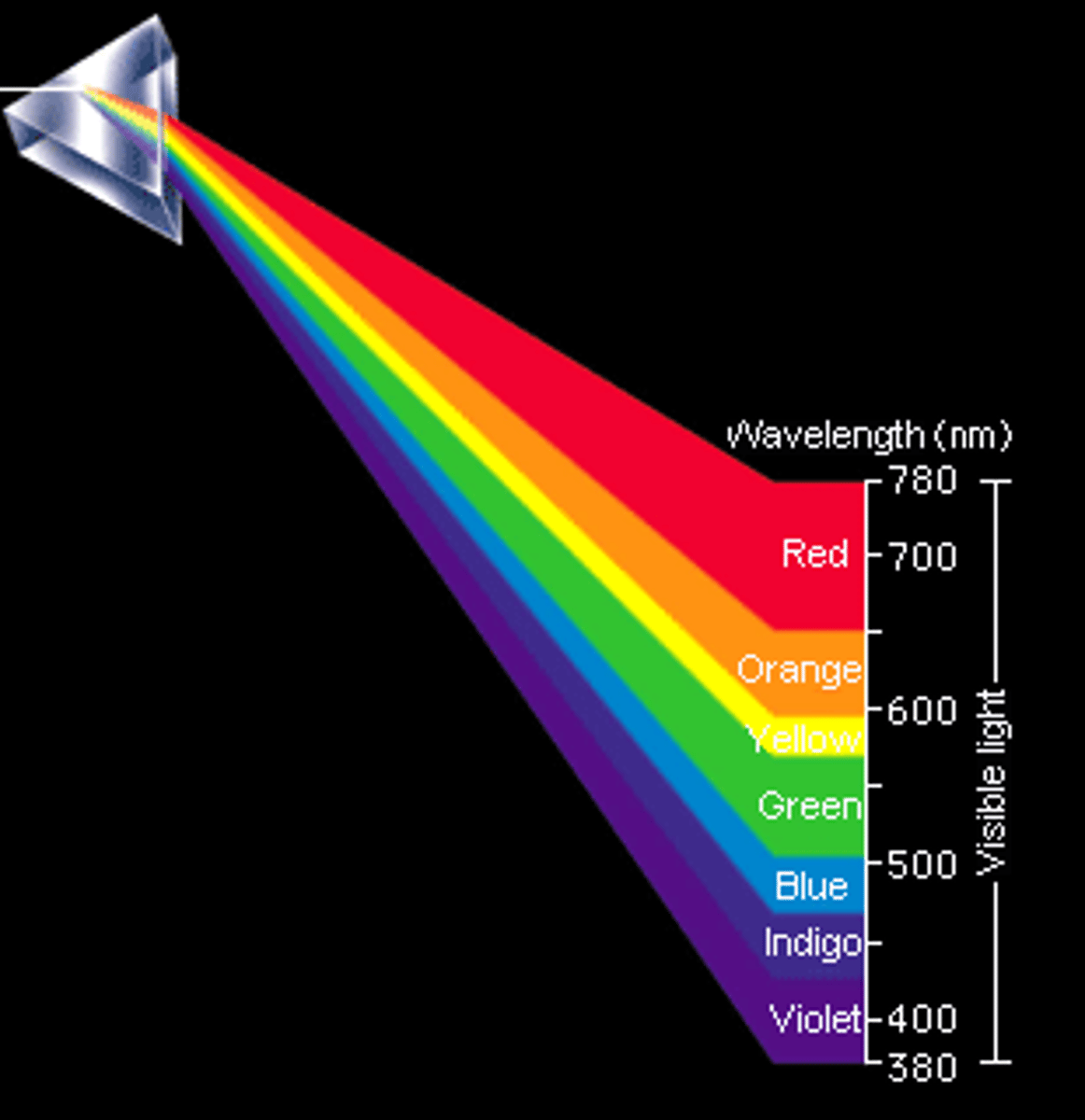
CRB Rainbows are a great way of remembering the order of colors of visible light! From longest to shortest wavelength, Label the rainbow!
When does a π Shift occur in terms of reflection?
A π Shift occurs when light is reflected off a medium that has a lower speed of light (aka a higher index of refraction) than the medium it is travelling through.

Why do we use the wavelength (λ) in the thin film as opposed to the wavelength of the light in the air/original medium?
This is because we are trying to determine by how far the light shifted, and the shifting occurs while the light is in the thin film.
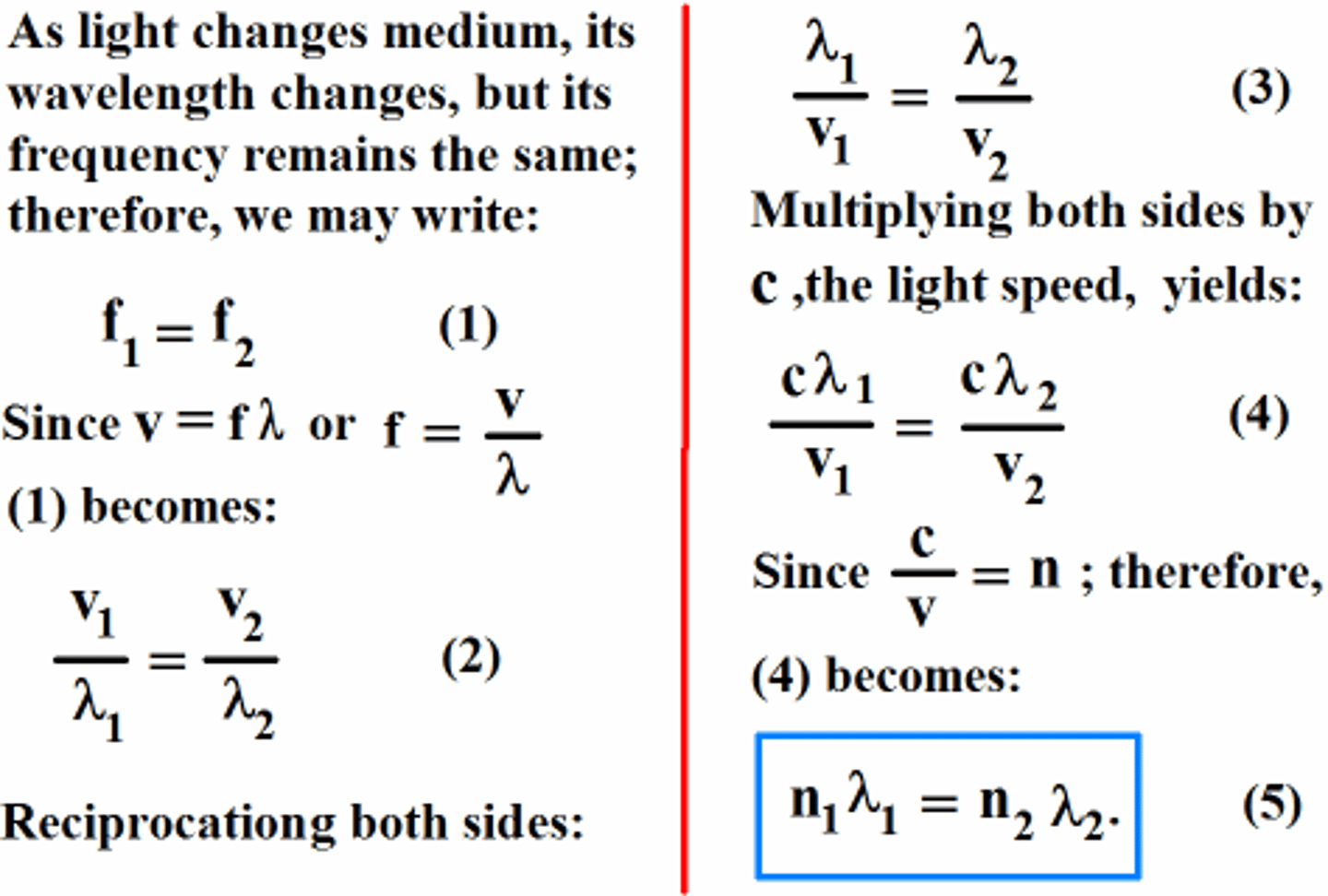
What equation can be used to determine the wavelength of light in the medium when given the speed of light in the air and in the medium? How is this equation derived?
v1 / λ1 = v2 / λ2
v1 = Velocity in the original medium
λ1 = Wavelength in the original medium
v2 = Velocity in the thin film
λ2 = Wavelength in the thin film
This equation can be derived by setting both equations equal to f as f is the same in both the air and the thin film. f is constant no matter the medium.
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What equation can be used to determine the wavelength of light in the medium when given the index of refraction in the air and in the medium? How is this equation derived?
n1 ⋅ λ1 = n2 ⋅ λ2
n1 = Index of Refection in the original medium
λ1 = Wavelength in the original medium
n2 = Index of Refraction in the thin film
λ2 = Wavelength in the thin film
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB The previous note card writes out Snell's Law (which relates the Index of Refraction with the wavelength of the traveling wave). Write this out in a proportion form. How would the velocities v1 and v2 of the wave relate to these other terms?
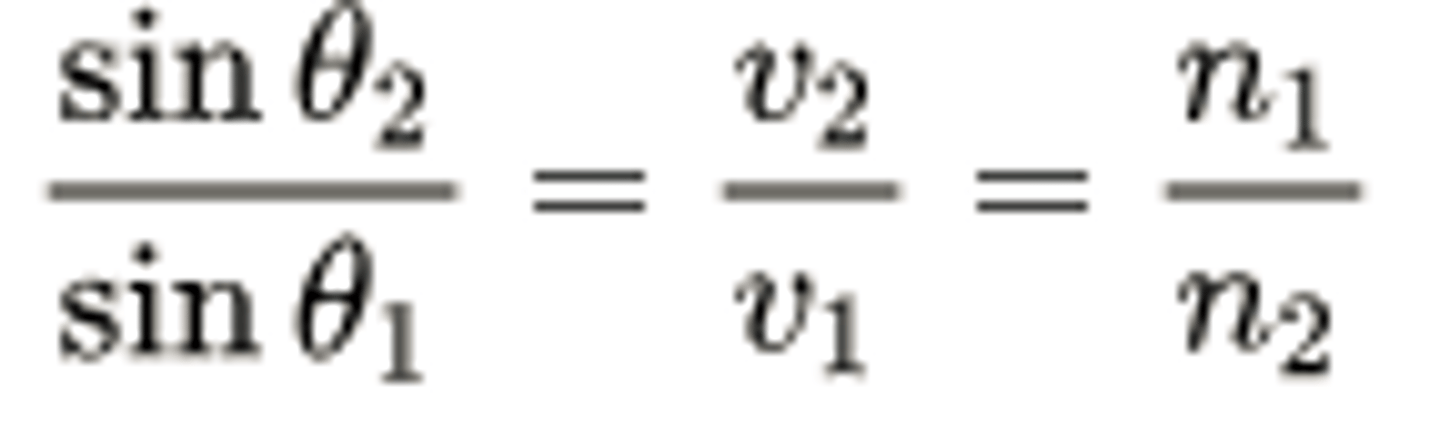
What equation can be used to relate wavelength to the thickness of the thin film (in the case of Constructive Interference) without a π Shift?
2t = mλ2
t = thickness of the thin film
m = integer (1,2,3...)
λ2 = wavelength of light in the thin film
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What equation can be used to relate wavelength to the thickness of the thin film (in the case of Destructive Interference) without a π Shift?
2t = (m + 1/2)λ2
t = thickness of the thin film
m = integer (1,2,3...)
λ2 = wavelength of light in the thin film
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
True or False? When a π Shift occurs simply use the opposite equation.
True. When a π Shift occurs simply use the opposite equation. You should do this because a π Shift shifts a wave by 180 degrees, which is the same thing as half a wavelength.
CRB Fill in the blanks: A π Shift will occur if the waves are reflected from a medium with _____________ ; no π Shift will occur if the waves are reflected from a medium with _____________.
(A) Higher index of refraction (n2 > n1), Equal index of refraction (n2 = n1).
(B) Lower index of refraction (n2 < n1), Equal index of refraction (n2 = n1).
(C) Lower index of refraction (n2 < n1), Higher index of refraction (n2 > n1).
(D) Higher index of refraction (n2 > n1), Lower index of refraction (n2 < n1).
(D) Higher index of refraction (n2 > n1), Lower index of refraction (n2 < n1).
A π Shift will occur if the waves are reflected from a medium with a higher index of refraction (n2 > n1); no π Shift will occur if the waves are reflected from a medium with a lower index of refraction (n1 < n2).
For further practice with thin film interference, look at the following example on a film of oil on water: http://physics.bu.edu/~duffy/PY106/Diffraction.html
For further practice with thin film interference, look at the following example on a film of oil on water: http://physics.bu.edu/~duffy/PY106/Diffraction.html
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
True or False. Electromagnetic Waves have both wave and particle characteristics.
True. Electromagnetic Waves have both wave and particle characteristics.
CRB Fill in the blanks: The Wave characteristics are best categorized as being ______________, whereas particle characteristics are best described as ____________.
(A) On a continuous spectrum, Quantized
(B) Discrete, Quantized
(C) Quantized, Discrete
(D) Discrete, On a continuous spectrum
(A) On a continuous spectrum, Quantized
The Wave characteristics are best categorized as being on a continuous spectrum, whereas particle characteristics are best described as Quantized.
Quantized means confined to a defined set of values, including a smallest value that can't be subdivided.
How was it discovered that Electromagnetic Waves have particle-like character?
It was found that they have discrete chunks of energy.
What equation is used to relate the energy of a photon to frequency?
E = hf
E = Energy of a photon
h = Plank's Constant (6.626⋅10^-34 J⋅s)
f = Frequency of the light
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You are doing an Infrared Spectroscopy during O Chem lab. You look deep down inside yourself and ask, "Why am I doing this?!!??!??!" If you are a true scientist, how might you respond?
You would say that you are performing IR spectroscopy in order to determine which functional groups your compound of interest contain. Now, why you are taking O Chem lab and spending your life with chemicals, that's another story... :)
You produce a beautiful IR spectra and notice that there is 100 percent transmittance in some areas but not in others. What is happening in those areas that do not have 100 percent transmittance?
At that wavelength of light, 100 percent of the wave is not being transmitted through the compound because it is being absorbed by a bond causing it to stretch.
CRB Which of the following best describes the relationship between Transmittance and Absorbance?
(A) Transmittance + Absorbance = 100%
(B) Transmittance x Absorbance = 100%
(C) Transmittance / Absorbance = 100 %
(D) Transmittance - Absorbance = 100%
(A) Transmittance + Absorbance = 100%
This also means that 100%- (Transmittance) = Absorbance!
You take a closer look at your IR spectra and notice that instead of wavelength on the x axis, it says, "wavenumber." What in the heck is wavenumber?!!?
Wavenumber is the inverse of the wavelength (1/λ) with units of cm^-1. It directly correlates with frequency according to the relationship f = c/λ. The larger the wavelength, the smaller, the wavenumber.
Compare the Diagnostic Region and the Fingerprint Region of an IR Spectra.
The Diagnostic Region of an IR Spectra occurs above a wavenumber of 1500. It is useful for identifying which functional groups are present in a compound.
The Fingerprint Region of an IR Spectra occurs below a wavenumber of 1500. It is not especially useful for determining functional groups, but every compound has a unique fingerprint region, which can allow you to exactly identify a compound given the proper tools.
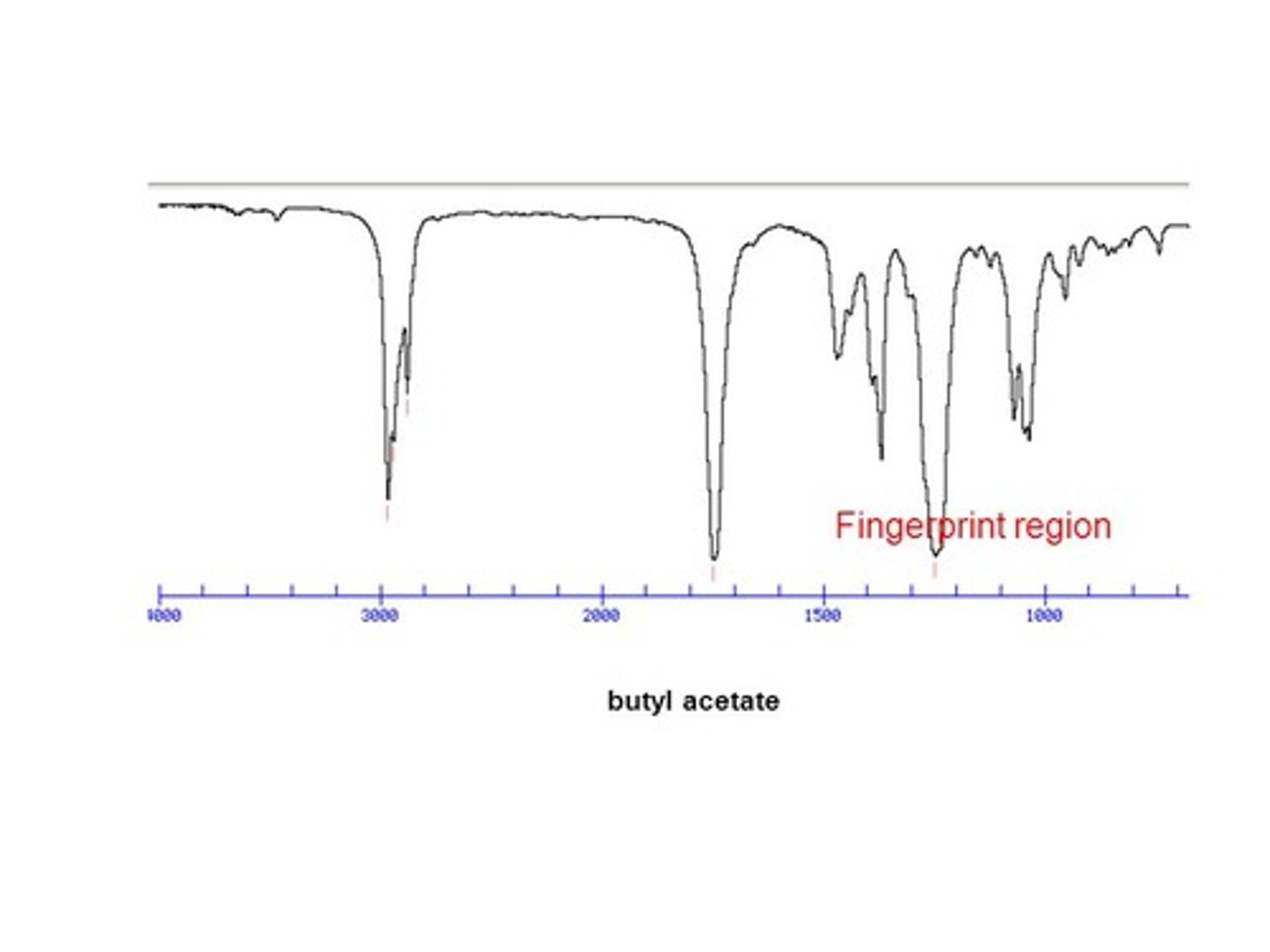
CRB Between the Fingerprint Region and the Diagnostic Region, which will be most helpful in identifying compounds from multiple-choice options on the MCAT?
The Diagnostic Region will be much more helpful! It would take an IR Master to recognize Fingerprint Regions, but by comparing the functional groups seen on the IR and the multiple choice options, an astute student should be able to pick out the option that best fits the diagnostic region of the IR Spectroscopy graph.
What equation relates the Force required to displace a spring and its displacement?
F = -kx
F = Force
k = Spring Constant
x = Displacement
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What equation can be used to relate frequency of a Spring (v) with the Spring constant (k)?
v = (1 / 2π)√(k/m)
v = Frequency
k = Spring Constant
m = Mass
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
As k increases, v ___________. As m increases, v ____________.
(A) Increases, Increases
(B) Increases, Decreases
(C) Decreases, Decreases
(D) Decreases, Increases
(B) Increases, Decreases
As k increases, v increases. As m increases, v decreases.
As k increases, v increases. As m increases, v decreases. How does this relate to IR Spectroscopy?
As k increases, v increases means that stronger bonds will vibrate faster and thus have a higher wavenumber.
As m increases, v decreases, which means that heavier atoms are going to vibrate slower, resulting in a smaller wavenumber.
CRB Based on how m relates to v, would you expect a Carbon-Oxygen bond or a Carbon-Nitrogen bond to have a smaller wavenumber? Why?
Because Oxygen is a slightly heavier atom than Nitrogen, we would expect that Carbon-Oxygen bond would have a slightly lower wavenumber than that Carbon-Nitrogen bond. The difference in mass is small, however, so it is not a huge difference!
OH results in a very broad or narrow signal in an IR Spectra? Why?
OH results in a broad signal because the Hydrogen bonding can be strong or weak between the various molecules that make up the substance of interest. There is a high amount of variability in the bond strength.
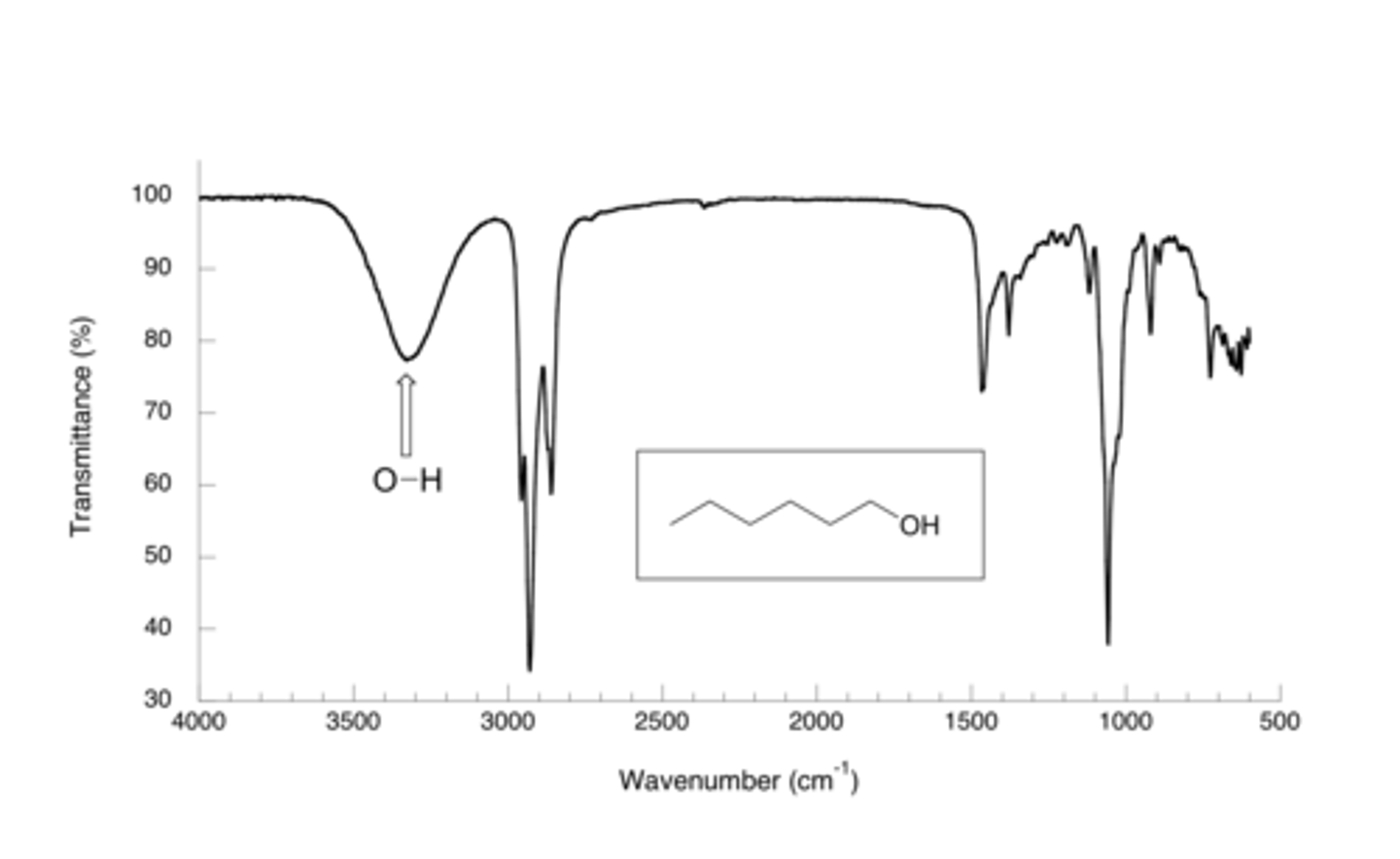
CRB Would you expect that same broad range to come from an N-H bond that you would of an O-H bond?
(A) Yes, because both Nitrogen and Oxygen are electronegative atoms and should Hydrogen Bond.
(B) Yes, because the Nitrogen has a less polarized bond with Hydrogen than Oxygen does, so the Hydrogen Bonding will be weaker but still there.
(C) No, because only Oxygen is an electronegative atom and should Hydrogen Bond.
(D) No, because the Nitrogen has a less polarized bond with Hydrogen than Oxygen does, and that less-partially-positive Hydrogen is less likely to Hydrogen bond.
(D) No, because the Nitrogen has a less polarized bond with Hydrogen than Oxygen does, and that less-partially-positive Hydrogen is less likely to Hydrogen bond.
The O-H bond has a broad peak around 3300 cm^-1, whereas the N-H bond has a narrow peak around 3300 cm^-1.
CRB Hey, my carbonyl group has a double bond to Oxygen, so it must also have a broad peak too, right?
No, because there is no ability to Hydrogen Bond! That partially-positive Hydrogen is needed to bond to the partially-negative Oxygen.
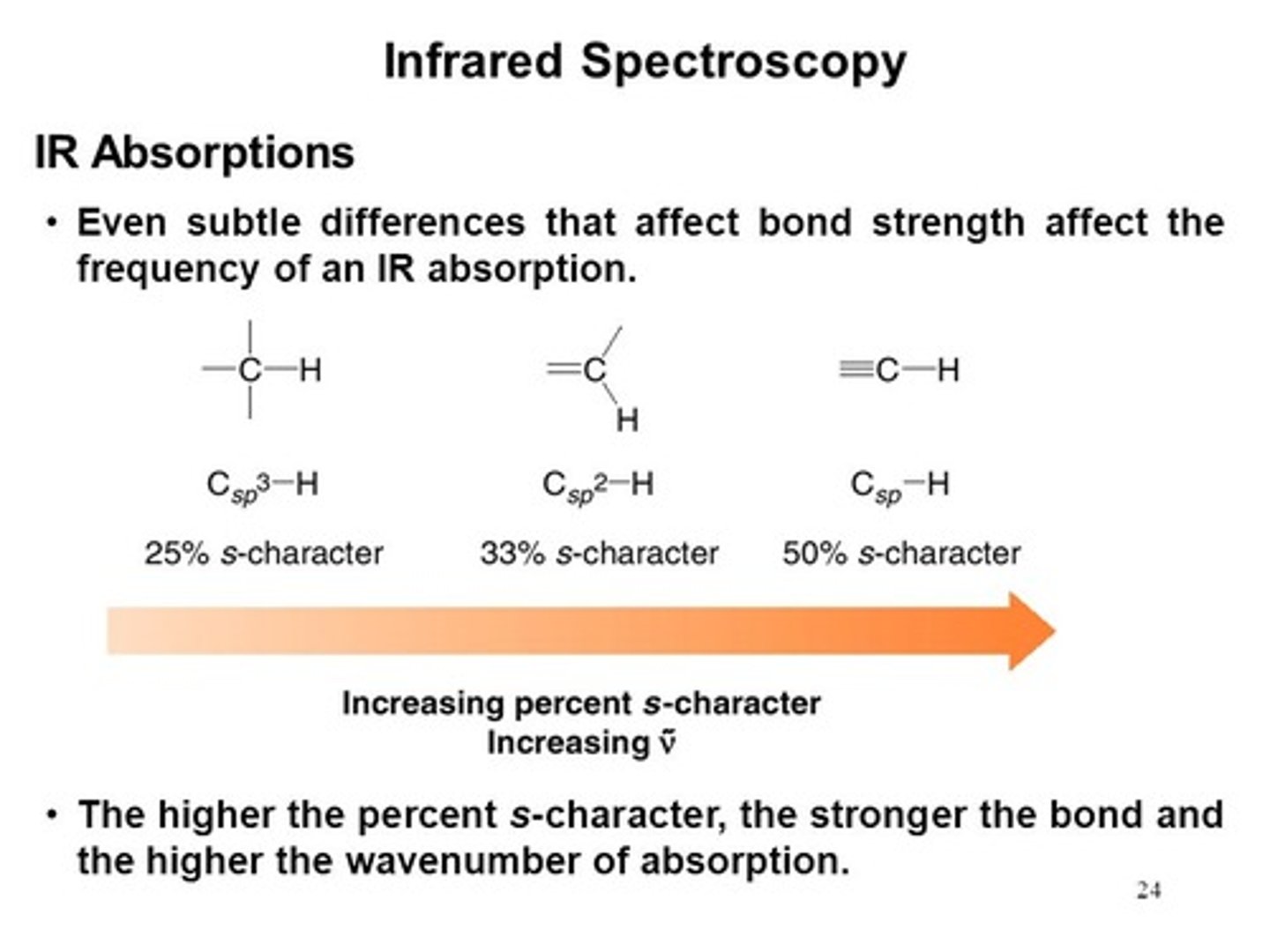
Put the following in order of lowest wavenumber to highest wavenumber:
I. Csp3-H
II. Csp2-H
III. Csp-H
(A) I < II < III
(B) I < III < II
(C) III < II < I
(D) III < I < I
(A) I < II < III
In order of lowest wavenumber to highest wavenumber: Csp3-H < Csp2-H < Csp-H. This is due to increasing s character in the bonds.
Which results in a stronger signal? C-C double bond or a C-O double bond? Why?
A C-O double bond will have a stronger signal than a C-C double bond as a C-O double bond has a larger dipole moment. A bond with a large Dipole Moment will result in a strong IR signal.
You see a narrow signal at 3600. What functional group are you dealing with?
An OH group without Hydrogen bonding will have a narrow signal at 3600.
You see a single narrow peak at 3100. What functional group are you dealing with?
A Csp2-H bond will have a narrow peak at 3100.
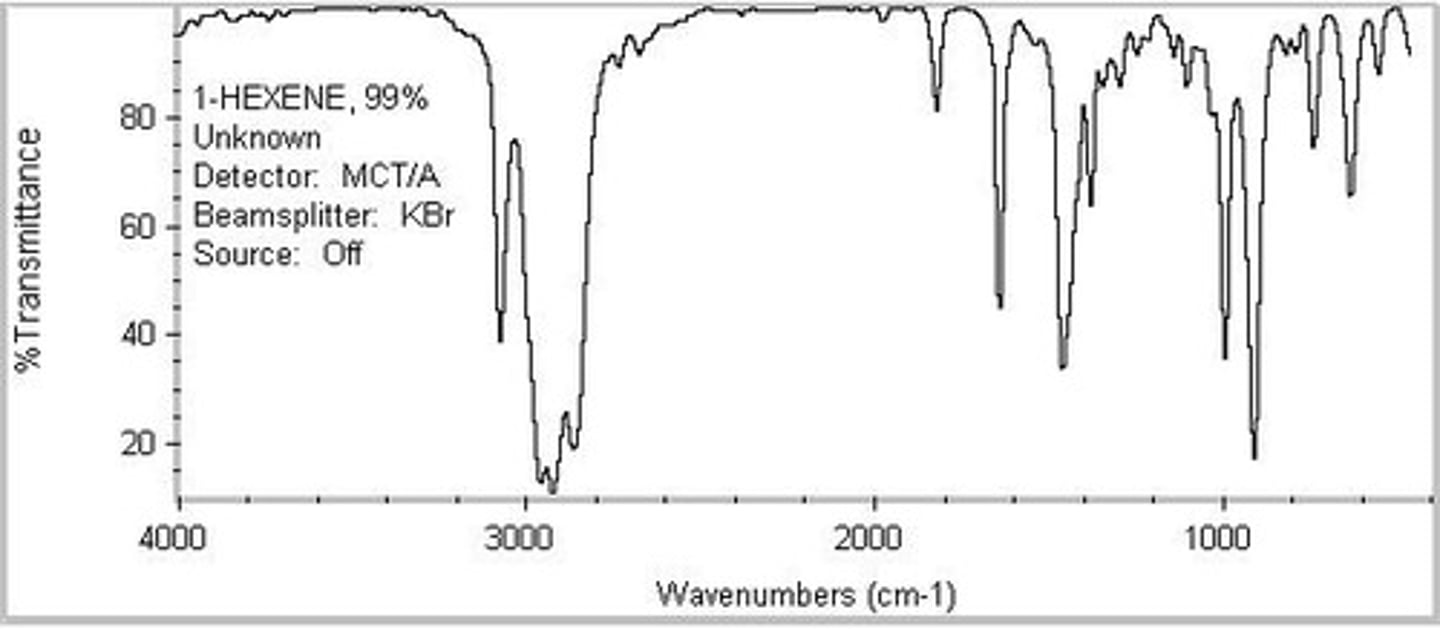
You see a broad signal between 2700 and 3600 (centered at 3000) with another narrow signal at 1700. What functional group are you dealing with?
A COOH group will have a broad signal between 2700 and 3600 (centered at 3000) with another narrow signal at 1700.
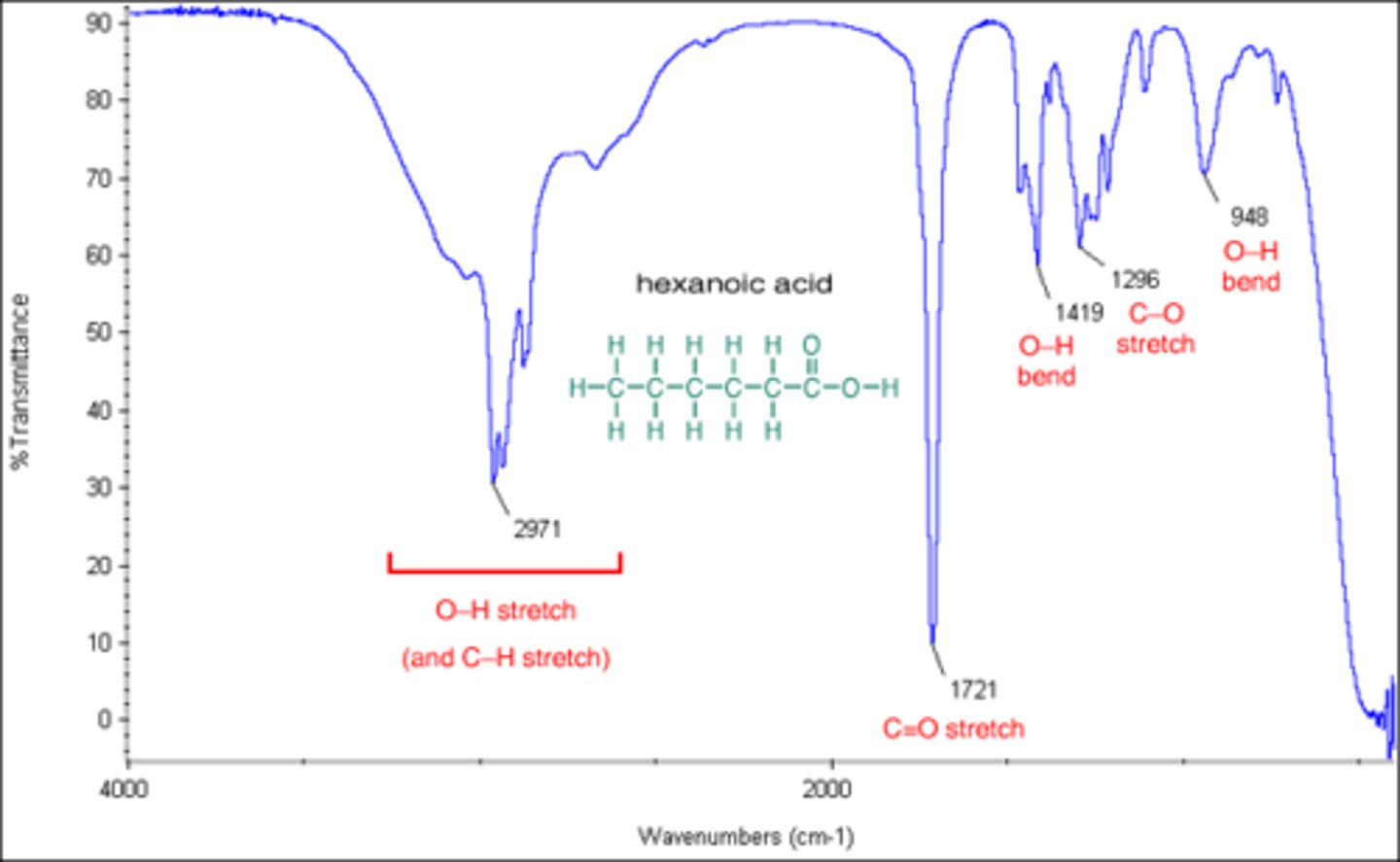
You see a single narrow peak at 3300. What functional group are you dealing with?
A Csp-H bond will have a narrow peak at 3300.
You see a narrow peak at 1540. What functional group are you dealing with?
A C-C Aromatic Double Bond will have a narrow peak between 1600 and 1450.
You see a broad signal between 3000 and 3600. What functional group are you dealing with?
An OH group with Hydrogen bonding will have a broad signal between 3000 and 3600.
You see a single narrow peak at 2900. What functional group are you dealing with?
A Csp3-H bond will have a narrow peak at 2900.
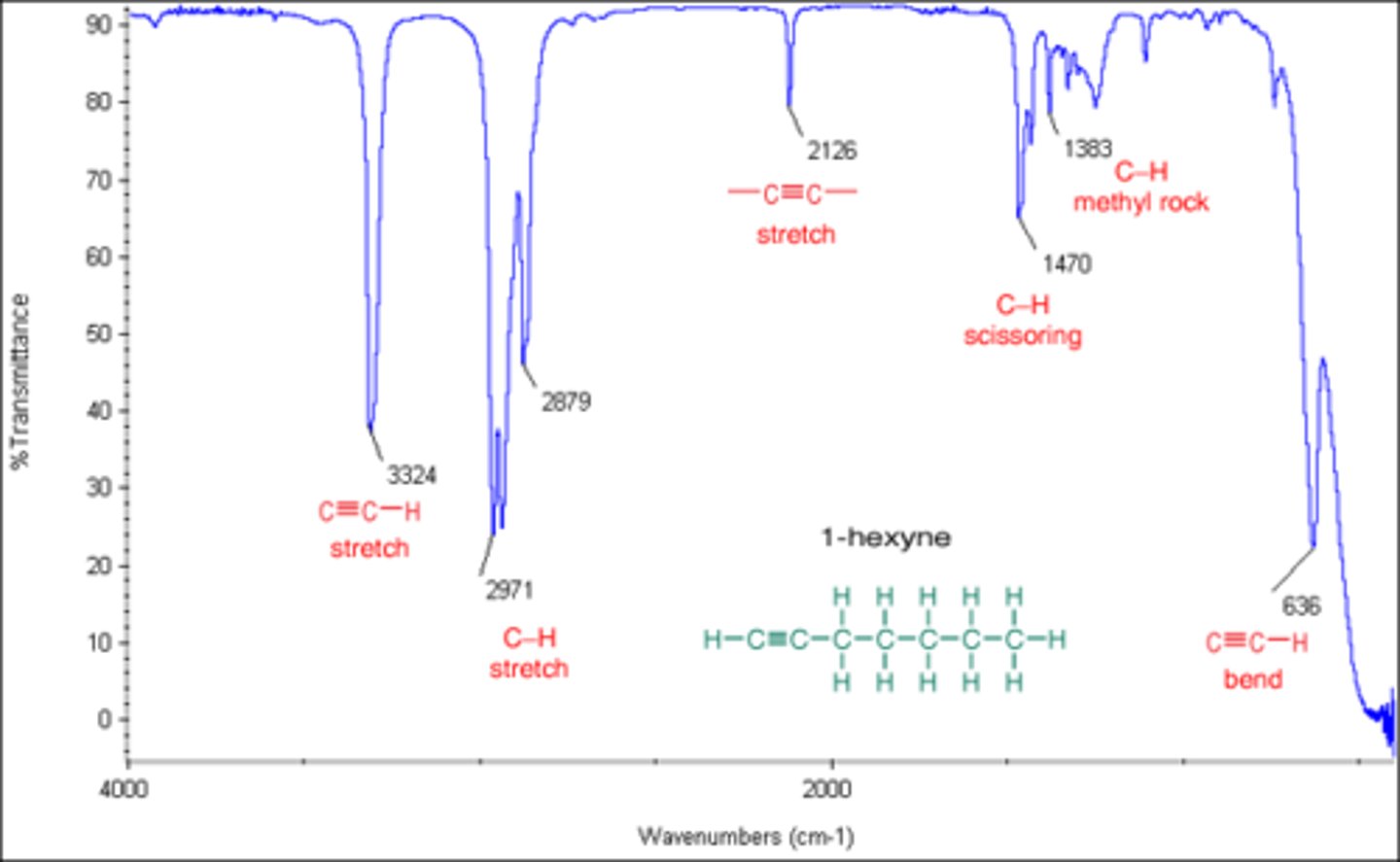
You see a narrow peak at 2100. What functional group are you dealing with?
A C-C Triple Bond will have a narrow peak at 2100.
CRB True or false? A C-C Triple bond will have two absorbances over 1000 cm^-1 apart if it is a terminal alkyne.
True. A C-C Triple bond will have two absorbances over 1000 cm^-1 apart if it is a terminal alkyne.
This is because the C-C triple bond itself has a narrow peak around 2100, and that sp-C-H bond has a narrow peak around 3300!
CRB Which of the following would have multiple, clearly separated absorbances in the Diagnostic Region of an IR Spectroscopy Graph?
I. Ether
II. Ester
III. Carboxylic Acid
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) III only
An Ether would have 2 C-O bonds around 1100 cm^-1, making it appear in the Fingerprint Region.
By the same token, the Ester would have that C=O peak around 1750, but its other peak would be that C-O peak around 1100 cm^-1, making it appear in the Fingerprint Region.
The Carboxyllic Acid will have the broad O-H peak around 3300 and the C=O peak around 1750, both clearly inside the Diagnostic Region.
You see a narrow peak at 1650. What functional group are you dealing with?
A C-C Double Bond will have a narrow peak at 1650.
You see a weak signal at 3400 and another at 3300. What functional group are you dealing with?
You are dealing with a Nitrogen bound to two Hydrogens.
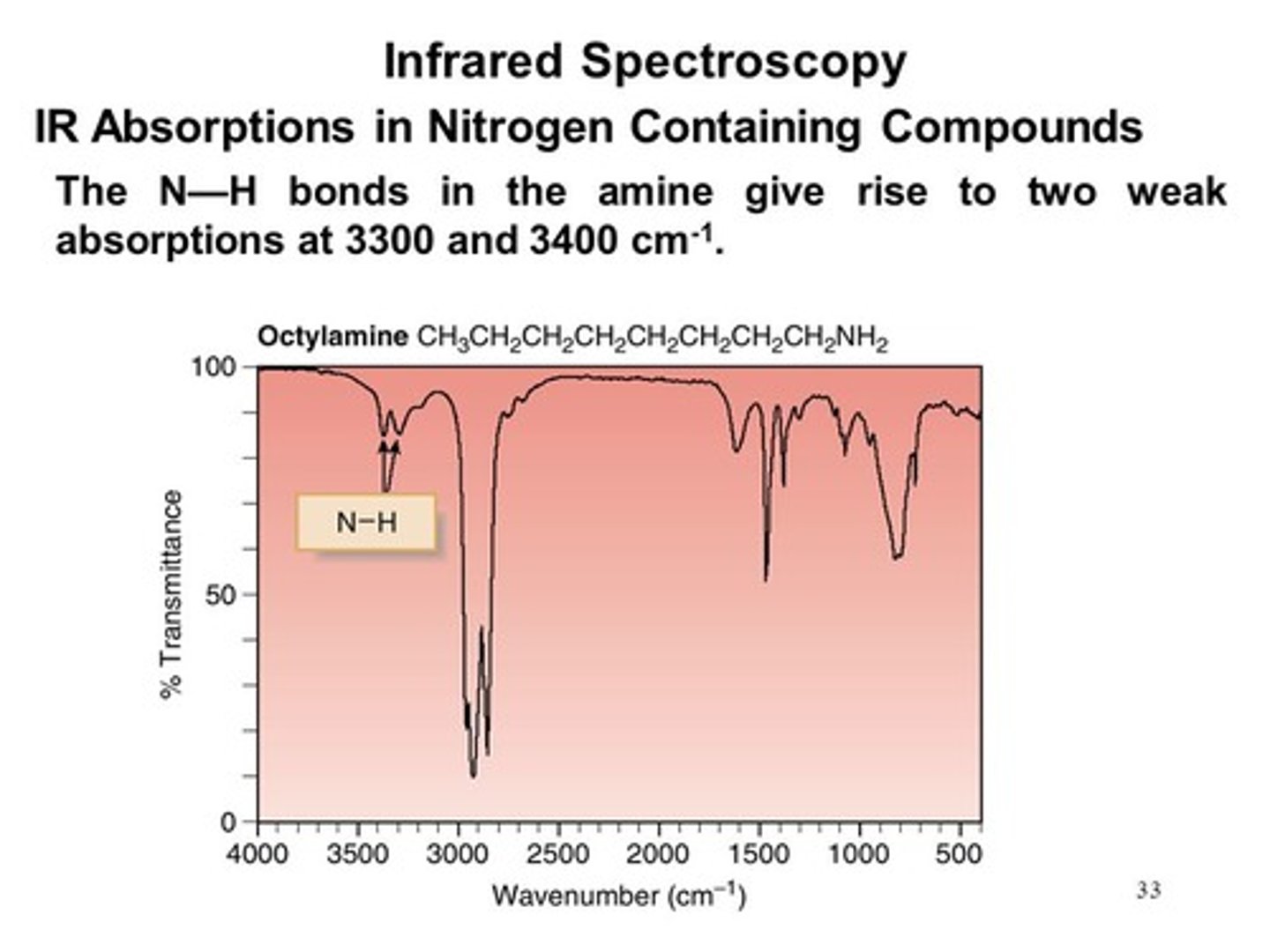
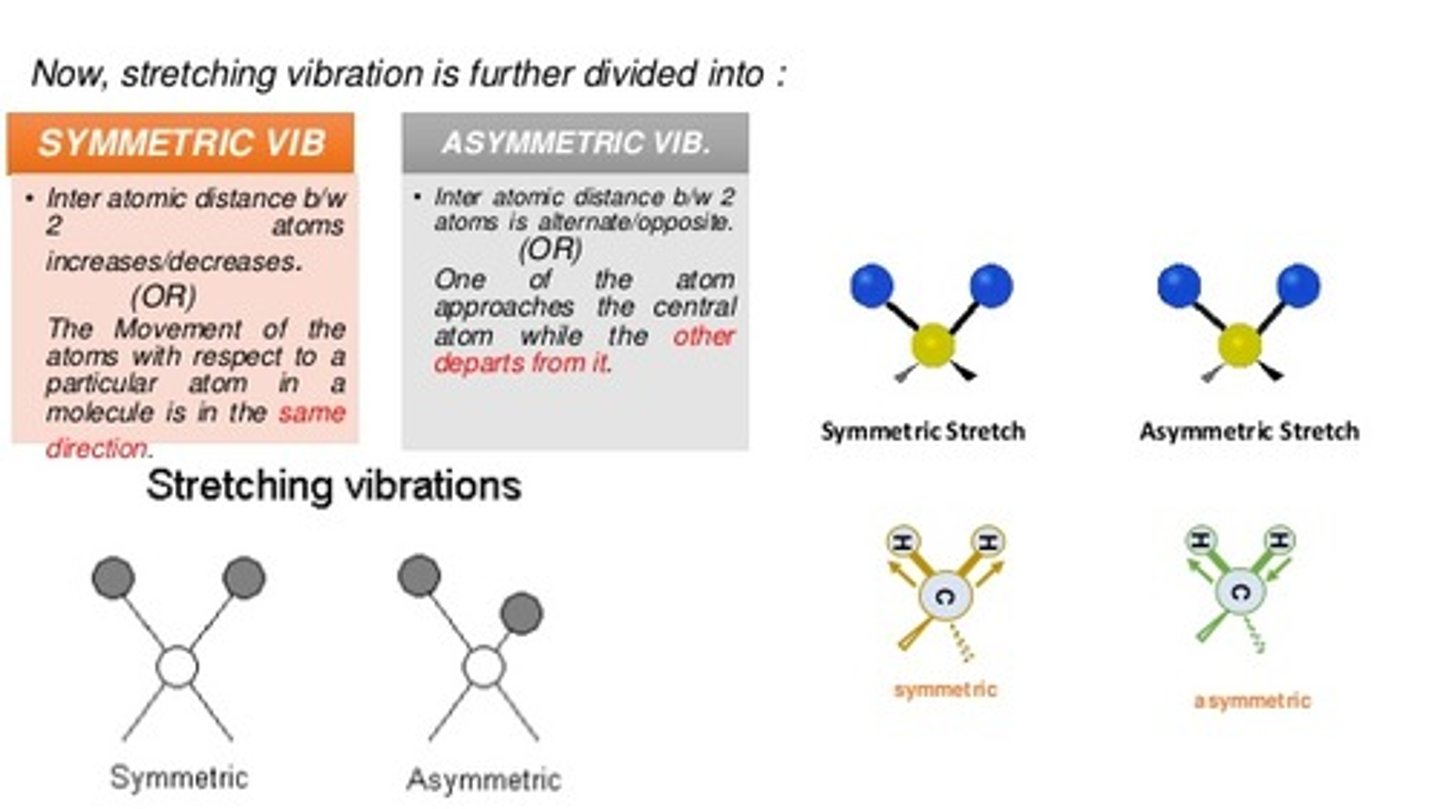
Why do you get two signals for NH2?
The signal at 3400 results from a higher energy Asymmetric stretch while the signal at 3300 results from a lower energy Symmetric stretch.
You see a very weak signal at 3300. What functional group are you dealing with?
A N-H bond will have a weak signal at 3300.
You see a strong signal at 1700 and 1800. What functional group are you dealing with?
You are dealing with an Anhydride.
Why do you get two signals for an Anhydride?
The signal at 1800 results from a higher energy Asymmetric stretch while the signal at 1700 results from a lower energy Symmetric stretch.