Southeastern Archeaology Exam II
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Shell mound Archaic sites are located in the
Interior lowlands of the midsouth
At the Iddins site, hundreds of notched cobbles are thought to have been
Net weights for fishing
The earliest dated pottery in the southeast, stallings fiber tempered ware, first appears on the south Atlantic coasts about
4800 yrs bp
Which of the following is true for the poverty point site?
None of the above (poverty point was a vacant ceremonial site that local populations visited rarely; like Watson-brake, there is little evidence for long distance trade; burials with grave goods indicate status differentiation and social hierarchies)
Classen (2010) has hypothesized that the large shell mound archaic sites are
Ritual sites for dispersed groups
According to Anderson and Sassaman, pottery became widespread in the southeast by
2700 yrs bp (700 BC)
During the early woodland period, which of the following is important to southeastern native subsistence?
the eastern agricultural complex
According to Anderson and Sassaman, the first maize is documented in the southeast at approximately
1800 yrs bp
A defining feature of the southeastern middle woodland period is
the spead of hopewellian ceremonialism
Bow and arrow technology becomes important and widespread in the southeast during the
late woodland period
maize first becomes common in the southeastern united states about
AD 900 (1100 yrs bp)
Anderson and Sassaman suggest that the woodland period worldviews regarded the land as the ________ of labor
subject
Which area of the southeast appears to have been most heavily involved in this domestication and cultivation of native seed crops (Eastern Agriculture Complex)?
The midsouth (north of the lower Mississippi valley and west of the Appalachians)
Biltmore mound is identified as a
hopewellian platform mound
Kimball, et al., argue that the variously colored mound stages, the ditch, the mound structure, and the central ritual post at Biltmore represent
the axis mundi
Societies with central communities, temple mounds with plazas, and reliance on maize agriculture first appear in the southeast about ____
AD 900 (1100 yrs bp)
Corn production is first documented in the American bottom during the _____ period
middle woodland?
The medieval warm period, a climatic span that favored the spread of agriculture, spanned approximately
AD 800-AD 1200 (1200yrs bp- 800 yr bp)
At its peak around AD 1100, Cahokia was home to about ____ people
15,000
Archaeologists infer personal status in Mississippian societies through
Associated grave goods buried with individuals, differences in foods and serving vessels in different site areas, and differences in grave locations
At the height of the Mississippian period, Southeastern indigenous populations were probably totaled around
75,000-100,000 people
The span of the Woodland period is approximately
1200 B.C.-A.D. 1000
Eating acorns, particularly as a staple food, is called ______________.
Balanophagy
Pits filled with stones, and used for cooking are called _______________.
earth oven/rock oven
Poverty Point “objects” (those little clay cubes/balls/other shapes) were most likely used for _______________.
cooking (heat retention in hearths)
The term “Adena” describes a ritual/mortuary complex that dates to the _________ _________ period.
Early Woodland
The jumbling or overlaying of archaeological contexts from different times on a single surface is called a _______________. The same term is used for overwritten manuscripts, where messages from different times are superimposed.
Palimpsest
Bow and arrow technology shows up in the Southeast during the _____ ___________ period.
Late Woodland
The _____ axe form shows up during the Early Woodland period, and persists through European contact. It was a significant technology that allowed actual chopping of trees
ground celt
Pigeon Check Stamped vessels with podes (legs/feet) were probably specialized containers for ______________.
cremains (mortuary contexts)
The first domesticated EAC crop was
Squash
Kimball’s microwear analyses of Flint Ridge chalcedony bladelets shows that they were used to cut
mica
Kimball suggests that sharpened bone needles/awls found at Biltmore were used for ___________
tattooing
Mica found in Hopewellian contexts in Ohio likely came from the
Blue ridge region
Discuss changing subsistence (foodways) trends during the Late Archaic and Woodland periods.
The late archaic period saw the expansion of wetland and estuarine habitats, allowing for the use of mollusks and fish. Notched pebbles were found that are considered net sinkers for catching fish, but could generally be used for net hunting on land. The focus was on first-line foods like vertebrae and nuts, while second-line foods are mussels and seeds. Rock-filled pits (earth ovens) expanded the amount of food that could be eaten (tough veggies) and also allowed for large gatherings of people because you could make mass quantities of food. Fiber-tempered pottery and soapstone vessels that show up in the late archaic period were revolutionary in food processing. Soapstone slabs were heated up and allowed for indirect boiling in pottery and soapstone vessels could be used over fire. At poverty point, there was enough subsistence security that there was no need for agriculture.
The terminal archaic period saw the increased use of the Eastern Agricultural Complex, which began in the middle archaic period. By the terminal archaic and early woodland periods, food production through gardening/cultivating became important. EAC continues to grow in importance in addition to hunting/gathering. The use of coil pottery in the early woodland period could be used over direct flame, which expanded the types of food/quantities available as well as supporting higher populations and survival (softer food for babies and the elderly). This continues through the middle woodland.
After the volcanic eruption near the end of the Middle Woodland period, EAC is affected. there is still an importance on wild plants and animals, and the bow and arrow changes hunting strategies. By the late woodland, maize agriculture grows in importance (900AD) and completely changes things- but there is variety throughout the landscape: ashe ferry depends heavily on mast and still focuses on hunting/gathering
What is the EAC and what is its significance? Be specific with species/common names, dates, etc
The EAC stands for Eastern Agricultural Complex, which was the beginning of food production in the southeast that gained momentum during the terminal archaic and early woodland periods, although it was documented to begin in the middle archaic. Throughout the archaic period, a variety of plants were collected and gathered and became domesticated through human selection. Initial domestication is dated around 3000-5000 yrs bp, and early occurrences were found in the upper south and lower midwest.
Plant species include: squash, goosefoot, sunflower seeds, marsh elder, maygrass, knotweed, and little barley. Cultivation is shown through larger seeds with thinner seed coats
This is important because it reflects settlement modes. The climatic shift caused reotganization of archaic period networks and spurred greater shifts towards horticulture and food production during the woodland period. It predates maize in the area and shows the patterns of increased sedimentism.
It also shows that people have known how to cultivate and propagate plants for a very long time. An asian species of bottle gourds that were native to Africa ended up in the Americas, and were not used for eating. Plant propagation was familiar to people long before EAC
What is the Hopewell Interaction Shere, and what does it represent?
The Hopewell interaction sphere was a pan eastern woodlands phenomenon that was an exchange network of exotic goods and information. This lasted throughout the middle woodland period and spanned from most of the deep south and to the plains. This network was directly related to and derived from early woodland adena patterns with lots of overlap. Different regions all had their own takes on the Hopewell phenomenon and its core was in Ohio. There were elaborate mortuary rituals and contexts, geometric earthworks, burial mounds, and effigy mounds. The large-scale network of items and ideas was shared between vary diverse communities and led to “pax hopewelliana”, the pacification of landscapes that led to less violent deaths and landscapes.
What is the timing, impact, and significance of maize agriculture in the Southeast?
Maize had existed in the southeast since the middle woodland period in small amounts but maize agriculture took off in AD 900. This had a direct impact on health (especially dental) and caused diseases/death if not prepared properly. Processing is called nixtamalization (boiling corn in ash to remove outer shell of kernel). You can get many carbs, almost unlimited, by processing corn as opposed to foraging for acorns. Corn is revolutionary and turns into a lifeway- corn ceremoialism and mother corn. Gardening and corn is the womens domain and this used to leverage political power. Women created the Mississippian world.
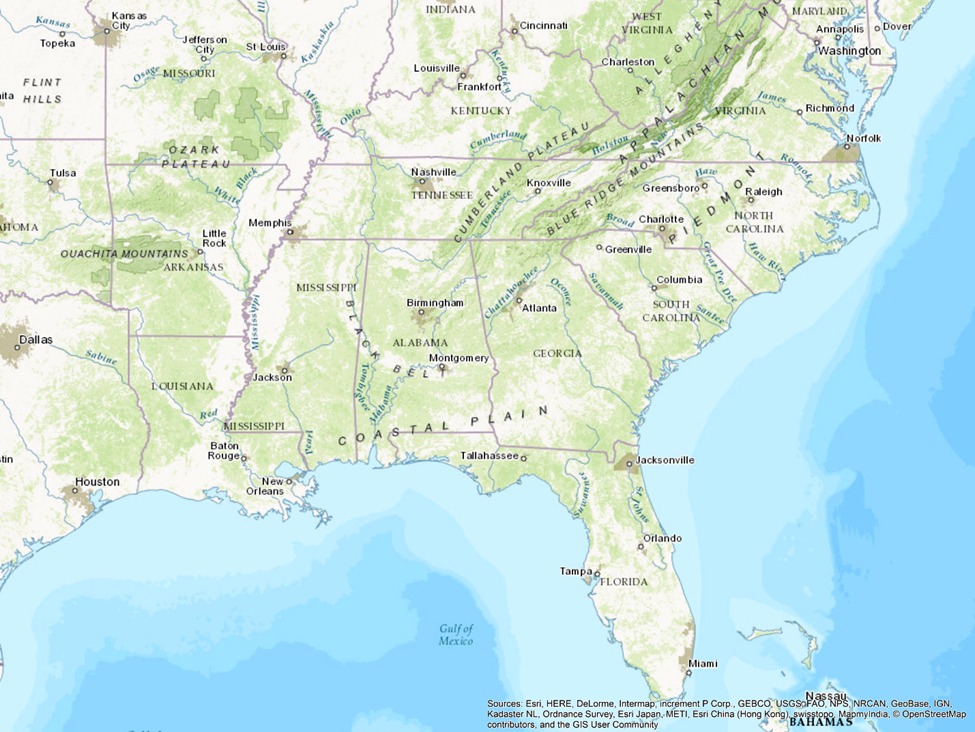
Coastal Plain Mississippi River Great Pee Dee River
Piedmont Tennessee River Oconee River
Blue Ridge Savannah River Red River
Valley and Ridge Cumberland River
Appalachian Plateaus Chattahoochee River
Interior Low Plateaus Tombigbee River
Central Lowlands Cape Fear River
Ozark Plateaus Arkansas River
NC sites

memorize
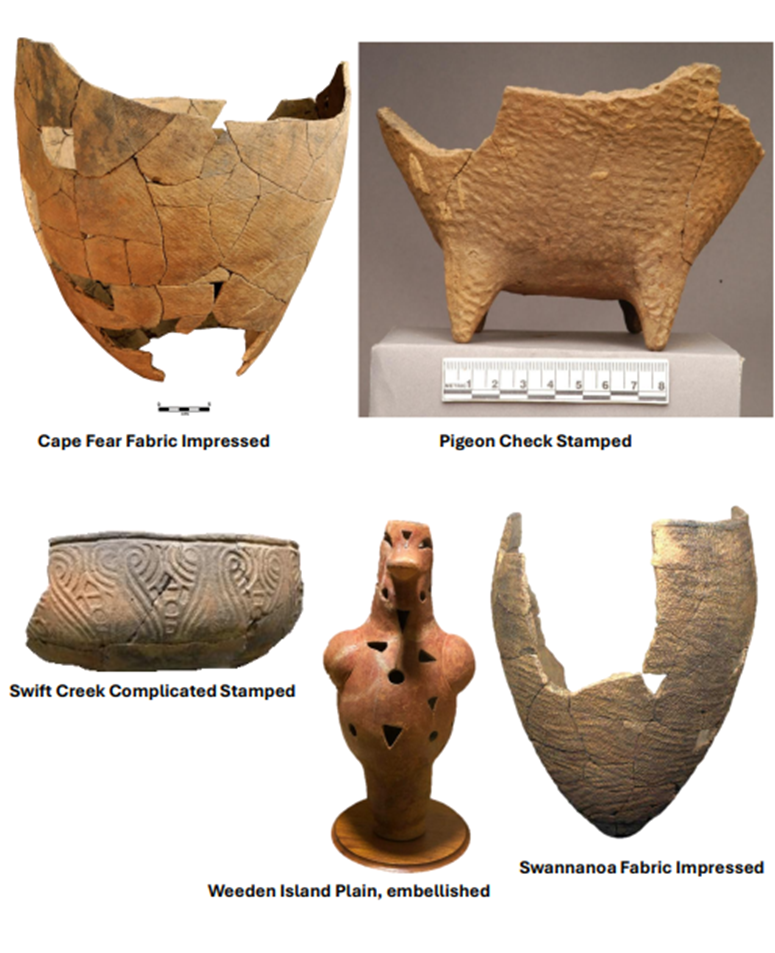

study