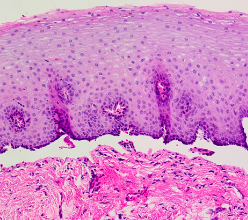
Histology/Pathology: Pathologies of the Stratified Epithelium
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is pseudostratified columnar epithelium and where is it found?
one layer of nonuniform cells
all cells are in contact with the basal membrane
found in the trachea, bronchi, and Eustachian tubes
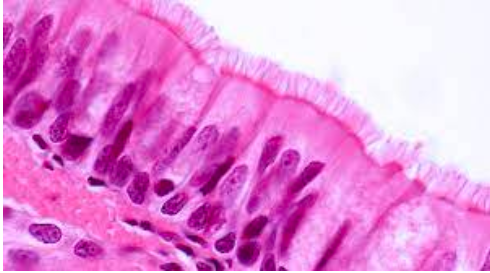
What are cilia?
elongated, motile structures that are longer than microvilli
Core is composed of microtubules, which are inserted into basal bodies
Basal cells are short, located in the basal membrane, and do not reach the lumen
What is the function of cilia?
aids in transport of material along the surface of cells, such as moving mucus and particulate matter out of the respiratory tract
What is bronchitis?
associated with pseudostratified columnar epithelium
inflammation of bronchial tubes
Can be acute or chronic
What causes bronchitis?
cigarette smoking (leading cause)
infection (virus, bacteria)
exposure to irritants (inhalation of chemical pollutants or dust)
What are the histological features of bronchitis?
Hyperplasia, loss of cilia
pseudostratified epithelium is replaced by squamous epithelium
What is stratified cuboidal epithelium?
lines the ducts of glands - salivary
uncommon type of epithelium, has very limited distribution
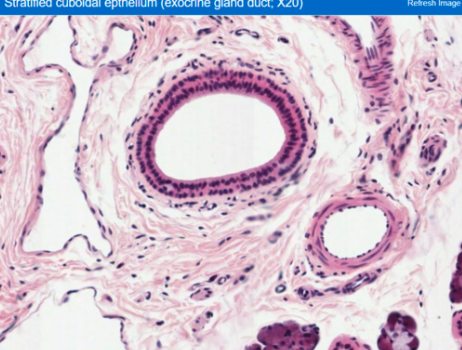
What is Sialadenitis?
associated with stratified cuboidal epithelium
a clinical condition resulting from the blockage of a duct, so saliva can not exit into the mouth
salivary stone (calculi), which forms from salts in the saliva
patient will feel pain when chewing food and swelling before mealtime
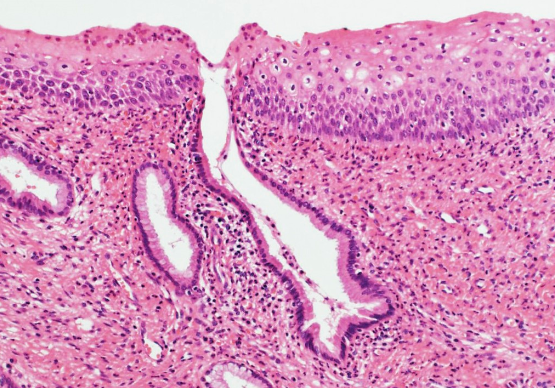
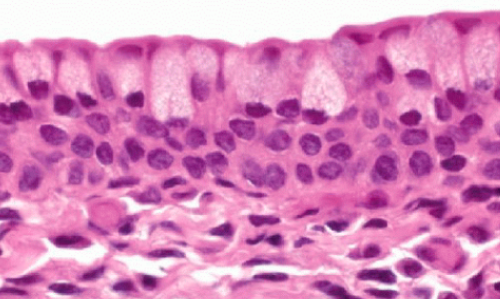
What is stratified columnar epithelium?
2-3 layers of columnar cells
posterior side of eyelid, in contact with surface of eyeball
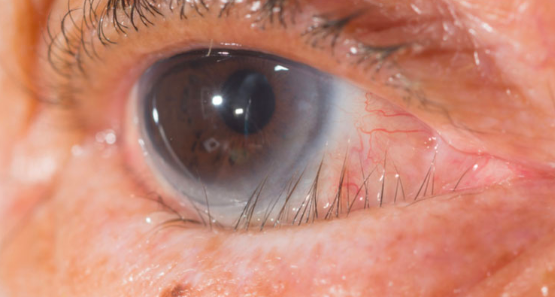
What is Trachoma?
associated with stratified columnar epithelium
chronic contagious conjunctivitis characterized by inflammatory granulation on the epithelium surface caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis
eyelash deformities
What are the symptoms of Trachoma?
tearing, discharge, photophobia, pain, and swelling of the eyelids
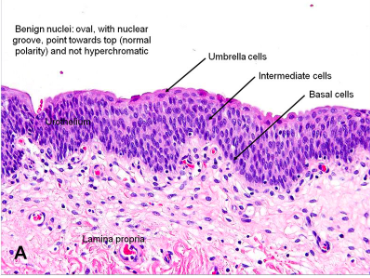
What is Transitional Epithelium?
can change shape to accommodate a volume change in the organ it lines
4-6 layers of dome-shaped cuboidal cells in its relaxed state
each surface cell appears umbrella shaped
found in bladder, major calcyes, and uterus
Also known as urothelium
When stretched, top layer dome-shaped cells become flat/squamous and epithelium becomes thin
What is urothelial carcinoma?
associated with transitional epithelium
characterized by hematuria and papillary morphogy
low and high grade depending on cytologic features and amount of disorder present
Cancer of the bladder
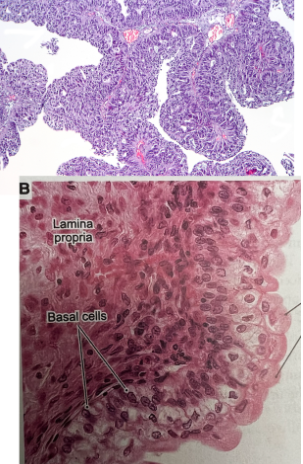
What are the risks for urothelial carcinoma and who is it most common in?
cigarette smoking, exposure to radiation, infection by parasite schistosoma haematubium
most prevalent in older men, but any age may occur
What are the symptoms of urothelial carcinoma?
painless gross hematuria, frequency, urgency, and dysuria
What is stratified squamous epithelium?
the skin
layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer/hypodermis
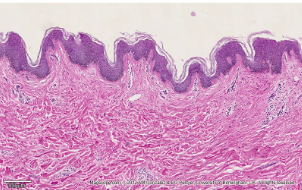
Where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
found in the skin
layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer/hypodermis
thick skin: palms and soles
thin skin: most other surfaces
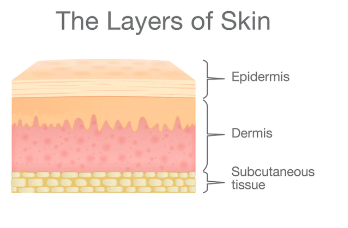
What is the epidermis and dermis?
Epidermis: stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis: connective tissue
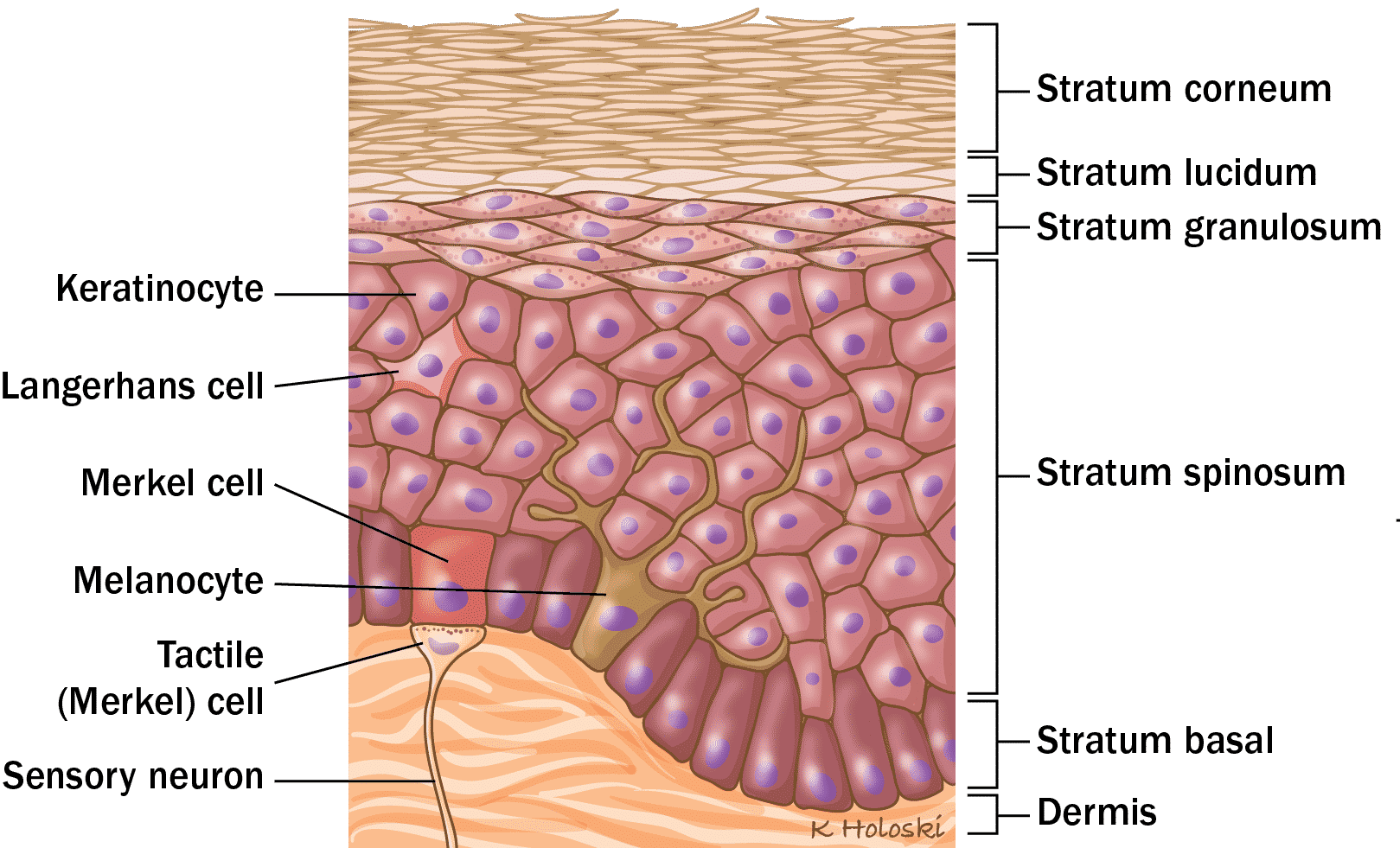
What is the top layer of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium consisted of?
Corneocytes (dead cells) which lack nuclei
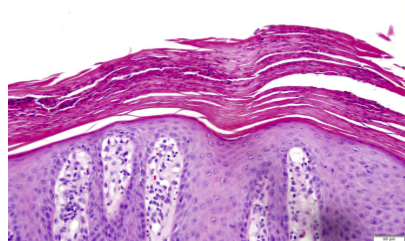
What is Psoriasis?
associated with stratified squamous epithelium
a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by pink to salmon colored plaques with silver scales and sharp margins
an autoimmune chronic inflammatory condition of the skin characterized by the formation of fluid filled blisters
microabcesses
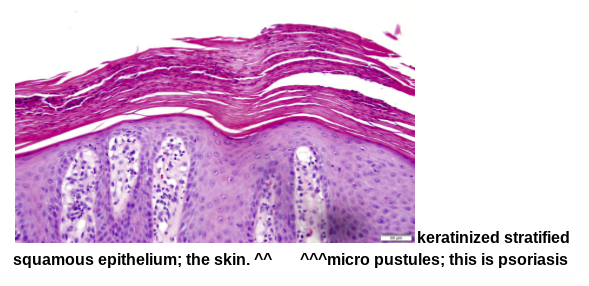
What are the symptoms of psoriasis?
itching
joint pain
nail pitting (peeling back)
nail discoloration
What is bullous pemphigoid?
a rare, autoimmune skin condition characterized by fluid-filled blisters (bulla)
caused by radiation exposure, medication, and vaccinations
What is the histology of BP?
separation of epidermis at the subepidermal interface