Science exam revision
5.0(2)Studied by 7 people
Card Sorting
1/134
Last updated 12:16 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
metal + acid --> ???
salt + hydrogen
2
New cards
Acid + Base --> ???
salt + water
3
New cards
Acid + Carbonate -> ???
salt + water + carbon dioxide
4
New cards
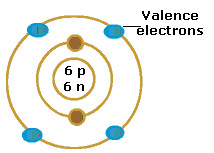
What is a Bohr shell diagram?
A diagram that shows electrons orbiting around the nucleus of an atom. The capacity of each circle is as follows:
2 in the first shell
8 in the second shell
8 in the third shell
2 in the fourth shell
2 in the first shell
8 in the second shell
8 in the third shell
2 in the fourth shell
5
New cards
What type of bonding occurs between two metals and how are the electrons arranged?
Metallic bonding and the electrons are free floating (sea of electrons)
6
New cards
What type of bonding occurs between two non metals and how are the electrons arranged?
Covalent bonding and the electrons are shared.
7
New cards
What type of bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal and how are the electrons arranged?
Ionic bonding and the electrons are transferred
8
New cards
Ion
an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
9
New cards
What is a positive ion called?
cation
10
New cards
What is a negative ion called?
anion
11
New cards
monoatomic ion
an ion made of 1 element e.g., Li+ , S-2
12
New cards
polyatomic ion
an ion made up of more than 1 element e.g., NH4+ , Cr2O7-2
13
New cards
combination/synthesis reaction
a chemical change in which two or more substances react to form a single new substance.
A + B --> AB
A + B --> AB
14
New cards
decomposition reaction
When something is broken down into smaller molecules (AB→A+B)
15
New cards
combustion reaction
a chemical reaction that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
16
New cards
What can speed up a reaction?
high temps, large surface area, higher concentration, catalysts.
17
New cards
Characteristics of a base
Produces Hydroxide Ions
Has a pH higher than 8
Turns litmus paper blue
Neutralizes acids
Bitter taste & soapy feel
Bases that are soluble in water are called Alkalis
Concentrated forms are corrosive
Has a pH higher than 8
Turns litmus paper blue
Neutralizes acids
Bitter taste & soapy feel
Bases that are soluble in water are called Alkalis
Concentrated forms are corrosive
18
New cards
What is pH?
a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is.
It is measured by the amount of H+ ions in solution.
It is measured by the amount of H+ ions in solution.
19
New cards
Characteristics of acids
An Acid is something that is Soluble
it generally has a sour taste
pH lower than 7.
Acids produce lots of Hydrogen Atoms
neutralize bases.
it generally has a sour taste
pH lower than 7.
Acids produce lots of Hydrogen Atoms
neutralize bases.
20
New cards
NH4 (+1 charge)
ammonium ion
21
New cards
NO2 (-1 charge)
nitrite ion
22
New cards
SO3 (-2 charge)
sulfite ion
23
New cards
OH (-1 charge)
hydroxide ion
24
New cards
PO4 (-3 charge)
phosphate ion
25
New cards
CO3 (-2 charge)
carbonate ion
26
New cards
CrO4 (-2 charge)
chromate ion
27
New cards
Cr2O7 (-2 charge)
dichromate ion
28
New cards
MnO4 (-1 charge)
permanganate ion
29
New cards
what does aqueous mean?
the solution is dissolved in water. water is the solvent - it is called aqueous
30
New cards
Soluble
capable of being dissolved
31
New cards
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
32
New cards
Why does a catalyst increase the rate of reaction?
This is because they decrease the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur. Catalysts aren't used up in a reaction
examples:
-chemicals
-enzymes
examples:
-chemicals
-enzymes
33
New cards
Why does surface area affect the rate of a reaction?
Tiny surface area exposes more of the substance making it easier for the particles to collide
34
New cards
what is an enthalpy diagram
What is an enthalpy diagram?
An enthalpy diagram plots information about a chemical reaction such as the starting energy level, how much energy needs to be added to activate the reaction, and the ending energy.
An enthalpy diagram plots information about a chemical reaction such as the starting energy level, how much energy needs to be added to activate the reaction, and the ending energy.
35
New cards
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Examples:
pesticide resistance in insects, development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, drug resistant strains of HIV
Examples:
pesticide resistance in insects, development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, drug resistant strains of HIV
36
New cards
artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits.
Examples:
Breeding for different dogs, racehorses bred for strength, corn bred for size
Examples:
Breeding for different dogs, racehorses bred for strength, corn bred for size
37
New cards
Micro evolution
evolutionary change within a species or small group of organisms, especially over a short period.
38
New cards
Macro evolution
Large scale changes in biological traits resulting in different species
39
New cards
Fossil record
Chronological collection of life's remains in sedimentary rock layers
40
New cards
Fossilisation process
1. Organism dies
2. Organism needs to be preserved
3. Mineralization
4.Erosion removes sediments/rocks above the fossil revealing it.
2. Organism needs to be preserved
3. Mineralization
4.Erosion removes sediments/rocks above the fossil revealing it.
41
New cards
Types of fossils
1. Indirect fossils
- Not actual organism
- But are remains
- Mold and cast
2. Carbon Film
- organism or plants compressed between different layers
- Organic matter decays
- Leaving a carbon film
3. Replacement
- The original organism's fossil is replaced by minerals
4. Original fossil
- Whole part of the organism has been preserved.
- Skeleton bones, teeth
- Not actual organism
- But are remains
- Mold and cast
2. Carbon Film
- organism or plants compressed between different layers
- Organic matter decays
- Leaving a carbon film
3. Replacement
- The original organism's fossil is replaced by minerals
4. Original fossil
- Whole part of the organism has been preserved.
- Skeleton bones, teeth
42
New cards
weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
43
New cards
Relative dating
Method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock
44
New cards
index fossil
a fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found
45
New cards
fluorine dating
Another relative dating method. It compares the amount of fluorine in different bones found in the same rock. Bones absorb fluorine from the water in the surrounding rock. This happens at a slow rate and depends how much fluorine is in the water surrounding the bone.
46
New cards
Absolute dating
dating methods that give the actual age of rocks and fossils are called absolute dating methods. Absolute dating still gives an estimate, but the estimate is far more specific than estimates provided by relative dating methods. There are many methods of absolute dating, one often used to be radioactive dating.
47
New cards
Radioactive dating
A technique used to determine the actual age of a fossil on the basis of the amount of a radioactive element it contains.
48
New cards
species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
49
New cards
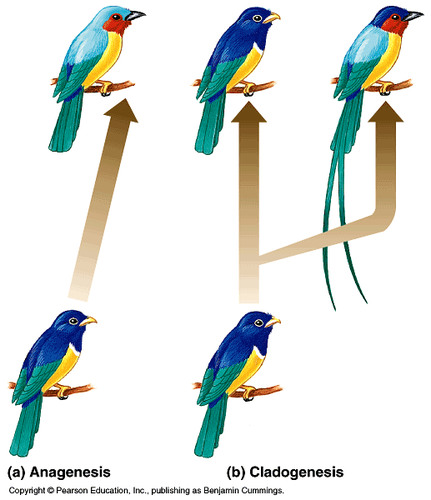
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which native populations evolve to become distinct species.
50
New cards
Hybrid
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits
51
New cards
Level of classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
(D.K.P.C.O.F.G.S)
(D.K.P.C.O.F.G.S)
52
New cards
adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiation is the rapid diversification of an ancestral population into several ecologically different species, associated with adaptive morphological or physiological divergence.
53
New cards
How does speciation occur?
Variation: There must be variation in the population or speciation cannot occur. This is because natural selection is involved, and selection can only act on variation that is already present in the population.
Isolation: The formation of new species requires isolation. This means different groups of the population are prevented in some way from interbreeding. Isolation prevents gene flow through the population, stopping any differences in one population from reaching the other population.
Selection: Once groups of a population are isolated by barriers, natural selection affects the genotype of each group. This can lead to changes that prevent each group from each other even if they come back together sometime in the future.
Isolation: The formation of new species requires isolation. This means different groups of the population are prevented in some way from interbreeding. Isolation prevents gene flow through the population, stopping any differences in one population from reaching the other population.
Selection: Once groups of a population are isolated by barriers, natural selection affects the genotype of each group. This can lead to changes that prevent each group from each other even if they come back together sometime in the future.
54
New cards
What is the order of the planets?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
(M.V.E.M.J.S.U.N)
(M.V.E.M.J.S.U.N)
55
New cards
moon
A celestial body that orbits a planet, is also viewable through sun reflected by the sun
56
New cards
planet
a celestial body moving in an elliptical orbit around a star.
57
New cards
black holes
Formed when massive stars explode in a supernova. The core of the massive star collapses in on itself and keeps on collapsing. They have a gravitational pull so strong that not even light can escape from it.
58
New cards
star
A large, glowing ball of gas held together by its own gravity also generates heat and light through nuclear fusion. Made up of Helium and Hydrogen
59
New cards
galaxy
a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction.
60
New cards
nebula
a large, diffuse cloud of dust and gas in space
61
New cards
What are the three types of galaxies?
Spiral, Elliptical, and Irregular; The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy
62
New cards
Nuclear Fission
A type of nuclear reaction that is used to release energy from large and unstable atoms by splitting them into smaller atoms
63
New cards
Why is the 'Steady State theory' no longer accepted by scientists?
After the discovery of the cosmological microwave background radiation, which had been predicted as part of the big bang theory but had absolutely no reason to exist within the steady-state theory.
64
New cards
What are 3 theories for the creation of the universe?
1. Big Bang Theory 2. Creation theory 3. Constant State theory
65
New cards
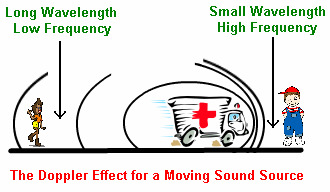
Doppler Effect
an increase (or decrease) in the frequency of sound, light, or other waves as the source and observer move toward (or away from) each other. When relating to a star, stars change colors depending on how they are moving. If a star is moving away, there would be a slight color change to red (called Redshift) and if a star is moving towards Earth there would be a slight color change to blue (called Blueshift).
66
New cards
Cosmic Background Microwave Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation (leftover from the big bang) comes from every direction and can be detected in all areas of the universe. It is evidence of the big bang
67
New cards
Heliocentric
The sun is the center of the solar system
68
New cards
Geocentric
Earth is the center of the solar system
69
New cards
absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is a measure of the luminosity (light) of a celestial object, on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale.
70
New cards
spectral type
Spectral type is the temperature of a depending on the colour it emits.
71
New cards
H-R diagram
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a graph that shows the relationship between a star's surface temperature and absolute magnitude
72
New cards
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations (Ww, RR, cc, FF)
73
New cards
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
74
New cards
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait (Aa, Bb, Cc)
75
New cards
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait (aa, bb, cc)
76
New cards
Dominant trait
dominant trait is one that is phenotypically expressed in heterozygotes. A genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of the gene. Dominant traits can't skip a generation.
77
New cards
Recessive trait
a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor. This trait can skip a generation and Affected children can be born from two unaffected parents.
78
New cards
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
79
New cards
Nitrogenous bases
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracail
80
New cards
Nucleotide
Nitrogenous base + sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and phosphate group
81
New cards
sugar-phosphate backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached
82
New cards
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
83
New cards
Complementary pairing
Adenine = Thymine Cytosine = Guanine
84
New cards
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
85
New cards
Apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
86
New cards
What regulates the cell cycle?
proteins
87
New cards
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
88
New cards
What are the stages of mitosis?
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
89
New cards
Prophase (poles)
- Chromosomes become visible
- nuclear membrane dissolves
- spindle fibre forms
- Centrioles move to the POLES of the cells
- nuclear membrane dissolves
- spindle fibre forms
- Centrioles move to the POLES of the cells
90
New cards
Metaphase (middle)
Chromosomes line up across the middle/center of the cell
Spindle fibres extend and attach to centromeres
Sister chromatids start to be pulled apart
Spindle fibres extend and attach to centromeres
Sister chromatids start to be pulled apart
91
New cards
Anaphase (away)
Chromatids move along the spindle fibres away from the middle towards the poles (centrioles)
92
New cards
Telephase (two)
nuclear membrane reforms
Spindle fibres dissolve
We now have 2 sets of chromosomes
Spindle fibres dissolve
We now have 2 sets of chromosomes
93
New cards
Somatic cells
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
94
New cards
Why is meiosis necessary?
- For the production of gametes for sexual reproduction
- Genetic variation ( offspring of 2 individuals are different )
- Genetic variation ( offspring of 2 individuals are different )
95
New cards
The stages of meiosis
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
96
New cards
Meiosis
Cell division of cells to form gametes occurs in sex organs.
97
New cards
Prophase I (Meiosis)
Same as prophase in Mitosis
-In meiosis chromosomes pair up to create a homologous pair
-In meiosis chromosomes pair up to create a homologous pair
98
New cards
Metaphase 1 ( Meiosis )
Same as Metaphase in Mitosis
In meiosis chromosomes line up in homologous pairs
In meiosis chromosomes line up in homologous pairs
99
New cards
Anaphase 1 (Meiosis)
Same as Mitosis
Instead of chromatids being taken, homologous pair are taken
Instead of chromatids being taken, homologous pair are taken
100
New cards
Telophase 1 (Meiosis)
same as mitosis
Two haploid cells are formed
Two haploid cells are formed