CH 1: An intro to Biology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Biology
The scientific study of life on Earth
What is the purpose of scales (e.g., levels of organization) in biology?
To help us organize our study of life on Earth
How do we define “life?”
Life is defined by a set of characteristics
What are the characteristics of living things?
Order, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, energy transformations, and evolution
What are the characteristics of living things products of?
All of the characteristics are products of chemical reactions that manifest themselves as physical, physiological, or behavioral (animals only) phenotypes
Are manifestations of the chemical and physical properties, and interactions of matter
Levels of Biological Organizations
Atoms
Molecules and Macromolecules
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ systems
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biosphere
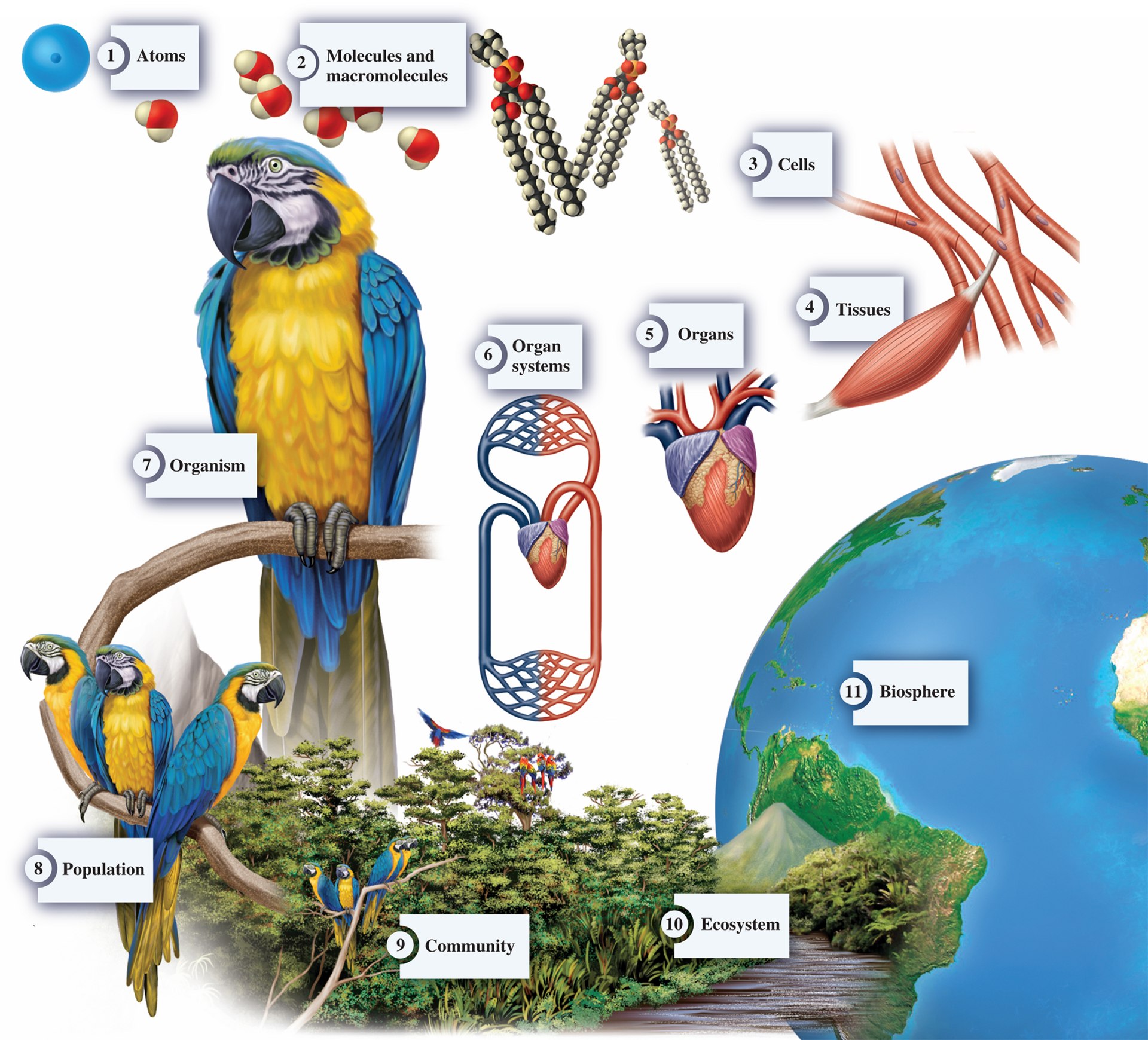
Atom
Is the smallest unit of an element that has chemical properties of the element
All matter is composed of atoms
Molecules and Macromolecules
Atoms bond with each other to form molecules
A polymer (polypeptide) consists of many molecules bonded together and is called a macromolecule
Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are important macromolecules found in living organisms
Cells
The simplest unit of life is the cell
A cell is surrounded by a membrane and contains a variety of molecules and macromolecules
Unicellular organisms are composed of one cell, whereas multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals, contain many cells
Tissues
In multicellular organisms, many cells of the same type associate with each other to form tissues
Ex: muscle tissue
Organs
In complex multicellular organisms, an organ is composed of two or more types of tissue and carries out a particular function
Ex: heart is composed of several types of tissues including muscle, nervous, and connective tissue
Organ Systems
In multicellular species, organs are typically a part of a larger, interacting system
In animals, such as birds and mammals, the heart is apart of the circulatory system
Organism
All living things can be called organisms
Biologists clarify organisms as belonging to a particular species (related group of organisms that share a distinctive form and set of attributes in nature)
The members of the same species are closely related genetically
Population
A group of organisms of the same species that occupy the same environment
Community
A biological community is an assemblage of populations of different species
The types of species found in a community are determined by the environment and by the interactions of the species with each other
Ecosystem
Are formed by the interactions of a community of organisms with their physical environment
Biosphere
The biosphere includes all of the places on Earth where living organisms exist
Life is found in the air, in bodies of water, on the land, and in the soil
Five Fundamental Themes of Biology
Evolution
Structure and function
Information
Energy and matter
Systems
Evolution
The diversity of life evolved over time by processes of mutation, natural selection, and genetic exchange
As a result populations become better adapted to the environment in which they live
Structure and function
Basic units of structure define the function of all living things
Information (flow, exchange, and storage)
The growth and behavior of organisms are activated through expressions of genetic information
Genetic material composed of DNA provides a blueprint for the organization, development, and function of livings things
During reproduction a copy of this blueprint is transmitted from parents to offspring (is heritable)
Pathways and transformations of energy and matter
Biological systems grow and change via processes that are based on chemical transformation pathways and are governed by the laws of thermodynamics
All living organisms acquire energy and matter from the environment and use them to synthesize essential molecules and maintain the organization of their cells and bodies
Systems
Living systems are interconnected and interacting
The interactions of living systems result in emergent properties, which are properties that manifest themselves as the result of various system components working together, not as a property of any individual component
When the parts of an organism interact with each other or with the external environment to create novel structures and functions, the resulting characteristics are called emergent properties
What are the subdisciplines of biology?
Ecology
Anatomy and Physiology
Cell biology
Molecular Biology
Systems Biology
Ecology
Population, community, and ecosystem levels
Ecologists study the impact of the environment on living organisms

Anatomy and Physiology
Levels tissue, organ, and organism levels
Anatomists and physiologists study how the structures of organisms are related to their functions

Cell Biology
Cellular levels
Cell biologists often use microscopes to learn how cells function

Molecular Biology
Atomic and molecular
Molecular biologists and biochemists study the molecules and macromolecules that make up cells

Systems Biology
All levels, shown here at the molecular level
Systems biologists may study groups of macromolecules. The microarray shown in the inset determines the expression of many genes simultaneously

What are the steps of the scientific method?
Observations
Hypothesis
Experiment
Analyze results/data
Draw Conclusion
Observations
What you see and your five senses
Hypothesis
Is a proposed explanation for a natural phenomenon
Based on observations
Must be stated as a prediction (expected outcome that can be shown correct or incorrect)
that is testable (can be shown consistent or inconsistent with data obtained from experiment)
And is falsifiable (can be shown to be incorrect by additional observations or experimentation)
Explain the phenomenon
Experiment
Is conducted to determine if the predictions in hypothesis is correct
Two ways data is collected in experiments:
Control group- the sample in the experiment that is treated just like an experimental group except that it is not subjected to one particular variable, dependent variable
Experimental group- the sample in an experiment that is subjected to some type of variation that does not occur for the control group, independent variable
Data/Analyze Results
Result of experimentation
Statistics and graphing
Conclusion
Draw a conclusion
Accept or reject hypothesis
Hypothesis consistent with data or not
Who follows the scientific method?
Biologists
Other scientists
Scientific Method
The analysis of scientific evidence, ie, data, requires the use of mathematical modeling and statistics