EXP 3: Precipitation Reactions of Proteins
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Heat Coagulation
Organic Solvents
Salting Out
Heavy Metal Ions
Alkaloidal Reagents
ALL Types of Precipitation Conducted in the Experiment
False (Casein does not coagulate when heated.)
True or False: Casein coagulates when heated.
Casein (since there’s no coagulation)
What is the protein present in the test tube?

True
True or False: Albumin coagulates in heat.
Albumin
What is the protein present in the test tubes?
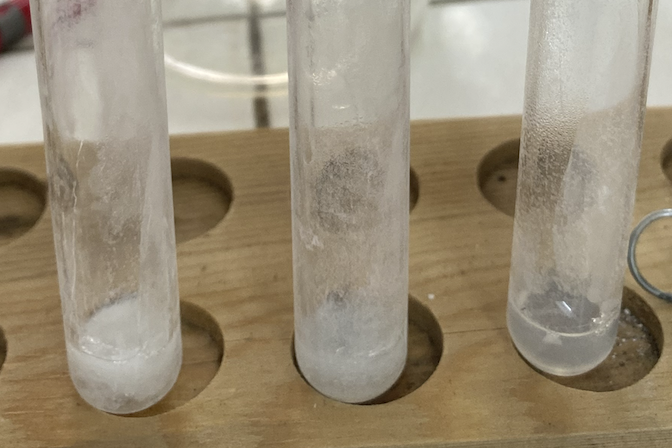

1st Test Tube: 1 N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
2nd Test Tube: 5 N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
3rd Test Tube: None
What are the reagents added in each test tube?
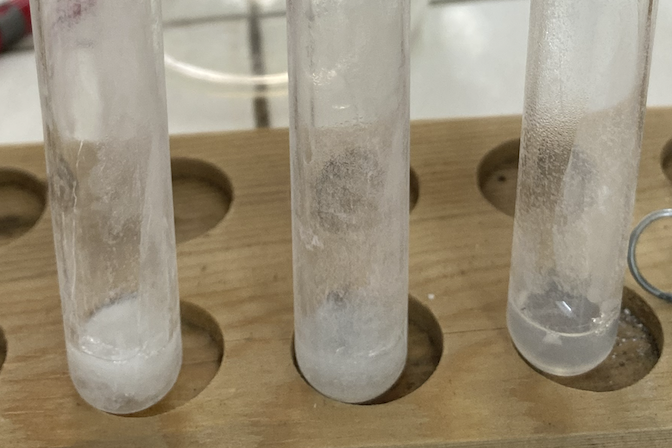

1st Test Tube (with 1N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH))
Which test tube exhibits the most coagulation?

Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH)
Water
What are the reagents added?

Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH)
What is the name and formula of the organic solvent added to precipitate the albumin?
True
True or False: The precipitate in the test tube will exhibit coagulation after a few days.

B. With NaOH
Select an option:
In which does more coagulation occur?
A. Without NaOH
B. With NaOH
Potassium Ferrocyanide (K4Fe(CN)6)
Tannic Acid (C76H52O46)
Picric Acid (C6H3N3O7)
What are the 3 Alkaloidal reagents?
Precipitation by Heat Coagulation
What is the name of (Part 1)?
isoelectric point
(Part 1) Heat Coagulation and precipitation occur best near the ___ ___ of the protein.
Proteoses
Peptones
Gelatine
Casein
(Part 1) 4 proteins that are not coagulated by heat
Casein does not coagulate.
(Part 1) What occurs when casein is heated?
Casein does not coagulate.
(Part 1) What is exhibited in the following photo?

1N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
5N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
Nothing (Control)
(Part 1) 3 test tubes of albumin were prepared. What was added to each test tube?
Albumin + 1N Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
(Part 1) Among the three different albumin solutions, which exhibited the best coagulation?
The solution with albumin and 1 N CH3COOH (1st test tube) had the best coagulation compared to the tubes with 5N CH3COOH and nothing.
(Part 1) What is exhibited in the following photo?

Heated to boiling
(Part 1) What is conducted to both the test tubes with casein and albumin?
Precipitation by Organic Solvents
What is the name of (Part 2)?
Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH)
(Part 2) What is the organic solvent added to the albumin?
No
(Part 2) Does the precipitate formed from the reaction between albumin and CH3CH2OH dissolve in water?
The alcohol is able to shrink and preserve tissue especially those that are damaged.
(Part 2) How is the process of protein precipitation by organic solvents applied in the fixing of tissue for histological purposes?
Proteins become denatured and insoluble in water.
(Part 2) What occurs with proteins when made to stand with organic solvents?
Precipitation by Salting Out
What is the name of (Part 3)?
Albumin
Ammonium Sulfate ((NH4)2SO4)
Millon’s Reagent (Hg(NO3)2)
What are present in the test tube?
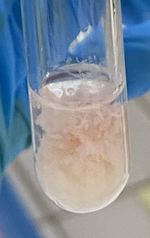
Millon’s Test
What is the test present?
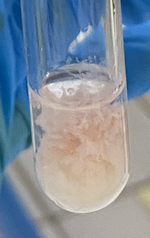
Biuret Test
What is the test present?

There are no more proteins present in the filtrate since they were completely salted out.
What does the color of the test indicate?

Peptone
Ammonium Sulfate ((NH4)2SO4)
Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4)
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
What are present in the test tube?

There remains the presence of peptide bonds in the filtrate.
What does the color indicate?

Ammonium Sulfate ((NH4)2SO4)
(Part 3) What is the name of the neutral salt added to the albumin?
Millon’s Reaction & Biuret Test
(Part 3) What are the tests conducted on the (NH4)2SO4 + Albumin solution?
A red precipitate forms (positive reaction)
(Part 3) When the (NH4)2SO4 + Albumin solution is tested with Millon’s reaction, what occurs?
A blue color developed (negative reaction)
(Part 3) When the (NH4)2SO4 + Albumin solution is tested using the Biuret test, what occurs?
Peptone
(Part 3) Other than albumin, what is the (NH4)2SO4 also added to in a separate test tube?
Biuret Test
(Part 3) What test(s) is/are conducted on the (NH4)2SO4 + Peptone?
Pink/purple color forms, indicating the peptone hasn’t been completely salted out
(Part 3) What occurs in the Biuret test on (NH4)2SO4 + Peptone, indicating what?
Precipitation by Heavy Metal Ions
What is the name of (Part 4)?
Lead Acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2)
Silver nitrate (AgNO3)
Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4)
(Part 4) What are the heavy metal ions added to the albumin solutions?
Lead Acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2) & Albumin
Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) & Albumin
Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4) & Albumin
(Part 4) Identify the chemicals that were added to each test tube to produce the following color reactions (left to right)?
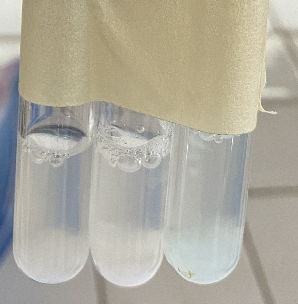
white
(Part 4) What is the color of the precipitate formed from the reaction between Lead-Acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2) and acid?
white
(Part 4) What is the color of the precipitate formed from the reaction between AgNO3 (Silver Nitrate) and acid?
Blue
(Part 4) What is the color of the precipitate formed from the reaction between cupric sulfate (CuSO4) and acid?
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
(Part 4) In the second trial, before adding the heavy metal ion, what is added to the albumin?
Egg albumin is able to precipitate with the metallic ion, which is then vomited by the individual.
(Part 4) Why is egg albumin used as an antidote for mercury or lead poisoning?
Precipitation by Alkaloidal Reagents
What is (Part 5)?
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
(Part 5) Aside from the alkaloidal reagents, what is added to the albumin?
Potassium Ferrocyanide (K4Fe(CN)6)
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
What are the reagents in the 1st test tube (leftmost)?

Tannic Acid (C76H52O46)
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
What are the reagents in the 2nd test tube (middle)?

Picric Acid (C6H3N3O7)
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
What are the reagents in the 3rd test tube (rightmost)?

White
(Part 5) What is the color of the reaction between potassium ferrocyanide (K4Fe(CN)6) + HCl + Albumin?
Brown
(Part 5) What is the color of the reaction between tannic acid (C76H52O46) + HCl + Albumin?
Yellow
(Part 5) What is the color of the reaction between picric acid (C6H3N3O7) + HCl + Albumin?
Picric acid because it can inhibit bacterial growth and cause shrinkage of tissue.
(Part 5) What alkaloidal reagent is used in the treatment of burns and why?
Tannic acid because it can help strengthen epithelial barrier of the stomach, preventing pathogens that cause diarrhea.
(Part 5) What alkaloidal reagent is used in the treatment of diarrhea and why?