AP Bio Unit 1: Chapter 2 - 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Anything that takes up space or mass
2
New cards
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances through chemical reactions
3
New cards
Compound
A substance made up of two or more chemical substances that are chemically bonded
4
New cards
Make up 96% of living matter
C, H, O, N
5
New cards
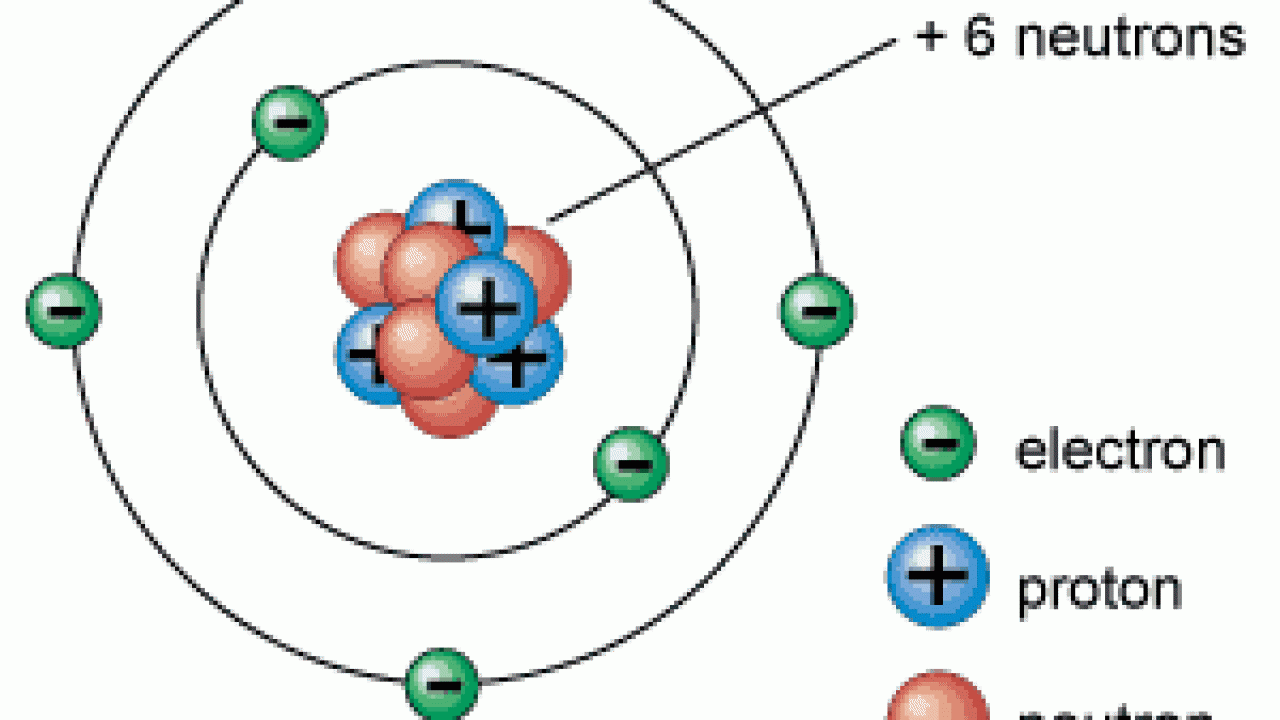
Atoms
Smallest units of elements that contain the properties of an element
6
New cards
Protons
Positively charged particles in the nuclues of an atom, determine what element and atom is
7
New cards
Neutron
an elementary particle with 0 charge and mass about equal to a proton; in the atomic nucleus
8
New cards
Electrons
Negatively charged particles that rotate around nuclues in elctron cloud. Thier movement determines atom properties
9
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but different number or nuetrons
10
New cards
Chemical bonds
Interactions between valence elctrons in different atoms
11
New cards
Molecule
the simplest structural unit of an element or compound, when different atoms are held together by chemical bonds
12
New cards
Covalent bonds
Bonds in which atoms share valence electrons to both complete thier outer shells
13
New cards
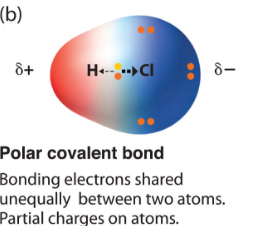
Polar covalent bonds
Covalent bond in which one atom's greater electronegativity allows it to control the orbit of a shared elctron more often. Creates - and + charged poles in molecule
14
New cards
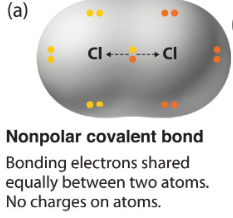
Nonpolar covalent bonds
Covalent bond in which both atoms have a similar electronegativity and equally share the orbit of shared elctrons
15
New cards
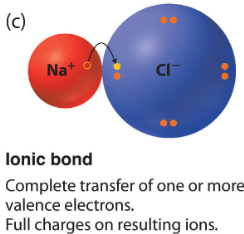
Ionic bond
Bond where one atom's electronegativity is great enough to completly take an eltron from another atom. As a result, the atoms are bonded.
16
New cards
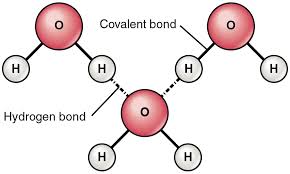
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds that form between positively charged hydrogen atoms and negatively charged oxygen or nitrogen atoms of another molecule
17
New cards
Van der waals interactions
Weak, constantly forming and breaking bonds that are caused by slight charges due to electron distribution
18
New cards
Chemical reaction
a process in which one or more substances are changed into others
reactants -> products
number of atoms should be the same on each side
reactants -> products
number of atoms should be the same on each side
19
New cards
Characteristics of water structure
- Polar molecules
- Hydrogen bonding, each molecule can form 4 at a time
- Cohesion
- Adhesion
- Less dense as solid than as liquid
- Hydrogen bonding, each molecule can form 4 at a time
- Cohesion
- Adhesion
- Less dense as solid than as liquid
20
New cards
Cohesion
Linking of like molecules, creates surface tension
21
New cards
Adhesion
Clinging of one substance to another substance
22
New cards
Specific heat
the heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance one degree celcius
23
New cards
Solvent
a liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
24
New cards
Solute
the dissolved matter in a solution; the component of a solution that changes its state
25
New cards
Solution
a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances; frequently a liquid solution
26
New cards
Hydrophillic
Attracted to water, any polar molecules will be hydrophillic
27
New cards
Hydrophobic
Repels water, typically nonpolar molecules
28
New cards
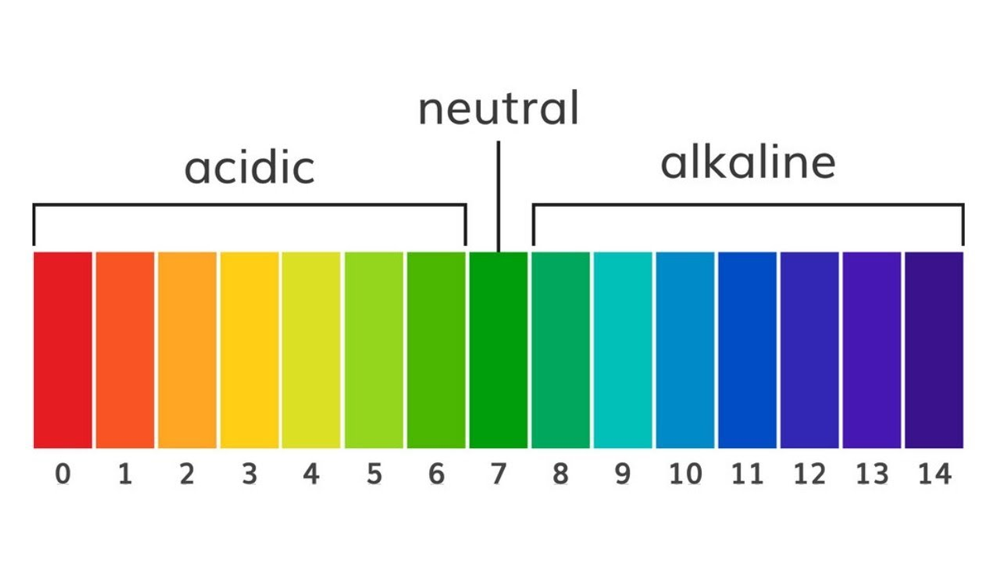
the pH scale
Concentration of H+ vs OH-
29
New cards
Acids
Have exess of H+ ions and pH below 7.0
H+ > OH-
H+ > OH-
30
New cards
Bases
Have an exess of OH- ions and pH above 7.0
31
New cards
Pure water pH
7.0, true nuetral
32
New cards
Buffers
Substances that minimize changes in pH, provide and take away H+
33
New cards
Carbonic Acid (H2CO3)
Important buffer in living systems
34
New cards
Major elements for life
C, H, O, N, S, P
35
New cards
What do all organic compounds contain?
Carbon
36
New cards
Why is carbon so capable of forming complex molecules?
- 4 Valence e-
- Can form up to 4 covalent bonds
- Can create chains, ring-shaped, and branched molecules
- Can form up to 4 covalent bonds
- Can create chains, ring-shaped, and branched molecules
37
New cards
Isomers
Molecules with the same formula but different arrangement of atoms
38
New cards
Functional groups
Chains of atoms attatched to a carbon skeleton