Microbiology - Chp. 6 | Viruses
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
oxidation
loses electrion(s)
reduction
gains electron(s)
choose a correct statement
electrons move to less electronegative atoms from more electronegative atoms.
electrons move to more electronegative atom from less electronegative atoms
both aboves
neither aboves
electrons move to more electronegative atom from less electronegative atoms
when does the electron release energy
when electrons move from less to more electronegative atoms
protons accumulated outside the cell membrane, by ________ gradient, rush through enzyme: _________ to synthesize ATP by combining ADP & Pi
chemiosmotic, ATP synthesis
electrons are transferred in the cell membrane to the more electronegative acceptor from an electron donor, which in turn releases energy that is used to generate a proton gradient, finally all electron are transferred to _____ to produce water
oxygen
in gluconeogenesis, protein breaks down by __________ and fat breaks down by _________
deamination, beta oxidation
which is not related with anabolism
synthesizes molecules
is endergonic reaction
release energy
all of the above are correct
release energy
which is wrong statement about enzymes?
are reusable
are highly specific
have an active site
are required in large amounts
are required in large amounts
NAD+ + 2e- + H+ → NADH + H+
reduction reaction
NADH → NAD + 2e-
oxidation reaction
XH → X+ e-
oxidation reaction
A → AH
reduction reaction
FAD + 2e- + 2H → FADH2
reduction reaction
BH2 → B
oxidation reaction
competitive inhibition
a molecule competes with the substrate for binding to the enzyme’s active site
noncompetitive inhibition
a molecule binds to a site other than the active site, causing a change in the enzyme’s shape and reducing its activity
T/F: ATP releases energy when it breaks to ADP and a phosphate group
T
T/F: ATP is made of adenosine, deoxyribose, & 3 phosphates
F
T/F: phosphorlylation means the addition of a phosphate group to another molecule
T
T/F: ATP is not a stable structure enough to store energy for long itme
T
T/F: ATP molecules are relatively stable due to negatively charged phosphate groups
F
ATP is degraded to ADP in exergonic reaction
T
glycolysis location in prokaryotes
cytoplasm
krebs cycle location inprokaryotes
cell membrane and cytoplasm
electron transport sytdem
cell membrane
NAD+ can carry __ hydrogen ion(s) and __ electrons
1,2
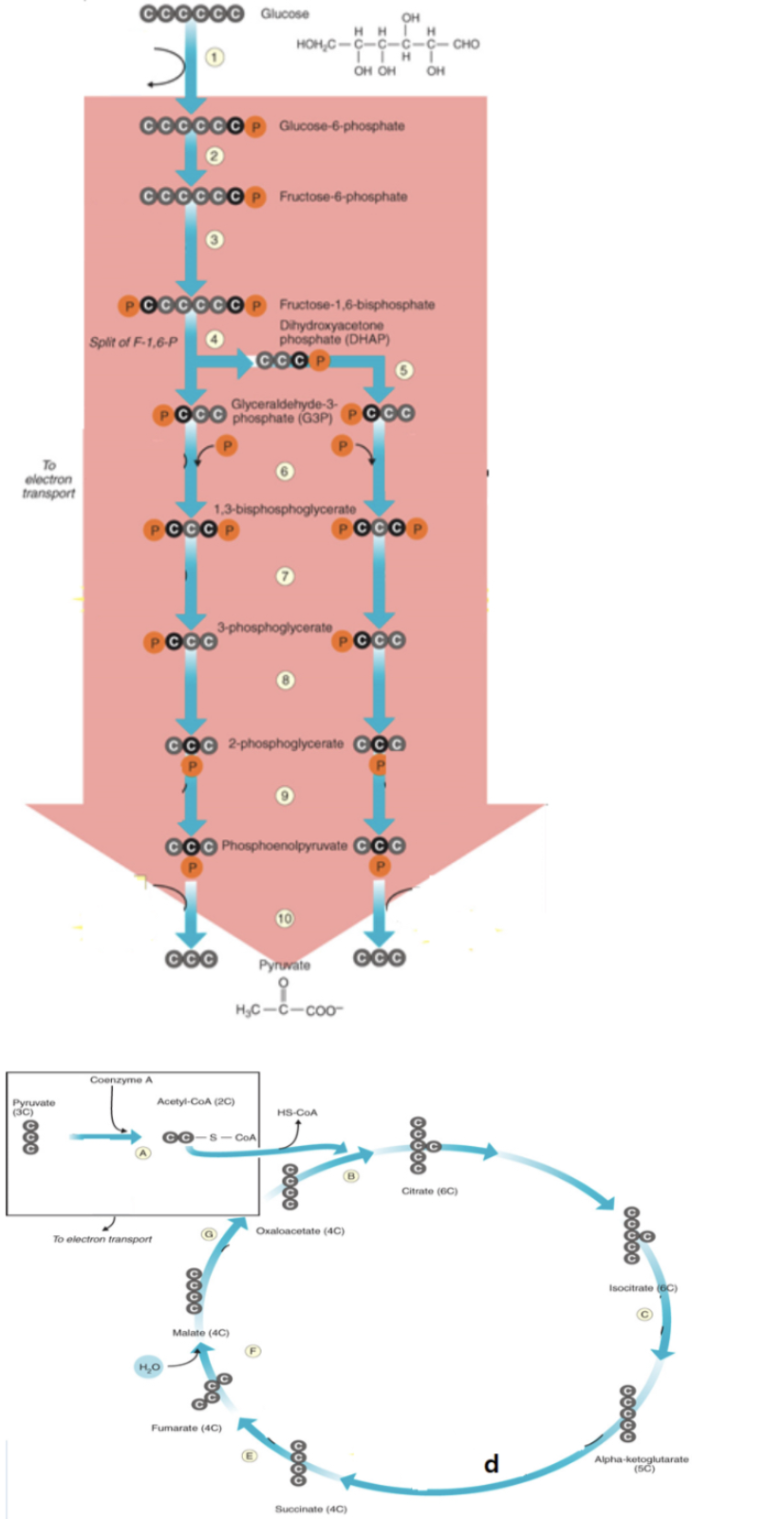
glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate
1
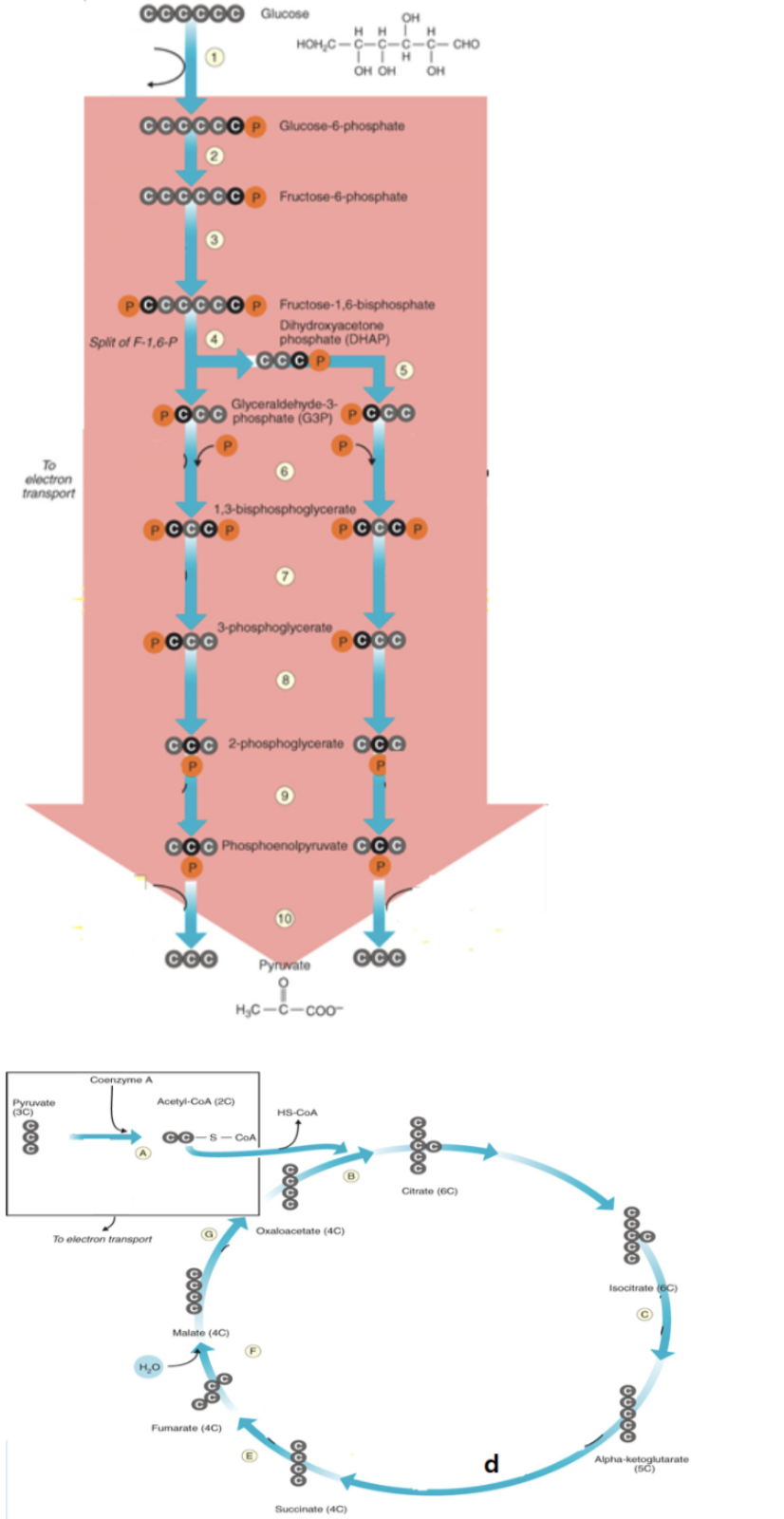
acetyl CoA binds to oxaloactate to form citrate
b
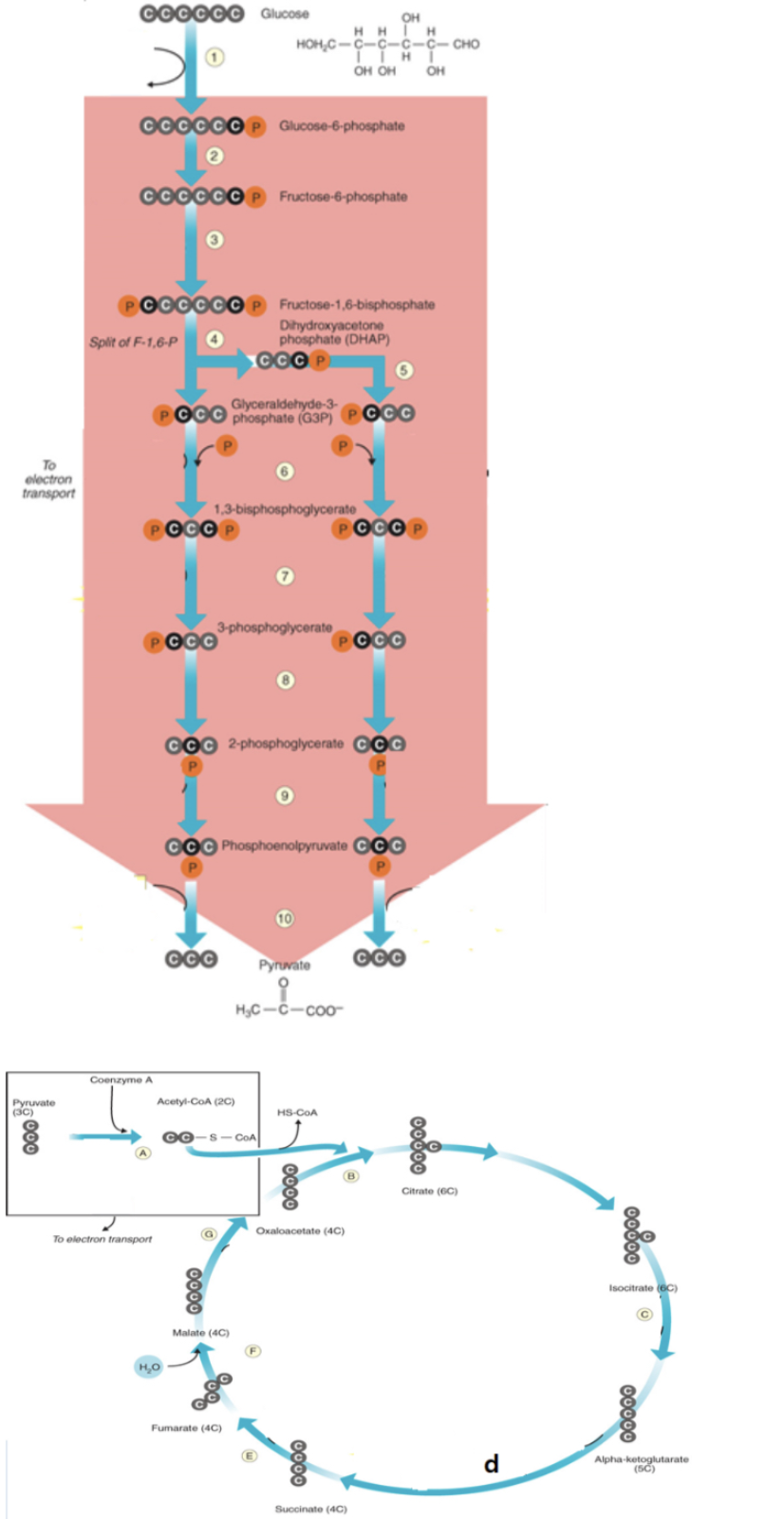
NADH is produced
6, a, c, d, g
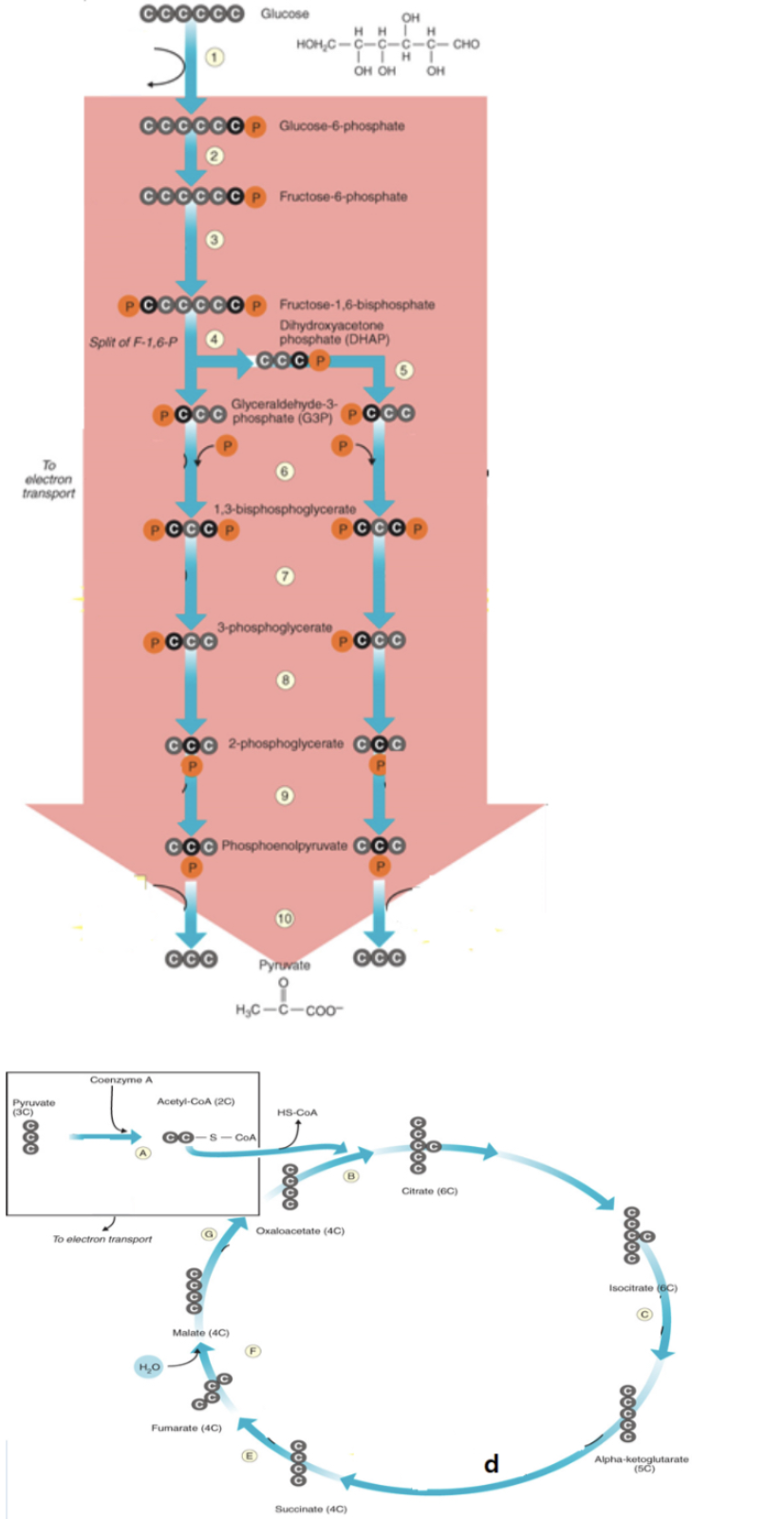
FADH2 is produced
e
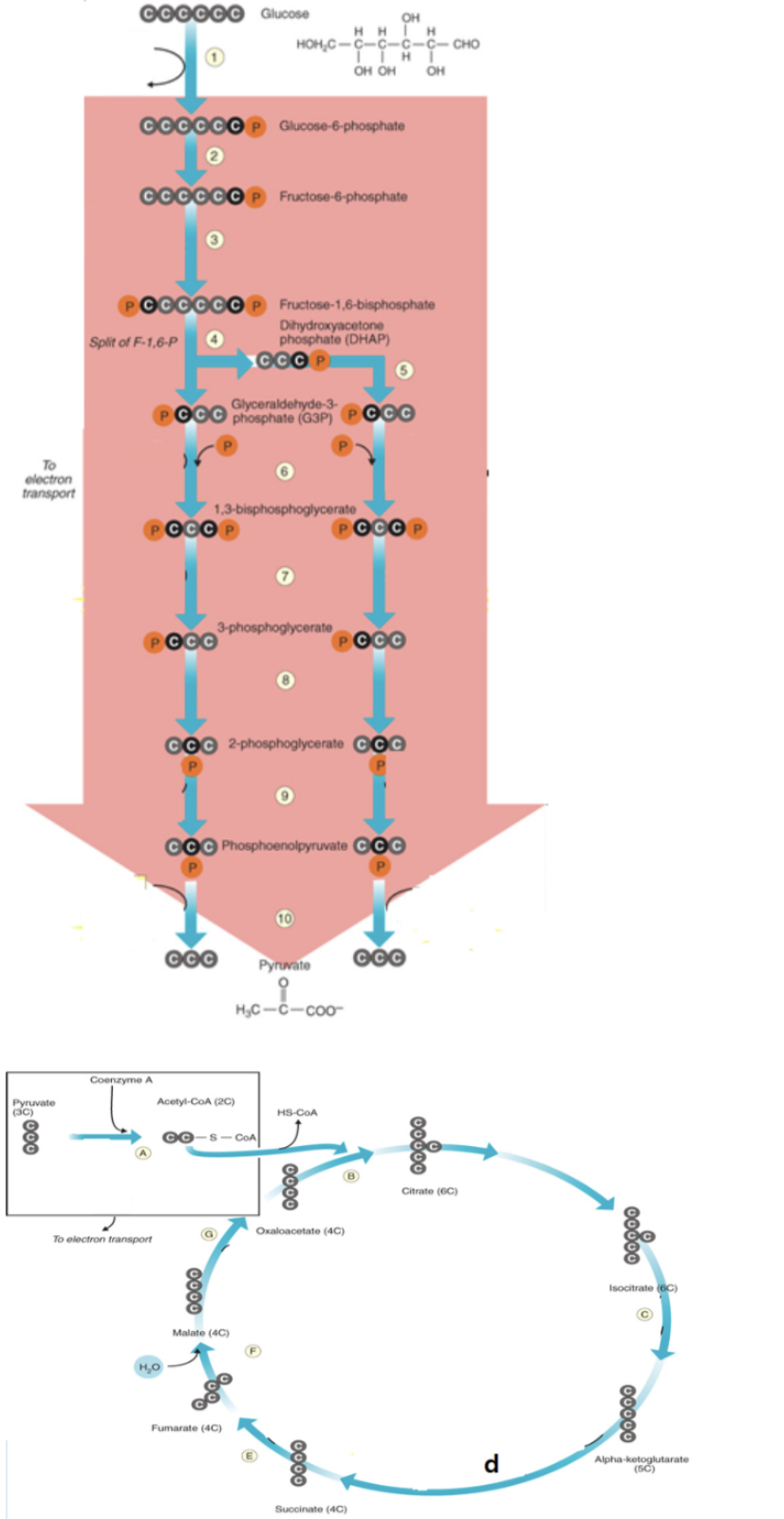
ATP is consumed
1,3
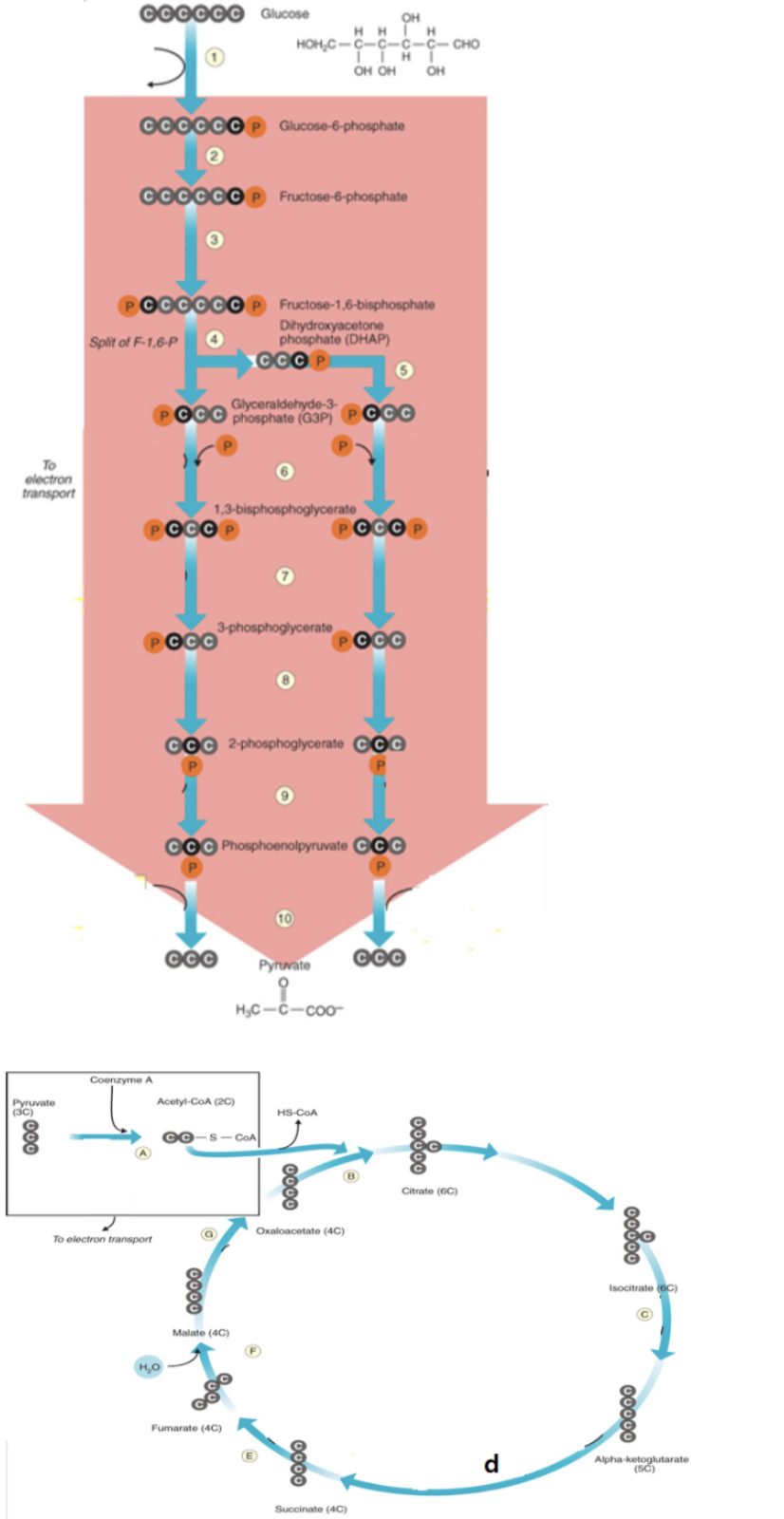
ATP is produced
7,10, d
in cell metabolism, NADH or FADH2 are made in the reaction step that has an enzyme [term] because this enzyme separates hydrogen from the reactant to transfer to NAD+ or FAD
dehydrogenase
what is the final electron acceptor in the oxidative phosphorylation?
oxygen
role of electrons
releases energy that is used to produce ATP during cellular respiration
the role of hydrogens
flows down the concentration gradient through ATP synthase to generate ATP
choose a right statement in electron transport
electron transport chain is composed of cytochromes I, II, III, & IV
electrons in NADH & FADH2 can transport hydrogen ions from inside the cells to the outside
electrons eventually are accepted to oxygen to form water molecule
all of the above are correct
all of the above are correct
fructose
fructose-1-phosphate
glucose
enters glycolysis path
galactose
glucose-6-phosphate
starch, or glycogen
glucose-6-phosphate
alanine
pyruvate
aspartic acid
oxaloacetate
glycerol
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
anaerobic organisms can have the following final electron acceptors such as ____
NO3-
SO42-
CO3
CO2
all of the above
all of the above
requires endogenous organic compounds as both electron donors acceptors
fermentation
requires oxygen as electron acceptor
aerobic respiration
requires inorganic substances as electron acceptor
anaerobic respiration
it does not have oxidative phosphorylation process
fermentation
fermentation is an aerobic process that reoxidixes NADH to NAD+ by converting organic materials into fermentation end products. what kind of product is formed?
lactic acid
ethanolk
carbon dioxide
acid
all of the above
all of the above
fermentation reaction can be identified by _____
methyl red test
voges-proskauer test
biuret test
ninhydrin reaction
methyl red test & voges-proskauer test