Tides & Salt Marsh Ecosystems
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Tides
Waves caused by gravitational pull of moon and sun
2 high and 2 low tides a day. The moon moves around Earth, increased gravitational pull where it is near causing a high tide, and a bulge on the other side also causes a high tide
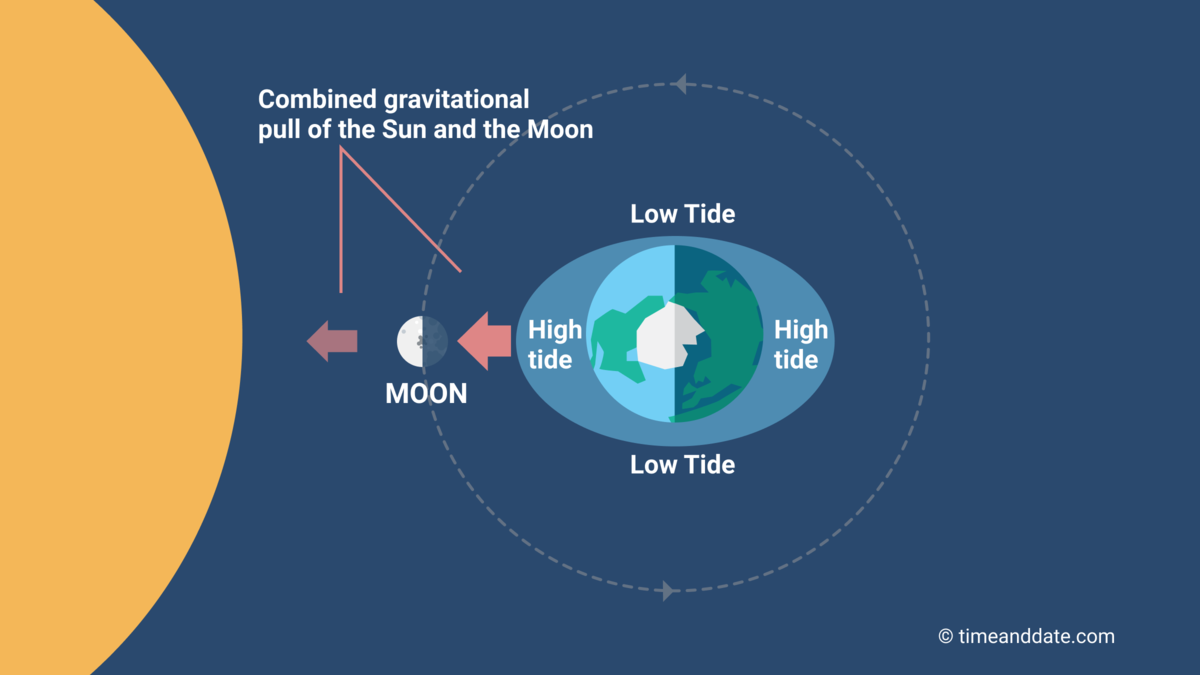
Spring Tides
during full and new moon phases when the sun, Earth, and moon are in line so the gravitational force of sun amplifies that of moon, causing max vertical range (highest high tide and lowest low tide)
2 each lunar month (29.5 days)
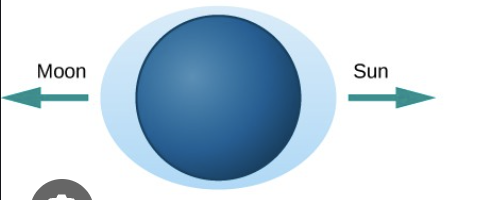
Neap Tides
sun, Earth, and moon form 90º angle (quarter moon) so gravitational affects cancel out, making a minimum vertical range (lower high tides, higher low tides)
Salt Marsh Ecosystem
driven by tides and dominated by Spartina alternifora. Found worldwide, but under 30º is more mangroves. Protects coasts and filters nutrients from water. Functions as a carbon sink
Carbon Sink
sequesters carbon and stores carbon. can store a lot because new plants grow every year and anaerobic soil decomposes soil slowly. If a marsh is damaged, it will release gasses and carbon
Carbon Sequesteration
pulls carbon dioxide out of atmosphere via photosynthesis, then released back
Carbon storage
anoxic soil can’t decompose plant material so its buried
Spartina alternifora
smooth cordgrass dominant in Eastern America and Gulf Coast near lowest intertidal zone, so can tolerate long periods of salt water immersion. has smooth blades that taper to points, round and hollow stems and strong interconnected root systems. Bloom tiny white flowers in July-September
short form is 2 ft, and tall form in 7 ft
Aerenchyma tissue
Spartina alternifora anoxic adaptation. Open space in stems. Oxygen is taken out of air then transported to roots. The connection between aerobic leaves, stems, roots, and the anaerobic sediment
Ribbed Mussels
Geukensia demissa mussel that moves nitrogen from water to sediment, which stimulates Spartina growth. In return mussels get refuge from predators and heat stress

Fiddler Crabs
their burrows aerate Spartina roots, helps mycorrhizal fungi. In return, Spartina binds the soil for them to burrow and feed.

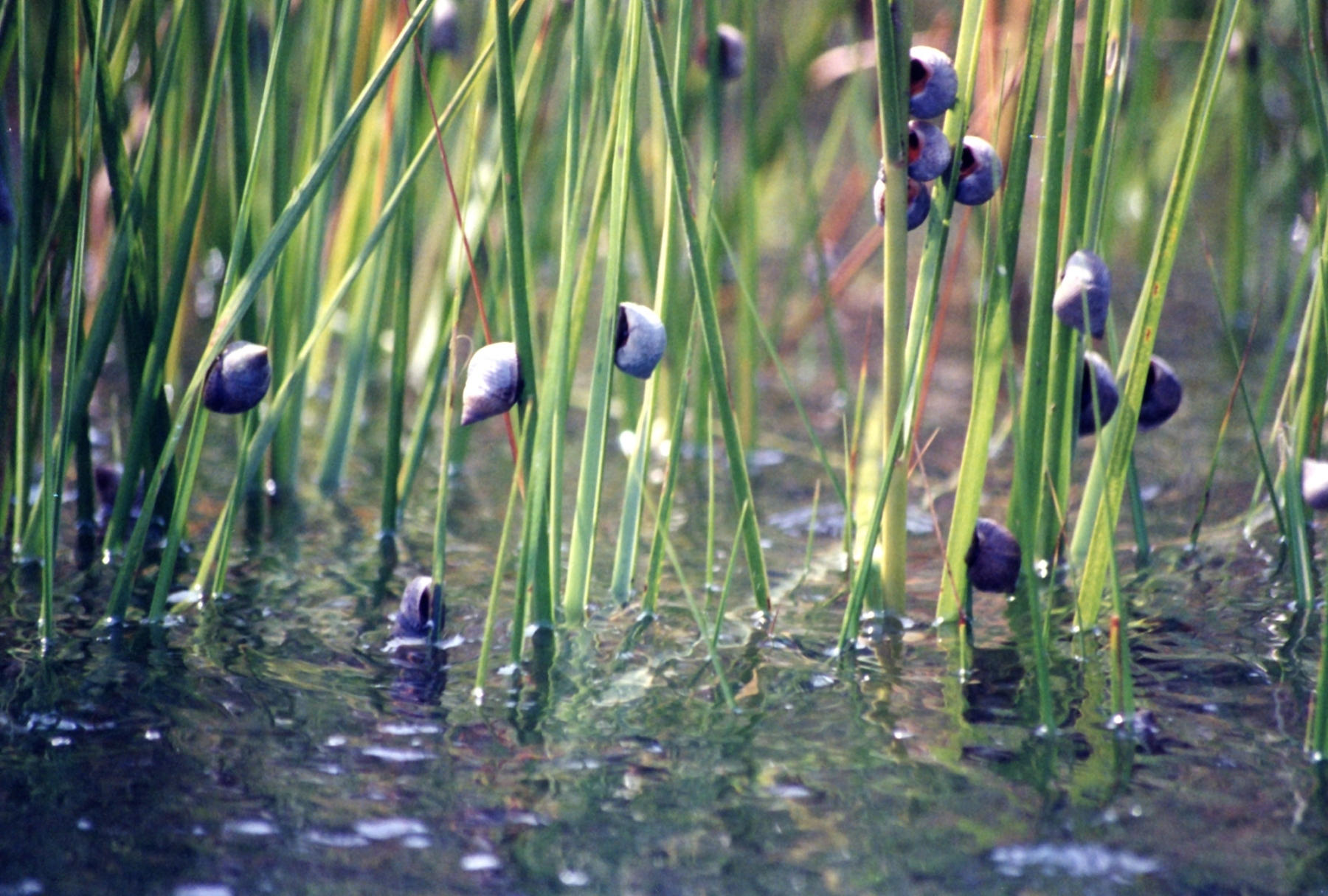
Periwinkle shells
Littoraria irrorata. Keeps Spartina growth in check and food source for Blue Crabs. Will farm fungi on blades by using radula to bore holes and deficate in them, they eat the fungi that grows

Asexual Reproduction
vegetative fragmentation/rhizomes extend laterally and shoots grow up, provide a baffle against water and encourages sedimentation. major form of local spread → meadows
Sexual Reproduction
develop flowers and set seeds
Peat
single plants colonize via rafting or setting seed, developing density to slow currents and accelerating deposition of fine sediment. Rising of sediment surface → spread/meadows, and the sediment becomes ____
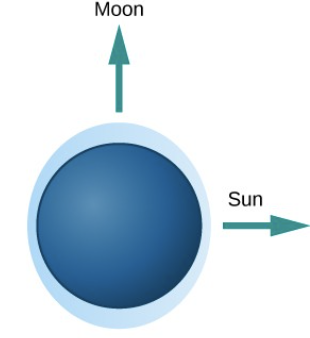
Vegetational zonation
changes in vegetation because of competition and physical ability to survive salinity and drowning. Each zone is dominated by different species, since Spartina is not competitive. Away from water is more diverse, and becomes maritime forest eventually.
From low to high intertidal: Tall Spartina alternifora→ short Spartina alterniflora → Spartina patens → Juncus gerardi → Iva frutescens → terrestrial shrubs
Wrack
floating raft of decaying stems created when stems sever in fall ahead of spring growth, formed by currents concentrating stems which then float on top of grass and smother, resulting in a bare zone. Bare zone is impacted by evaporation and results in saline environment bad for germination, allowing for more genetic diversity because new populations can grow in

Decline Factors
sea level rise floods out marshes, that can’t push back because human development
Pollution - can’t store carbon as well
Land use change - coastal development and filling for agricultural fields
Invasive species shade out Spartina and effect ecosystem function
Phragmities australis also spreads via rhizomes and has dense strands