Lipids 4- Metabolism Flashcards
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Lipid Metabolism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Metabolism
Molecules burned up via complex chemical processes to generate energy, also known as catabolism
Cellular respiration
A series of metabolic pathways that convert carbon fuels into CO2 and H2O to generate energy (i.e., ATP)
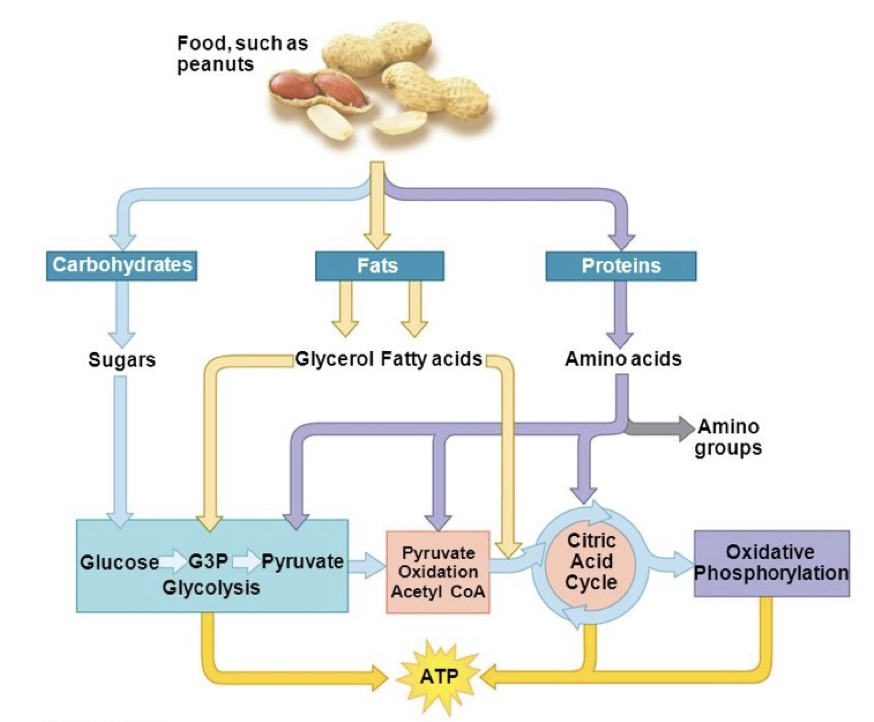
Epinephrine and glucagon
Hormones that induce lipases
Globular protein albumin
Carbon fuel transported from adipose tissue
FABP
Enzymes used by fatty acids to enter muscle cells since fatty acids are not soluble in aqueous solutions
Lipases
Enzymes: ATGL, HSL, MGL
β-oxidation pathway
Pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes, but in mitochondria of muscle cells
observed in eukaryotic adipocytes but considered minor
Activation
Fatty acids must be activated by reacting with coenzyme A to form acyl CoA. This activation takes place on the outer mitochondrial membrane
Acyl CoA synthetase
Enzyme that catalyzes the attachment of a fatty acid to coenzyme A
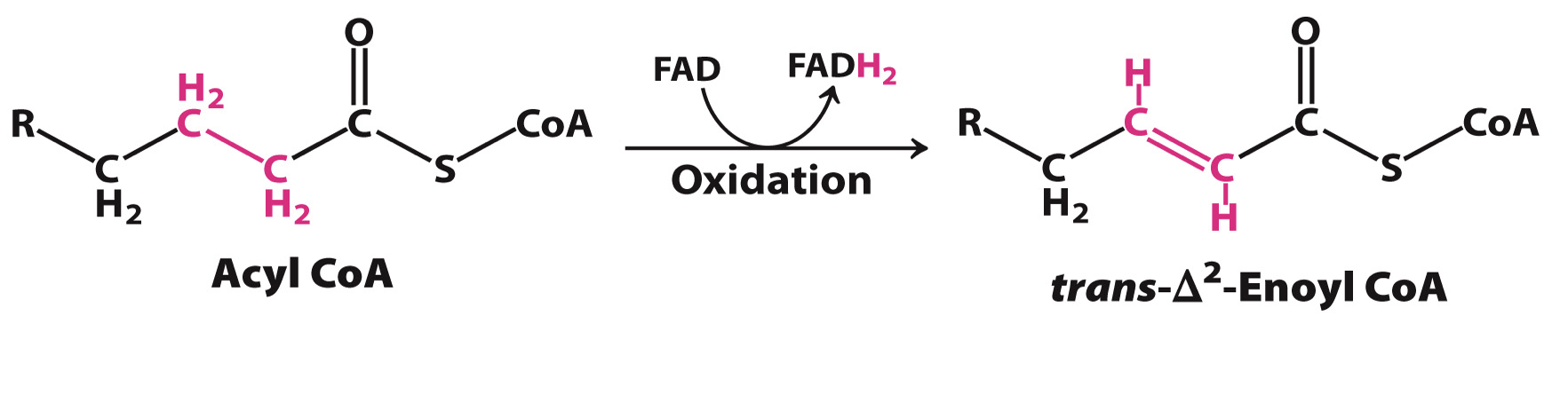
Oxidation by FAD
1st Reaction in the beta-oxidation pathway that generates trans double bond between carbon-2 and -3;
enzyme = Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
Products: Trans-delta2-enoyl CoA and FADH2
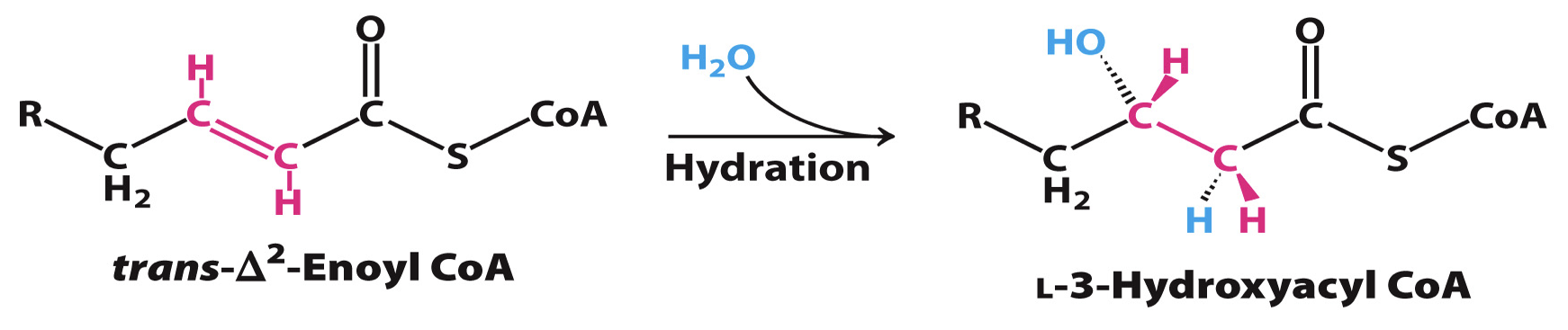
Hydration
2nd Reaction in the beta-oxidation pathway that is hydration of trans-Δ2-enoyl CoA by a hydratase;
enzyme: Enoyl CoA hydratase
Rxn generates hydroxyl group; single bond between carbon -2 and -3
products: L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA
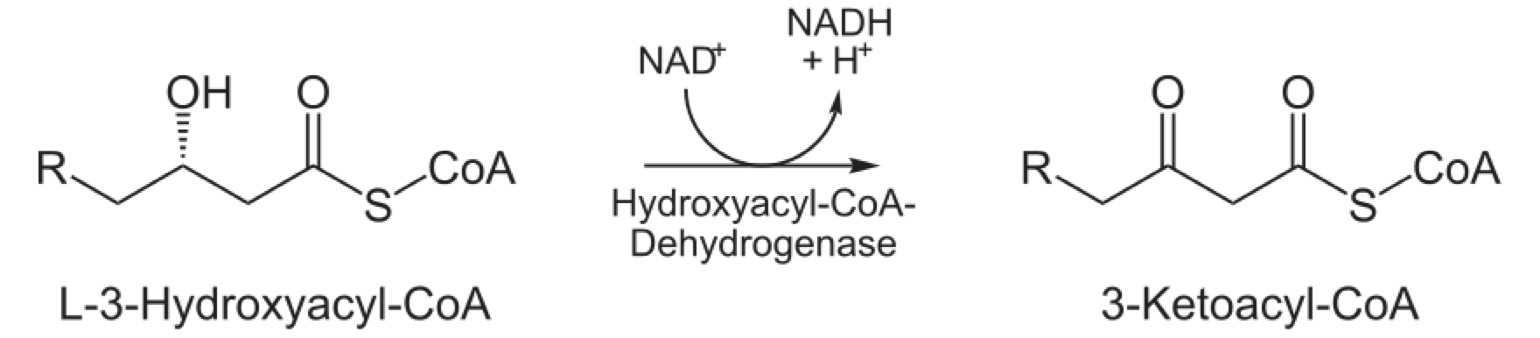
Oxidation by NAD+
3rd Reaction in the beta-oxidation pathway is oxidation L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA by a dehydrogenase
enzyme = L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase
reaction converts hydroxyl group to keto group at carbon-3
Products: 3-ketoacyl CoA and NADH
Thiolysis by coenzyme A
4th Reaction in the beta-oxidation pathway that cleaves 3-ketoacyl CoA by thiol group of a second coenzyme A molecule;
enzyme: β-ketothiolase
reaction cleaves 3-ketoacyl CoA into two molecules
products: acetyl CoA and a fatty acid chain two carbons shorter
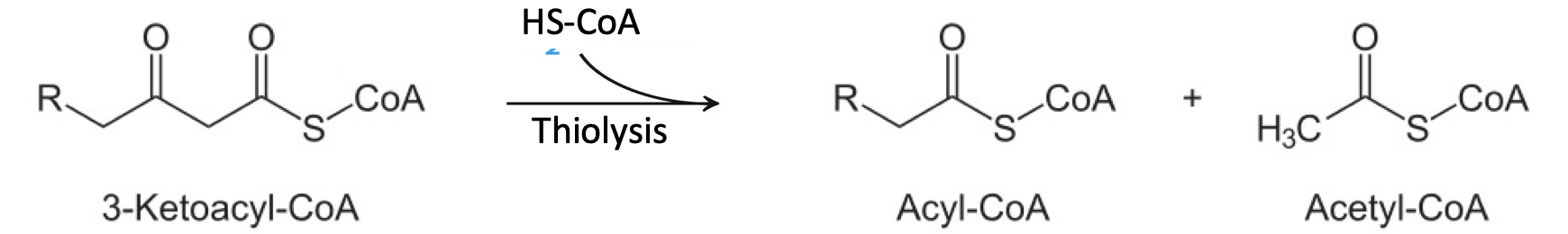
Thiolysis
Chemical reaction in which a sulfhydryl (R-SH) functional group cleaves one compound into two.
Enoyl CoA hydratase
Enzyme suppressed by L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA
steps 1-3 are each controlled by feedback inhibition
PGC-1α
Activates transcription factors, increasing gene expression and regulates the beta oxidation pathway
Cytoplasmic malonyl-CoA, NADH, and acetyl CoA
Suppresses activity of beta-oxidation pathway
Glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate
Molecule directed into glycolysis (generate ATP) or gluconeogenesis (generate glucose), depending on cell’s needs
Mobilization selective
Fatty acids with shorter chains and more unsaturation are metabolized first
FABP
Fatty acids use this to enter muscle cells
Beta-oxidation pathway consists of 4 repeating steps
Each round shortens the FAs hydrocarbon chain by 2 carbons and generates products that can enter cellular respiration
Biochemical activity within the muscle cells
Bringing fatty acids into mitochondria requires activation and ion channels
Ion Channel
Acyl CoA crosses outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) via
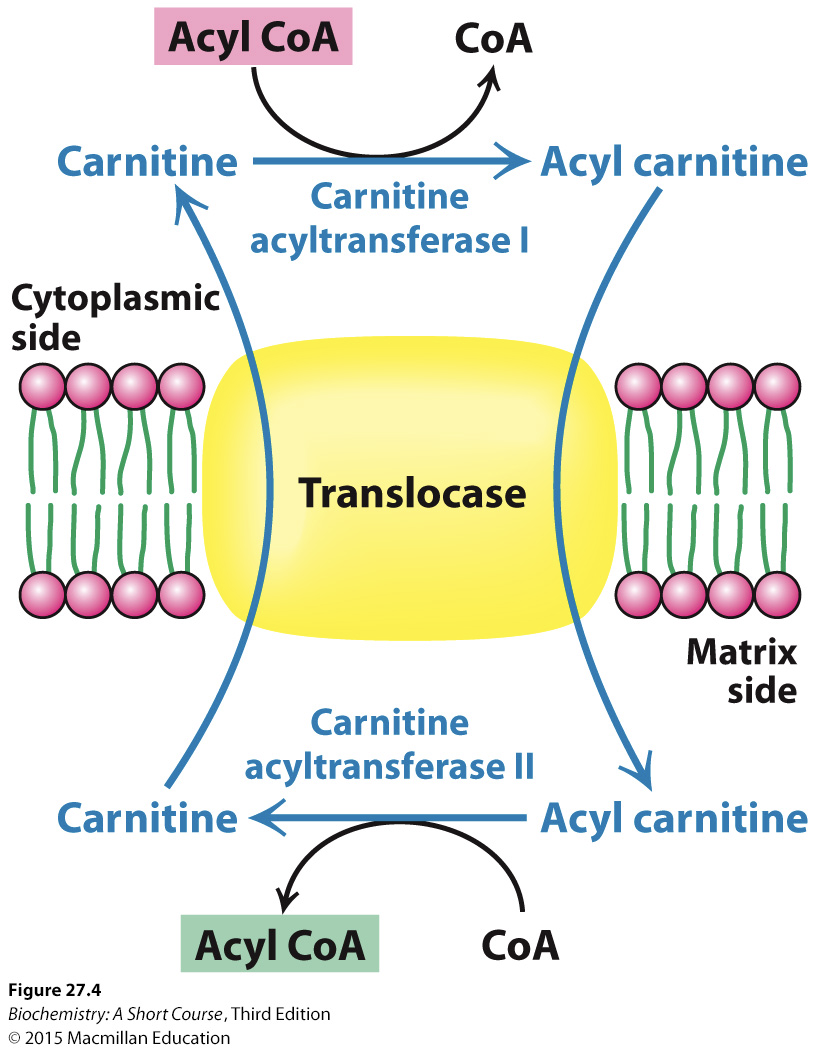
Carnitine in acyl transport
Transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane requires FAs to be linked to an alcohol-carnitine
95% of carnitine is located within the skeletal muscles
activities at this channel are the rate-limiting step
Beta Oxidation and the Citric Acid cycle
steps 1-3 in beta-oxidation are similar to 6-8 in TCA cycle
example: oxidation by FAD, hydration, and oxidation by NAD+
Both beta oxidation and citric acid cycle occur within
the mitochondrial matrix
reduced coenzymes donate electrons into the electron-transport chain
What happens to the product Acetyl CoA
Can enter citric acid cycle and generate ATP
What happens to the product NADH and FADH2
Can donate electrons to electron-transport chain
What happens to the shortened FA (acyl group)
continues to be metabolized via beta oxidation
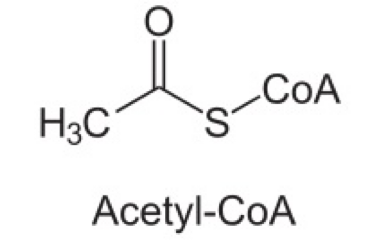
Final thiolysis products for an even chain fatty acid
two acetyl CoA
36 ATP
Combustion of saturated fatty acid hexanoate produces
Odd chain fatty acids
metabolism also occurs via mucles beta-oxidation pathaway
final thiolysis products: yield propionyl CoA and acetyl CoA rather than two molecules of acetyl CoA
Propionyl CoA
This three-carbon unit is not an intermediate for cellular respiration, but a carboxylase and a mutase convert it into succinyl CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle
Aside from this: its a key metabolite for the breakdown of isoleucine, valine, and methionine
Very long chain fatty acids
22 carbons or more are sent to peroxisome first- an organelle containing oxidative enzymes
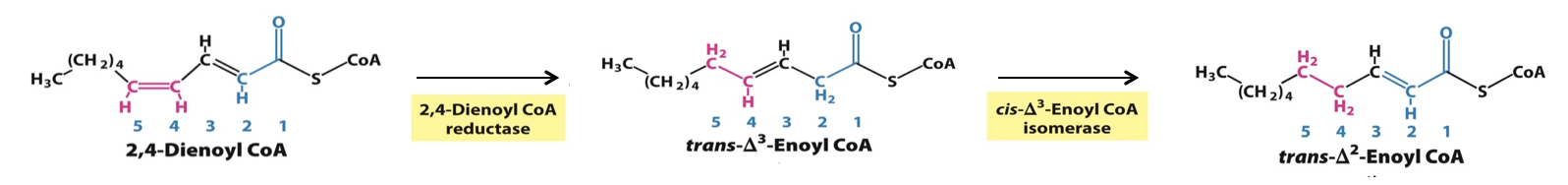
Unsaturated fatty acids
They require additional enzymes to shift the position and configuration of the carbon-carbon double bonds
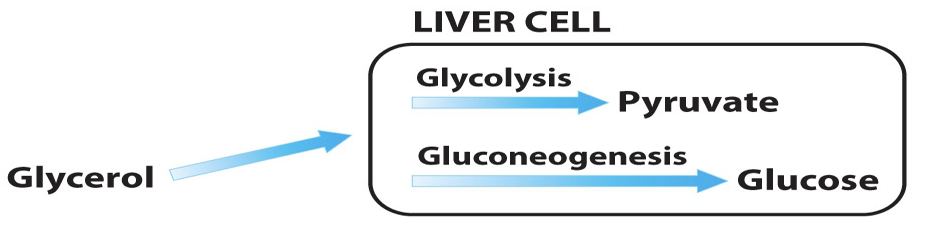
Glycerol metabolism
liberated from tri glycerols during dietary lipid digestion and lipolysis
sent to the liver, where it is phosphorylated by glycerol kinase
Triacylglycerols in adipose tissue are converted into free fatty acids in response to hormonal signals
such as glucagon and epinephrine, stimulating lipolysis and releasing stored energy for use by the body.

Translocase
Acyl carnitine is shuttled across the inner membrane by a