Gene Mapping
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Class 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Parental types (independent assortment)
1:1 ratio
total is 4 types (1:1:1:1)
gametes having the allele combination seen in the original female of the earliest generation
gametes having the allele combination seen in the original male of the earliest generation
Recombinant types (independent assortment)
1:1 ratio
total is 4 types (1:1:1:1)
gametes having the allele combination NOT seen in the original female or male of the earliest generation
produced by a reshuffling of alleles during independent assortment
Linkage
the number of F2 progeny with parental genotypes exceed number of F2 progeny with recombinant genotypes
instead of independent assortment, particular alleles are connected most of the time
will NOT see 9:3:3:1 mandelian phenotypic ratio
RF less than 50%
will never be more than 50%, though can have a distance greater than 50 m.u.
Map units (m.u.)/centimorgan (cM)
used to gauge physical distance separating any two genes on the same chromosome
an index of recombination probabilities assumed to reflect gene distances
corresponds to 1 million base pairs in humans
Linkgage group
genes chained together by linkage relationships
number of groups equates to number of pairs of chromosomes in species
humans have 23
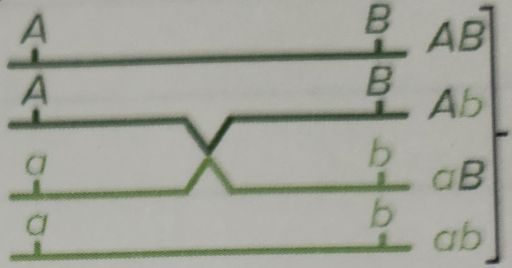
No crossovers (NCOs)
NO recombinant type gametes
ALL parental chromosomes

Double crossover (DCOs), 2-strand
NO recombinant type gametes
ALL parental type

Double crossover (DCOs), 3-strand
HALF recombinant type gametes
HALF parental type
one of two ways this event can happen
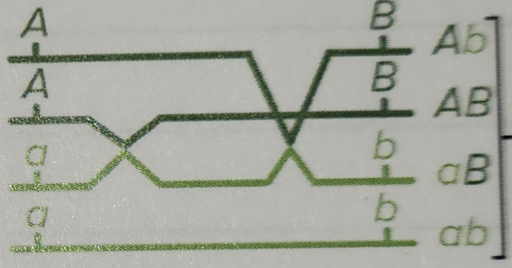
Double crossover (DCOs), 3-strand
HALF recombinant type gametes
HALF parental type
one of two ways this event can happen
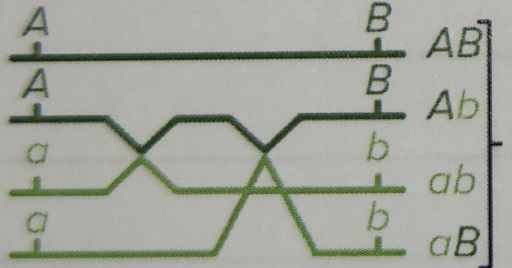
Double crossover (DCOs), 4-strand
ALL recombinant type gametes
NO parental type
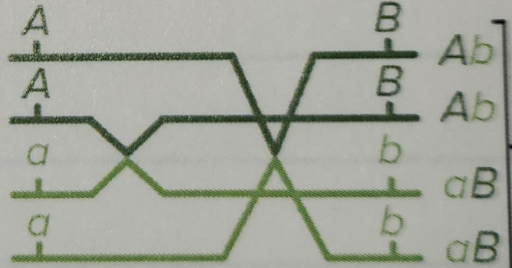
Single crossover (SCOs)
HALF recombinant type gametes
HALF parental type
Double crossover (DCOs), all types
all four types are EQUALLY likely
would happen more on smaller chromosomes (as opposed to larger ones)
more rare than a single crossover event
rare events occurring simultaneously is more rare than the individual event occurring
are not independent due to chromosomal interference
interference: making sure homologous chromosomes have at least one crossover

Crossing over event (COs)
reciprocal exchange of parts between maternal and paternal chromosomes
contributes to genetic diversity
happens in meiosis I with homologous chromosomes
helps with orientation at metaphase plate
without which, chromosomes would segregate improperly
the closer genes are, the less likely crossing over will happen
frequency increases as distance between genes increases
Recombination frequency (RF)
is equal to map units
less than 50% = linkage (< 0.5)
is NEVER more than 50%
Two-point test cross
used to calculate RF of two linked genes
useful for determining frequency of gametes produced
dominant phenotype x recessive phenotype to estimate zygosity of dominate phenotype
not great for judging accurate distances between genes
only involving two genes makes it difficult to know the order in which the genes are placed on the chromosomes
accuracy declines the smaller the distance between genes
Three-point test cross
involves three genes
a more accurate judge of distances between genes that a closer together
accounts for double crossovers
Gene mapping (summary)
help prediction of inheritance patterns of specific traits
all about ordering genes and their distances from each other