AP Bio Unit 4
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
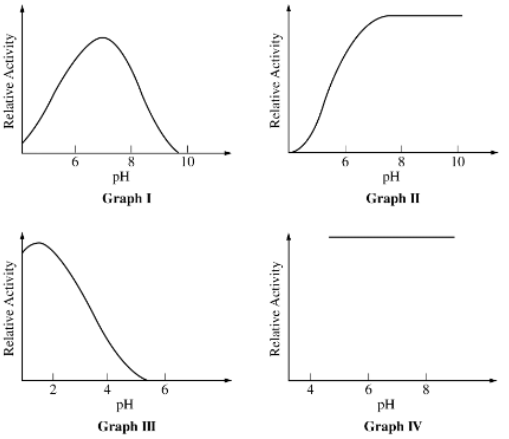
Enzymes with their highest activity at an alkaline (basic) pH are represented by which of the following graphs?
II only
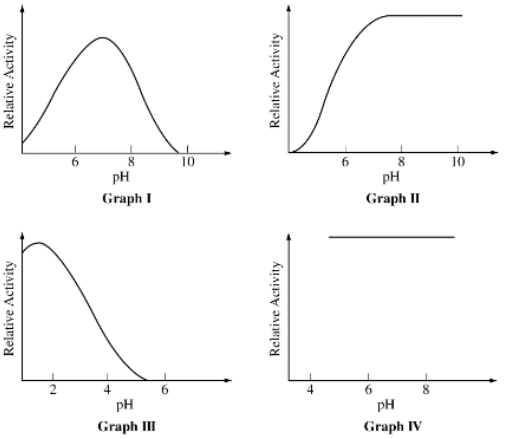
Graphs representing enzymes sensitive to changes in pH include which of the following?
I, II, and III only
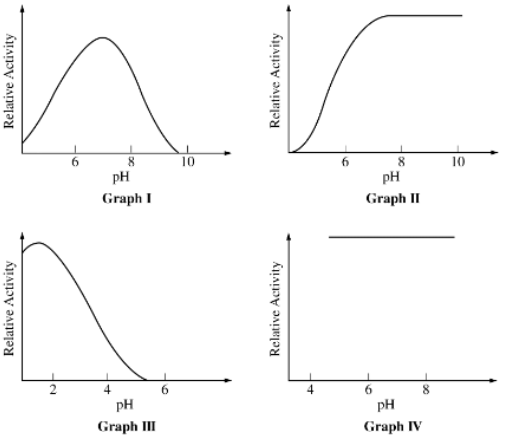
The most likely explanation for the results shown in Graph I is that
pH affects the shape of the active site of the enzyme
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is further metabolized in the Krebs cycle. A researcher measured the accumulation of acetyl-CoA in a reaction containing pyruvate and pyruvate dehydrogenase under several different conditions (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Accumulation of acetyl-CoA under different conditions
Which of the following best describes the cellular location where pyruvate dehydrogenase is most likely active?
The mitochondrial matrix
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is further metabolized in the Krebs cycle. A researcher measured the accumulation of acetyl-CoA in a reaction containing pyruvate and pyruvate dehydrogenase under several different conditions (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Accumulation of acetyl-CoA under different conditions
The maximum production rate of acetyl-CoA under condition 1 is closest to which of the following?
1 micromole/sec
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is further metabolized in the Krebs cycle. A researcher measured the accumulation of acetyl-CoA in a reaction containing pyruvate and pyruvate dehydrogenase under several different conditions (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Accumulation of acetyl-CoA under different conditions
Which of the following observations provides the best evidence that acetyl-CoA negatively regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase activity?
The rate of the pyruvate dehydrogenase–catalyzed reaction is slower in the presence of a higher concentration of acetyl-CoA.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is further metabolized in the Krebs cycle. A researcher measured the accumulation of acetyl-CoA in a reaction containing pyruvate and pyruvate dehydrogenase under several different conditions (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Accumulation of acetyl-CoA under different conditions
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency is a genetic disease most commonly linked to a mutation in the α-subunit of the mitochondrial enzyme that causes the enzyme to cease functioning. As a result of the mutation, affected individuals build up dangerous amounts of lactic acid. Which of the following best explains the buildup of lactic acid in individuals with the mutation?
Cells undergo fermentation because pyruvate cannot be metabolized to proceed into the Krebs cycle.
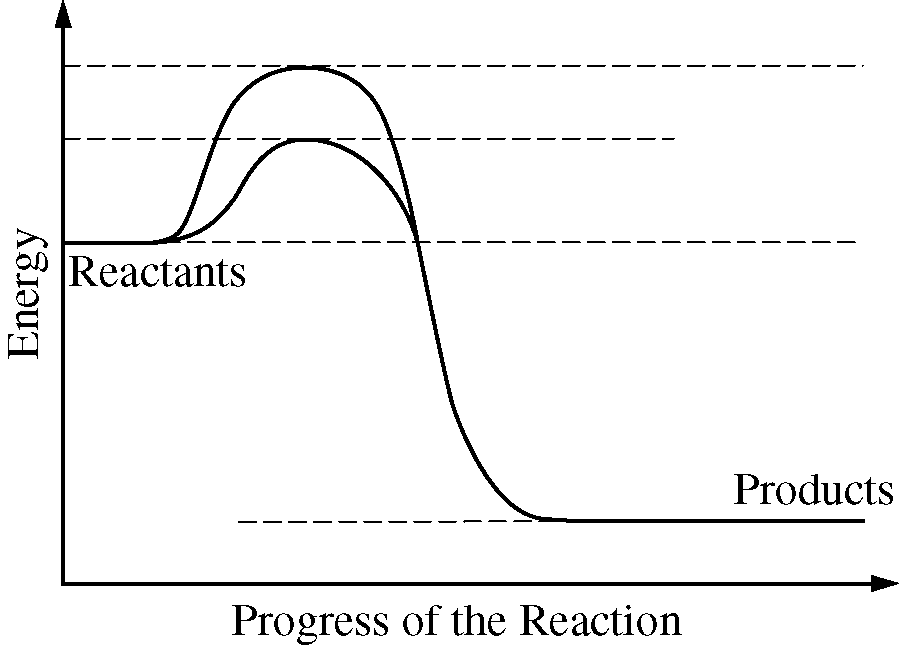
The diagram below shows energy changes in a specific chemical reaction with and without the addition of an enzyme to the reaction.
Which of the following questions can best be answered by the diagram?
Does the addition of an enzyme reduce the activation energy required for a reaction?
A researcher proposes a model of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in which a reactant is converted to a product. The model is based on the idea that the reactant passes through a transition state within the enzyme-substrate complex before the reactant is converted to the product.
Which of the following statements best helps explain how the enzyme speeds up the reaction?
The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes the transition state, which decreases the activation energy of the reaction.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that aids in the decomposition of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) into nontoxic substances. Methyl alcohol acts as a competitive inhibitor of ethyl alcohol by competing for the same active site on ADH. When attached to ADH, methyl alcohol is converted to formaldehyde, which is toxic in the body.
Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of increasing the concentration of substrate (ethyl alcohol), while keeping the concentration of the inhibitor (methyl alcohol) constant?
Competitive inhibition will decrease because the proportion of the active sites occupied by substrate will increase.
Amylase is a protein that catalyzes the conversion of starch to simple sugars. Amylase activity in an aqueous solution can be measured by using iodine as a starch indicator. A solution containing iodine and starch will have a dark-blue color, whereas a solution containing iodine but no starch will have a light-brown color. The color change of an iodine solution from dark blue to light brown can be used to measure the rate at which starch is converted to simple sugars.
A student designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental pH on amylase function. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1.
Table 1. An experiment for investigating the effect of pH on amylase function
Test Tube | Environmental pH | Starch Added | Amylase Added | Iodine Added | Pretreated by Boiling |
I | 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
II | 6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
III | 7 | No | Yes | Yes | No |
IV | 7 | Yes | No | Yes | No |
V | 7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
VI | 7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
VII | 8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
VIII | 9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
Which of the following statements best justifies the inclusion of test tube V as a control in the experiment?
It will show the color change that occurs in the absence of enzyme activity.
Directions: This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances.
(A) Cytochrome
(B) FADH2
(C) NAD+
(D) NADP+
(E) Oxygen (O2)
An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions
NAD+
Directions: This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances.
(A) Cytochrome
(B) FADH2
(C) NAD+
(D) NADP+
(E) Oxygen (O2)
Coenzyme that transfers electrons from the Krebs cycle to the mitochondrial electron-transport chain at a lower energy level than that of electrons entering at the beginning of the chain
FADH2
A researcher claims that the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is essential to cellular function.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher’s claim?
ATP hydrolysis is an energy-releasing reaction that is often coupled with reactions that require an input of energy.
ATP serves as a common energy source for organisms because
its energy can be easily transferred to do cellular work
During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the net movement of
protons down a concentration gradient
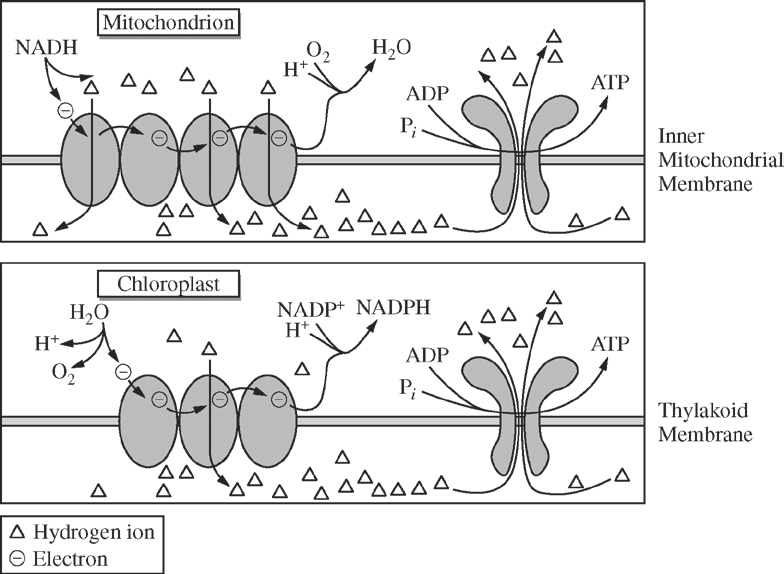
The figures below illustrate the similarities between ATP synthesis in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
The figures can best assist in answering which of the following questions?
Do electron transport chains create a gradient so that ATP synthase can generate ATP molecules?
To investigate bacterial metabolism, a researcher divided a population (culture) of Staphylococcus capitis bacteria into two sets of culture tubes containing glucose. The researcher added a chemical to one set of tubes and measured the pH of the cultures at 5-minute intervals as the bacteria metabolized the glucose into lactic acid. The data are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1. AVERAGE CHANGE IN pH IN CONTROL AND TREATMENT GROUPS OVER A 40-MINUTE PERIOD |
Time (min) | Average pH of Control(±2 SEx¯) | Average pH of Treatment(±2 SEx¯) |
0 | 8.04±0.05 | 8.04±0.06 |
5 | 7.96±0.03 | 7.91±0.04 |
10 | 7.88±0.02 | 7.85±0.04 |
15 | 7.82±0.02 | 7.79±0.06 |
20 | 7.76±0.03 | 7.70±0.04 |
25 | 7.71±0.04 | 7.67±0.02 |
30 | 7.63±0.03 | 7.63±0.02 |
35 | 7.65±0.02 | 7.60±0.02 |
40 | 7.65±0.01 | 7.59±0.02 |
Which of the following best describes the process by which the bacteria are breaking down the glucose to produce lactic acid?
The bacteria are breaking down sugars in the absence of oxygen.
To investigate bacterial metabolism, a researcher divided a population (culture) of Staphylococcus capitis bacteria into two sets of culture tubes containing glucose. The researcher added a chemical to one set of tubes and measured the pH of the cultures at 5-minute intervals as the bacteria metabolized the glucose into lactic acid. The data are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1. AVERAGE CHANGE IN pH IN CONTROL AND TREATMENT GROUPS OVER A 40-MINUTE PERIOD |
Time (min) | Average pH of Control(±2 SEx¯) | Average pH of Treatment(±2 SEx¯) |
0 | 8.04±0.05 | 8.04±0.06 |
5 | 7.96±0.03 | 7.91±0.04 |
10 | 7.88±0.02 | 7.85±0.04 |
15 | 7.82±0.02 | 7.79±0.06 |
20 | 7.76±0.03 | 7.70±0.04 |
25 | 7.71±0.04 | 7.67±0.02 |
30 | 7.63±0.03 | 7.63±0.02 |
35 | 7.65±0.02 | 7.60±0.02 |
40 | 7.65±0.01 | 7.59±0.02 |
Which of the following was the dependent variable in the researcher’s experiment?
pH
To investigate bacterial metabolism, a researcher divided a population (culture) of Staphylococcus capitis bacteria into two sets of culture tubes containing glucose. The researcher added a chemical to one set of tubes and measured the pH of the cultures at 5-minute intervals as the bacteria metabolized the glucose into lactic acid. The data are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1. AVERAGE CHANGE IN pH IN CONTROL AND TREATMENT GROUPS OVER A 40-MINUTE PERIOD |
Time (min) | Average pH of Control(±2 SEx¯) | Average pH of Treatment(±2 SEx¯) |
0 | 8.04±0.05 | 8.04±0.06 |
5 | 7.96±0.03 | 7.91±0.04 |
10 | 7.88±0.02 | 7.85±0.04 |
15 | 7.82±0.02 | 7.79±0.06 |
20 | 7.76±0.03 | 7.70±0.04 |
25 | 7.71±0.04 | 7.67±0.02 |
30 | 7.63±0.03 | 7.63±0.02 |
35 | 7.65±0.02 | 7.60±0.02 |
40 | 7.65±0.01 | 7.59±0.02 |
Which of the following graphs best represents the data in Table 1 ?

To investigate bacterial metabolism, a researcher divided a population (culture) of Staphylococcus capitis bacteria into two sets of culture tubes containing glucose. The researcher added a chemical to one set of tubes and measured the pH of the cultures at 5-minute intervals as the bacteria metabolized the glucose into lactic acid. The data are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1. AVERAGE CHANGE IN pH IN CONTROL AND TREATMENT GROUPS OVER A 40-MINUTE PERIOD |
Time (min) | Average pH of Control(±2 SEx¯) | Average pH of Treatment(±2 SEx¯) |
0 | 8.04±0.05 | 8.04±0.06 |
5 | 7.96±0.03 | 7.91±0.04 |
10 | 7.88±0.02 | 7.85±0.04 |
15 | 7.82±0.02 | 7.79±0.06 |
20 | 7.76±0.03 | 7.70±0.04 |
25 | 7.71±0.04 | 7.67±0.02 |
30 | 7.63±0.03 | 7.63±0.02 |
35 | 7.65±0.02 | 7.60±0.02 |
40 | 7.65±0.01 | 7.59±0.02 |
Based on the data in Table 1, which of the following is the earliest time point at which there is a statistical difference in average pH between the control and treatment groups?
35 minutes
To investigate bacterial metabolism, a researcher divided a population (culture) of Staphylococcus capitis bacteria into two sets of culture tubes containing glucose. The researcher added a chemical to one set of tubes and measured the pH of the cultures at 5-minute intervals as the bacteria metabolized the glucose into lactic acid. The data are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1. AVERAGE CHANGE IN pH IN CONTROL AND TREATMENT GROUPS OVER A 40-MINUTE PERIOD |
Time (min) | Average pH of Control(±2 SEx¯) | Average pH of Treatment(±2 SEx¯) |
0 | 8.04±0.05 | 8.04±0.06 |
5 | 7.96±0.03 | 7.91±0.04 |
10 | 7.88±0.02 | 7.85±0.04 |
15 | 7.82±0.02 | 7.79±0.06 |
20 | 7.76±0.03 | 7.70±0.04 |
25 | 7.71±0.04 | 7.67±0.02 |
30 | 7.63±0.03 | 7.63±0.02 |
35 | 7.65±0.02 | 7.60±0.02 |
40 | 7.65±0.01 | 7.59±0.02 |
According to the data, which of the following best explains the results of the experiment?
The pH of the treatment culture was lower than the pH of the control because the chemical increased the bacterial metabolic rate.
Which of the following statements about mitochondrial chemiosmosis is NOT true?
Heat energy is required to establish the electron transport chain.
According to the chemiosmotic theory (chemiosmotic coupling), the energy required to move protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space against a concentration gradient comes most directly from
electrons flowing along the electron transport chain
Which of the following best describes the function
of the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD in eukaryotic
cellular respiration?
They accept electrons during oxidation-reduction reactions.
Within the cell, many chemical reactions that, by themselves, require energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because the reactions
may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP

Figure 1. Diagram of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase in the membrane of mitochondria
On average, more ATP can be produced from an NADH molecule than can be produced from a molecule of FADH2. Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains the difference in ATP production between these two molecules?
The electrons of FADH2 are transferred through three complexes of the electron transport chain whereas those of NADH are transferred through all four complexes.
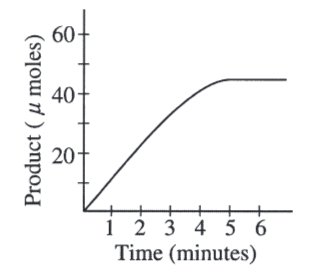
A scientist determined the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by measuring the amount of product formed over time. The following curve was generated from the data collected.
During which time interval is the reaction rate lowest?
4-5 minutes
Newborn babies and hibernating animals contain a large amount of brown adipose (fat) tissue (BAT). Certain proteins in the BAT cells increase the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane to protons, disrupting the proton gradient.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of disrupting the proton gradient in BAT?
Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation will be decoupled, generating more heat but less ATP.
Melanocytes are skin cells that can become cancerous and develop into a cancer known as melanoma. Some cancerous melanocytes have developed resistance to the drugs currently used to treat melanoma. As a result, researchers are investigating the effects of a new compound (drug X) on four different melanoma cell lines. Researchers analyzed cell survival in two cell lines (Figure 1) and oxygen consumption in the presence of drug X in all four cell lines (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows the proposed mechanism by which drug X affects cells.

Figure 1. Percent survival of normal melanocytes and cancerous melanocyte (melanoma) lines 1 and 2 after treatment with different concentrations of drug X

Figure 2. Oxygen consumption per cell in four melanoma lines after treatment with either solvent alone or solvent containing drug X. Error bars represent ±2SEx¯.

Figure 3. Pathway leading to cell survival, growth, and proliferation and the likely effect of drug X
Based on the information presented, which of the following best explains why the researchers measured oxygen consumption as an indicator of the effectiveness of drug X?
Oxygen accepts electrons in oxidative phosphorylation, a process necessary for melanoma cell survival
Melanocytes are skin cells that can become cancerous and develop into a cancer known as melanoma. Some cancerous melanocytes have developed resistance to the drugs currently used to treat melanoma. As a result, researchers are investigating the effects of a new compound (drug X) on four different melanoma cell lines. Researchers analyzed cell survival in two cell lines (Figure 1) and oxygen consumption in the presence of drug X in all four cell lines (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows the proposed mechanism by which drug X affects cells.

Figure 1. Percent survival of normal melanocytes and cancerous melanocyte (melanoma) lines 1 and 2 after treatment with different concentrations of drug X

Figure 2. Oxygen consumption per cell in four melanoma lines after treatment with either solvent alone or solvent containing drug X. Error bars represent ±2SEx¯.

Figure 3. Pathway leading to cell survival, growth, and proliferation and the likely effect of drug X
Which of the following best describes the data in Figure 1 ?
At a concentration above μ10 μM, drug X reduces melanoma cell survival.
Melanocytes are skin cells that can become cancerous and develop into a cancer known as melanoma. Some cancerous melanocytes have developed resistance to the drugs currently used to treat melanoma. As a result, researchers are investigating the effects of a new compound (drug X) on four different melanoma cell lines. Researchers analyzed cell survival in two cell lines (Figure 1) and oxygen consumption in the presence of drug X in all four cell lines (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows the proposed mechanism by which drug X affects cells.

Figure 1. Percent survival of normal melanocytes and cancerous melanocyte (melanoma) lines 1 and 2 after treatment with different concentrations of drug X

Figure 2. Oxygen consumption per cell in four melanoma lines after treatment with either solvent alone or solvent containing drug X. Error bars represent ±2SEx¯.

Figure 3. Pathway leading to cell survival, growth, and proliferation and the likely effect of drug X
Based on Figure 2, which of the following best supports the claim that drug X inhibits oxygen consumption?
Melanoma line 3 consumes statistically less oxygen per cell in the presence of drug X than it does in the presence of the solvent alone.
Melanocytes are skin cells that can become cancerous and develop into a cancer known as melanoma. Some cancerous melanocytes have developed resistance to the drugs currently used to treat melanoma. As a result, researchers are investigating the effects of a new compound (drug X) on four different melanoma cell lines. Researchers analyzed cell survival in two cell lines (Figure 1) and oxygen consumption in the presence of drug X in all four cell lines (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows the proposed mechanism by which drug X affects cells.

Figure 1. Percent survival of normal melanocytes and cancerous melanocyte (melanoma) lines 1 and 2 after treatment with different concentrations of drug X

Figure 2. Oxygen consumption per cell in four melanoma lines after treatment with either solvent alone or solvent containing drug X. Error bars represent ±2SEx¯.

Figure 3. Pathway leading to cell survival, growth, and proliferation and the likely effect of drug X
A researcher has identified a compound that reverses the effect of drug X. Based on Figure 3, which of the following best explains how the compound acts in the pathway to reverse the effects of drug X?

Scientists were interested in testing the effects of rotenone, a broad-spectrum pesticide, on a cell culture. Cell culture A was used as a control, while culture B was treated with rotenone. After a period of time, the scientists measured the concentration of several metabolites in the mitochondria of cells in both cultures. Their results are shown in the table below.
Metabolites | MetabolitesConcentration in Culture A (μM) | Concentration in Culture B (μM) |
Pyruvate | 25 | 25 |
NADH | 55 | 550 |
NAD+ | 55 | 5 |
ATP | 85 | 5 |
ADP+Pi | 55 | 100 |
FADH2 | 25 | 26 |
FAD | 25 | 25 |
Based on the data in the table, which of the following best explains the effects of rotenone on cellular respiration?
Treated cells are not able to break down NADH because certain enzymes of the electron transport chain are inhibited.
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.

Figure 1. Key steps in the metabolic pathway of glucose
If NaF is added to cells undergoing cellular respiration, which of the following will most likely accumulate in the cells?
2-phosphoglycerate
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.

Figure 1. Key steps in the metabolic pathway of glucose
Based on Figure 1, the net number of ATP molecules produced during glycolysis from the metabolism of a single glucose molecule is closest to which of the following?
2
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.

Figure 1. Key steps in the metabolic pathway of glucose
An increase in the concentration of protons in the cytosol will most likely have which of the following effects on glycolysis?
Glycolytic enzymes will denature as a result of the increased H+ concentration.
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.

Figure 1. Key steps in the metabolic pathway of glucose
Which of the following describes why a glucose transporter is needed to move glucose into the cell?
Glucose is large and polar and cannot pass through the phospholipid layer
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF.

Figure 1. Key steps in the metabolic pathway of glucose
Tarui disease is an inherited disorder that is caused by mutations in PFKM, the gene that encodes a subunit of phosphofructokinase, an enzyme in the glycolysis pathway. Individuals with Tarui disease produce little or no functional phosphofructokinase in skeletal muscle cells. Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains why a low carbohydrate diet is recommended for those with Tarui disease?
Carbohydrates metabolism requires all the reactions of glycolysis, and amino acids and fatty acids do not.

Figure 1. Change in energy over the course of four chemical reactions
Based on the data in Figure 1, which of the following most likely represents the change in energy that occurs when ATP hydrolysis is coupled with the phosphorylation of a substrate?
Line 1 represents ATP hydrolysis, and line 4 represents phosphorylation of a substrate.
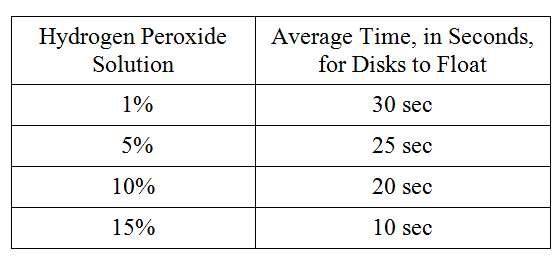
For following group of questions first study the description of the data and then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
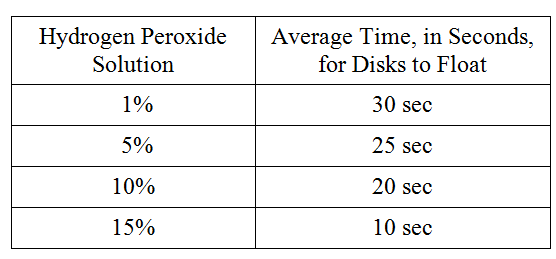
To study the actions of the enzyme catalase on hydrogen peroxide, students performed the following experiment. Catalase was extracted from potatoes by blending raw potatoes in a blender with cold distilled water. The filtrate was stored on ice. The following hydrogen peroxide solutions were made: 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, and 15 percent. Filter paper disks were soaked in the catalase filtrate and dropped into beakers containing the various solutions. The activity of the enzyme was measured by the amount of time it took for the disks to float to the surface of the solution on the bubbles produced by the reaction. The following data were obtained.
Which of the following best describes why the disks rose to the surface faster in the more concentrated hydrogen peroxide solutions?
The higher substrate concentrations in the more concentrated solution speeded the reaction
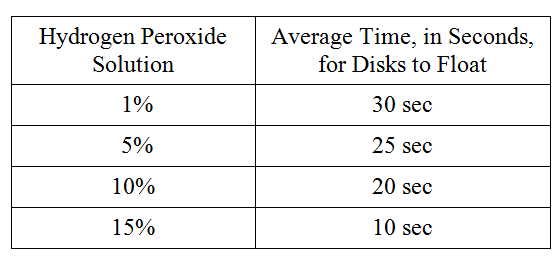
For following group of questions first study the description of the data and then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
To study the actions of the enzyme catalase on hydrogen peroxide, students performed the following experiment. Catalase was extracted from potatoes by blending raw potatoes in a blender with cold distilled water. The filtrate was stored on ice. The following hydrogen peroxide solutions were made: 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, and 15 percent. Filter paper disks were soaked in the catalase filtrate and dropped into beakers containing the various solutions. The activity of the enzyme was measured by the amount of time it took for the disks to float to the surface of the solution on the bubbles produced by the reaction. The following data were obtained.
Which of the following experimental designs should the students use as a control for the experiment?
Place a catalase-soaked disk in a beaker of water
For following group of questions first study the description of the data and then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
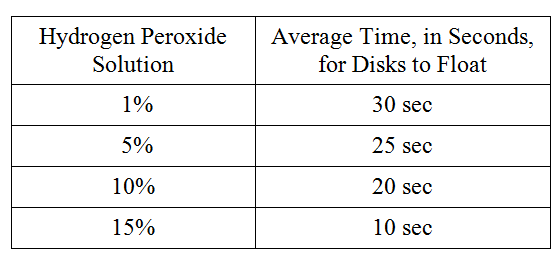
To study the actions of the enzyme catalase on hydrogen peroxide, students performed the following experiment. Catalase was extracted from potatoes by blending raw potatoes in a blender with cold distilled water. The filtrate was stored on ice. The following hydrogen peroxide solutions were made: 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, and 15 percent. Filter paper disks were soaked in the catalase filtrate and dropped into beakers containing the various solutions. The activity of the enzyme was measured by the amount of time it took for the disks to float to the surface of the solution on the bubbles produced by the reaction. The following data were obtained.
Which of the following best describes why ice was used during this experiment?
To retard the breakdown of the catalase
For following group of questions first study the description of the data and then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet.
To study the actions of the enzyme catalase on hydrogen peroxide, students performed the following experiment. Catalase was extracted from potatoes by blending raw potatoes in a blender with cold distilled water. The filtrate was stored on ice. The following hydrogen peroxide solutions were made: 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, and 15 percent. Filter paper disks were soaked in the catalase filtrate and dropped into beakers containing the various solutions. The activity of the enzyme was measured by the amount of time it took for the disks to float to the surface of the solution on the bubbles produced by the reaction. The following data were obtained.
If the potato solution was boiled for 10 minutes and cooled for 10 minutes before being tested, the average time for the disks to float to the surface of the hydrogen peroxide solution would be
more than 30 seconds
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme?
The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
Which of the following can be used to determine the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
Rate of disappearance of the substrate

Figure 1. Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after 5 minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following best describes how an increase in the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture affected the frequency of enzyme‑substrate interactions?
The frequency o enzyme-substrate interactions increased until all of the active sites were interacting with substrate.

Figure 1. Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after 5 minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following experimental designs would best allow researchers to investigate the effect of pH on the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Measure the reaction rates at different pH levels when the enzyme concentration remains the same and the concentration is 100μM.

Figure 1. Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after 5 minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following questions best addresses whether a particular inhibitor is competitive or noncompetitive?
Does the inhibitor bind to allosteric site or the active site of the enzyme

Figure 1. Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after 5 minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following graphs predicts the most likely rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction if the concentration of the enzyme in the mixture were doubled?


Figure 1. The electron transport chain of cellular respiration. The bold arrows passing through the complexes in the membrane represent the path of electron flow in mitochondria.
Compound X binds to complex IV of the mitochondrial electron transport chain and prevents complex IV from accepting electrons.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best explains why the cells of an animal exposed to compound X have an increased ratio of NADH to NAD+?
NADH cannot be oxidized to NAD+ because complexes I, II, and III cannot accept electrons if electrons cannot be passed to complex IV.
Gelatin is a protein that is derived from collagen which is found in the bones, skin, and connective tissue of animals. To investigate the ability of various enzymes to digest gelatin, a group of students set up an assay involving camera film. Camera film contains gelatin and appears black when exposed to light but turns clear as the gelatin gets broken down. The students incubated pieces of exposed camera film in test tubes, each containing one of three different enzyme solutions (trypsin, lipase, or amylase) as indicated in Figure 1. The students recorded the time it took for the enzymes to digest the gelatin in each test tube, turning the film from black to clear.

Figure 1. Diagram of experimental setup.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate control for this experiment?
A test tube containing a piece of exposed camera film submerged in water
The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which is an important step in glycolysis. The reaction involves the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to glucose.
Either a glucose molecule or a water molecule can fit in the active site of hexokinase. The presence of a water molecule in hexokinase’s active site would result in the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP instead of the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of hexokinase?
Glucose has the right shape and charge to cause hexokinase to undergo a structural change needed for catalysis, whereas water does not.
Pyruvate kinase, a key enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, is inhibited by the amino acid alanine. The ability of alanine to inhibit the enzyme is not affected by increasing the concentration of substrate.
Which of the following best explains the mechanism by which alanine inhibits pyruvate kinase activity?
Alanine binds to an allosteric site of the enzyme, changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site.
In an experiment, a scientist isolates mitochondria from living cells and suspends them in two different buffered solutions. One solution is maintained at pH 4, while the other solution is maintained at pH 9. The scientist finds that mitochondria in the solution at pH 4 continue to produce ATP but those in the pH 9 solution do not.
The results of the experiment can be used as evidence in support of which of the following scientific claims about mitochondrial activity?
ATP production in mitochondria requires a hydrogen ion gradient that favors movement of protons into the mitochondrial matrix.
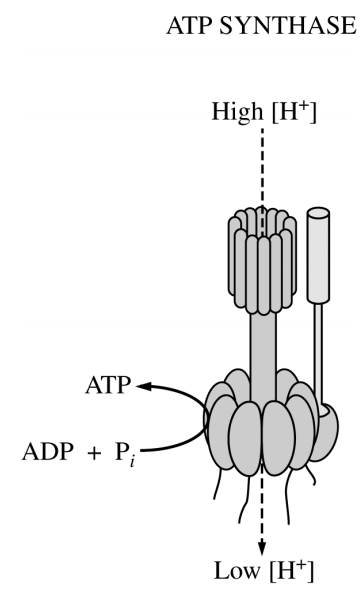
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation of the mechanism of ATP synthase?
Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient?
Which of the following describes a metabolic consequence of a shortage of oxygen in muscle cells?
A buildup of lactic acid in the muscle tissue due to fermentation
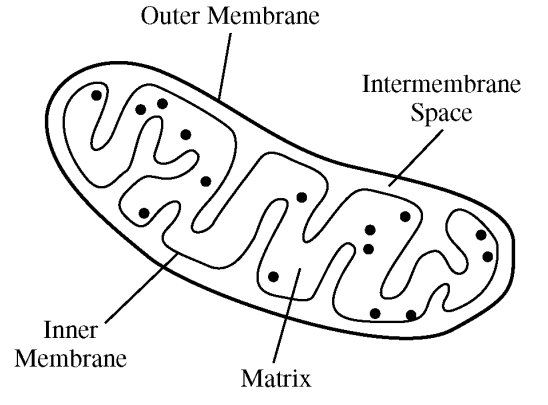
The figure above shows an organelle typically found in eukaryotic cells. Which of the following best describes the function of the double membrane system of this organelle?
The inner membrane has specialized proteins that create a hydrogen ion concentration gradient between the inter-membrane space and the matrix.
Muscle contraction depends on ATP hydrolysis. During periods of intense exercise, muscle cells rely on the ATP supplied by three metabolic pathways: glycolysis, mitochondrial respiration, and the phosphagen system. Figure 1 shows the rates at which the three metabolic pathways produce ATP following the start of an intense period of exercise.

Figure 1. ATP production by three metabolic pathways following the start of an intense period of exercise
Which of the following correctly uses the data to justify the claim that the phosphagen system is an immediate, short-term source of ATP for muscle cells?
ATP production by the phosphagen system increases and decreases rapidly following the start of the exercise period.
Two nutrient solutions are maintained at the same pH. Actively respiring mitochondria are isolated and placed into each of the two solutions. Oxygen gas is bubbled into one solution. The other solution is depleted of available oxygen. Which of the following best explains why ATP production is greater in the tube with oxygen than in the tube without oxygen?
The rate of proton pumping across the inner mitochondrial membrane is lower in the sample without oxygen.

Figure 1. Activity levels of two digestive enzymes over a range of pH
Trypsin and pepsin are enzymes that function in different areas of the digestive tract. One functions in the stomach, where the pH is between 1.5 and 3.5, while the other functions in the small intestines, where the pH is between 6 and 8.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes where each enzyme functions?
Pepsin works in the stomach because the optimal pH for pepsin is acidic
Oxygen consumption can be used as a measure of metabolic rate because oxygen is
necessary for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
A researcher claims that different enzymes exhibit maximal function over different pH ranges. To test the claim, the researcher carries out an experiment that includes three different enzymes: pepsin, salivary amylase, and arginase. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.

Figure 1. The effect of pH on three different enzymes
Which of the following actions will provide the most appropriate negative control for the experiment?
Repeating the experiment with denatured enzymes
The enzyme peroxidase is found in many organisms. It catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. The rate of peroxidase activity at different pH values was assessed by students in the lab. The students’ results are shown in graph 1.

Graph 1. Effect of pH on peroxidase activity
If the experiment is repeated at pH 11, the observed activity level of the enzyme will most likely be
lower than the level at pH 9
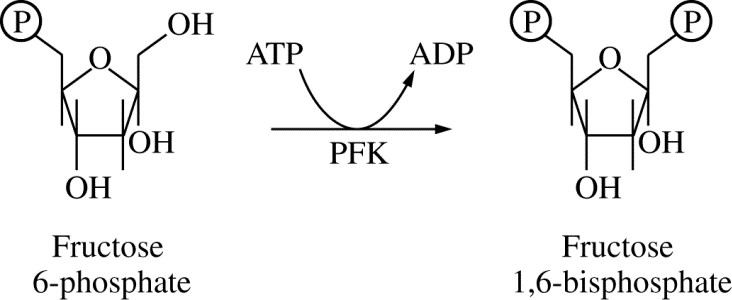
Figure 1. Reaction catalyzed by phosphofructokinase (PFK) during glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate during glycolysis, as represented in Figure 1.
PFK can be allosterically inhibited by ATP at high concentrations. Which of the following is the benefit of regulating glycolysis by the concentration of ATP?
Glycolysis proceeds when the intracellular concentration of ATP is low, which provides ATP to drive cellular reactions
When hydrogen ions are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix, across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the space between the inner and outer membranes, the result is
the creation of a protein gradient
Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it.

A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line.
Which of the following best accounts for the shape of the solid line between points A and D?
ATP acted as an allosteric inhibitor on one or more of the enzymes
Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it.

A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line.
The rate of pyruvic acid formation fluctuates because
the reaction is affected by negative feedback
Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it.

A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line.
It is most reasonable to hypothesize that, in the breakdown of glucose, substance X is
an inhibitor
Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it.

A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line.
Which of the following is most likely to result if oxygen is added to the tissue culture?
For each glucose molecule consumed, more ATP will be formed

Figure 1. Change in the relative concentration of product over time
Figure 1 shows the amount of product produced in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction over five minutes. Which of the following best explains how the rate of the reaction changes over time?
The rate decreases because the ratio of product to substrate increases
The reaction of glycolysis occurs in the
cytosol
Which metabolic process is common to both aerobic cellular respiration and alcohol fermentation?
Glycolysis
An experiment to measure the rate of respiration in crickets and mice at 10o C and 25o C was performed using a respirometer, an apparatus that measures changes in gas volume. Respiration was measured in mL of O2 consumed per gram of organism over several five-minute trials, and the following data were obtained.

During aerobic cellular respiration, oxygen gas is consumed at the same rate as carbon dioxide gas is produced. In order to provide accurate volumetric measurements of oxygen gas consumption, the experimental setup should include which of the following?
A substance that removes carbon dioxide gas
An experiment to measure the rate of respiration in crickets and mice at 10o C and 25o C was performed using a respirometer, an apparatus that measures changes in gas volume. Respiration was measured in mL of O2 consumed per gram of organism over several five-minute trials, and the following data were obtained.

According to the data, the mice at 10o C demonstrated greater oxygen consumption per gram of tissue than did the mice at 25o C. This is most likely explained by which of the following statements?
The mice at 10ºC had a higher rate of ATP production than the mice at 25ºC.
An experiment to measure the rate of respiration in crickets and mice at 10o C and 25o C was performed using a respirometer, an apparatus that measures changes in gas volume. Respiration was measured in mL of O2 consumed per gram of organism over several five-minute trials, and the following data were obtained.

According to the data, the crickets at 25o C have greater oxygen consumption per gram of tissue than do the crickets at 10o C. This trend in oxygen consumption is the opposite of that in the mice. The difference in trends in oxygen consumption among crickets and mice is due to their
mode of internal temperature regulation
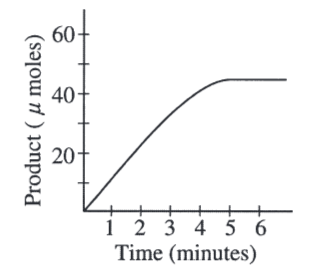
A scientist determined the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by measuring the amount of product formed over time. The following curve was generated from the data collected.
The rate of the reaction could also be determined by
measuring the change in the amount of substrate
Protein digestion in humans is primarily carried out by three enzymes. Pepsin is found in the stomach (pH2), where it aids in the breakdown of large proteins into smaller peptides, while trypsin and chymotrypsin are found in the small intestine (pH8), where they aid in the further breakdown of the proteins into amino acids and dipeptides that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Graph 1 shows the effect of pH on the activity levels of the three enzymes.

Graph 1. Relative activity of pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin at pH 0 through 11
Which of the following best predicts how the structure and function of pepsin will change as it enters the small intestine?
Pepsin will change in shape because of the basic environment of the small intestine; therefore, its enzymatic activity will decrease

Figure 1. The rate of O2 uptake for three species of Saccharomyces yeast at 30°C and 35°C
Researchers studied the effect of increased temperature on the rate of respiration of three species of Saccharomyces yeast (Q, R, and S) by measuring the rate of oxygen uptake in each species at 30°C and at 35°C (Figure 1).
Based on Figure 1, which of the following statements about the effect of the temperature increase on the respiratory rate of one of the species, Q, R, or S, is most likely true?
The median O2 uptake rate for species S at 35°C is μ0.1 μL·mg-1·min-1 less than it is at 30°C.