AP Psychology- Unit 2 (Cognition)
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Hierarchies (as they pertain to grouping)
a system where individuals or concepts are organized into ranked levels, essentially creating a structured order based on a specific criteria
often used to explain how information is categorized and processed in the brain
Categories (as they pertain to grouping)
cognitive process of mentally sorting and organizing stimuli (objects, ideas, or events) into distinct groups based on shared characteristics or attributes
allows us to understand and interpret information more efficiently
Elaborative Rehearsal
memory strategy where new information is actively linked to existing knowledge, creating a deeper level of processing and enhancing the likelihood of long-term retention and recall
Maintenance Rehearsal
process of repeatedly saying or thinking about a piece of information to keep it active in your short-term memory
shallow level of processing
Recency Effect
tendency for people to remember the most recently presented information or items in a sequence better than those presented earlier
Cognition
process involving thought and knowledge that includes mental activities such as perception, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Bottom-Up Processing
analysis begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information
Schema
a collection of basic knowledge about a concept or entity that serves as a guide to perception, interpretation, imagination, or problem solving
Gestalt Psychology
movement in psychology
we perceive objects as well-organized patterns rather than separate components
based on the concepts of “grouping”
proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, connectedness, figure/ground relationships
Law of Closure
people tend to fill in blanks to perceive a complete object whenever an external stimuli partially matches that object
Figure/Ground Relationships
the ability of our brain to distinguish an object or figure from its background
Law of Proximity
principle that objects that are closer together are perceived as more related than objects that are farther apart
Selective Attention
process of reacting to certain stimuli selectively when several occur simultaneously
Cocktail Party Effect
the ability to focus on a single sound while filtering out other distracting sounds
Inattentional Blindness
occurs when someone fails to notice an unexpected object or event that is in plain sight
Change Blindness
occurs when a person doesn’t notice a change in a visual blindness due to a lack of attention to that aspect of the scene
Binocular Depth Cues
rely on the coordinated effort of both eyes to perceive depth
slight differences in the images projected onto each retina
Retinal Disparity
slight difference between right + left retinal images
different positions of the eyes produces a disparity of visual angle
provides an important cue to depth perception
Convergence
the rotation of the 2 eyes inward toward an object so that the image falls on corresponding points on the foveas
Texture Gradient
idea that the details of an object become less apparent as it moves farther away
Memory Consolidation
process of the brain transforming short-term memories into more stable, long lasting memories
strengthens and stabilizes newly encoded information
involves neural changes in the brain over time (typically the hippocampus)
Apparent Movement
the perception of continuous movement when there is none
Prototypes
mental representation of idealized form of an object or concept
3 Levels of Processing…
Shallowest:
Structural → visual appearance
Phonemic → sound
Semantic → meaning
Deepest
Law of Effect
responses that produce a satisfying effect after a particular stimulus are likely to occur again
responses that produce a negative effect after a particular stimulus are less likely to occur again
Split-Half Reliability
measure of reliability in which a test is split into 2 parts and scores on both halves are compared
Construct Validity
how well a test or tool measures the construct that it was designed to measure
Test-Retest Reliability
the degree to which test results are consistent over time when the same participants take the same test at different times
Repression (Psychodynamic)
defense mechanism where an individual unconsciously pushes distressing thoughts, memories, or emotions out of conscious awareness
happens automatically without conscious awareness
buries them to avoid emotional pain and anxiety
Constructive Memory
idea that when we recall a memory, our brain actively reconstructs it by incorporating new information, perceptions, beliefs, and expectations
Misinformation Effect
where a person’s memory of an event is altered or distorted after being exposed to misleading information about that event
Levels of Processing Model
cognitive psychology theory that described how the depth of mental processing affects how well information is remembered
shallow processing + deep processing
Law of Similarity
principle that described how the brain organizes visual information by grouping similar elements together
Perceptual Set
cognitive bias that influences how people perceive and interpret sensory information based on their expectations, past experiences, and other factors
Monocular Depth Cues
visual cues that allow people to perceive depth and distance using only one eye
Relative Clarity
idea that objects farther away appear hazier and less sharp than closer objects
Relative Size
helps us perceive how far away objects are based on their size in relation to other objects
Multi-Store Model
theory that describes how information is stored and processed in the human mind
proposes that memory is made up of 3 separate systems
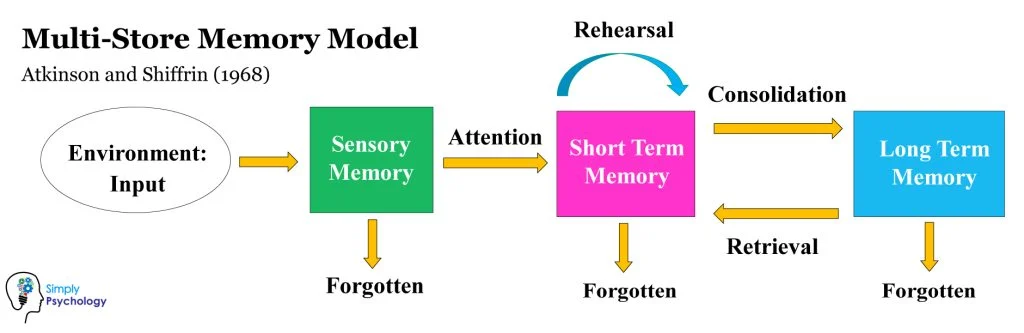
Linear Perspective
visual perception where parallel lines appear to converge in the distance, creating the illusion of depth, and only requiring one eye to perceive it
Interposition
helps people perceive depth by using the positioning of objects in a scene
Algorithms
problem solving strategy for decision making
Heuristics
mental shortcut that allows an individual to make a decision, pass judgement, or solve a problem quickly (from past experience)
Availability
Representativeness
Mental Set
the brain’s tendency to stick with the most familiar solution to a problem and ignore alternatives
Priming
when an individual’s exposure to a certain stimulus influences their response to a subsequent prompt, without awareness
ex: “pepper” → “salt and pepper”
Framing
cognitive bias that described how the presentation of information influences a person’s decisions
Gambler’s Fallacy
cognitive bias in which someone believes that the probability of an event changed based on a series of previous events
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
cognitive bias that describes one tendency to continue an endeavor despite the current cost outweighing the benefits
Divergent Thinking
thought process that involves generating multiple ideas or solutions to a problem
Convergent Thinking
cognitive process that involves analyzing information to reach a single, correct solution to a problem
Explicit Memory
conscious recollection of facts, events, and personal experiences
Episodic Memory
ability to consciously remember and recall specific past events and the contextual details surrounding them
Implicit Memory
memory for information that is expressed unconsciously or automatically through improved performance on related tasks
knowledge slowly gained
ex: learning to ride a bike
Procedural Memory
process of retrieving information necessary to perform learned skills
ex: talking, eating, walking
Prospective Memory
ability to remember to carry out a planned action in the future
involves retaining and activating intentions at the right time and place
Long-Term Potentiation
process that strengthens connections between neurons through repeated stimulation
Working Memory Model
theoretical framework that explains how the working memory system functions
proposes that short-term memory is made up of multiple components that work together
Primary Memory System
short-term memory system that holds information for a brief period of time
Working Memory
system that temporarily stores and manipulates information to complete cognitive tasks
Visuospatial Sketchpad
ability to temporarily hold visual and spacial information
ex: where the car is parked
Central Executive
part of working memory that controls and coordinates other processes, such as attention, memory retrieval, and decision making
Phonological Loop
component of working memory that stores and processes verbal and auditory information
Memory Retention
the ability to store and retrieve information over a period of time
Spacing Effect
information better remembered when study sessions are spaced out over time
distributed rather than crammed
Chunking
dividing large pieces of information into smaller, more manageable units
easier to remember and store information in short-term memory
Deep Encoding
processing information that involves relating it to other ideas, words, or prior knowledge
leads to long-term memory retention and recall
relates to personal experiences and emotions
Shallow Encoding
processing information that focuses on the surface-level characteristics of a stimulus, such as its appearance or sound
information is retained for a short time but not moved to long-term memory
Effortful Processing
process of actively encoding information through conscious attention and effort
Automatic Processing
mental process that involves performing tasks with little to no conscious thought
Iconic Memory
type of sensory memory that stores visual information for a brief period of time after the physical image is no longer present
allows people to recall visual images for a few milliseconds after the image has disappeared
Retrograde Amnesia
memory loss where a person is unable to recall events or information that occurred before a specific traumatic event or brain injury
Anterograde Amnesia
memory loss where a person is unable to form new memories after a traumatic event
Encoding Failure
inability to effectively store information in memory due to insufficient processing during the initial encoding stage
Assimilation
cognitive process of making new information fit in with your existing understanding of the world
Accommodation
modifying our cognitive schemas in order to incorporate new information or experiences
Executive Functions
cognitive skills that help people manage everyday tasks, solve problems, and adapt to new situations
Retroactive Interference
newer information pushes out older, similar information
Proactive Interference
older information makes it more difficult to carry out the present task
Availability Heuristic
judging how likely a certain event is to happen, based on how easily information regarding this topic is available
Representativeness Heuristic
a mental shortcut in which one thinks of the best example or prototype of a given category
Functional Fixedness
cognitive bias that limits a person’s ability to use an object for more than it’s intended purpose
Semantic Memory
long-term storage of general knowledge about the world, including facts, concepts, and word meanings
Primacy Effect
tendency for people to remember information presented at the beginning of a list or sequence better than information presented later on
Mnemonic Devices
memory aid technique used to help students recall information more easily by associating it with something easily remembered
ex: acronyms, rhymes, or vivid imagery
Encoding
process of perceiving and learning new information and putting it into the memory system
Echoic Memory
brief sensory memory of audible sounds
allows the brain to retain spoken syllable is order for the brain to process them into intelligible speech
Sensory Memory
short-term shortage of information gathered through the 5 senses
Long-Term Memory
the process of storing and retrieving information for extended periods, ranging from days to a lifetime
Autobiographical Memory
a person’s recollection of significant events and experiences from their own life, which contributes to their sense of self
Alzheimer’s Disease
progressively deteriorates an individual’s memory, cognitive abilities, and personality
symptoms: difficulty learning new info in early stages + severe decline in thinking, speaking, and performing basic tasks
Infantile Amnesia
inability of adults to recall personal memories from their early childhood (before 3-4)
Context-Dependent Memory
information is best recalled when the retrieval environment closely matches the context in which it was originally learned
Mood-Congruent Memory
tendency to recall memories that align with your current emotional state
more likely to remember positive experiences when you’re feeling happy
State-Dependent Memory
individuals are more likely to recall information when their current physiological or psychological state closely matches the state they were in when the information was learned
Testing Effect
actively retrieving information from memory through self-testing or practice tests leads to better long-term retention
Metacognition
awareness and understanding of one’s own thought process
“thinking about thinking”
ability to reflect on and analyse one’s own thinking patterns
Forgetting Curve
graphical representation illustrating the rapid decline of memory retention over time
Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon
experience of being unable to recall a specific word or name, even though you feel like you know it
“it’s on the tip of my tongue”
Source Amnesia
inability to recall the origin or source of a memory
Imagination Inflation
where repeatedly imagining an event that never happened increases a person’s confidence that it actually occurred
g (general intelligence)
idea that an individual’s overall intelligence is a compilation of different specific abilities