Stream Processes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Fluvial geomorphology
Alteration of land by streams
ways rivers impact shape of earth
How can rivers impact the shape/ topography of earth
erosion and deposition
More water in a stream means
more sediment
Slower water results in
more deposition
change to land or water causes change in
stream system
Characteristics of rivers
self-sustaining( they will adjust as surroundings change)
retains the same general geometry over decase
maintain a Balance between sediment import and export
Increasing water conveyance capacity of a stream
get more water out faster so it doesn’t build up and flood
making the banks concrete
Consequences of Increasing water conveyance capacity
The river is no longer allowed to adjust
floods in an unnatural way in the unpaved areas
Heavy flooding and erosion downstream
Concrete doesn’t last forever
Basin Size increases
downstream
Basin starts as
rills, to gullies, to small channels
what can cause channel size increase
depends on amount of sediment and water
Stream Order
Means of comparing rivers of different size or importance
Strahler method
First order: no tributaries
Second order: joining of two first order streams
1+1=2
Third order: two second order streams come together
2+2=3
in strahler stream order method Order number should be proportional to
Channel dimensions
Watershed size
Stream discharge
Shreve Magnitude Stream Order
Considers streams as links
Magnitude of each “link” is sum of all tributary values
1+1=2, 2+1=3
Value represents number of first-order streams upstream from a given point
Used by rainfall-runoff estimators
Drainage Density
Length of all stream channels in drainage basin divided by total basin area
High drainage density
Generally distribute the flow more evenly
Little lag time to low-order streams
Greater lag time to downstream flooding
higher stream order indicates
high drainage density
Why would you want to know drainage density
tells you how the water is getting into our river
Low drainage density
Channels carry proportionately more water
Tend to be flashy
Drainage Patterns depend on
Shape of landscape
Composition of underlying material
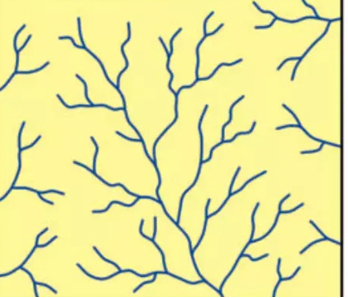
Dendritic
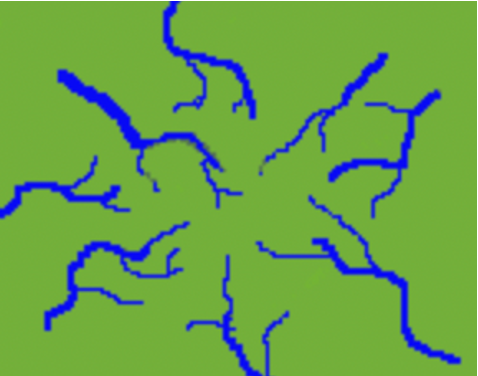
Radial
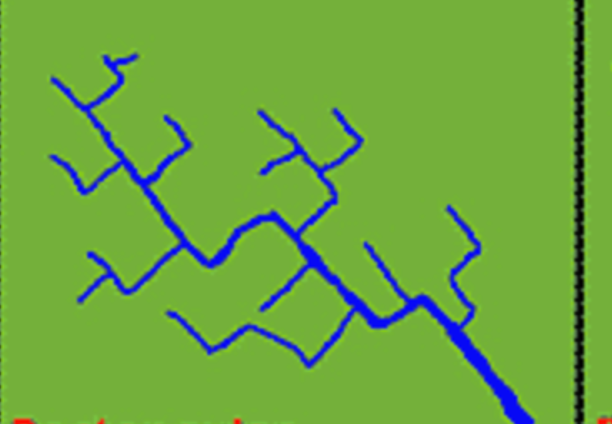
Rectangular
Trellis

Parallel

straight channel pattern
Least common natural form
unstable
Meandering channel patterns
Most common natural form due to inherent flow structure of water and roughness elements
Sinuosity
Braided channel
The channel has multiple internal splits and rejoins
Typically has high sediment load, highly variable discharge, and erodible banks
Proglacial zones, arid environments, and urban areas
seen in arid places
pt. bar
area of sediment deposition
Thalweg
line connecting deepest points
Cut bank
erosional area, often with overhanging edge
river speeds up faster on the outside of curve
As a river meanders it will
erode the bank materials and when the river moves the flood water sits in the flat eroded area
pools
finer sediment, low gradient, deep
greater depth and low velocity
riffles
coarser sediment, high gradient, shallow
large volume
faster( high gradient)
provides roughness
turbulent flow
changes in velocity and how water interacts with things around it
Helical flow
corkscrew
carves away
more erosion more migration of the river
Channel Shape is dictated/self formed by
the amount of water and sediment available
What does it mean that channel shape is self adjusting
Adjusts to changes by humans, climate, vegetation
Carve deeper if more water
Become more shallow if less water
Cross-section of a river
Gently rounded
Sometimes trapezoidal with straight sloping sides
Cross section of large rivers
much wider than deep
Cross section of small rivers
can be much deeper than wide
Shape depends on interaction between:
Factors related to debris load (size, lithology, amount, depositional forms)
Factors related to water flow
Bankfull
most effective time for river to change shape
when water fills up to banks
River Continuum Concept (RCC)
how geomorphology and river location impacts biological communites