Fetal Monitoring and Labor & Birth (Week 6 OB)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
5 Ps of Labor
passenger
passageway
power
position
psyche
Passenger
Fetal lie (how the fetus is laying)
Longitudinal Lie (vertical)
Transverse Lie (horizontal)
Oblique Lie (diagonal)
Fetal Presentation
Cephalic (head)
Breech (butt and cervix will want to dilate when it gets to neck and c-section)
Mentum (chin and will need C-section)
Transverse (shoulder and C -section)
Fetal Attitude
Flexion (chin tucked and we want this)
Extension
Fetal Position
Occiput is back of head
we want anterior occiput for easy delivery (back of head facing out in pelvis)
can still give birth for posterior occiput
Passageway
Components
pelvis
cervix
floor muscles
vagina
baby makes vagina bigger with each birth
Three principles
balance (want everything equal
gravity
movement
Powers
contraction frequency/duration/strength
contractions gets cervix to dilate
How cervix changes
old coke bottle during preg
turns into jar when it gets closer to labor
Effacement
Station
where top of baby head is compared to pelvis
-4 to 4
-4 is farther up and 4 is farther down
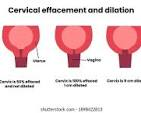
Effacement
Thining of cervix
0%-100%
Cardinal Movements
Engagement – Baby’s head enters the top of the pelvis.
Descent – Baby moves down further into the pelvis.
Flexion – Baby’s chin tucks to the chest, making the head smaller to fit.
Internal Rotation – Baby’s head turns to line up with the birth canal.
Extension – Baby’s head tilts back as it passes under the pubic bone.
External Rotation (Restitution) – Baby’s head turns to the side so shoulders can fit.
Expulsion – Baby’s shoulders and body are delivered.
Position
anything other than laying down during labor
forward leaning
squatting
hands and knees
Psyche
nurses role is to reassure/comfort/ask what would feel better/educate
First stage of labor
when your cervix opens (dilates) and thins (effaces) to prepare for birth
latent is 0-5 cm
active is 6-10 cm
Second stage of labor
pushing and birth
natural pushing relies on the mother's urge to push
coached pushing is care providers directing the timing and manner of pushing efforts
crowning is head appears and home stretch
perineal care
Third stage of labor
placenta delivery
passive management is when placental comes out naturally
active management is when you pull on cord so it can come out
Forth stage of labor
after birth and recovery
monitor BP and HR
repair of stitches
golden hour
fundal checks
check bladder
Lochia = bleeding and bright red
Artificial ROM (amniotomy)
more pressure so it INDUCES LABOR and more oxytocin released so more contractions
go in with hook to rupture (cord comes out)
Considerations
is baby low down enough
risk for infection
monitor baby baselines
Intermittent vs Continuous
no problems
problem
epidural
External vs Internal
outside
gives an idea
slightly dilated and ruptured
tracks when HR starts and ends
risk for infection
Leopold’s Maneuver
to determine the fetal position by palpation
Identifies best area for placement of the external monitors (put on baby back)
Station/effacement/cm
a way to describe labor
Fetal Heart Rate interpretations
110-160 is baseline
Variability
Accelerations
Decel
Artifact
Variability
How much the fetal heart rate fluctuates from the baseline
Moderate variability: (6-25 bpm) is a sign of a healthy fetus. WE WANT THIS
Minimal variability: (≤ 5 bpm) or absent variability (undetectable) can be concerning potentially indicating hypoxia or other problems
Accelerations
Temporary, short increases in the FHR compared to the baseline
Abrupt: less than 30 seconds increase from the baseline
15 acel by 15 sec is term
10 by 10 sec is preterm
Decelerations
Temporary decreases in the FHR
Nadir is lowest point of FHR
Early deceleration: gradual decrease and return to baseline with uterine contractions, nadir is at same time as peak
Late deceleration: gradual decrease and return to baseline with uterine contraction; nadir is occurs after the peak of the contraction
Variable deceleration: abrupt decrease in FHR below baseline; 15 bpm below baseline for a minimum of 15 seconds but less than 2 minutes
Prolonged deceleration: decrease in FHR below baseline with a minimum depth of 15 bpm and a duration of 2 minutes or greater but less than 10 minutes
Artifact
errors that lead to an inaccurate or misleading representation of the fetus's heart rate
Fetal Resuscitation
1. Reposition client (right or left side or hands and knees)
2. Increase fluid (bolus)
3. Apply Oxygen at 10L if client has low pulse ox
Category 1
Baseline 110-160
Moderate Variability
Accelerations: present or absent
Early Decelerations: present or absent
Variable or Late Decelerations: absent
Category 2 – contain ANY of the following
Baseline: Bradycardia or Tachycardia
Variability: Minimal/ Marked
Absent WITHOUT recurrent variable or late decelerations
Decelerations
Prolonged
Variable
Late
Category 3
Absent variability WITH
Recurrent variable decelerations
Recurrent late decelerations
Bradycardia
Sinusoidal pattern