AP hug unit 6 - urban settlements
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
squatter settlement/slums
highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty
2
New cards
central city
A city at the center of a metropolitan area. Ex.- Minneapolis and St. Paul.
3
New cards
exurb
Community located outside of a suburb in a more rural area within commuting distance to a large metropolitan area. Ex.-Carver, Northfield, Cannon Falls.
4
New cards
edge city
an area on the outskirts of a city with a high density of office buildings, shopping malls, hotels, etc., usually at the intersection of major highways. It has a large amount of recently developed retail and office space. Ex.- Eden Prairie, Maple Grove, St. Louis Park (where highways are located)
5
New cards
Metropolitan Statistical Area
Made up of 15 counties, of which 13 are in Minnesota and two are in Wisconsin. Ex.- Hennepin, Anoka, Ramsey, Dakota, Scott, etc. most of the United States and Canadian population live in.
6
New cards
suburb
Commercial, mixed-use, or residential areas. Ex.- Richfield, Bloomington, Crystal, Robbinsdale, etc.
7
New cards
Gentrification
The process whereby the character of a poor urban area is changed by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses, typically displacing current inhabitants in the process.
8
New cards
megacity
A city with at least 10 million inhabitants, Megacities demonstrate unplanned growth patterns and often contain squatter settlements.
9
New cards
Threshold
The minimum market (population or income) needed to bring about the selling of a particular good or service.
10
New cards
Range
The maximum distance consumers are prepared to travel to acquire goods or services.
11
New cards
important physical site characteristic
climate, water sources, topography, soil, vegetation, latitude, and elevation.
12
New cards
primate city
***a city that is the largest in its country, province, state, or region, and disproportionately larger than any others, examples include: Mexico city, Paris, Cairo, Seoul and Jakarta***
13
New cards
Central place theory
it states that in any given region there can only be one large central city, which is surrounded by a series of smaller cities, towns, and hamlets. spatial patterns of urban and outlying areas based on the flow of goods and services. for example, a small range would be a grocery store
14
New cards
Rank size rule
A principle that says that the rank of a city's population within a country will be approximately the largest city's population divided by the rank of the city in question. They have larger ranges and thresholds.
15
New cards
Gravity Model
a general theory in geography that can be used to quantify and predict the interaction between two cities based on population sizes, distance between the places, the number of migrants moving from one place to the other, or the flow of trade goods between the two locations
16
New cards
Worldcities
International company headquarters, significant global financial functions, and a polarized social structure are defining characteristics. Most are located on rivers or seacoasts. A world city status is based on economic and political factors.
17
New cards
world’s urban hierarchy
The top ten world cities have a significant impact on the international economy and are important drivers of globalization.
18
New cards
multiple-nuclei model
More than one focal point. Most applicable to the newer, fast-growing cities. The multiple-nuclei model is a US urban geography model that describes cities with more than one CBD or a single CBD and many secondary outlying business districts. The multiple-nuclei model recognizes that the automobile allowed people and jobs to move away from crowded and polluted city centers.
19
New cards
Central Business District (CBD)
The best-known and the most visually distinctive area of most cities is downtown.
20
New cards
The sector model of North American city structure
proposes that zones in a city extend outward by transportation, such as railroads and highways. Because the neighborhoods in the sector model lie along major transportation, a neighborhood could radiate outward from the city center to the farthest areas of the city.
21
New cards
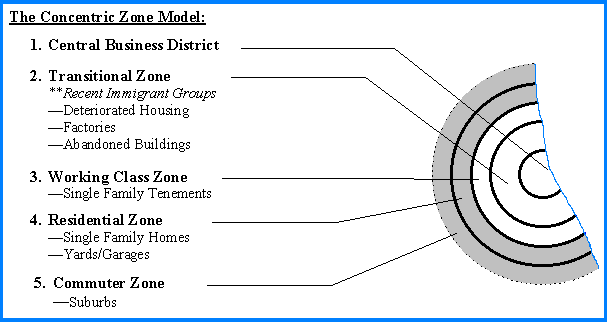
Centric Zone
Rings. Land is less expensive in the suburbs, which is why it is possible to build single-family homes in zones 4 and 5 for middle- and high-income residents who desire suburban living. 1- CBD 2- migrants apartments 3- working men’s zone 4- better residents (upper class) 5- commuters zone
22
New cards
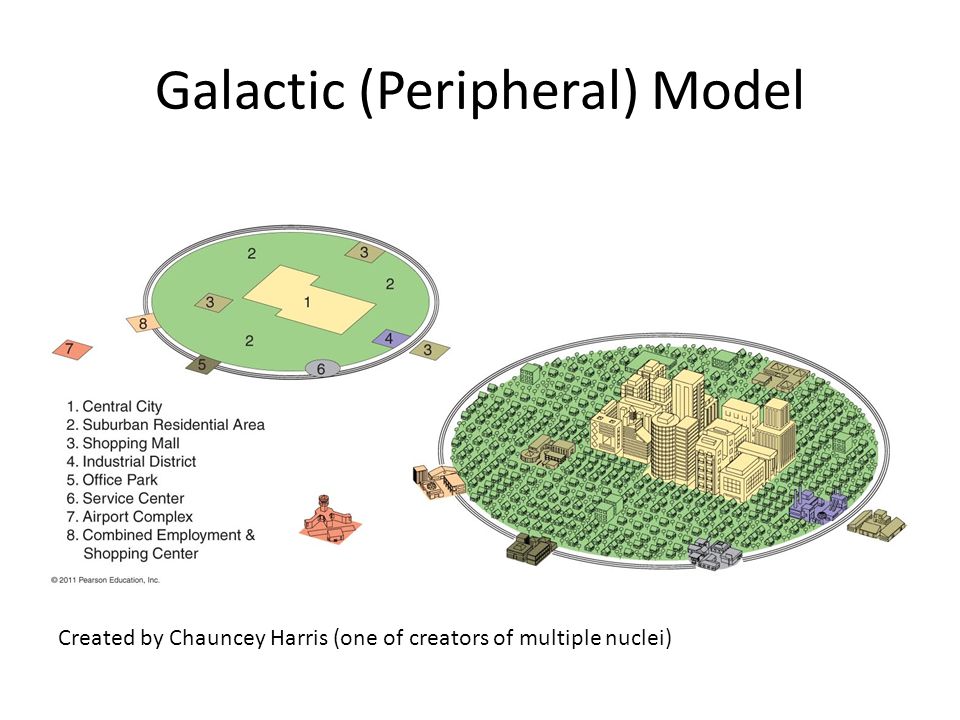
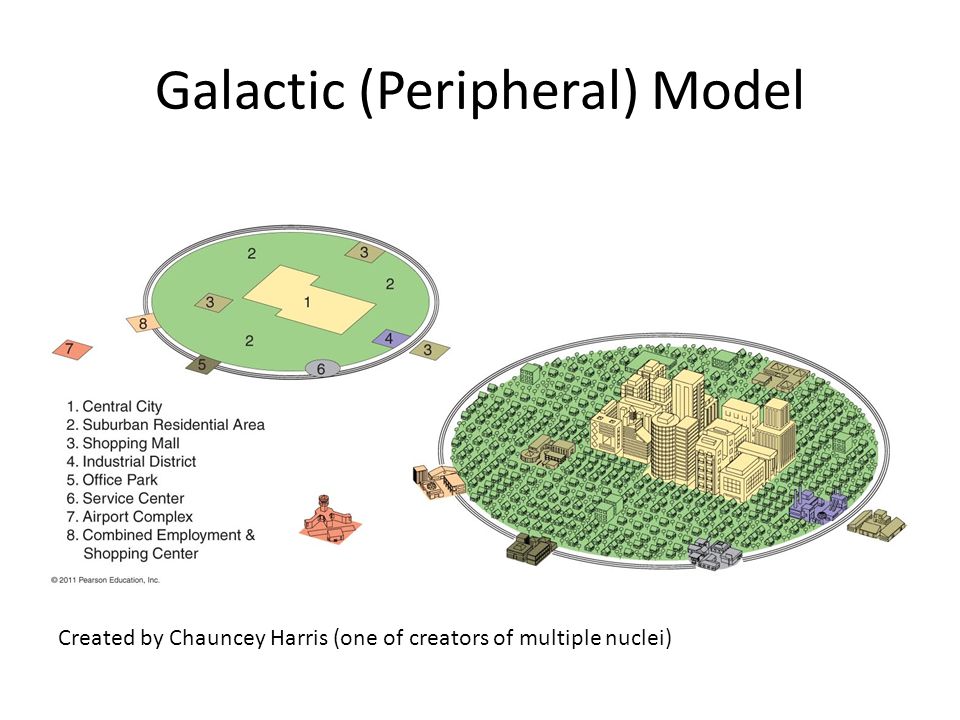
Galactic city model (peripheral)
inner city with suburban businesses with beltways. a city with growth independent of the CBD that is traditionally connected to the central city by means of an arterial highway or interstate.