health psych and disorders
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
stress
a physical or mental to a challenging or threatening situation

stressor
stressful stimulus or situation demanding adaptation

traumatic stressor
a situation that threatens one's physical activity, arousing feelings of fear

adverse childhood experiences
ACE's, affect a person over a lifetime
eutress
positive/motivating stress

distress
negative/debilitating stress

acute stress
short term - temporary pattern of stressor-activated arousal with a distinct onset, and limited duration

chronic stress
long term - continuous state of stressful arousal, persisting over time

response to normal stressor
initial arousal, fight or flight, autonomic nervous system, decrease in immune system
response to traumatic stressor
5 stages of dealing with catastrophic situations
psychic numbness
shock, confusion, lack of understanding

automatic action
little awareness of the experience, poor memory/recall

communal effort
people work together, but with little planning

letdown
setting-in of the magnitude and impact of the situation
recovery
survivors adapt to changes caused by the disaster

general adaptation syndrome
pattern of general physical responses that take the same form in responding to a serious chronic stressor
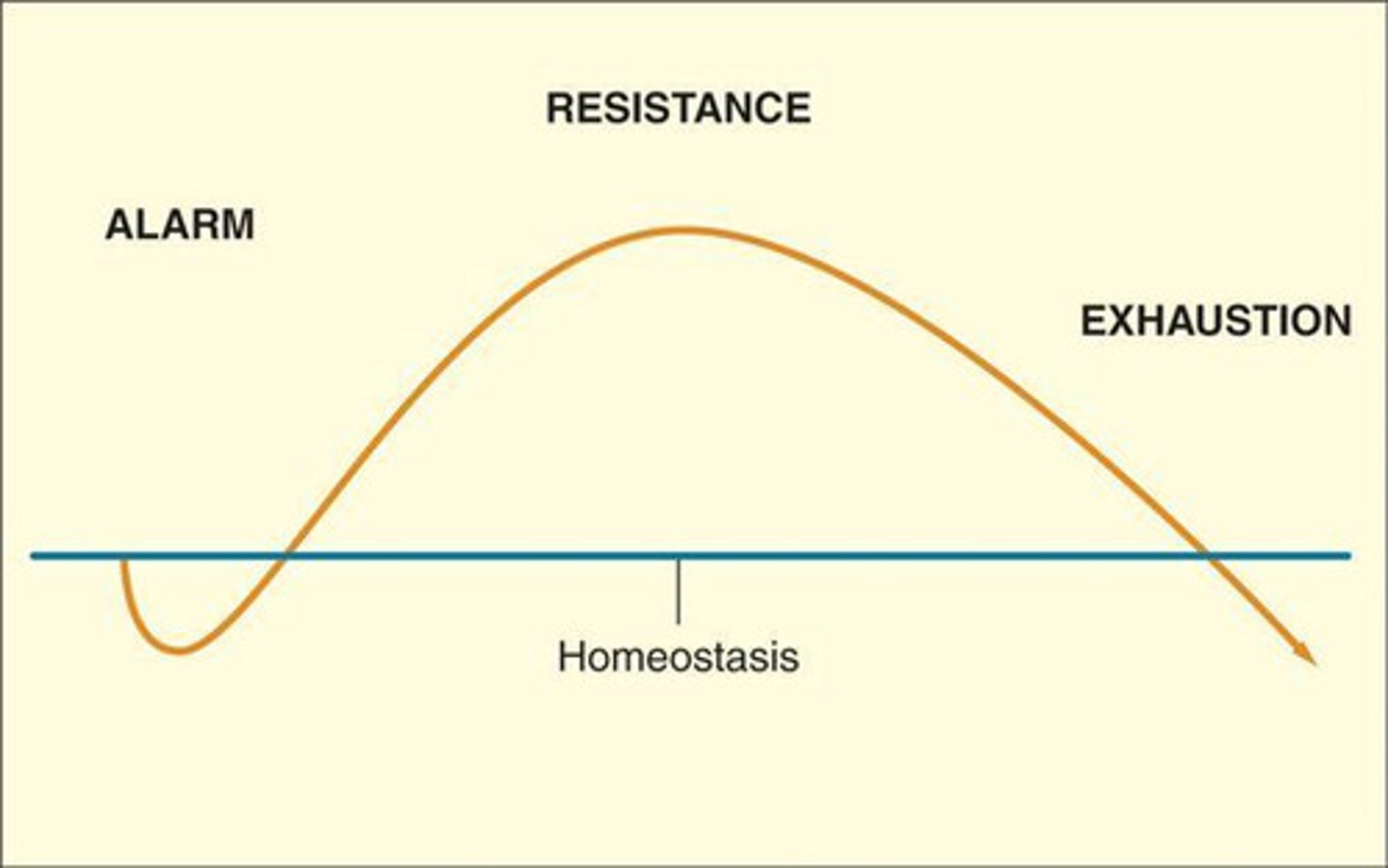
alarm reaction
fight or flight - body mobilizes its resources to cope with a stressor
resistance
adapt to the presence of a stressor
exhaustion
body depletes its resources
tend and befriend theory
some people react to stress by tending to the needs of others and seeking connection with others, especially the young

problem focused coping
managing emotional reactions to stress as a coping mechanism; breathing, meditation, medication

positive psychology
the scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive

effect size
a measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables or the extent of an experimental effect
hallucinations - psychopathy
false sensory experiences

delusions - psychopathy
persistent false beliefs

affect - psychopathy
characteristically depressed, anxious, manic, or no emotions

dsm-5
describes disorders, predicts its future, imply treatment, stimulate research

icd-10
like dsm-5, but international

psychoanalytic perspective of disorders
internal, unconscious drives
humanistic perspective of disorders
failure to strive to one's potential or being out of touch with one's feelings
behavioral perspective of disorders
reinforcement history, the environment
cognitive perspective of disorders
irrational, dysfunctional thoughts or ways of thinking

socio-cultural perspective of disorders
dysfunctional society

biomedical/neuroscience perspective of disorders
organic problems, biochemical imbalances, genetics
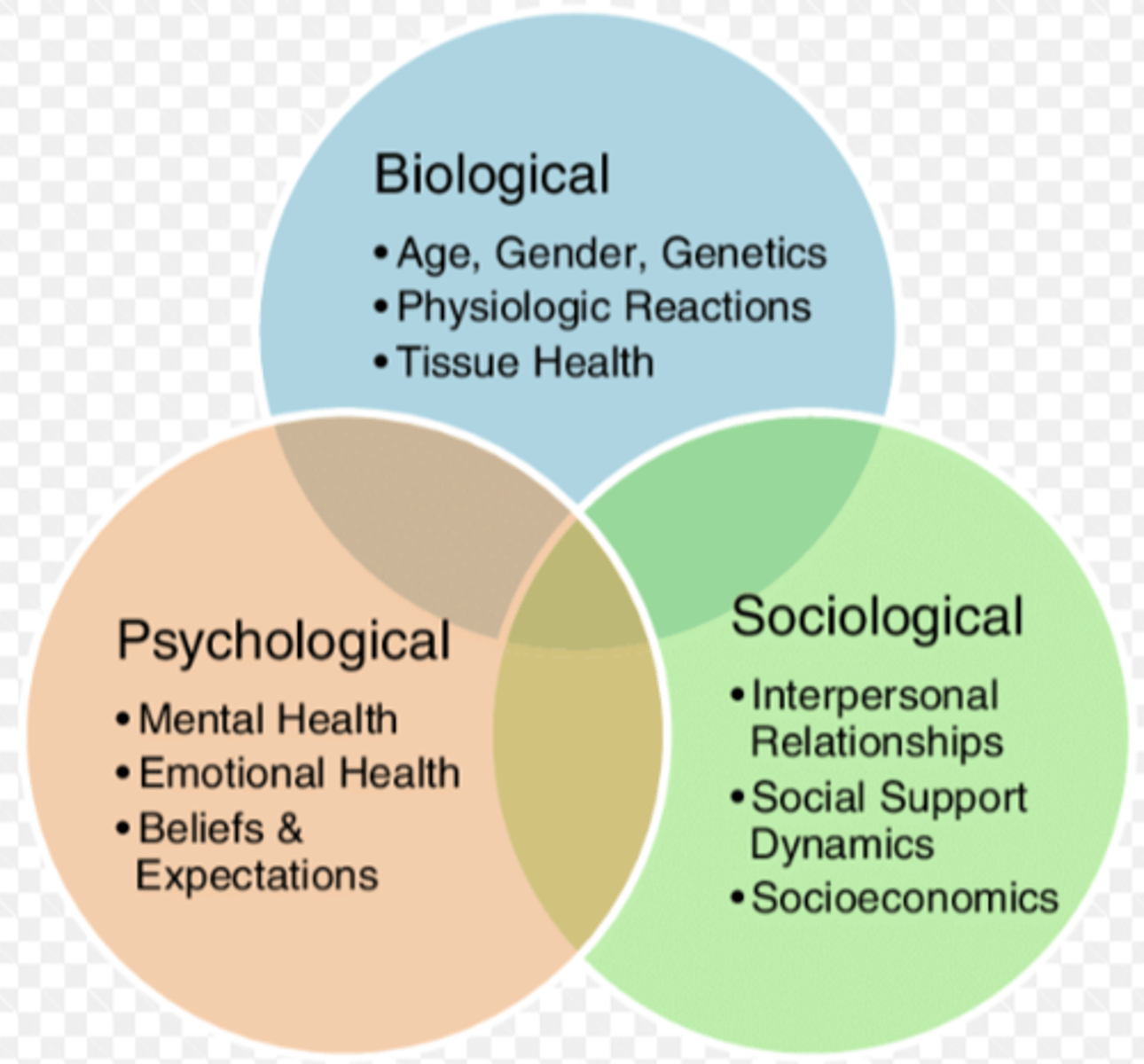
bio-psycho-social model
bio, psycho, and social factors contribute to disorders
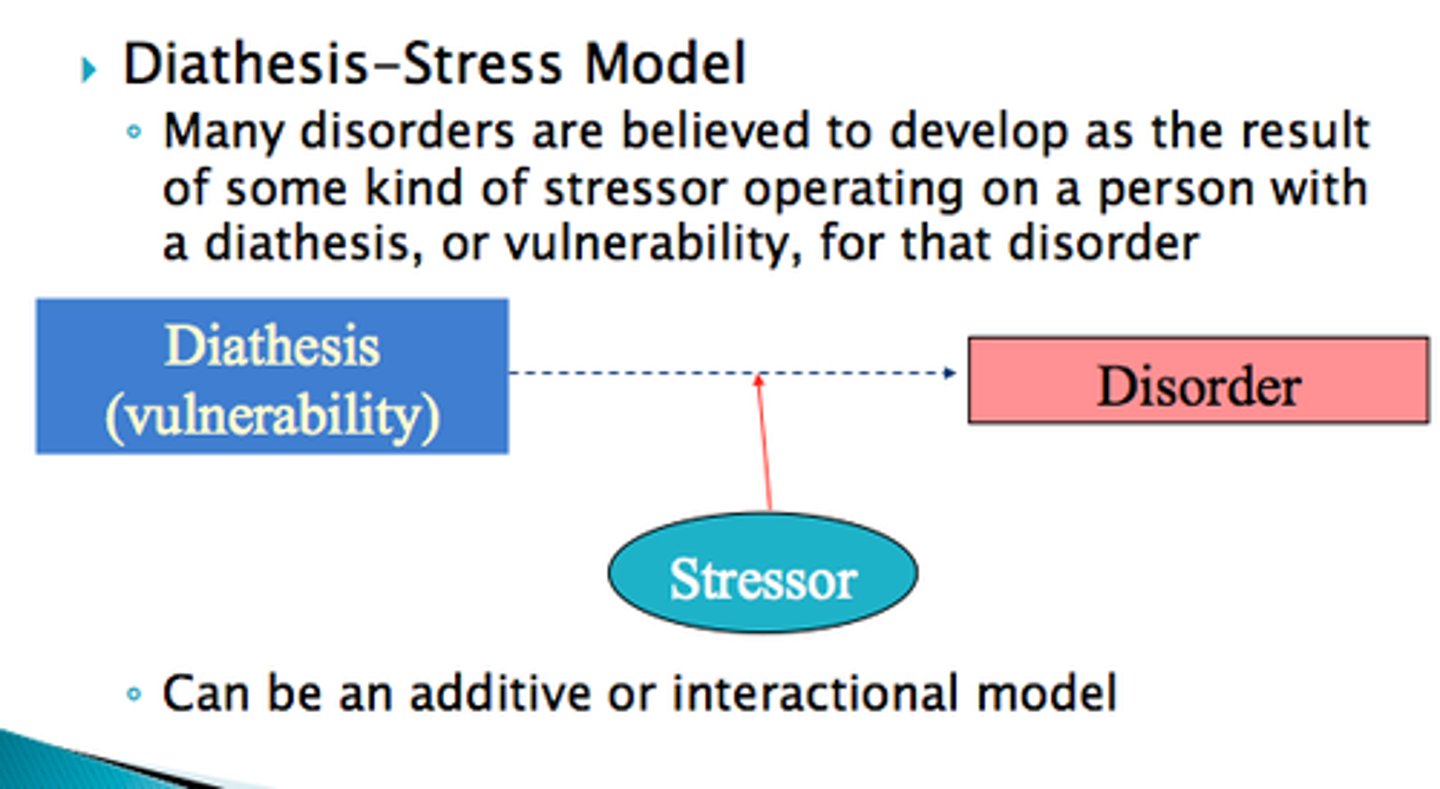
diathesis-stress model
proposes a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with a precipitating event
neurodevelopmental disorders
onset during the developmental period

neurodevelopmental symptoms
focus on whether the person is exhibiting behaviors appropriate for their age level
schizophrenic disorders
delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech/thoughts, disorganized motor, negative symptoms

catatonia
disorganized movement

excitement
positive movement

stupor
negative movement

negative symptoms
lack of typical behavior such as flat affect or catatonic movement

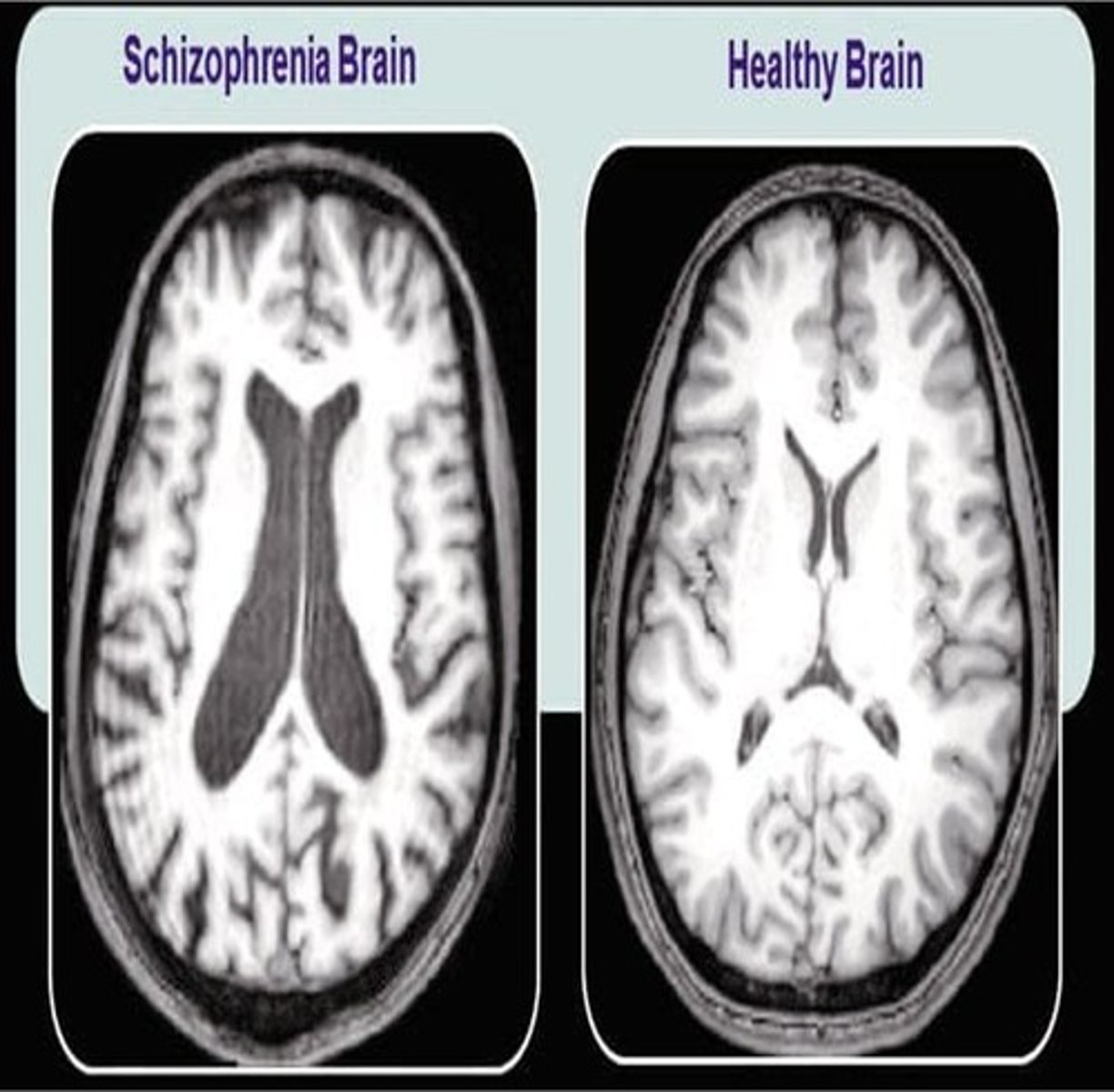
dopamine hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity and reduced grey matter
depressive disorders
sad, empty, or irritable mood with physical and cognitive changes that affect a person's ability to function

major depressive disorder
two or more weeks of significantly depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities

persistent depressive disorder
a form of depression that is not severe enough to be diagnosed as major depressive disorder
bipolar disorders
characterized by periods of mania and depression (bipolar cycling)

bipolar 1
involves severe mania

bipolar 2
less severe mania; more depressive periods

anxiety disorders
characterized by excessive fear and/or anxiety with related behavioral disturbances

specific phobias
anxiety toward a specific object

agoraphobia
fear of social situations

panic disorder
experience panic attacks

social anxiety disorder
intense fear of being watched or judged

generalized anxiety disorder (gad)
prolonged experiences of nonspecific fear or anxiety
obsessive-compulsive and related disorders
characterized by the presence of obsessions and compulsions

obsessive compulsive disorder
obsessions coupled with compulsions

hoarding disorder
difficulty parting with things you believe need to be saved

dissociative disorders
characterized by dissociations from consciousness, memory, identity, emotion, perception, body, motor, and behavior
dissociative amnesia
a sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting

dissociative identity disorder
disorder occurring when a person seems to have two or more distinct personalities within one body

trauma and stressor-related disorders
characterized by exposure to a traumatic event with subsequent distress

post traumatic stress disorder
an anxiety disorder associated with serious traumatic events

feeding and eating disorders
characterized by altered consumption or absorption of food that impairs health or psychological thinking

anorexia nervosa
starvation and excessive exercise

bulimia nervosa
binging and purging

personality disorders
characterized by enduring patterns of internal experience and behavior that is deviant from one's culture and remains stable over time

cluster a
odd, eccentric; paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal

cluster b
dramatic, emotional; antisocial, histrionic, narcissistic, borderline

cluster c
anxious, fearful; avoidant, dependant, ocpd
3 components of therapy
identify problem, identify cause, decide on form of treatment

psychodynamic therapy
uncover the unconscious mind
free association
patient says whatever comes to mind

dream analysis
patient relates a dream to be analyzed to a therapist

hypnosis
treats pain and anxiety; does not retrieve accurate memories or regression in age

cognitive therapy
comats maladaptive thinking using biofeedback
biofeedback
uses principles of conditioning to help clients regulate body systems that contribute to disorder
aversion therapy
uses punishment to decrease the frequency of undesirable behaviors

exposure therapy
involves confronting an emotion-arousing stimulus directly and repeatedly

token economy
given "tokens" for desired behaviors, which they can later trade for rewards

systematic desensitization therapy
visualize a graduated series of anxiety-provoking stimuli while remaining relaxed

cognitive-behavioral therapy
combines cognitive and behavioral approaches
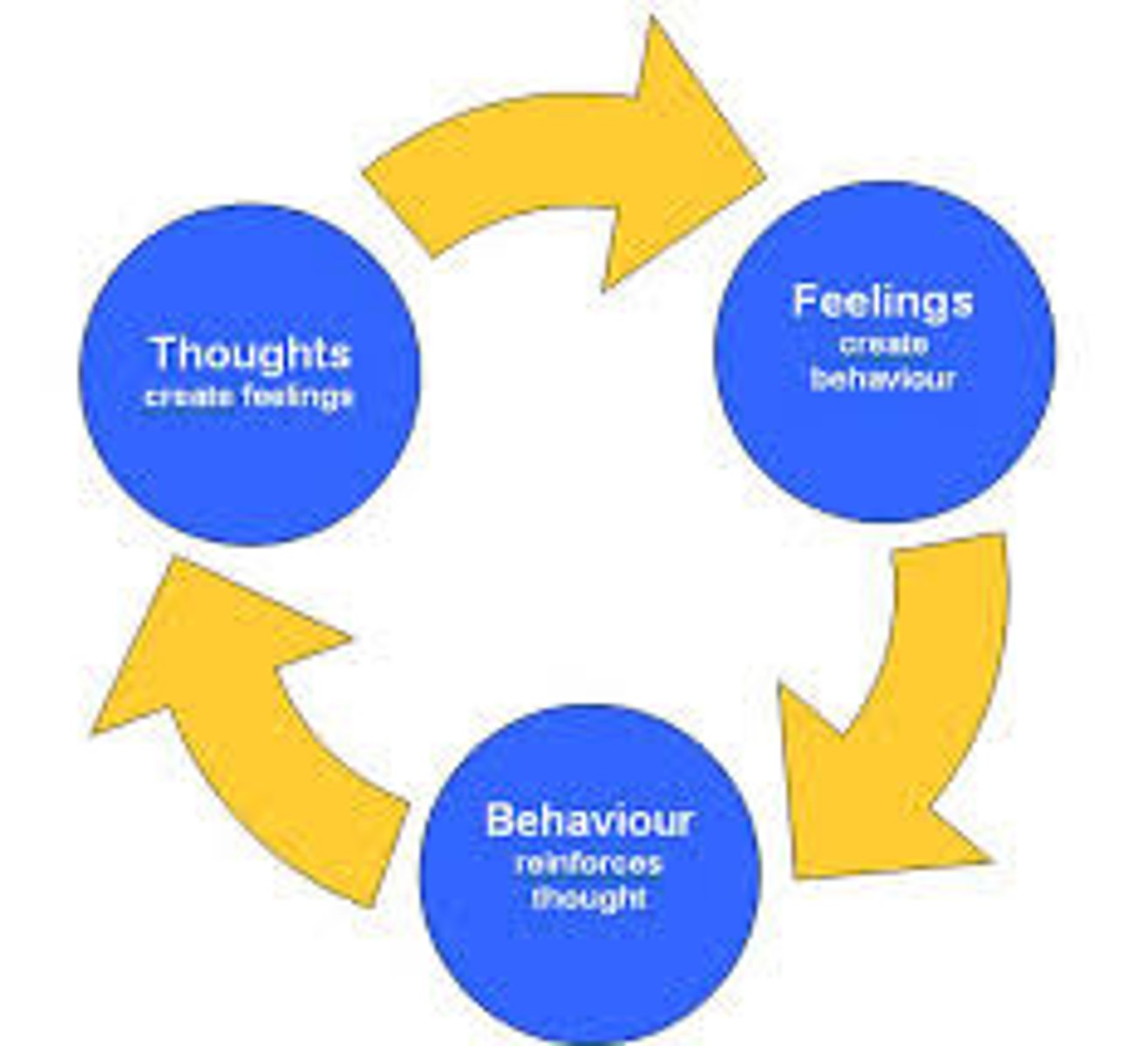
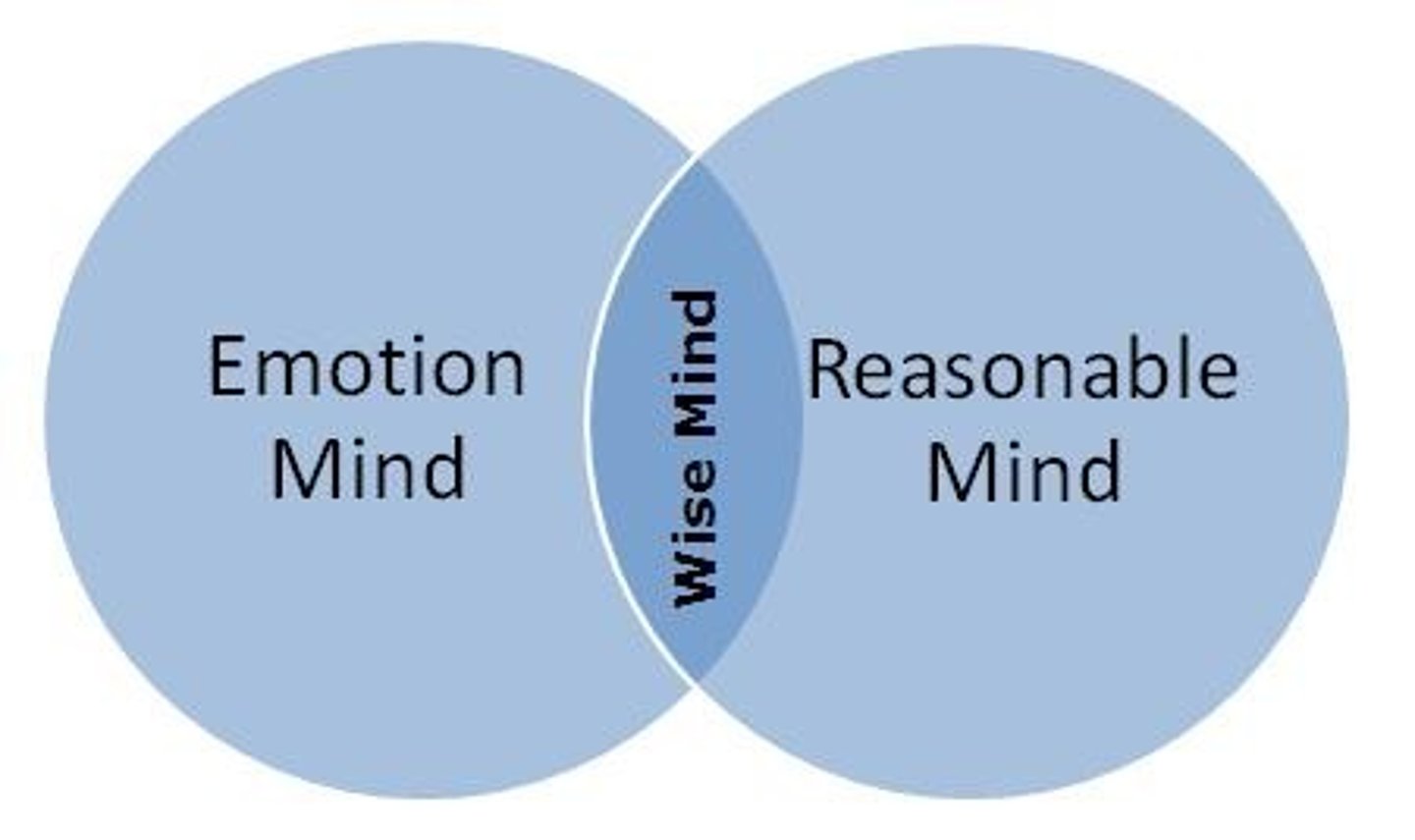
dialectical behavior therapy
focus is on getting people to accept who they are regardless of whether it matches their ideal
rational-emotive behavior therapy
challenges people's illogical, self-defeating attitudes and assumptions

humanistic therapy
person-centered, unconditional positive regard, active listening

anti-psychotics
decrease dopamine, often treats schizophrenia
stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
hallucinogens
psychedelic drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
transcranial magnetic stimulation
a treatment that involves placing a powerful pulsed magnet over a person's scalp, which alters neuronal activity in the brain
electroconvulsive therapy
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
lobotomy
cut the nerves connecting the frontal lobes to the emotion-controlling centers of the inner brain