Partial Pressures.
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
The weight of the atmosphere at sea level =?
760 mmHg
A partial pressure is a pressure exerted by each?
By each Individual Gas
In the Atmosphere
The partial pressure of each gas is determined by multiplying its?
Concentration in the Air x Total Atmospheric Pressure
Partial pressure is denoted by an upper case?
P Followed by Gas
E.G P02 = Partial Pressure of Oxygen
What is the Partial Pressure of oxygen?
Po2 = 159 mmHg;
Since oxygen takes up 21% of the atmosphere
(760 x 0.21) = 159mmHg
What is the Partial Pressure of Nitrogen?
P02 = 593 mmHg
Nitrogen takes up 78% of Atmosphere
760 × 0.78 = 593
One of the key functions of the respiratory systems conduction zone is to saturate the air with?
Water Vapour
Before Air reaches the Alveolus
Water vapour in the conducting zone has a partial pressure of?
47 mmHg
which contributes to the total air pressure
Why is the Partial Pressure of Other Gases Combined 713?
760 mmHg - 47 mmHg
760 mmHg = Atmospheric
47 mmHg = Water Vapour of Conducting Zone.
Dry atmospheric Po2= 0.21 (760) =?
159 mmHg
100% humid air Po2 = 0.21 (760-47) = ?
150mmg
The partial pressure of oxygen decreases in the conducting zone before mixing of the?
The gases has even occured.
As air is inspired we can consider the Po2 to be equal to …mmHg. However, as this air mixes with the depleted O2 air of the conducting zone, the Po2 drops to …mmHg by the time it has reached the alveoli?
we can consider the Po2 to be equal to 150 mmHg
However, as this air mixes with the depleted O2 air of the conducting zone, the Po2 drops to 105 mmHg
PC02 in the Alveoli is?
40 mmHg
Po2 and Pco2 of alveolar air and blood quickly reach an?
Equilibrium
Due to the Large Surface area of the Alveoli.
The concentration of a gas dissolved in the blood plasma is directly proportional to the?
Partial Pressure of Gas in that Air.
i.e. the more O2 in alveoli air, the more O2 in the blood
The cells of the body consume O2 for?
ATP Production
As O2 is consumed it reduces the Po2 within the?
The TIssues.
Creating a Stronger Concentration Gradient.
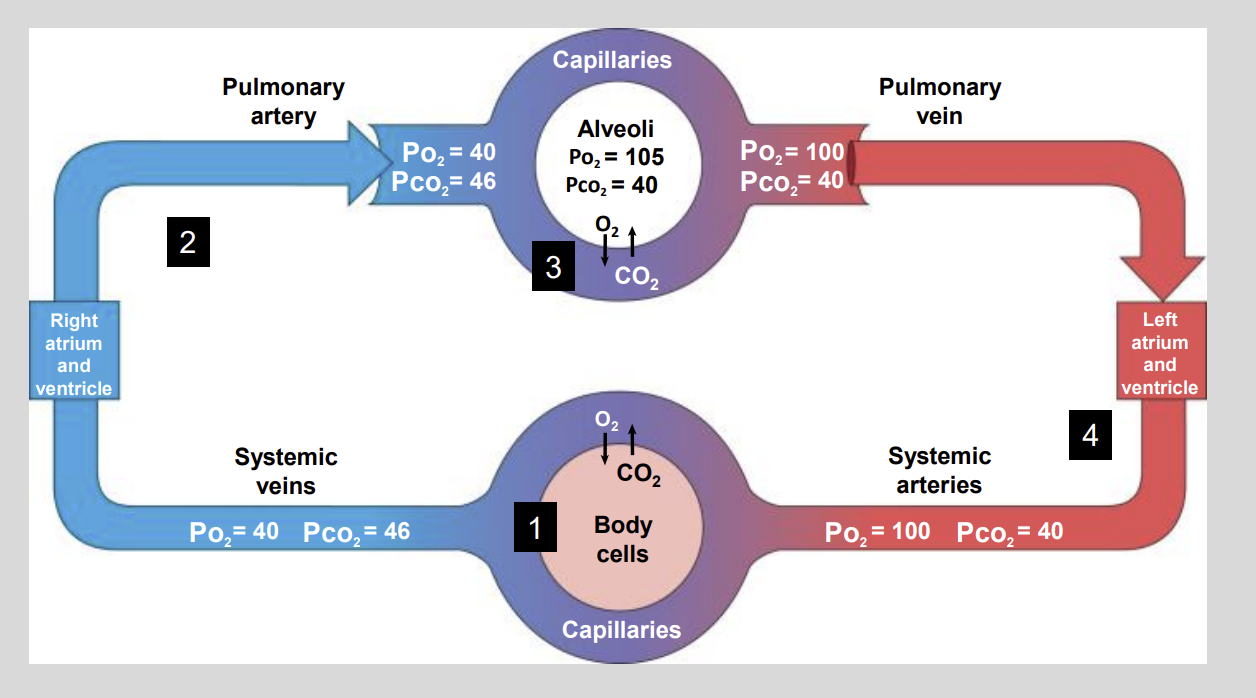
Partial Pressures of 02 AND C02 Diagram
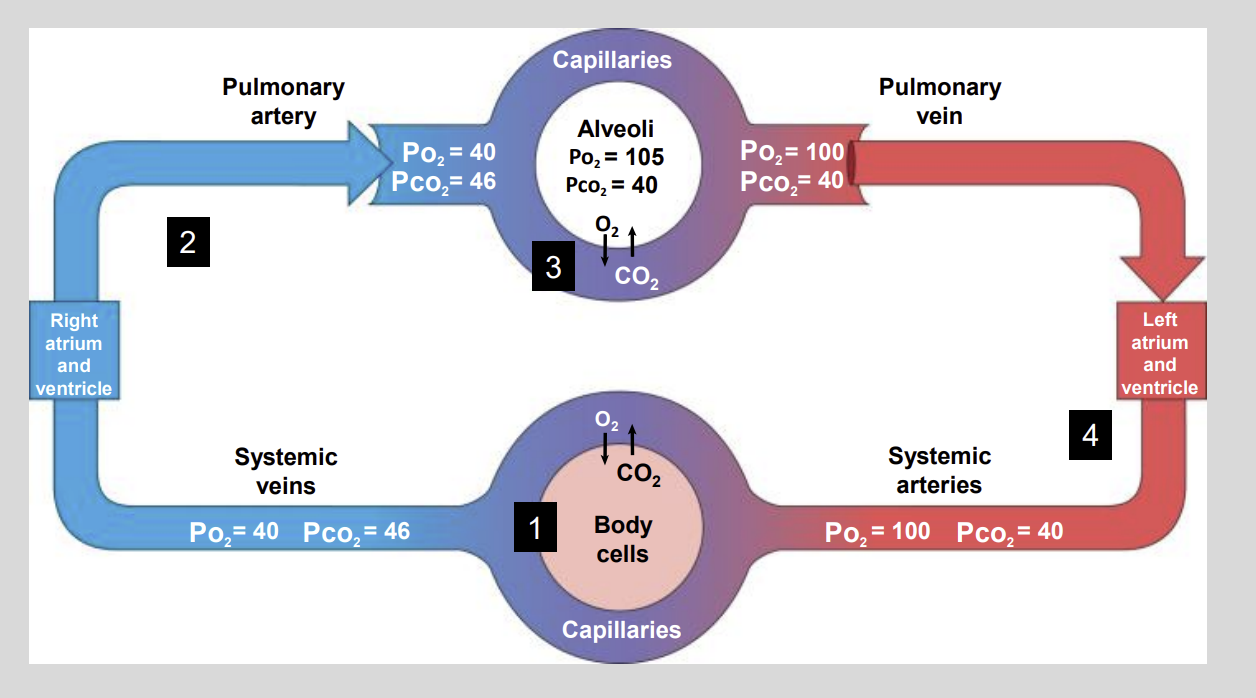
CO2 is a waste product of?
Cellular Respiration
As a result CO2 builds up in the tissues increasing the cellular Pco2
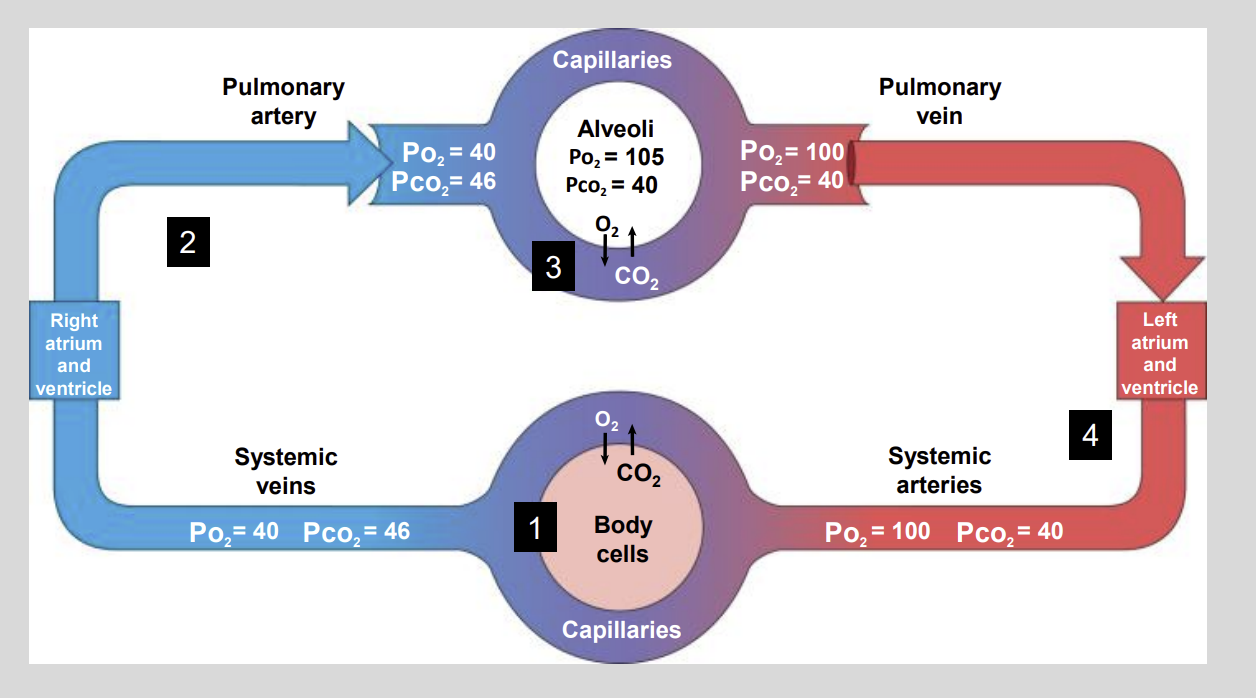
Normally, the arterial Pco2 that delivers blood to the capillaries of the body is?
40 mmHg
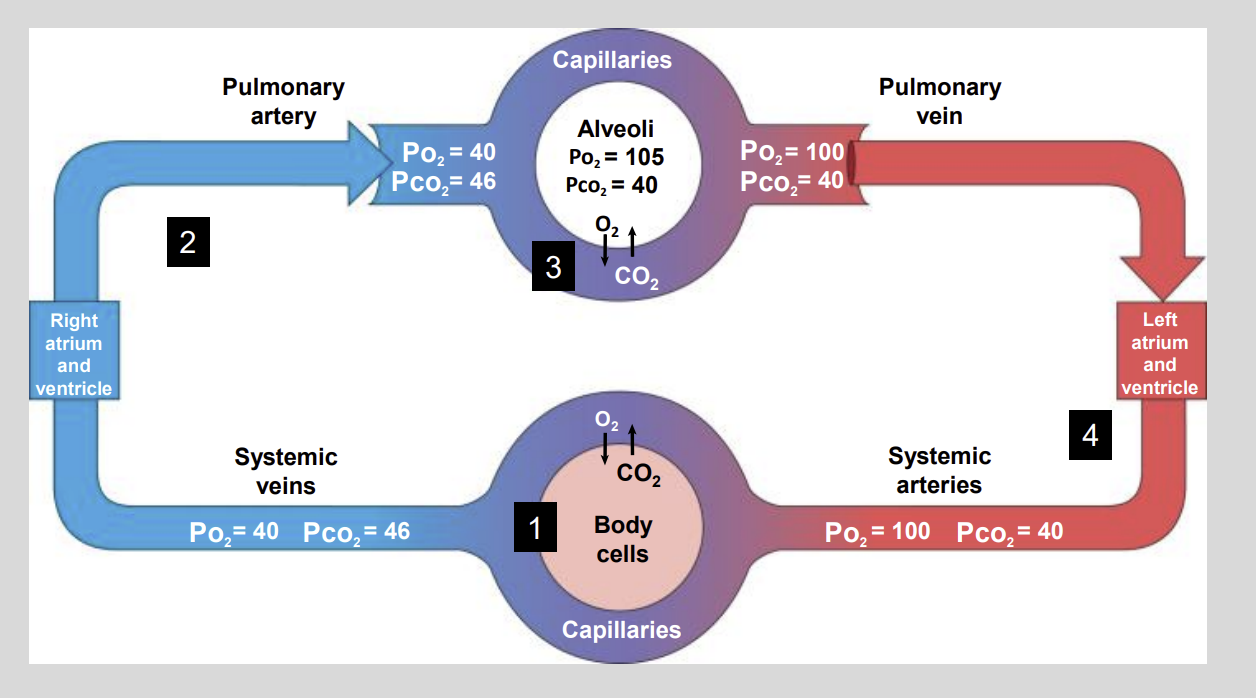
however the normal Pco2 of metabolically active tissues averages?
46mmHg
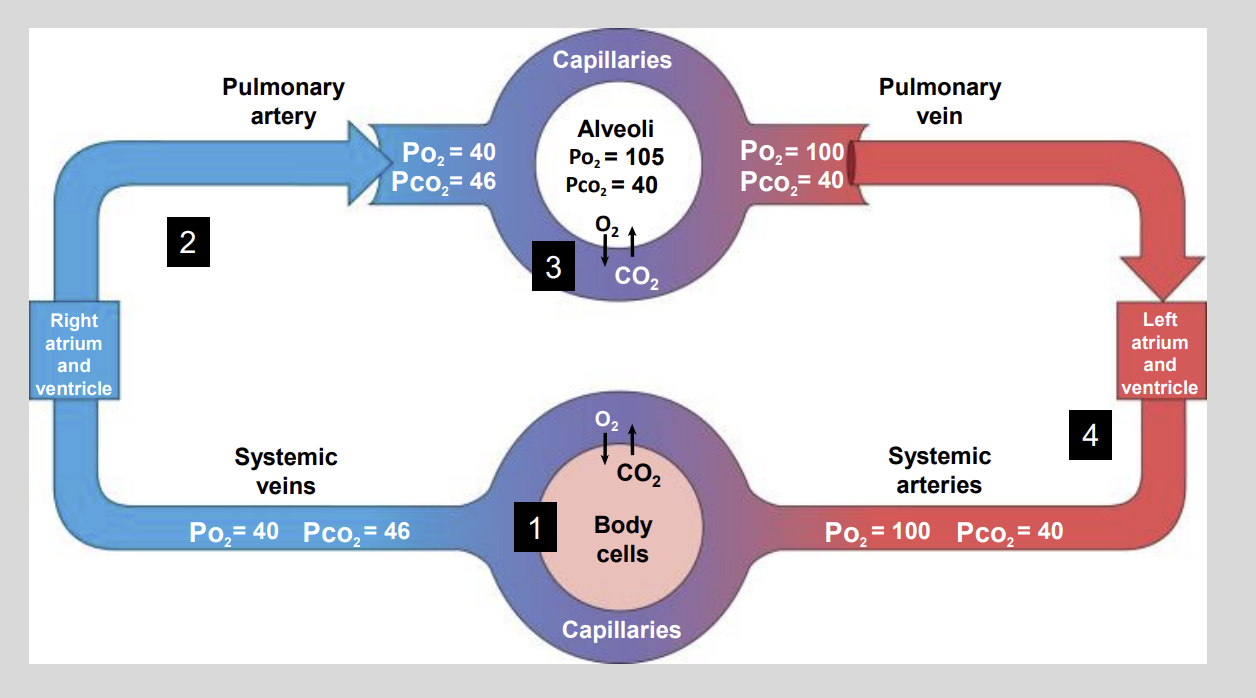
The blood that leaves the capillaries of the body is now considered to?
Hypoxic and Hypercapnic
Low 02 and High C02
Elevated [CO2] can make tissues very?
Acidiotic
The hypoxic and hypercapnic blood is returned to the?
Right Side of Heart
Into the Right ventricle then to the Lungs.
Venous blood contains a low Po2 …..mmHg and a high Pco2 of ….. mmHg?
Low P02 of 40 mmHg
High PC02 of 46 mmHg
As a result, there is a concentration gradient for O2 to enter the blood and for CO2 to leave the blood
As the blood leaves the lungs, it contains a high?
High P02 = 100 mmHg
Low C02 = 40 mmHg
Often, alveolar ventilation (V) does not match blood perfusion (Q)….?
Very well
not all over the alveoli are sufficiently?
Sufficiently ventilated during breathing.
During eupneic breathing, the tidal volume only?
Inflates a small portion of the lungs.
During eupneic breathing, the tidal volume only inflates a small proportion of the lung. This leaves huge reserves in the lung which can be called upon during?
During Exercise
Different Lung Regions =?
Different V/Q Ratios
What does V/Q Mean?
V = Ventilation
Q = Perfusion
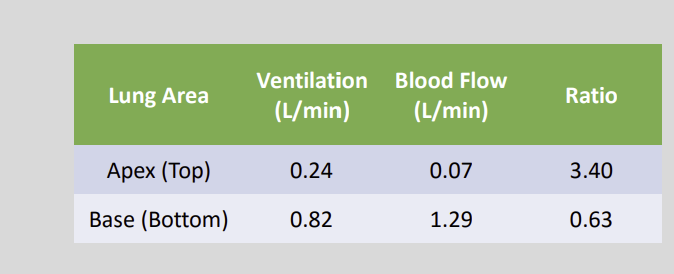
During normal breathing, ventilation is ….? fold higher at the base of the lung compared to the apex?
3 to 4 Fold Higher
However, blood flow is about …. fold higher at the base of the lung compared to the apex of the lung
18 Fold Higher
The apex of the lung is overventilated in relation to its?
Very low blood flow
The base of the lung is underventilated in relation to its?
Higher blood flow
What is a Pulmonary Shunt?
Pathological condition whereby the lungs are normally perfused with blood
but the ventilation of regions of the lung is impaired
Pulmonary Shunt results in?
It results in the perfused blood not being oxygenated as the blood passes through alveoli that are not ventilated.
This deoxygenated blood mixes with the rest of the oxygenated blood resulting in hypoxaemia (reduced blood oxygenation).
Since nitrogen is not used by the body, its concentration in the blood…?
Never changes drastically
However, if the PN2 was to rise dramatically in situations such as scuba diving, extreme?
Extreme Drowsiness & Dizziness can occur.
That mimics alchohol intoxication.
Every 10 meters that a scuba diver descends under water increases the pressure placed upon the body by?
1 Atmosphere
Due to the high PN2 of nitrogen rapid ascent from depth during scuba diving can result in?
Decompression Sickness
Increased Depth = Increased Pressure =?
Increased Partial Pressures.
Rapid Decompression =?
The bends,
If decompression occurs too rapidly the nitrogen will quick dissolve out of the blood and form?
Forming nitrogen bubbles in the bloodstream.
These bubbles result in an air embolism which can block blood vessels, potentially impeding flow to vital organs. This is known as decompression sickness or “the bends”