GCSE Computer Science - 3.1 Fundamentals of Algorithms
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Define the term Algorithm
A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer.
Define the term decomposition with examples
Breaking down a complex problem into smaller parts, e.g. Merge Sort Algorithm.
Define the term abstraction with examples
Removing unnecessary details to focus on the main goal, e.g. Driving a Car - don't need to know how turning key starts car.
Flowchart Symbols
Start/End:
Input/Output:
If:
Process:
Flowchart Symbols
Start/End: Oval
Input/Output: Parallelogram
If: Diamond
Process: Rectangle
Boolean Operators (Operator+Symbol)
AND:
OR:
NOT:
XOR:
Boolean Operators (Operator+Symbol)
AND: A • B =D-
OR: A + B +)>-
NOT: Ā -|>•-
XOR: A⊕B +))>-
Define with an example:
Sequence:
Selection:
Iteration:
Define with an example:
Sequence: The order in which instructions occur and are processed, e.g. normal code
Selection: determines which path a program takes when it is running, e.g. if statements
Iteration: repeated execution of a section of code when a program is running, e.g. for loop
Python example of selection:
age = int(input("Age: "))
if age >= 17:
print("Can drive a car.")
else:
print("Can't drive a car.")
Python example of iteration:
num = int(input("Enter number: "))
for num in range(num,0):
print(num)
Binary Search
Find 7:
3 7 9 10 | 11 21 33 42
<--
3 7 | 9 10
<--
3 | 7
-->
7
Linear Search
Find 6:
14 33 12 6 7 19 20
-> -> -> |
\/
6
Binary Search vs. Linear Search
Binary Search | Linear Search
Has to be sorted | Can be unsorted
Faster on longer lists | (on Avg.) | Slower on longer lists
Similar average speeds on short lists
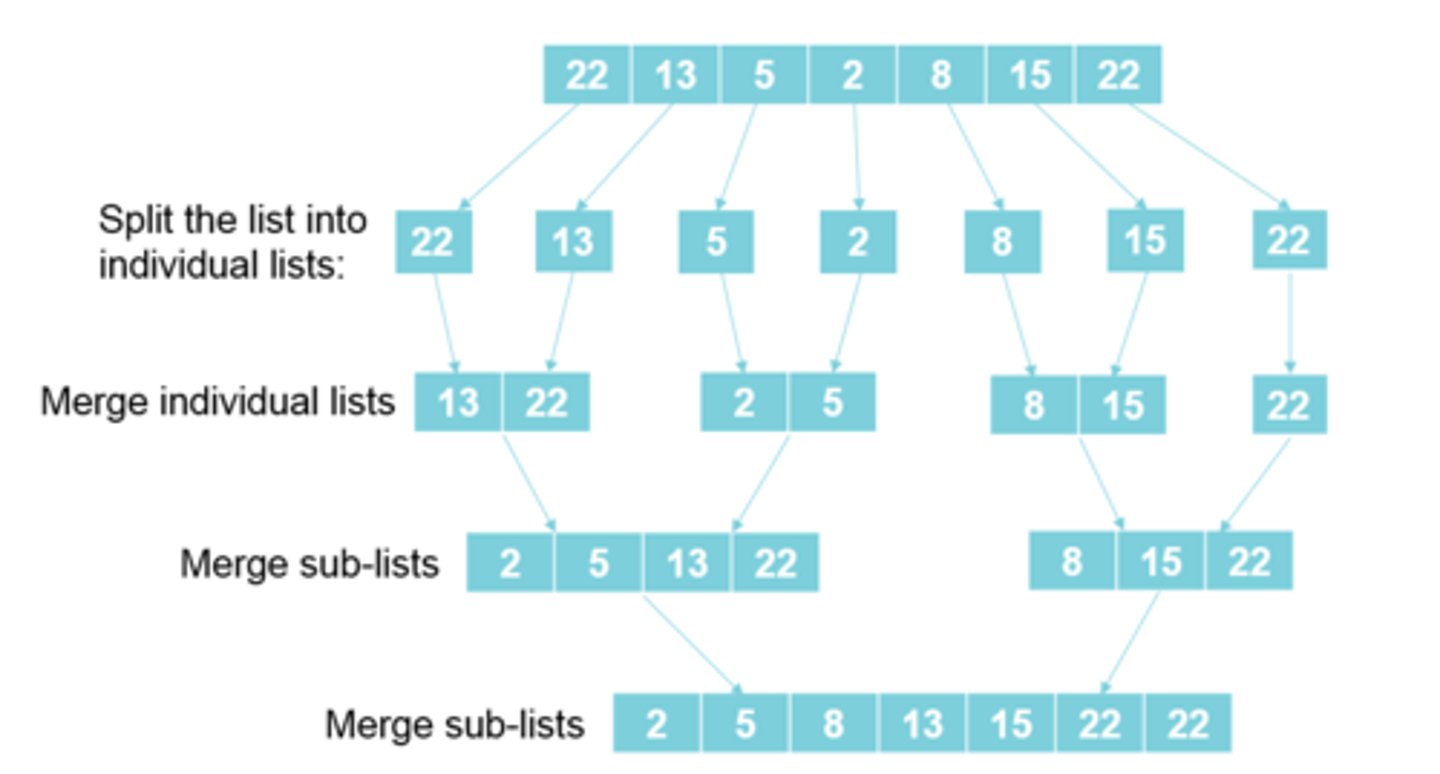
Merge Sort
Bubble Sort
Starts at the beginning of the list and compares each number to the next one in the list. If it is bigger than the next number they switch.
Merge Sort vs. Bubble Sort
Merge Sort | Bubble Sort
Faster on longer lists | Faster on shorter lists
Takes up more memory | Very slow on long lists