Social Networks Class 13
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is homophily?
The tendency for people to form social ties with others who are similar to themselves.
What kind of similarities cause Homophily?
race and ethnicity, age, education level, gender, religion, political views
An example of Homophily.
Most close friendships and marriages occur between people of similar age, race, or education level.
Why is homophily important in networks?
It explains why networks often form clusters of similar people, leading to segregation and information "echo chambers”.
What does the E-I Index measure?
The balance between external ties (to different groups) and internal ties (to your own group) .
What is the formula for the E-I Index?
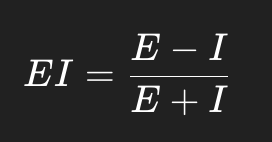
What does an E-I index of -1 mean?
Complete homophily — only in-group ties.
What does an E-I index of 0 mean?
Equal number of in-group and out-group ties.
What does an E-I index of +1 mean?
Complete heterophily — only out-group ties.
What is a relative rate?
The observed percentage of ties that go to in-group members .
What is an expected rate?
The predicted percentage of in-group ties based on group sizes in the population.
**How do we know if homophily exists based on rates?
If relative > expected → homophily
If relative ≈ expected → random mixing
If relative < expected → heterophily
What is a mixing table?
A table showing how frequently nodes from different groups are connected to each other.
What can mixing tables reveal?
Whether people are mixing randomly, showing homophily, or showing heterophily .
Does homophily stay the same over time?
No, it can strengthen or weaken depending on changes in the social environment.
What did Weber et al. (2020) find about homophily over time?
Gender homophily often increases in study groups over time, GPA homophily (studying with students of similar academic achievement) also increases over time.