Ions to Memorize
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
H3O^+
Hydronium
NH4^+
Ammonium
OH^-
Hydroxide
HCO3^-
Bicarbonate
CO3²-
carbonate
NO3^-
nitrate
NO2^-
nitrite
CH3COO^-
acetate
PO4³-
phosphate
SO4²-
sulfate
SO3²-
sulfite
MnO4^-
permanganate
polyatomic cations end in
-ium
polyatomic anions end in
-ate, -ite
monatmic anions end it
-ide
linear bond angle
180
trigonal planar bond angle
120
tetrahedral bond angle
109.5
trigonal bipyramidal bond angle
90, 120
octahedral bond angle
90
t shaped bond angle
90
bent bond angle
less than 109.5
steric number
number of atoms + lone pairs bonded to central atom
ion dipole forces
between an ion and a polar molecule with a permanent dipole
ion-induced dipole interactions
an ion and a nonpolar molecule that has a temporary dipole induced by the ion's charge
dipole dipole interactions
between two polar molecules
dipole induced dipole
between a polar and nonpolar molecule
Relative strengths of intermolecular forces
ion-ion > ion-dipole > hydrogen bonding > dipole-dipole > ion-induced dipole > dipole-induced dipole > london dispersion
combination reaction
reactants combine to form a single product
why is dissollving in water not a chemical change?
No new product was formed
decomposition reaction
only one reactant and more than one product.
single replacement reaction
2 Mg(l ) + TiCl4(g) → 2 MgCl2(s) + Ti(s)
precipitation reaction
double-replacement reaction involving the formation of a precipitate
acid base reactions are alwasy
double replacement
neutralization reaction.
strong acid + strong base → salt + water
critical point
highest temperature and pressure at which a liquid and gas can exist in equilibrium
triple point
all 3 phases coexist in equilibrium
Above the critical temperature on a phase diagram
The gas and the liquid phases become indistinguishable. A gas above its critical temperature cannot be liquefied no matter how high a pressure is applied
intermolecular forces
forces between neutral molecules
intramolecular forces
force between ions (chemical bond)
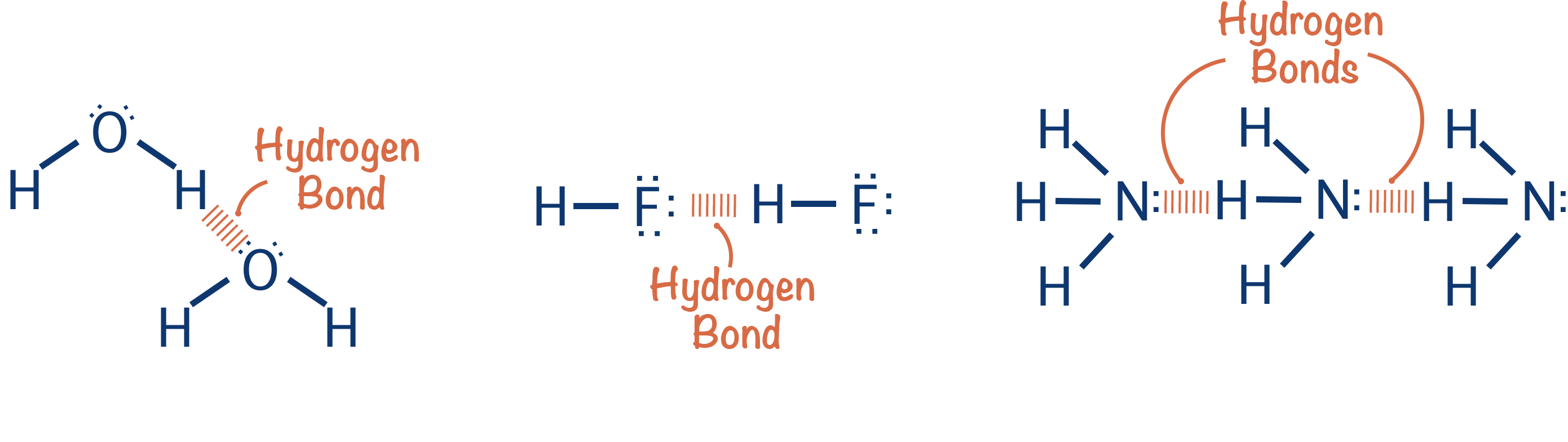
hydrogen bonding visual example
electrolytes vs nonelectrolytes
Electrolytes are typically ionic compounds (like salt) or strong acids, and they are essential for bodily functions like nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Nonelectrolytes are often covalent compounds that remain intact as molecules, such as sugar, alcohol, and many organic molecules