dt core content
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
printing, finishing, cutting, mechanical devices
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
what is direct printing?
when the image is directly transferred from the plate cylinder to the surface
what is indirect printing?
when the image is first transferred from the plate cylinder to a blanket cylinder, and then to the surface
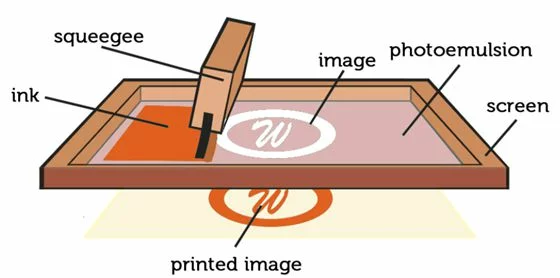
explain the process of screen printing
1) a mesh screen is coated with light-sensitive emulsion to block off areas as a negative of the image, leaving a stencil of the design
2) ink is spread across the screen with a squeegee to cover the open spaces of the stencil/mesh
3) the print is dried using air dryers or heat
what are the advantages of screen printing?
UV resistant, heat resistant, versatile printing surface
what are the disadvantages of screen printing?
long drying time, time-consuming screen preparation, only suitable for batch production
what is screen printing used for?
merchandise, plastic/metal signage, promotional items
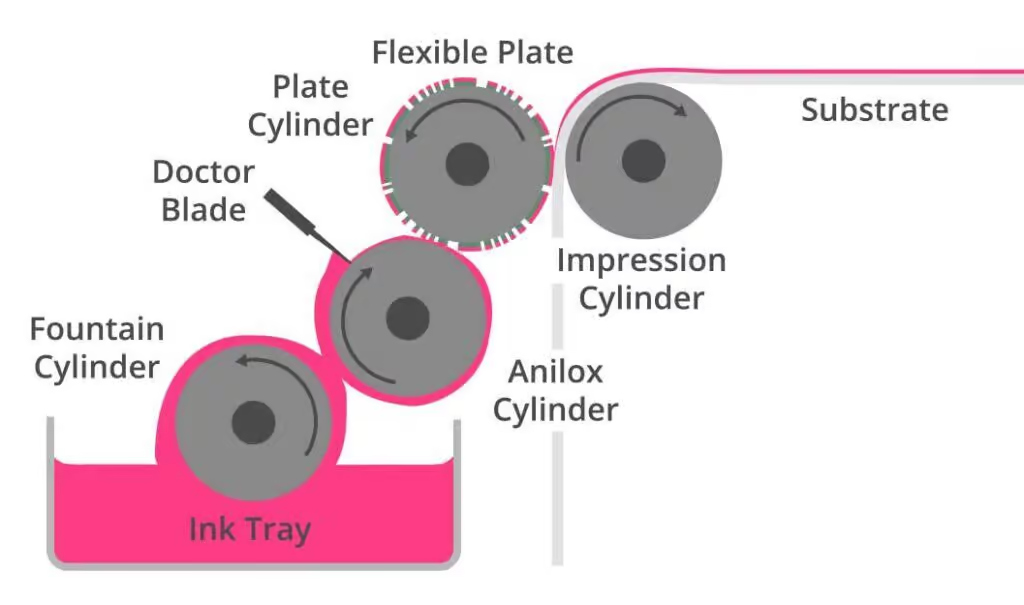
explain the process of flexography
1) a thin layer of ink is applied from the fountain cylinder to the anilox cylinder
2) a spatula (doctor blade) cleans the excess ink from the anilox cylinder, leaving the desired amount in the anilox cells
3) the anilox cylinder offsets the ink onto the plate cylinder, which then prints the image onto the surface
what are the advantages of flexography?
high printing speed, fast drying ink, versatile printing surface
what are the disadvantages of flexography?
high initial costs, difficult to achieve detail
what is flexography used for?
bottle labels, plastic bags, packaging
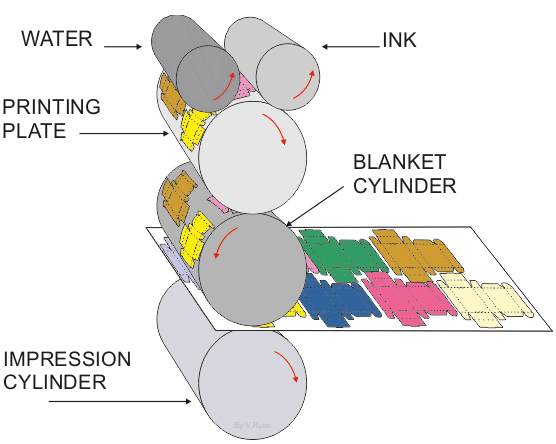
explain the process of offset printing
1) design is laser etched onto a plate and loaded into the plate cylinder
2) the non-image area is dampened with water
3) oil based ink is transferred onto the image area of the plate cylinder
4) the plate cylinder offsets the image onto the blanket cylinder
5) the blanket cylinder then prints the image onto the surface, which is pulled through by the impression cylinder
what are the advantages of offset printing?
high image quality, high printing speed, used for mass production
what are the disadvantages of offset printing?
high initial costs, paper can stretch, plate manufacture is time consuming
what is offset printing used for?
business stationery, brochures, magazines, newspapers
explain the process of digital printing
1) a design is made using a CAD software and the file is prepared for printing (eg resolution, printing size, colour settings)
2) the image is sent directly to the printer through digital files
3) an inkjet printer transfers the image directly onto the surface by spraying ink
a laser printer uses toner and heat to bond the image to the surface
what are the advantages of digital printing?
affordable, quick, easy last-minute changes
what are the disadvantages of digital printing?
low UV resistant ink, graphic problems, slightly lower quality
what is digital printing used for?
posters, brochures, business cards, art prints
what is lamination?
adding a film of PP, PET or LDPE to the surface or both sides of a printed sheet via heated roller
what are the advantages of lamination?
provides barrier protection against spills, smudges and UV, more pronounced than varnish
what are the disadvantages of lamination?
limited recyclability, laminate layer can peel off or bubble
what is lamination used for?
food packaging, consumer goods, school displays
what is varnish?
a liquid finish applied via printing press
what are the advantages of varnish?
seals and protects ink from smudging, distinctive, high quality shine, lightweight
what are the disadvantages of varnish?
difficult to recycle, limited protection
what is varnish used for?
magazines, comic books, brochures
what is spot varnishing?
applying varnish only to specific areas via a custom press plate
what are the advantages of spot varnishing?
highlights detail, distinctive and visually stands out
what are the disadvantages of spot varnishing?
difficult to apply in non-commercial settings, expensive
what is spot varnishing used for?
business cards, invitations, book covers
what is hot foil blocking?
pigment or metal foil being stamped onto a surface using heat and pressure by custom metal dies
what is hot foil blocking used for?
book covers, business cards, invitations
what is embossing/debossing?
using a personalised die to raise or sink images off a surface creating a 3D effect
what are the advantages of embossing?
adds texture, depth and a high-quality finish
what is embossing used for?
business/greeting cards, invitations, book covers
what is linear motion?
movement in a straight line in one direction (eg train tracks)
what is rotary motion?
movement following a circular path around a centre point (eg a bicycle wheel)
what is reciprocating motion?
linear movement back and forth (eg car engine’s piston)
what is oscillating movement?
circular movement back and forth (such as a pendulum)
what is a lever used for?
to lift loads with the least amount of effort
what is a first class lever?
effort, pivot, load (scissors)
what is a second class lever?
effort load pivot (wheelbarrow)
what is a third class lever?
pivot, effort, load (tweezers)
how do you calculate mechanical advantage?
MA=load/effort
what is a linkage?
a mechanism which creates movement around a pivot - they can change the direction of motion, type of motion or the size of a force
function of parallel motion linkages
uses two fixed pivots to make the input and output travel the same direction
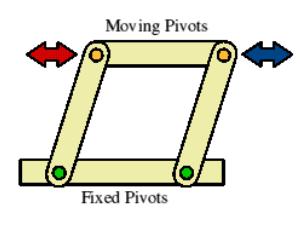
examples of parallel motion linkages
tool box drawers
function of reverse motion linkages
changes the direction of the input so the output travels the opposite direction
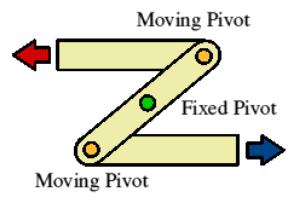
examples of reverse motion linkages
foldable clothing racks
function of bell crank motion linkages
transmits the direction of motion through 90 degrees
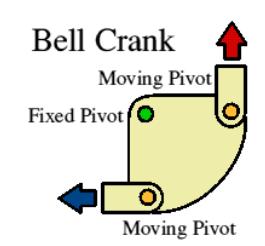
examples of bell crank linkages
bicycle brakes
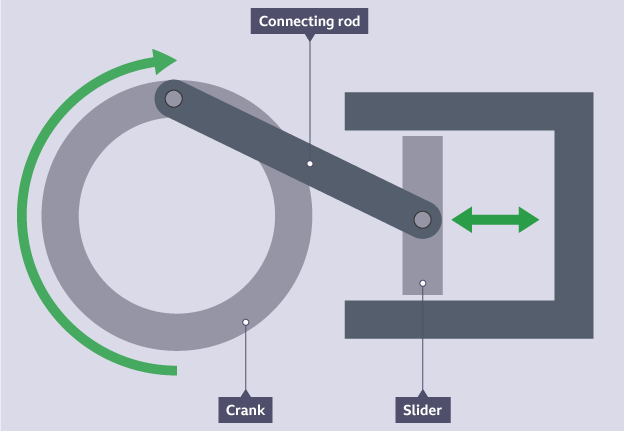
function of crank & slider linkages
transmits rotary motion to reciprocating motion using a fixed pivot attached to a crank which pulls/pushes a slider
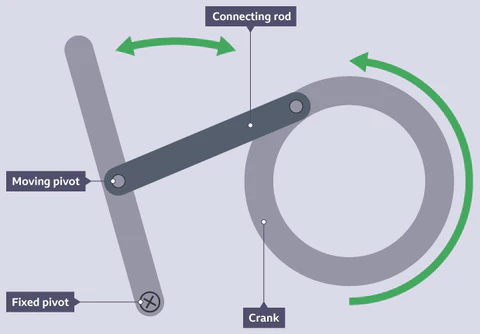
function of treadle linkages
uses a rotary input to turn a crank on a fixed pivot
converts rotary motion into an oscillating motion
movement of circular cams
uses an off-centre pivot to move the follower up and down
movement of pear cams
causes the follower to remain stationary for half a turn and then gently rises and falls
movement of snail cams
causes the follower to remain stationary for half a turn before rising and suddenly falling
movement of heart cams
causes the follower to rise and fall steadily with uniform velocity without a stationary period
pros and cons of flat followers
copes well under load, lacks accuracy, high friction
pros and cons of point/knife followers
very accurate, low friction, quick to wear away pointed edge
pros and cons of roller followers
accurate, low friction, can withstand load, costly to produce
what is a driver gear?
a gear which is attached to a motor or crank
what is a driven gear?
a gear turned by the driver gear
what is a compound gear?
a gear mounted on another gear’s shaft to change speed or direction of rotation
what is an idler gear?
a gear which rotates in the opposite direction of two gears allowing them to rotate the same way
what is a bevel gear?
a gear which transmits rotary motion through 90 degrees (eg hand drills)
what is a rack & pinion gear?
a gear that transmits rotary motion into linear motion (such as steering systems or pillar drills)