Computer Systems Study Guide
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from the Computer Systems study guide.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Memory Hierarchy
An arrangement of memory types that balances cost, speed, and storage capacity.
Memory Hierarchy Diagram
"Real Computers Make Fast Tasks Run."
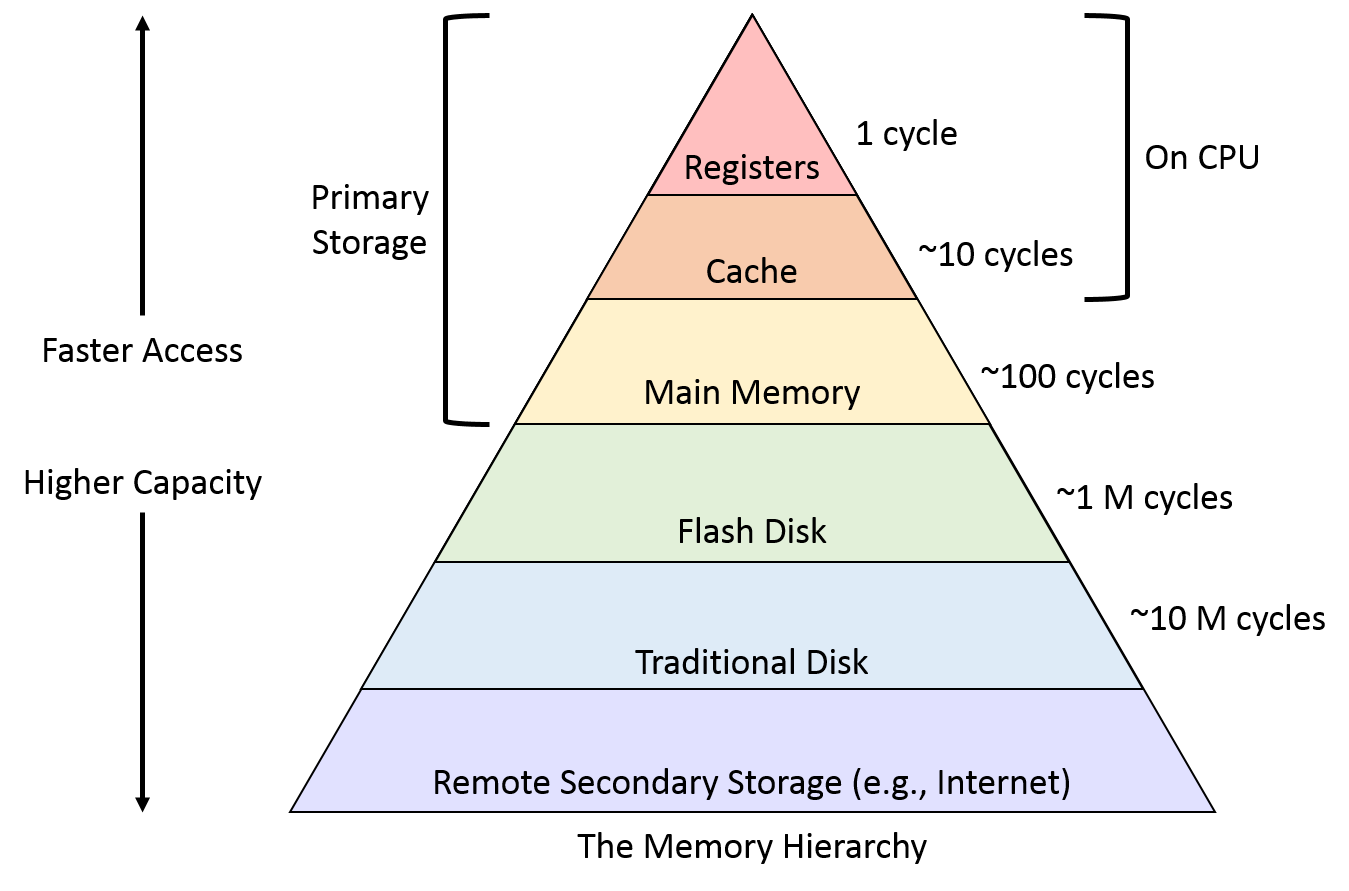
Primary Storage
Volatile memory directly accessible by CPU, used for running applications and active data. (RAM)
Secondary Storage
Non-volatile, long-term data storage, such as HDDs or SSDs, used for file storage and backups.
Cache Memory
L1: Fastest, smallest, closest to CPU cores
L2: Larger, slightly slower than L1
L3: Largest, slowest cache, shared among cores.
Cache Memory: Direct Mapping
Each block of main memory maps to exactly one cache line
Cache Memory: Associative Mapping
Any block can go into any cache line. (Flexible but slower)
Cache Memory: Set-Associative Mapping
Combines direct and associative; memory blocks map into a set of lines
Operating Systems
Software managing hardware resources, providing services to software.
Functions: Resource management, memory management, task scheduling, I/O control, security
Multiprogramming
A method where several programs run simultaneously to maximize CPU usage.
Multithreading
Multiple threads running within a single program, similar to multiprogramming but within one application
OS Kernel
Core component managing system resources, memory, processes, and hardware interaction.
User Mode
A restricted mode where applications run with no direct access to hardware.
Kernel Mode
A mode with full access to hardware and memory, allowing OS code execution.
Processes
A running instance of a program. Needed to allocate resources, manage tasks
Processes Diagram
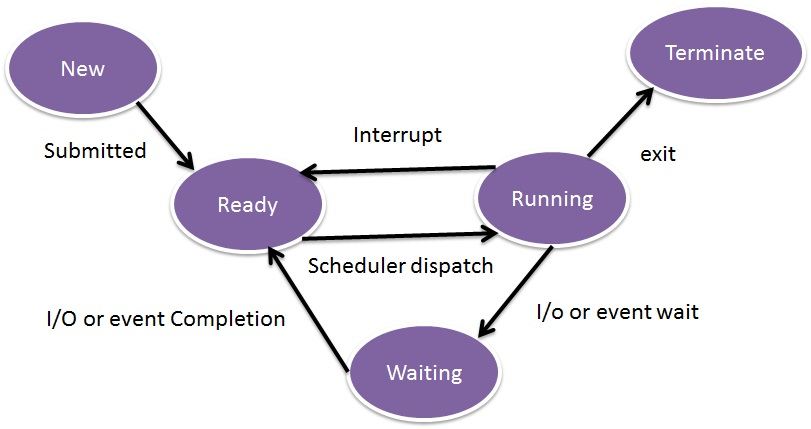
Interrupts
Hardware-generated signals that temporarily stop CPU tasks to handle important events.
Traps
Software-generated signals or errors requiring OS intervention.
Virtual Memory
A technique that provides the illusion of a large memory space to programs. Allows execution of processes larger than available physical memory.
Paging
The process of dividing memory into fixed-size blocks for easy management.
Paging Tables
Structures mapping virtual memory addresses to physical addresses
Memory Management Unit (MMU)
A component that translates virtual memory addresses to physical addresses.
Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB)
Fast memory storing recent page translations, improving access speed.