Psychology Chapters 1-3
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
what school of thought did Abraham Maslow belong to
the humanism school of thought
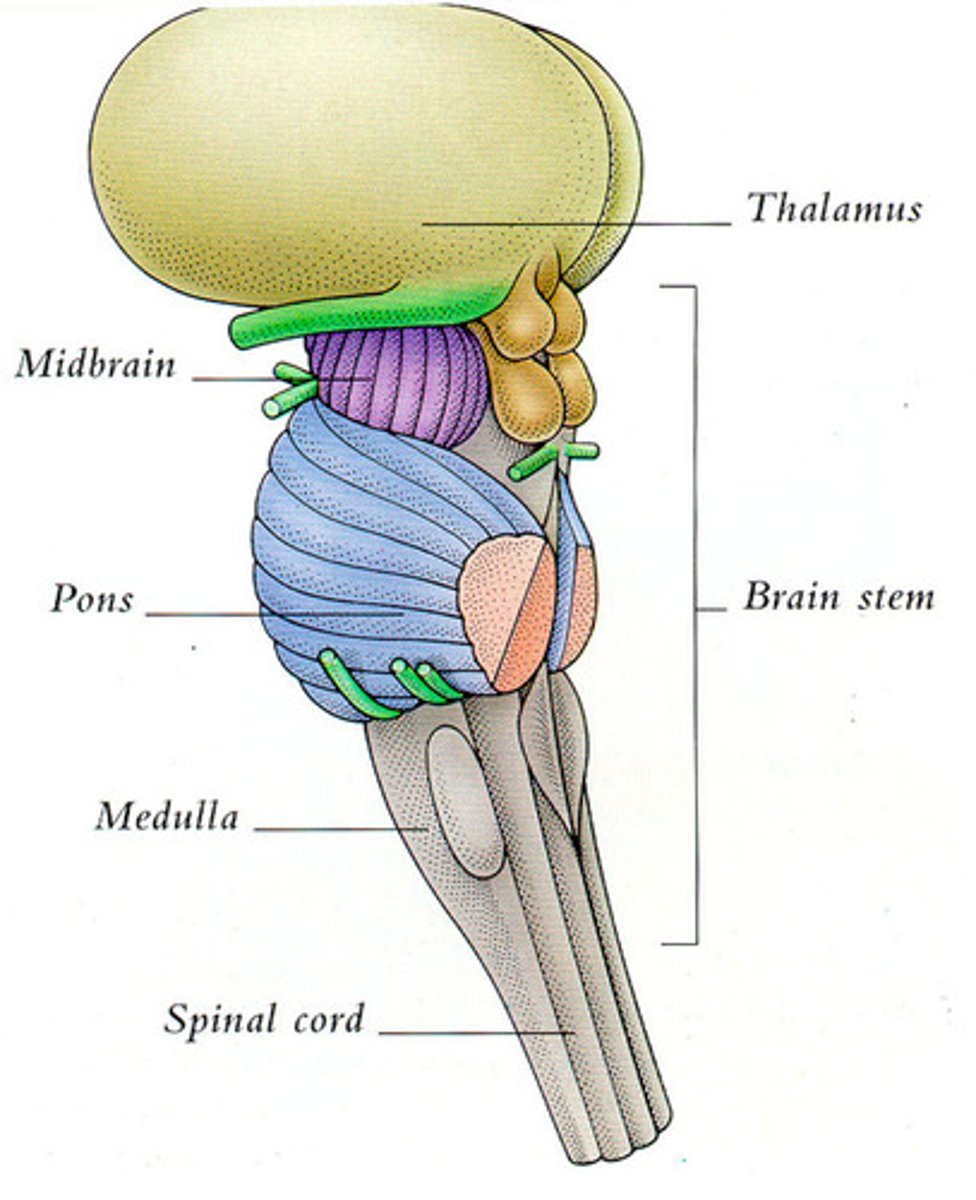
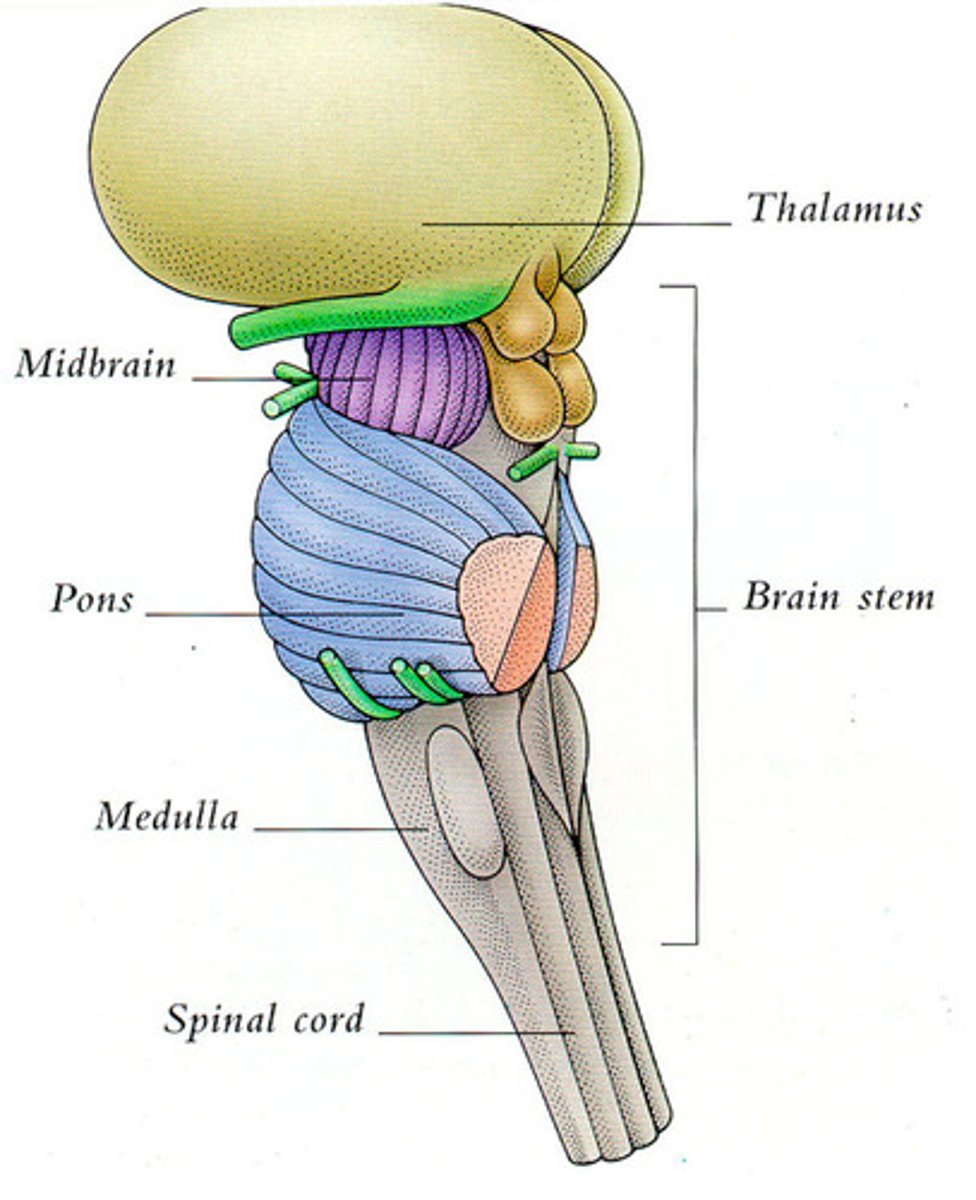
brain stem function
controls automatic behaviors necessary for survival (beneath the level of consciousness)
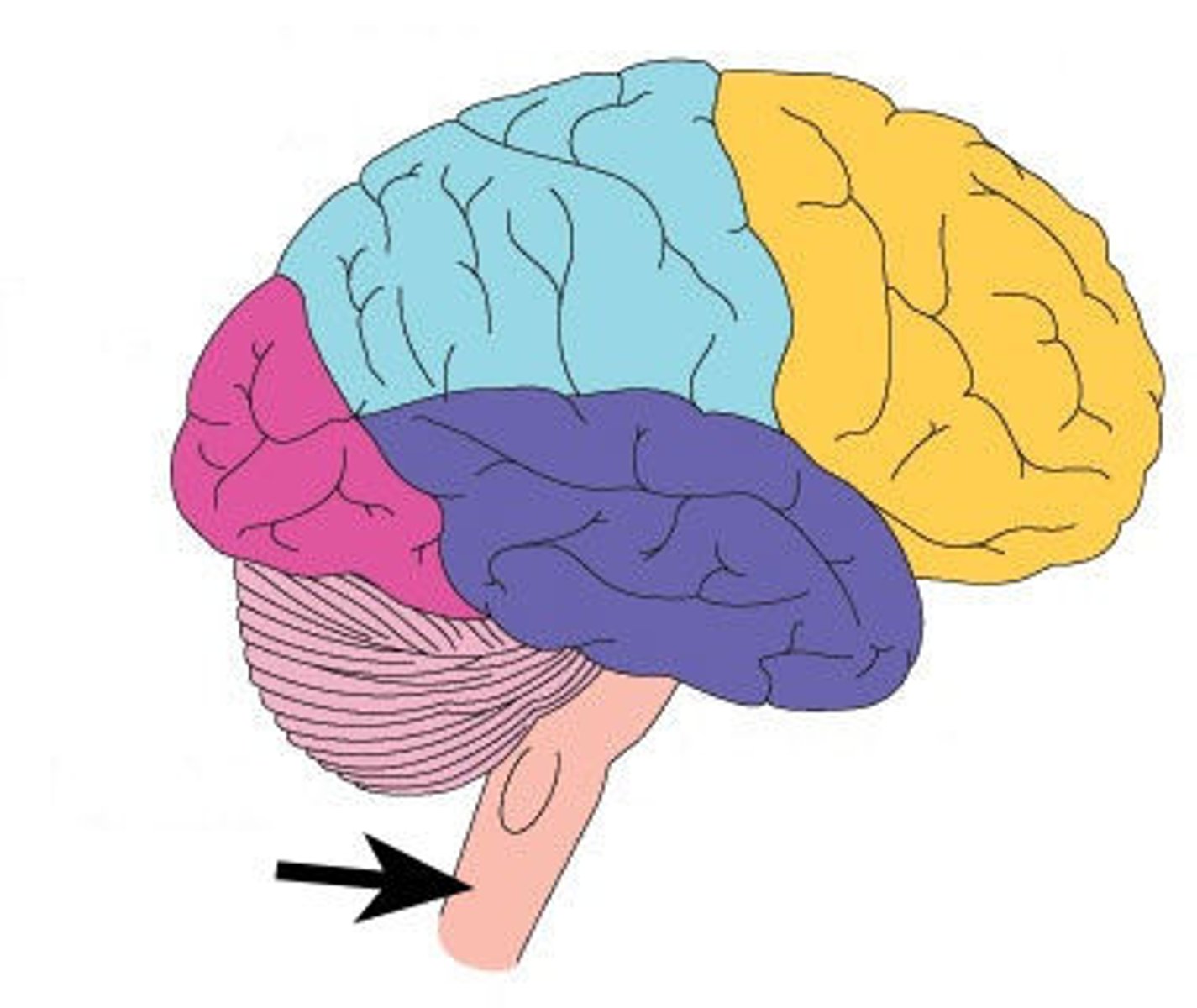
Medula
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
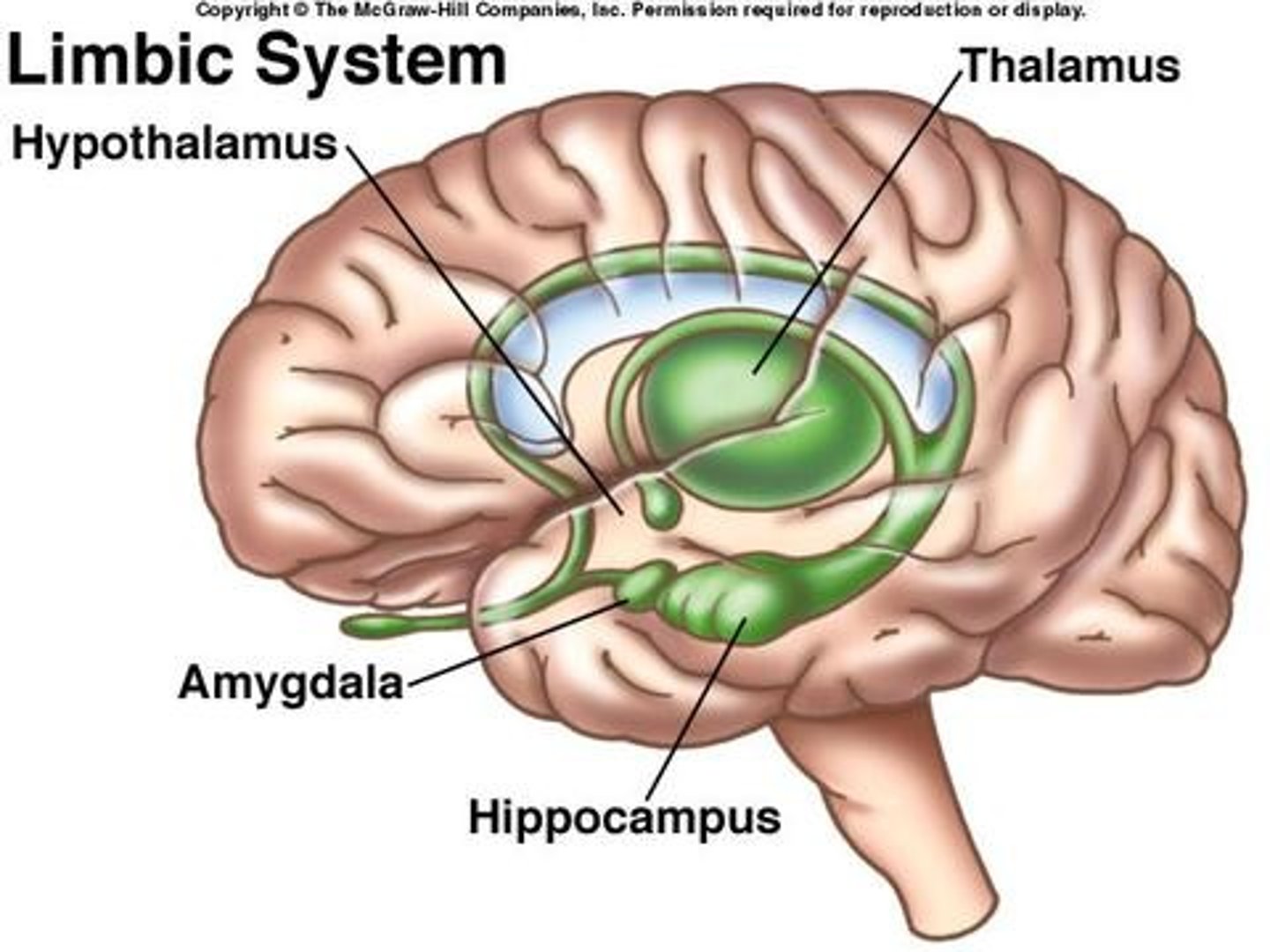
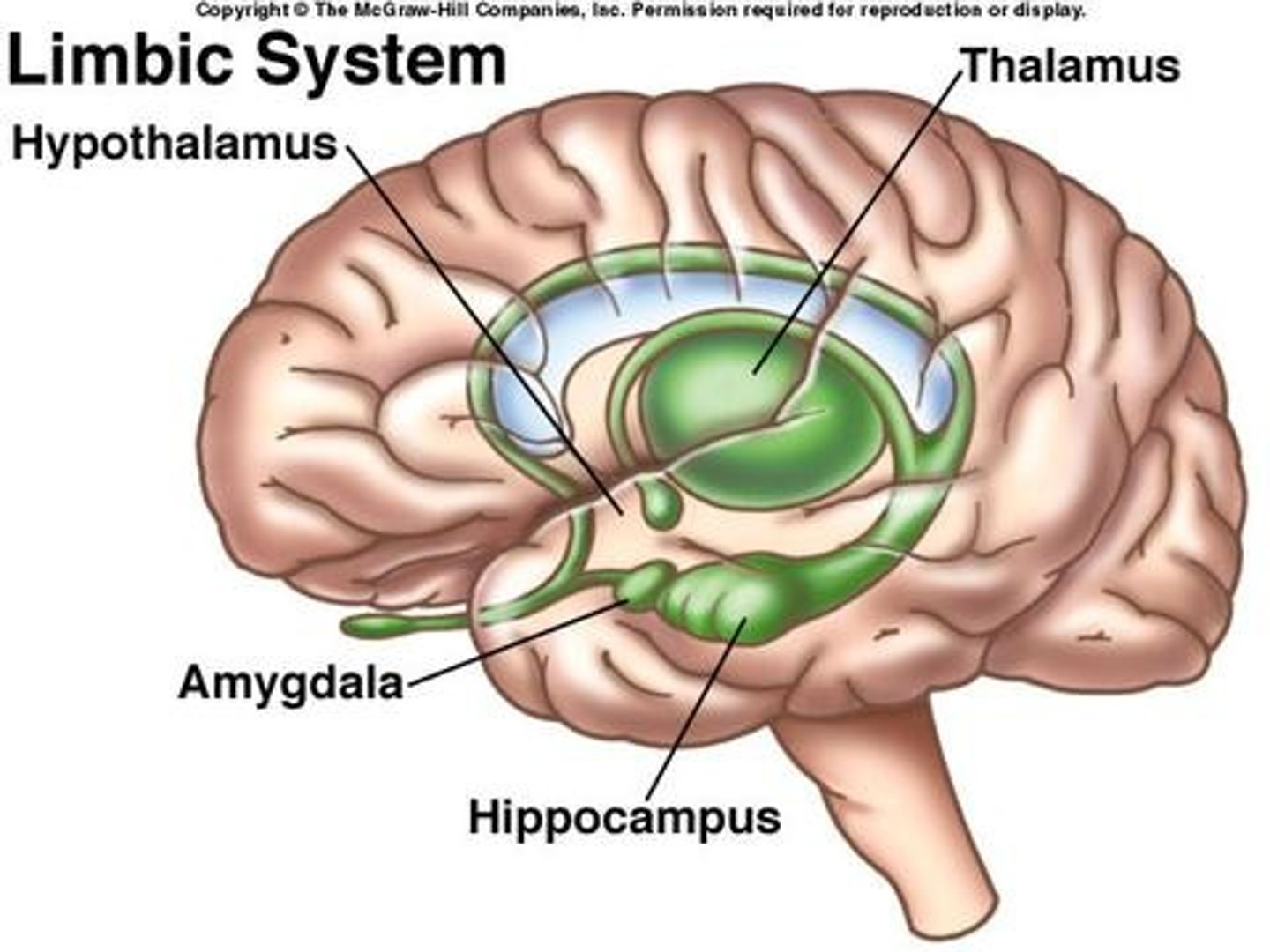
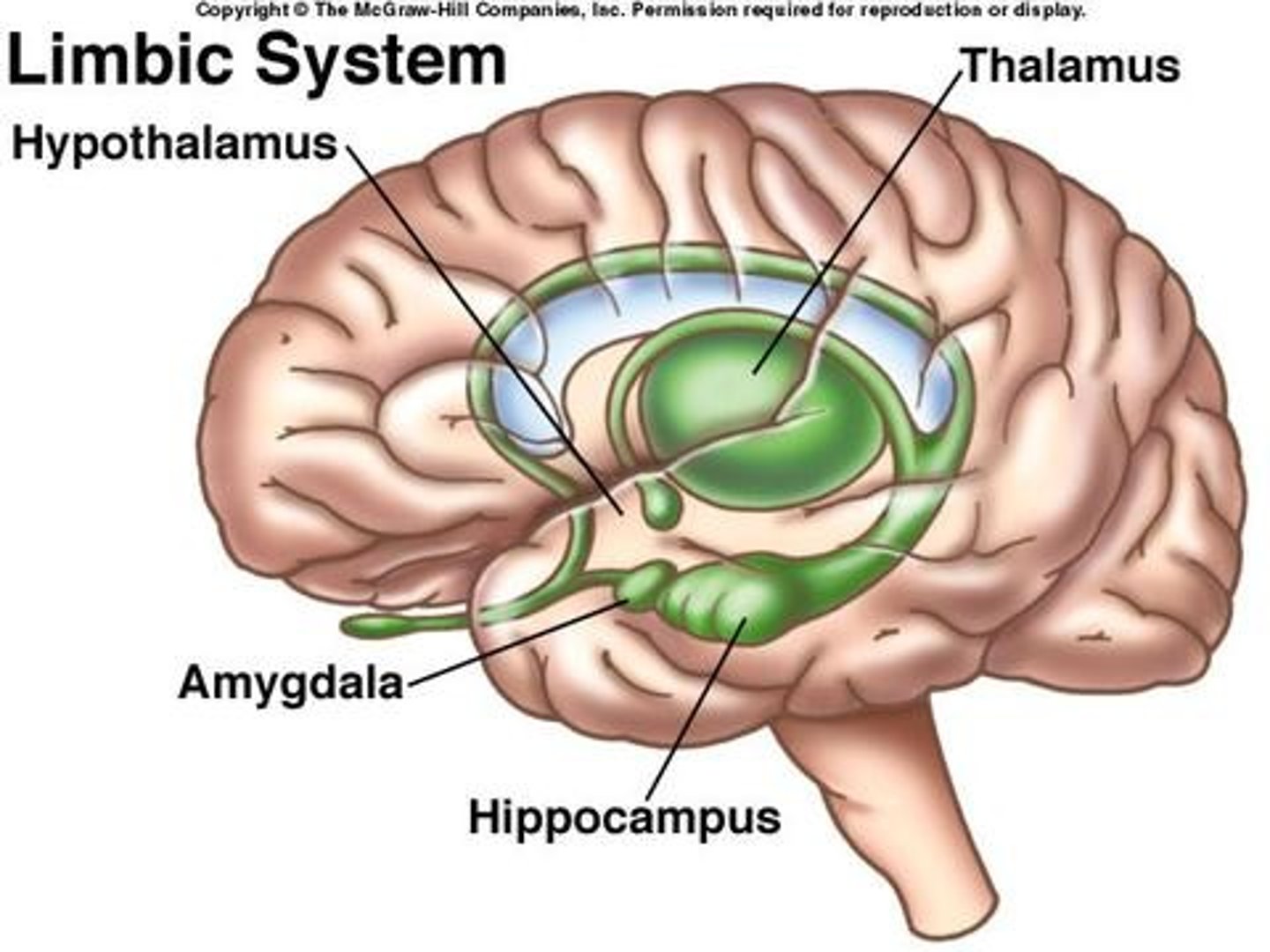
limbic system
neural system (including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus) located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives.
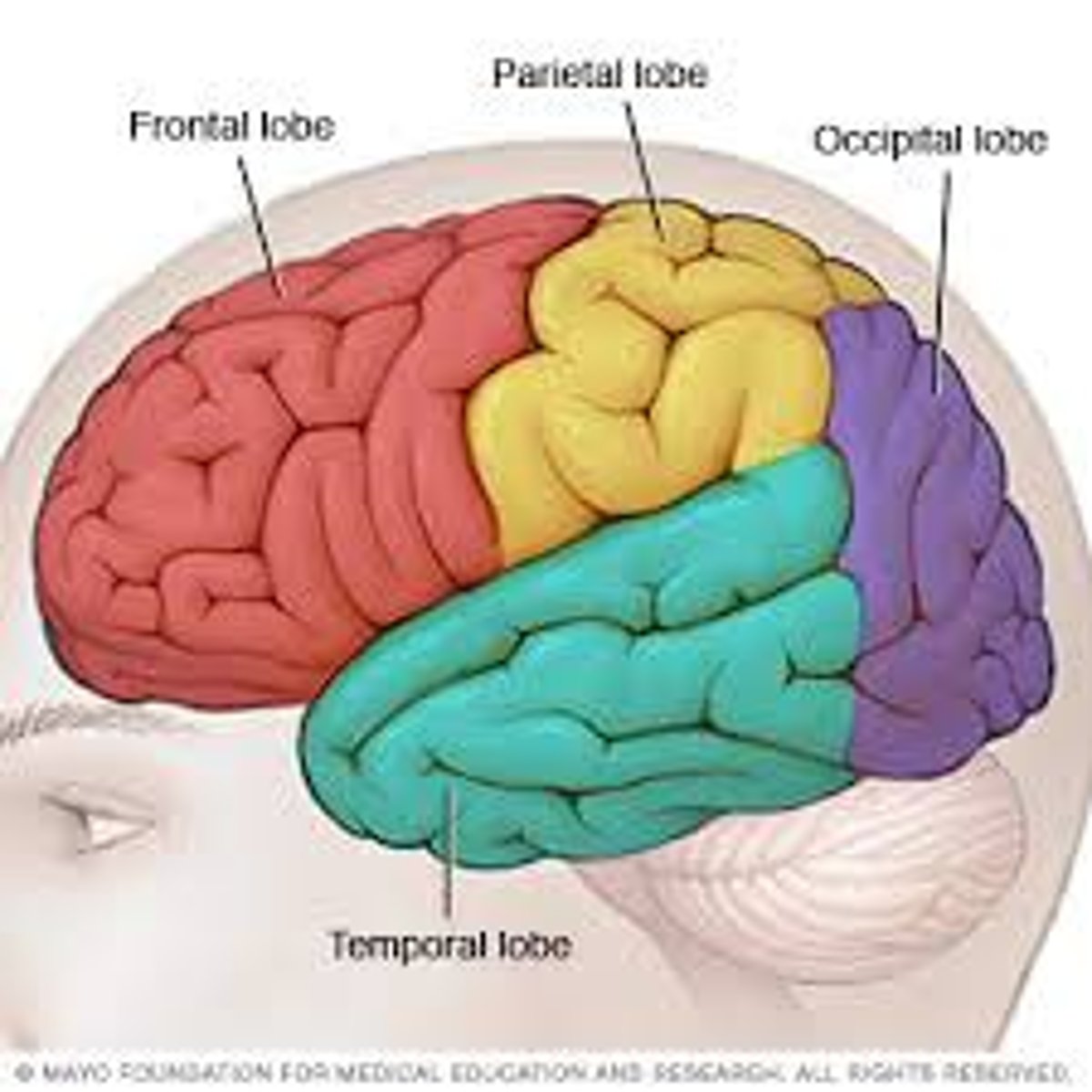
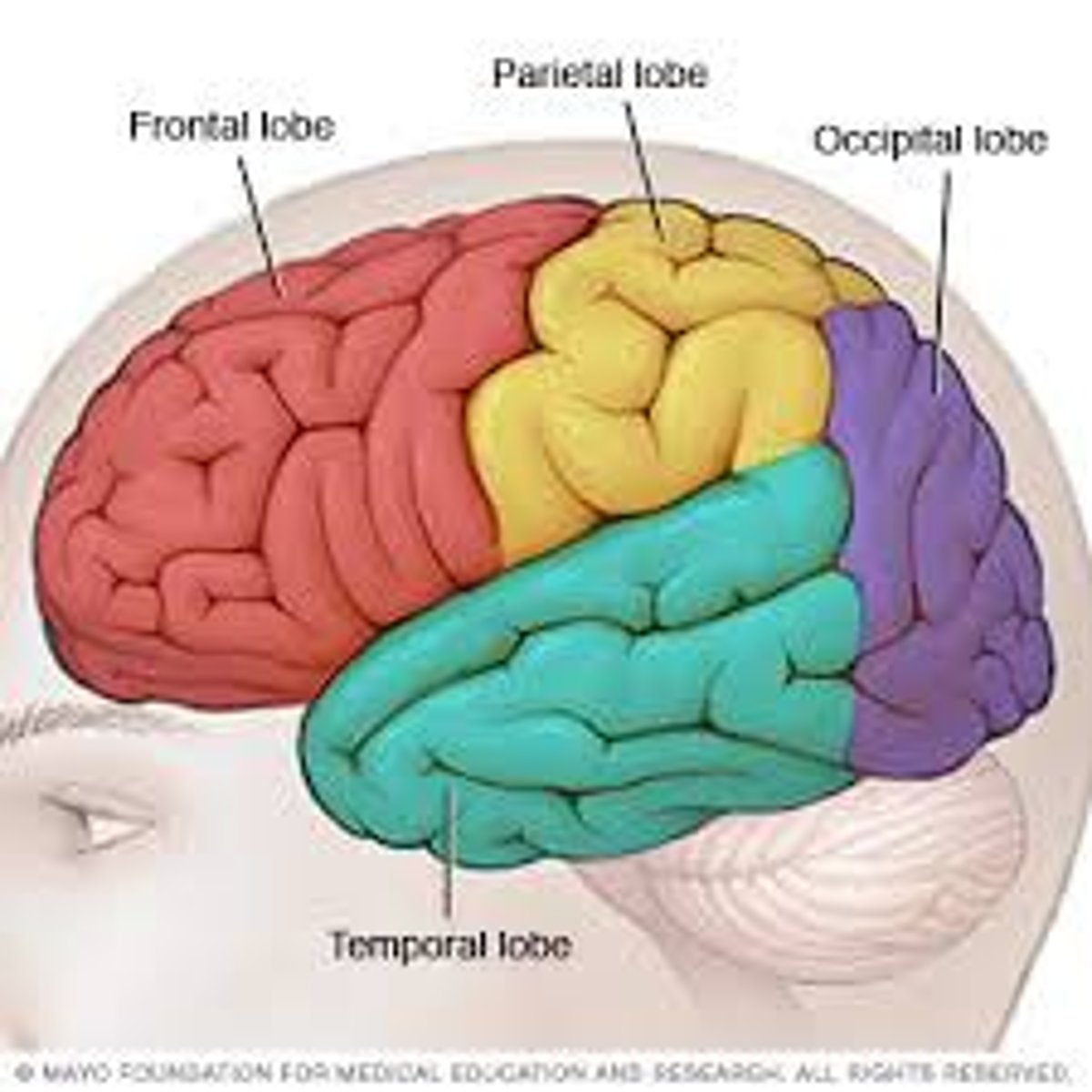
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
psychological science
the study through research of mind, brain , behavior
Psycodynamic
focuses on the interplay between conscious and unconscious mind
what school of thought did Freud belong to
Psychodynamic school of thought
what school of thought did john watson belong to
The behaviorism school of thought
what school of thought did Albert Bandura belong to
the cognitive school of thought
range
Distance between highest and lowest scores in a set of data.
third variable
a variable, often unmeasured in correlational research, that can be the true explanation for the relationship between two other variables
levels of significance
The probability that results obtained from one sample (experimental) group will differ significantly from those obtained from another (control) group. p value the lower the p value the higher significance of your results
Statistically significant research
p = .05 or less
meta-analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies to potentially reach an acceptable p value
informed consent
an ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Confidentiality
no names
Population
all those to whom results apply whether they are in the study or not
population sample
people chosen to be in the study
experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Crontrol Group
no treatment/ gets a placebo
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied "new" treatment
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Confounding Variables (CV)
AKA the extraneous variables, these variables cannot be controlled by the researcher and could influence any change in the Dependent Variables (DV). This is the third variable the mediator variable that can adversely affect the relation between the independent variable and dependent variable which then causes a bias to the experiment.
double-blind experiment
an experiment in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know which participants received which treatment
experimenter bias
consciously or unconsciously treating volunteers differently depending of which group they are in
reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem and thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal, redirecting attention
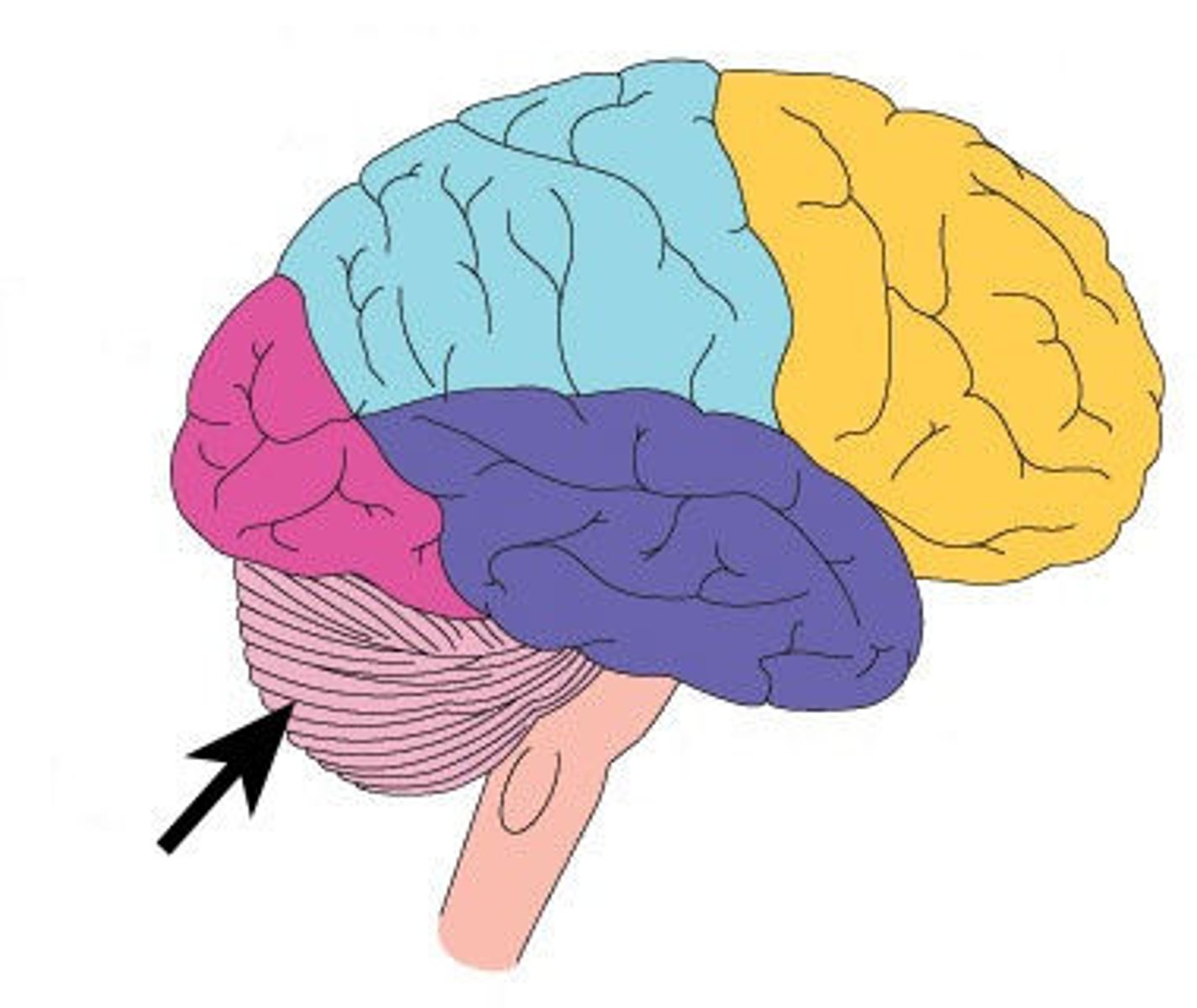
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills like muscle coordination
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
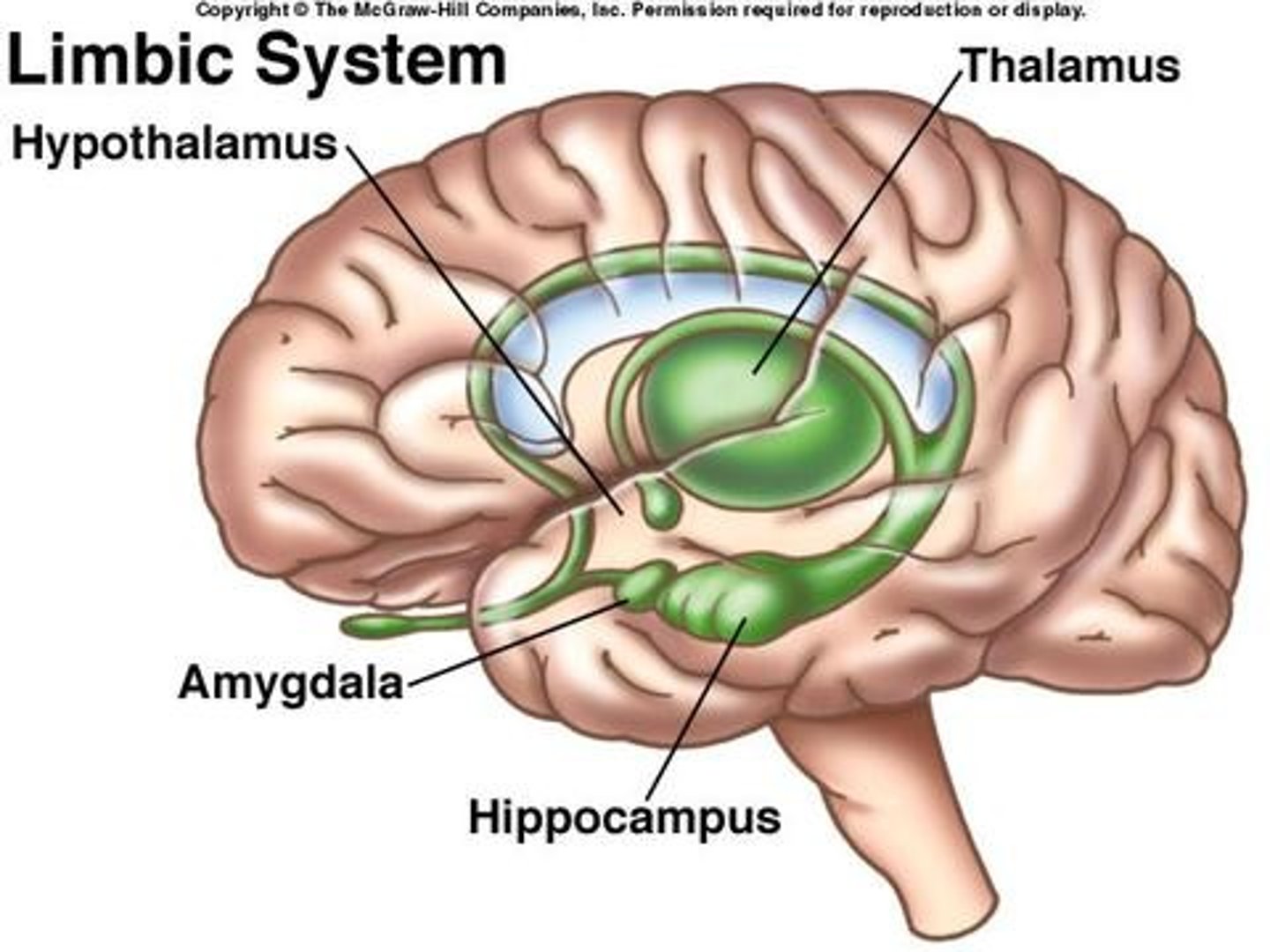
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
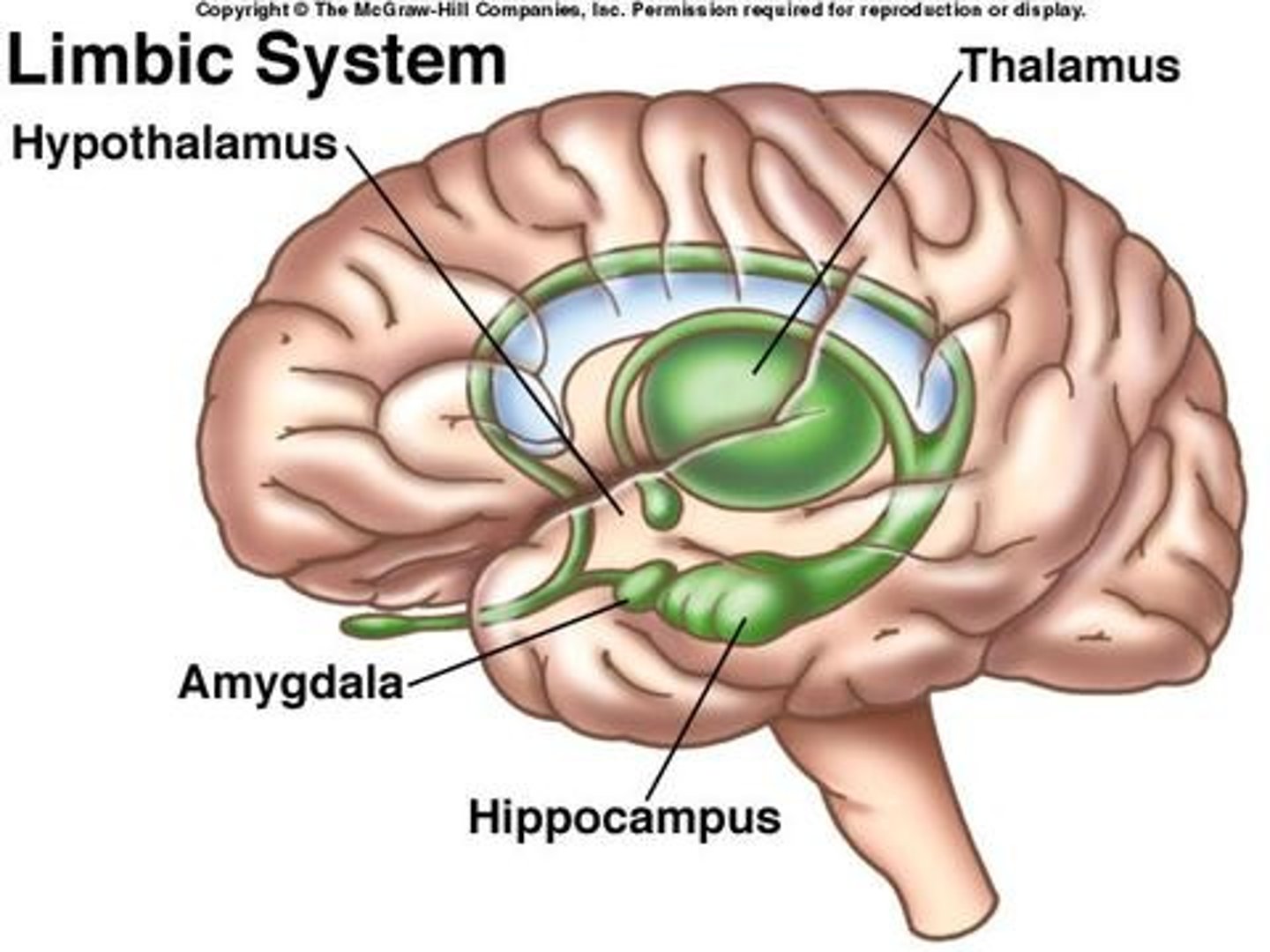
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
occiptal lobe
the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex
hemispheric lateralization
Functional differences between left and right hemispheres
Each cerebral hemisphere performs certain functions that are not ordinarily performed by the opposite hemisphere
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Dendrites
receive messages from other nerve cells
How do nerve messages end?
reuptake - chemicals go back into the axon for future use
enzymatic degradation - enzymes dissolve chemical
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
f MRI (functional MRI)
A technique for revealing bloodflow and brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. F MRI scans show brain function
Mind
Mental activity (feelings, perceptions, thoughts)
Psychology
"scientific" study of behavior, thought, feelings
who was Sigmund Freud
1st Psychiatrist, believed most mental life is in the unconscious, driving forces are evolutionary impulses
Behaviorism
It is all based on nurture and environment
what did the humanism school of thought focus on
free will and ability to ignore impulses, sense of self/ being self aware
what did the cognitive school of thought focus on
the human thought involving logic and reasoning
what did the biopsychology school of thought focus on
neurotransmitter interactions ( ceratonin) and genetics/heredity
Experimental method
alters one variable to see if it affects a second variable
Correlational Method
a research method used to examine relationships between variables, which are expressed in the form of a statistical measure called a correlation coefficient ex. smoking causes lung cancer
Observational Method
the technique whereby a researcher observes people and systematically records measurements or impressions of their behavior
survey method
a research method that involves gathering information from people through the use of surveys or questionnaires
case study
an observation technique in which one/two people are studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles (rare conditions ex. Einstein's brain)
anecdotal evidence
Personal stories about specific incidents and experiences.
standard deviation
a measure of variability that describes an average distance of every score from the mean ( what is normal/ what is average)
coefficient of correlation
a measure of correlation that ranges in value from -1.00 to +1.00
no undue harm
no stress (physical of psychological) beyond everyday life
Debriefing
after the experiment all deception is explained and results are available
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Assignment of Participants
The method by which the population sample is divided into experimental and control groups (MUST BE RANDOM)
blind experiment
An experiment in which the subjects do not know whether they are members of the experimental group or the control group.
Subject bias
When a study participate intentionally/unintentionally reports distorted measurements
Amygdula
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
Nucleolus Accumbens
a brain structure that plays a key role in motivation, reward, and addiction
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
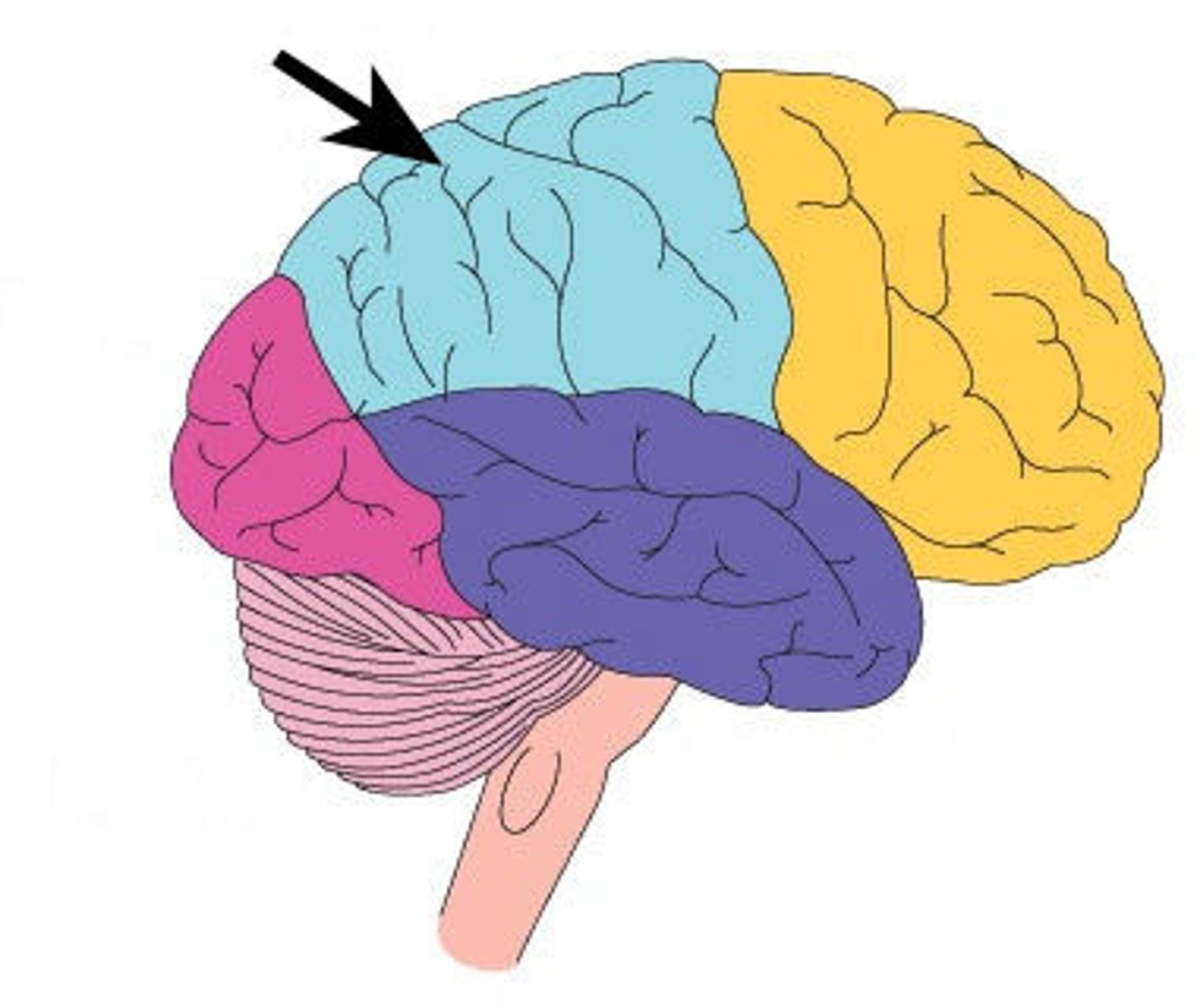
frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
left brain functions
controls the right side of the body, analytical thought, logic, language, science and math
right brain functions
controls the left side of the body, patterns, puzzles, maps, art and music, creativity
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task