Introduction to Radioactive Decay and Particles
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to radioactive decay, including the various particles involved and the different types of decay processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Alpha Particle
A particle with a mass of four and a charge of two, equivalent to the nucleus of a helium atom.
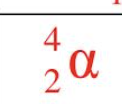
Beta Particle
A particle with a mass of zero and a charge of negative one, essentially an electron.
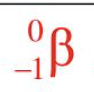
Positron
The anti-particle of an electron, with a mass of zero and a charge of positive one.
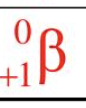
Proton
A subatomic particle with a mass of one and a charge of one.
Neutron
A neutral subatomic particle with a mass of one and a charge of zero.
Gamma Particle
A high-energy photon with no mass and no charge.
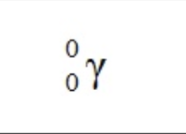
Beta Decay
A process where a neutron is converted into a proton and an electron, resulting in an increase in atomic number.
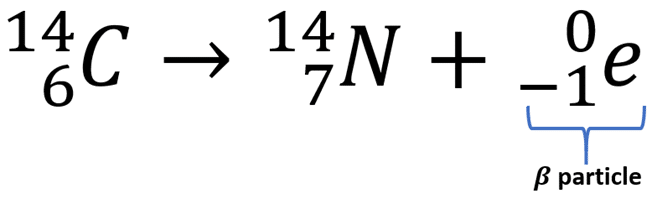
Positron Production
A reaction where a proton is converted into a neutron and a positron, resulting in a decrease in atomic number.
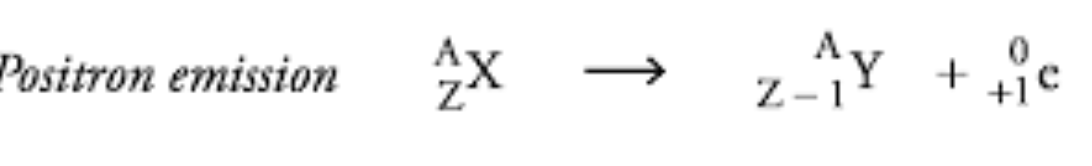
Electron Capture
A process where a nucleus captures an inner core electron, resulting in a decrease in atomic number and formation of a neutron.
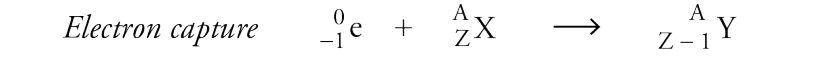
Alpha Particle Production
A reaction where an alpha particle is emitted, resulting in a decrease of two in atomic number and four in mass.
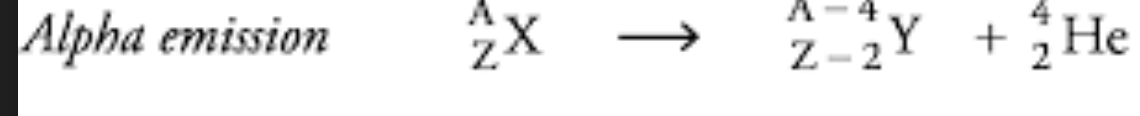
Gamma Decay…
reduces the charge of a nucleus
Neutron Proton Ratio
Higher neutron-proton ratios can indicate instability. (>1)
Nuclear Fission
the process by which a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei, along with the release of energy and neutrons.
Nuclear Fusion
the process in which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a significant amount of energy.
Subcritical
produces less than one neutron (not self sustaining)
Critical
the point at which a nuclear reaction becomes self-sustaining, creating a balance of neutron production and absorption, allowing for a steady state of fission.
Supercritical
a state of a nuclear reaction where more than one neutron is produced per fission event (increasing rate of reaction and a release of vast amounts of energy).
Heavier atoms with a atomic number less than 84…
are considered stable and typically do not undergo radioactive decay.