ID 11: Gram Negative Bacterial Disease of Aquatic Animals
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Describe Gram Negative Bacterial Disease of Aquatic Animals in terms of:
1. Definition/Description
2. Route of entry
3. How Skin/Gill Injury Occurs
4. How Excessive Bacteria Loads occur in Aquatic Environments
1. Important opportunistic pathogens of fish and crustacea
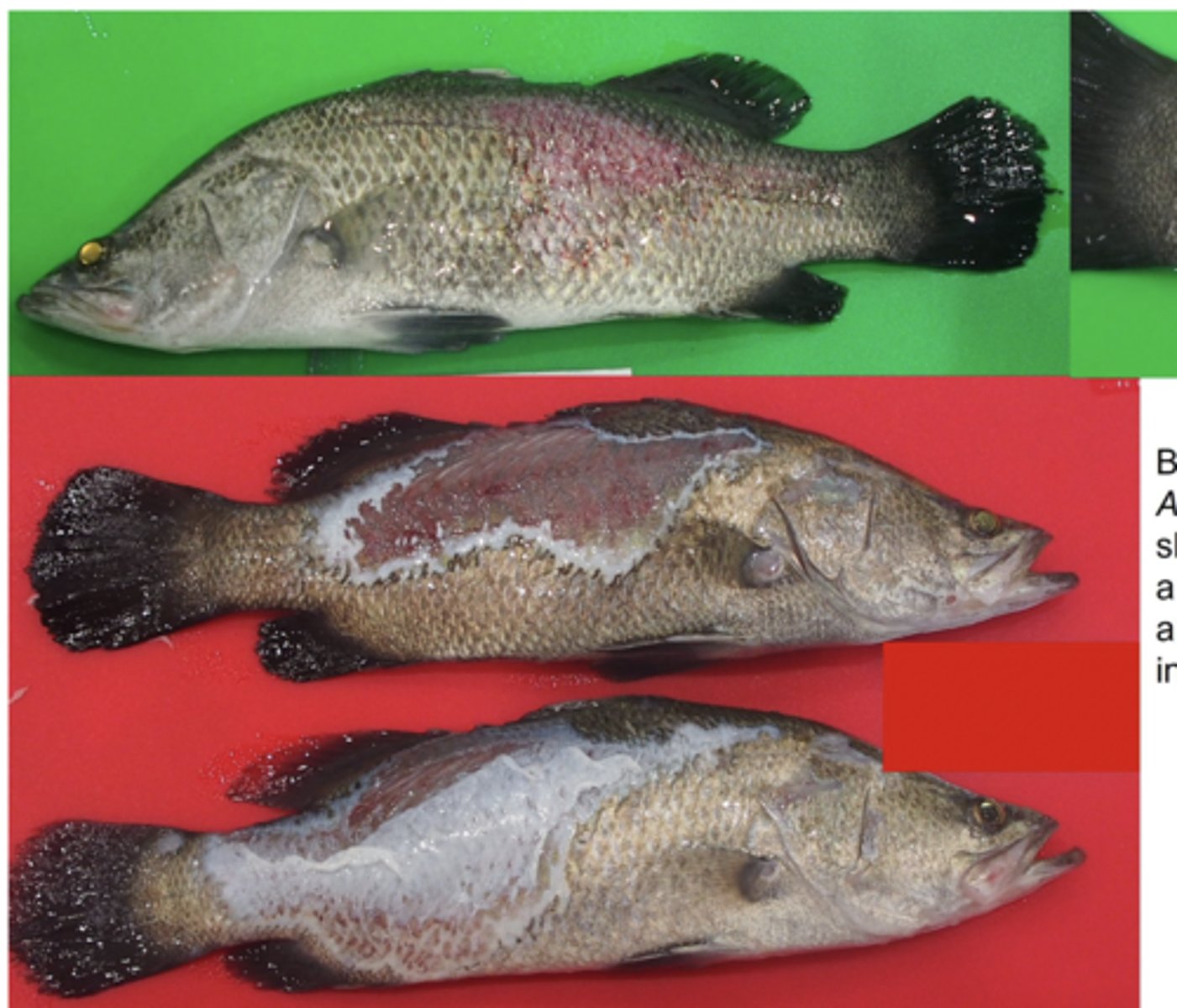
2. Enter via Skin/Gills Injury, occasionally cannibalism.
3. Skin injuries are caused by rough handling, parasitic infestations and viral infections.
Poor water quality such as excessive water ammonium levels can also damage the slime layer of fish and sensitive skins of frogs.
4. Overcrowding and excessive organic matter allow excessive bacterial loads that can overwhelm the immune systems of stressed animals. Higher water temperatures will also encourage bacterial overgrowth in water.
Describe the Following 2 Most Important Bacterial Diseases of Aquatic Animals in Australia:
1. Aeromonas spp.
2. Vibrio spp.
1. Most Common. Associated with the intestinal tract and skin of freshwater animals. Proliferation seen when there is lots of organic material in the water
2. Marine animals and their environments
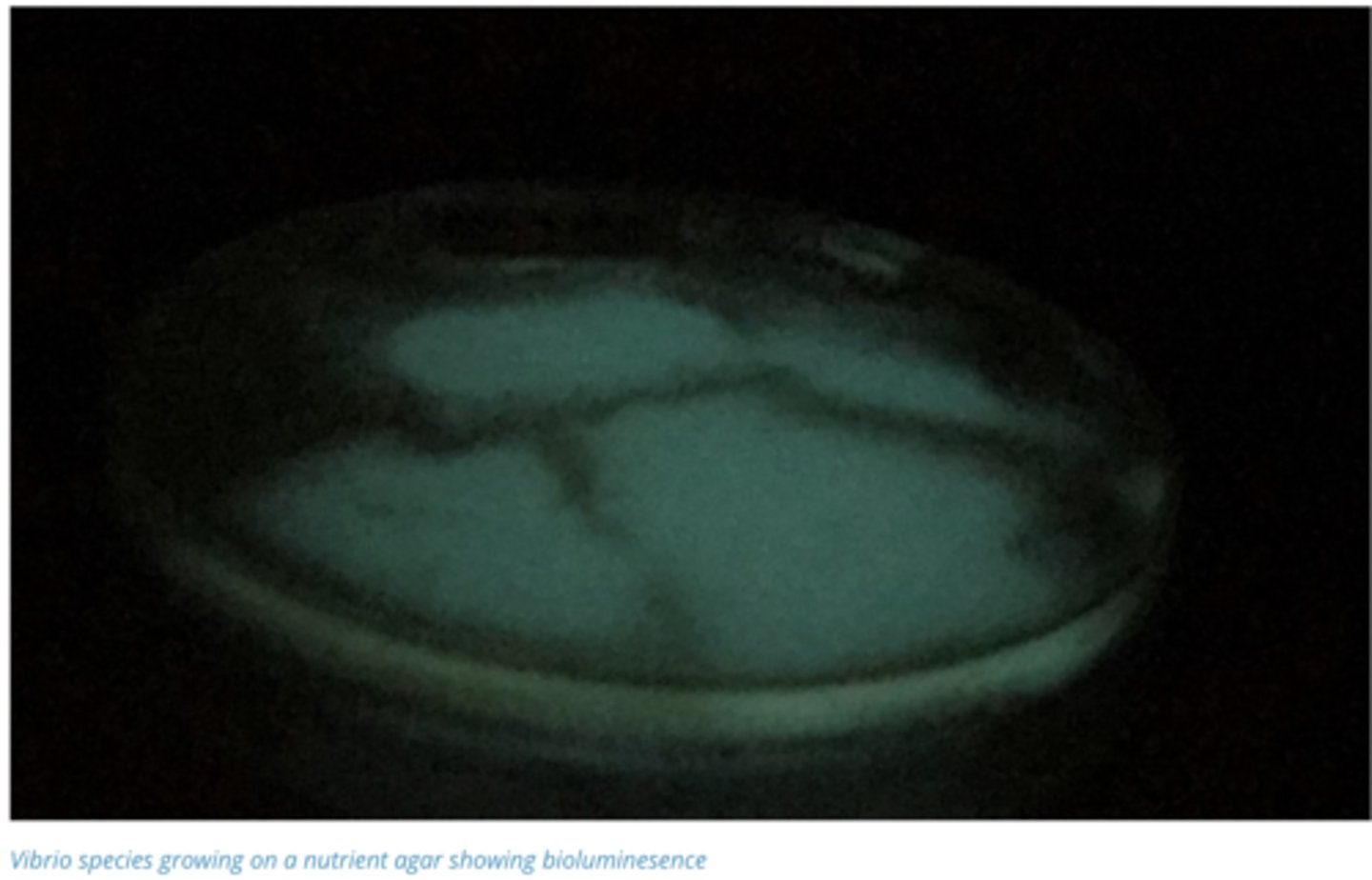
Describe Vibrionaceae (Vibrio spp.) in Terms of:
1. Where Bacteria are Present/Found
2. Disease Bacteria cause
3. Clinical Signs/Pathogenesis
1. Commensals in the in the intestinal tract and body surfaces of all marine animals
2. Causes Luminous vibriosis in shrimps and prawns
3. Can Result in sepsis as they produce two major exotoxins, a haemolysin and a protease.

Describe Aeromonacea (Aeromonas spp) in Terms of:
1. Where Bacteria are Present/Found
2. Pathogenesis
3. Clinical Signs/Consequences
4. A. salminocida
Most Common
1. Found in GIT
2. Common Opportunistic pathogen in fish
3. Kkin ulcers and haemorrhagic septicaemia in fish, gastroenteritis and sepsis in all animals, redleg in frogs and ulcerative stomatitis in snakes.
4. Cause of furunculosis, a skin disease of cold water fish. It is one of the most important diseases of farmed salmon.

Describe how Bacterial Infections of Aquatic Animals are Diagnosed in terms of
1. Cytology
2. Histopathology
3. Culture/Antimicrobial susceptibility
4. Molecular Diagnosis
1. Fresh lesions can be scraped and wet mounted
2. Fix in 10% buffered formalin
3. Fresh Samples
4. Species Specific qPCR for important viral pathogens