Humanistic Approach
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is it the only approach to focus on?
free will, conscious experience and personal responsibility
What does it believe determines human behaviour?
free will - people can choose how their behave and it isn’t caused by external or biological factors, or the past
What is it researched through?
discussion of experience - rather than the experimental method
What do humanistic psychologists believe about all people?
that they are inherently good and that they’re driven to achieve their full potential
When was it developed?
1950s
What was it developed as?
a ‘third force’ against behaviourism and psychodynamic approaches
Who was it developed by?
Maslow and Rogers
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: bottom/1st level?
physiological
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: examples for the physiological level (4)?
food, water, breathing and sleep
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: second level?
safety
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: examples for the safety level (4)?
health, safety of family, security of job/income and security of shelter
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: 3rd level?
love/belonging
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: examples for the love/belonging level (3)?
good family relationships, romantic relationships and friends
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: 4th level?
Esteem
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: examples for the esteem level (3)?
self esteem, confidence and achievement
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: 5th level?
self-actualisation
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: examples of the self-actualisation level (3)?
problem solving, creativity and morality
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: what type of needs are the 1st and 2nd levels?
basic needs
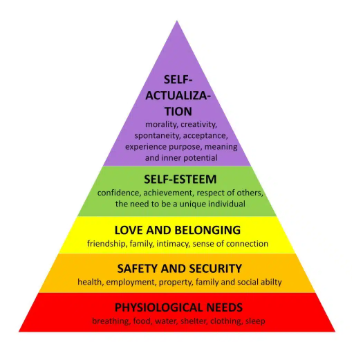
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: what type of needs are the 3rd and 4th levels?
psychological needs
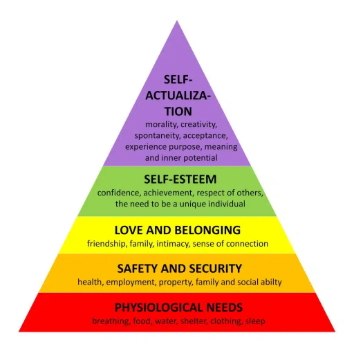
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: what type of need is the 5th level??
growth needs
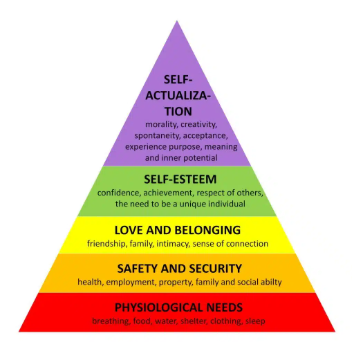
What did Maslow believe individuals that reach self-actualisation experience it as?
in the form of peak experiences
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: Where are the most basic needs located?
at the bottom
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: where are the most advanced needs located?
at the top
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: what must happen before moving to the next level?
each level must be satisfied
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs: what needs are harder to ignore?
the more basic needs
Congruence?
esteem
What has to be true for personal growth to be achieved?
an individuals concept of themselves must be similar to the person they want to be
Ideal selves?
the person we want to be
What is incongruence?
a significant gap between a person's real self (actual experience/self-image) and their ideal self (who they want to be)
What happens when a person experiences incongruence (the gap between real self and ideal selves is too big)?
self-actualisation becomes impossible - due to feelings of low self-esteem
What does the our ideal self being close to our perceived self cause?
greater feelings of self-esteem
High congruence Venn diagram?
…
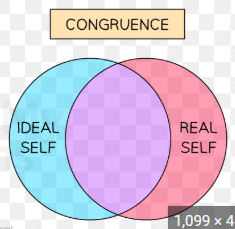
What is there positive feelings of with High congruence?
positive feelings of self-esteem
High congruence: what exists?
a state of congruence
High congruence: what is very rare?
a state of complete congruence
Low congruence/no congruence Venn diagram?
…
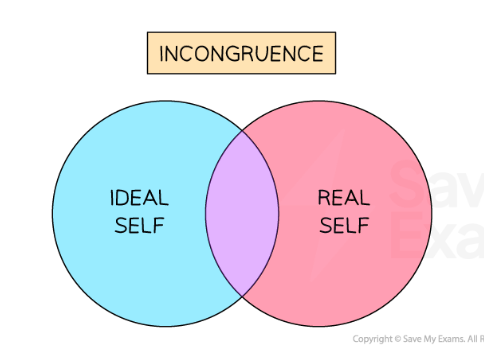
Low congruence/no congruence: what is there negative feelings of?
self-esteem
Low congruence/no congruence: examples of emotions that could occur?
worthlessness and insecure
Rogers’ conditions of worth: what did he believe hindered the process of self-actualisation?
other people
Rogers’ conditions of worth: the two ways respect by others can be given in?
conditional or unconditional regard
Rogers’ conditions of worth: what is unconditional regard?
accepted for who you are
Rogers’ conditions of worth: what is conditional regard?
accepted if you act as others want you to - stops us from being our authentic selves
Influence on counselling: What did Rogers claim psychological problems are a direct result of?
conditions of worth - specifically conditional regard
Influence on counselling: what can the counsellor give to the patient themselves?
unconditional regard
Influence on counselling: what can a counsellor suggest to a patient in terms of conditional regard?
putting limits on conditional regard situations - such as spending less time with some people
Evaluation strength: P - what has applications outside of psychology?
Maslow’s hierarchy
Evaluation strength: Ev - What did Hagerty (1999) look at at?
the relationship between Maslow’s hierarchy and economic growth
Evaluation strength: Ev - What did Hagerty find about countries that were at earlier stages of development?
they were at lower stages of the hierarchy
Evaluation strength: Ev - when did self-actualisation became important?
only in the advanced stages of economic development in the country
Evaluation strength: Ex - what did it show workers - who were concentrating on needs lower down in the hierarchy - were not focusing on?
areas such as successes in their careers - which would drive forward the economy
Evaluation strength: L - therefore, what can Maslow’s hierarchy explain?
economic development
Evaluation strength: P - what is there research to support?
the conditions of worth
Evaluation strength: Ev - What did Harter et al (1996) find out about teenagers?
those who feel they have to fulfil certain conditions to gain their parents approval - did not like themselves
Evaluation strength: Ex - What does this show individuals who feel like they can’t be their authentic selves won’t be able to reach?
self-actualisation
Evaluation strength: Ex - what is people feeling like you can’t be your authentic self a response to?
experiencing conditional regard
Evaluation strength: Ex - why won’t they be able to reach self-actualisation?
they will have low self-esteem - which is one of the needs in the esteem section of the hierarchy
Evaluation strength: L - what concept of Rogers’ does this support?
Rogers’ concept that experiencing conditional regard lowers self-esteem
Evaluation weakness: P - What do Humanistic research methods not establish?
causality
Evaluation weakness: Ex - what is used to support the humanistic approach?
non-experimental methods
Evaluation weakness: Ex - what does the use of non-experimental methods make it very difficult to do?
verify the results of counselling
Evaluation weakness: Ev - What does the research that shows personal growth, not show?
that it was the therapy that caused the growth
Evaluation weakness: Ev - example of why therapy may not be the only cause for the recorded personal growth?
people in the group that originally wanted to attend therapy are more willing and ready to better themselves than the people that originally didn’t want to go
Evaluation weakness: L - what does this prove could lead to growth in patients?
other factors other than counselling
Evaluation weakness: P - what could the humanistic approach be described as?
unrealistic
Evaluation weakness: Ex - What may people not be as much as the approach suggests that people are?
“growth oriented”
Evaluation weakness: Ev - what suggestion is an oversimplification?
that all problems arise from blocked self-actualisation
Evaluation weakness: Ex - example of something that isn’t considered that proves we aren’t directed by the ‘potential for growth’ at all times?
procrastination
Evaluation weakness: L - therefore, what are there that the humanistic approach can’t explain?
behaviours