Physic definitions (Electrostatics, magnets, electric current
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is vector and scolar?
directed / undirected quentities
2 examples of vectors and scalars
vectors
force
Velocity
Scalars
volume
Mass
Proparties of magnets
magnets have 2 poles
North and south→ opposite poles attract, like poles repel
Permanent magnets and ferromagnetic materials
Iron, cobalt, nickel always attract
If you break a magnet in half, each half still behaves as a complete magnet→ magnetic poles can not be separated.
What do magnetic materials contain on a microscopic level?
Magnetic domains
When is a material magnetized?
magnets and ferromagnetic materials contain magnetic domains. if the magnetic domains are aligned, the material is magnetized.
What is the difference between a soft magnetic material and a hard magnetic material?
soft
easily magnetized
Hard:
retain their magnetization
How can the magnetic domains be brought out of alignment?
When the magnet is dropped or heated.
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the space, surrounding a magnet, where other magnets experience a force.
Definition of the direction of a magnetic field line?
The direction of the field shows the direction in which a magnetic North pole is pushed.
Elementary charge
The smallest unit of electric charge that is possible→ 1.602 times 10^-19
Electric field
The region surrounding a charge wehre forces act upon other charges.
Electric field strength
The electric field strength is measured by the force on a test charge, and it‘s proportional to the force divided by the size of the test charge.
Definition of the direction of an electric field line
The direction of the electric field vector corresponds to the force acting on the positive test charge.
Uniform field
A field in which the force on a test charge is equal at every point in the field (same magnitude, same direction)
Voltage
Work done on a test charge divided by the magnitude of the test charge.
Electric current
A means of transportation for electrical energy
what is the purpose of the electric current?
It is a means of transportation for energy.
what requirements need to be met for an electric current to flow?
There must be a voltage source and a closed conducting loop.
Series circuit
All lamps share the same conducting loop. If one lamps is unscrewed from the socket, all lamps will go out.
Parallel circuit
Each lamp has its own conducting loop and its own connection to the voltage source. If one lamp is unscrewed from the socket, only the unscrewed lamp will go out.
Direct current
electrons always move in the same direction. Positive pole stays positive and negative pole stays negative.
Alternating current
The electrons move back and forth. The poles switch between negative and positive.
Electrical resistance
Consumers and wires (resistors) slow the the current down. Resistance is the hindrance to the flow of charge.
What does the electrical resistance of a wire depend on?
Temperature, cross sectional area, length and material
What is the short circuit? What happens to the current if a short circuit occurs?
A short circuit is a direct connection between the poles of the voltage source. The absence of resistance leads to a very large circuit.
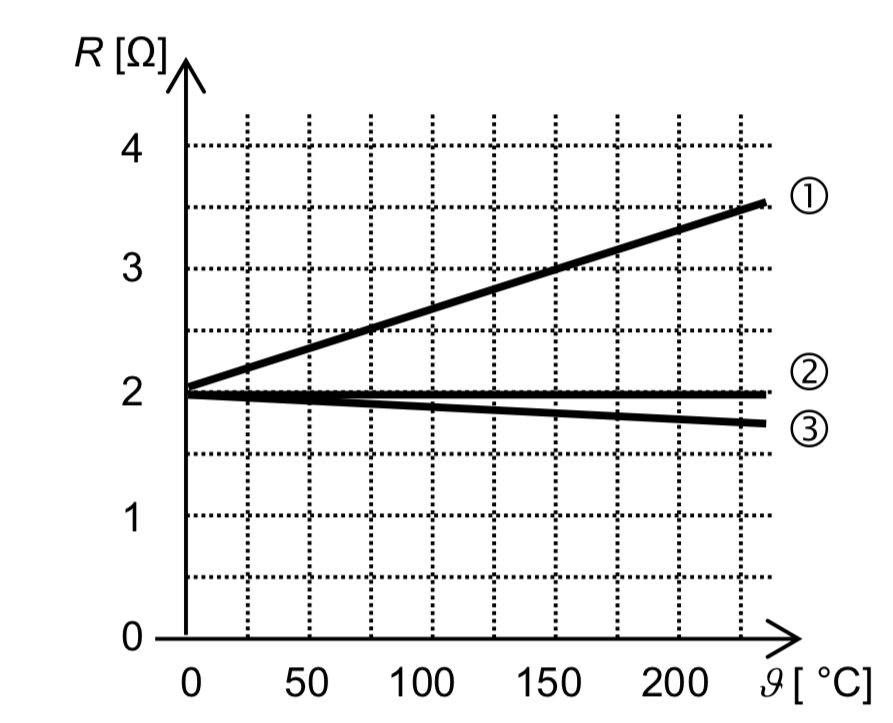
Here’s a graph showing how the electrical
resistance of three wires made of three
different materials 1, 2 and 3 relates to
temperature.
Describe in your own words how the electrical
resistance of three different materials 1, 2
and 3 changes, while the temperature
increases.
1: The resistance increases with increasing temperature
2: The resistance does not depend on the temperature
3: The resistance decreases with increasing temperatur