TOPIC 6- Animal Reproduction and Development
1/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
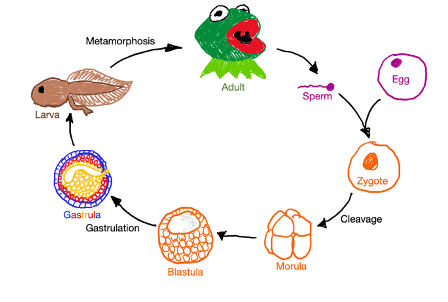
diplontic animal life cycle
zygote produced through fertilization
haploid gametes (sperm and egg cells)
embroyos are created- they are all full of yolk
morula- solid ball of cell
blastula= hollow, single-layer cell
gastrula- three-layered embryo
larvae formed- looks different structurally from adult stage
juvenile ==> adult
the only difference between juvenile and adult stage is maturity of reproductive organs
sexual reproduction
reproduction as a result of meiosis and recombination
causes a lot of genetic variation because of the crossing over step in meiosis
asexual reproduction

gemmules

budding

fission

parthenogenesis
asexual reproduction without sperm, only eggs
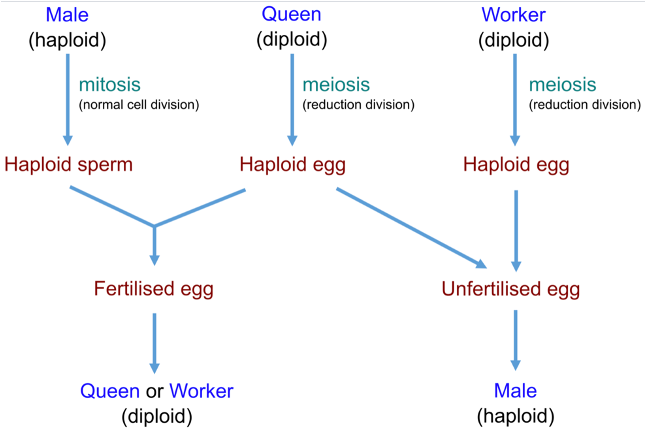
hymenoptera
queen is diploid and produces haploid gametes (meiosis)
male bees are haploid and produce haploid sperm (mitosis)
haploid egg from queen + haploid sperm = female bees (sexual reproduction)
haploid egg = male bees (parthenogenesis)
daphnia
organism that can choose to produce sexually or asexually depending on threats from the environment
sexual reproduction produces males- females make haploid eggs that get fertalized by males
when there is threat of population extermination
asexual reproduction make females- females make genetically identical diploid eggs
when conditions are favourable
whiptail lizards

poultry
males have ZZ gametes
females have ZW gametes
whenever parthenogenesis occurs, a male is produced because females do not have the proper gametes to self-replicate (they need the W chromosome)
monoecious species
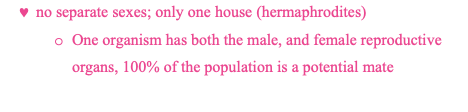
diecious species

oogenesis
MITOSIS: Germ cell undergoes mitosis into the oogonium. The oogonium undergoes mitosis again to make the 1º oocyte.
MEIOSIS I: The latter step takes place in the embryo. The 1º oocyte is arrested in prophase of meiosis I when ovulation does not occur. Once ovulation can occur at puberty, meiosis I goes to completion and now makes one polar body and a 2º aoocyte.
MEIOSIS II: The latter step takes place in a female that can undergo ovulation. The 2º oocyte is arrested at the metaphase of meiosis II, and can only go further once a sperm has entered. Once the sperm has entered, the 2º oocyte can resume to completion of meiosis II, wherein we get a second polar body an an ootid that can mature into an ovum
spermatogenesis
MITOSIS: Germ cells undergo mitosis into spermatogonial stem cell, which also undergo mitosis to become spermatogonium, which then undergo mitosis to become 1º spermatocyte, which has 2 sets of chromosomes with 46 chromosomes total. One set is from mom, one is from dad.
MEIOSIS: 1º spermatocyte undergo meiosis I to create 2º spermatocyte. 2º spermatocyte then undergo meiosis II to create early spermatids.
The early spermatids mature into sperm cells
fertilization
acrosome reaction breaks down jelly coat as the sperm embeds itself into the 2º oocyte
molecular recognition between the sperm and the ovum must occur to ensure species compatibility
the different nuclear membranes fuse as the sperm nucleus enters the 2º oocyte
this prompts the 2º to finish maturation
cortical granules fuse with the egg plasma membrane and forms the fertilization envelope
nuclear fusion occurs and a zygote nucleus is formed
fast block
block to polyspermy that works immediately after the sperm enters the cell
ions like calcium make the internal environment of the cell more positive which makes the membrane negatively charged
this causes other sperm cells to be temporarily repulsed from the surface of the egg cell
external fertilization


internal fertilization

oviparity
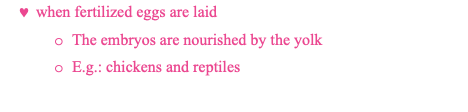
ovoviviparity

viviparity
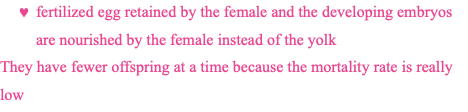
gastrulation

neurulation

endoderm
makes up the digestive tract, lungs, and urogenital tract
ectoderm
forms the epidermis and the central nervous system
mesoderm
forms muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys and dermis