Board Review - Random Embalming
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this man ate my son
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
This is when sound and practical judgement are exercised in all professional interactions:
Judicial council
Is the manner or death and condition of the body strictly confidential?
(Hint: Yes or No?)
Yes
Who must you give ppe to?
A.) The decedent
B.) Decedent’s family
C.) Any person authorized into the prep room
D.) Any unauthorized person into the prep room
Any person authorized into the prep room
When are facial features set?
Before embalming
Why are facial features not set after embalming?
Features will become less flexible after embalming
When packing the mouth with cotton, what can you coat the cotton in to prevent the cotton from absorbing purge?
A.) Lanolin
B.) Arterial fluid
C.) Tissue builder
D.) Massage cream
Massage cream
This involves a barb attached to a wire being driven by a manual device into the center of the maxilla and another barb being driven into the mandible:
Hint: What is this tool?
Needle injector
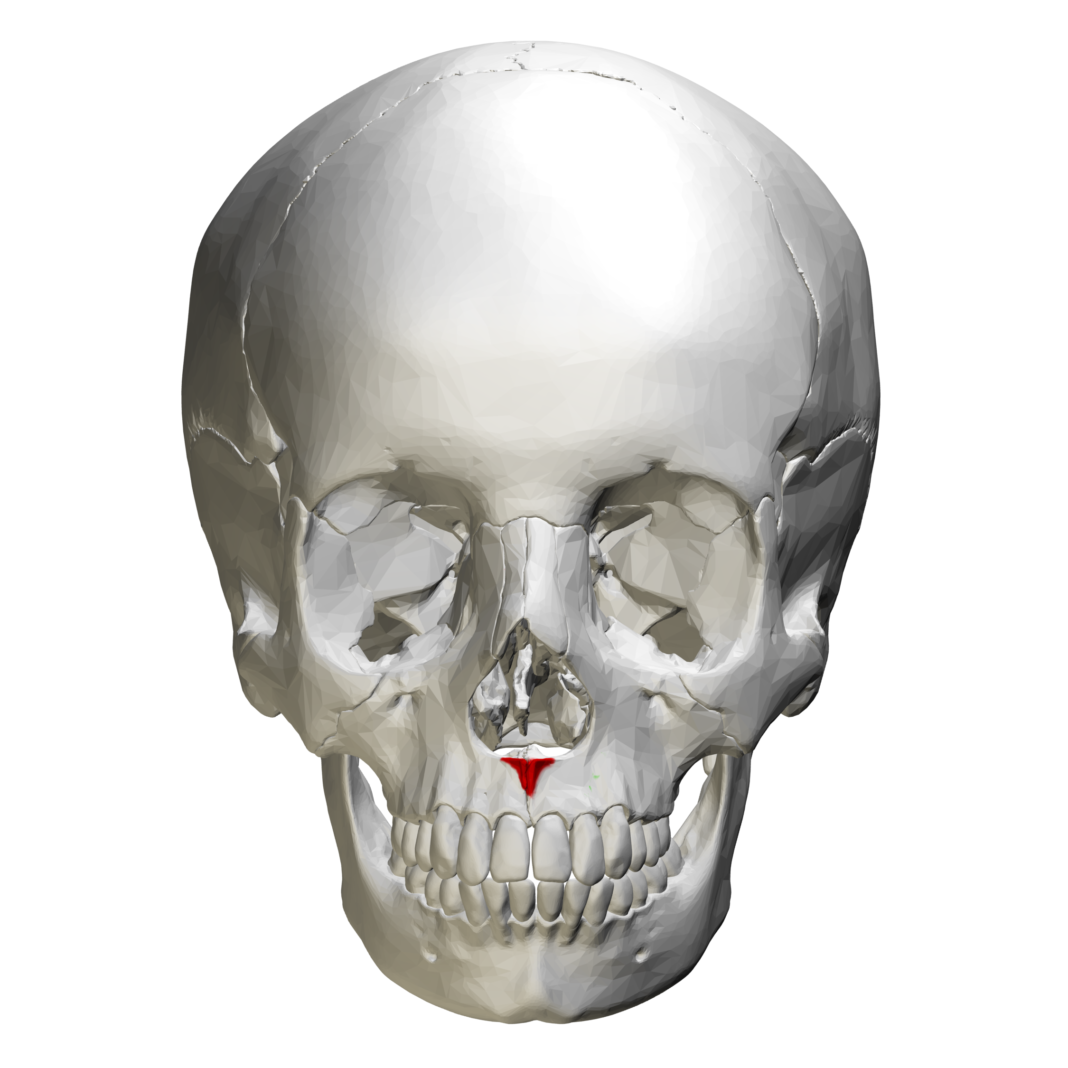
This is the center where the two maxialle fuse:
A.) Body of the mandible
B.) Anterior nares
C.) Nasal spine
D.) Septum
Nasal spine
When there are dentures present, and you choose to use the needle injector as the method of mouth closure, would you insert the dentures before or after needle injecting?
Before
If the decedent’s jaw bones are soft, which mouth closure method is the best?
Suturing
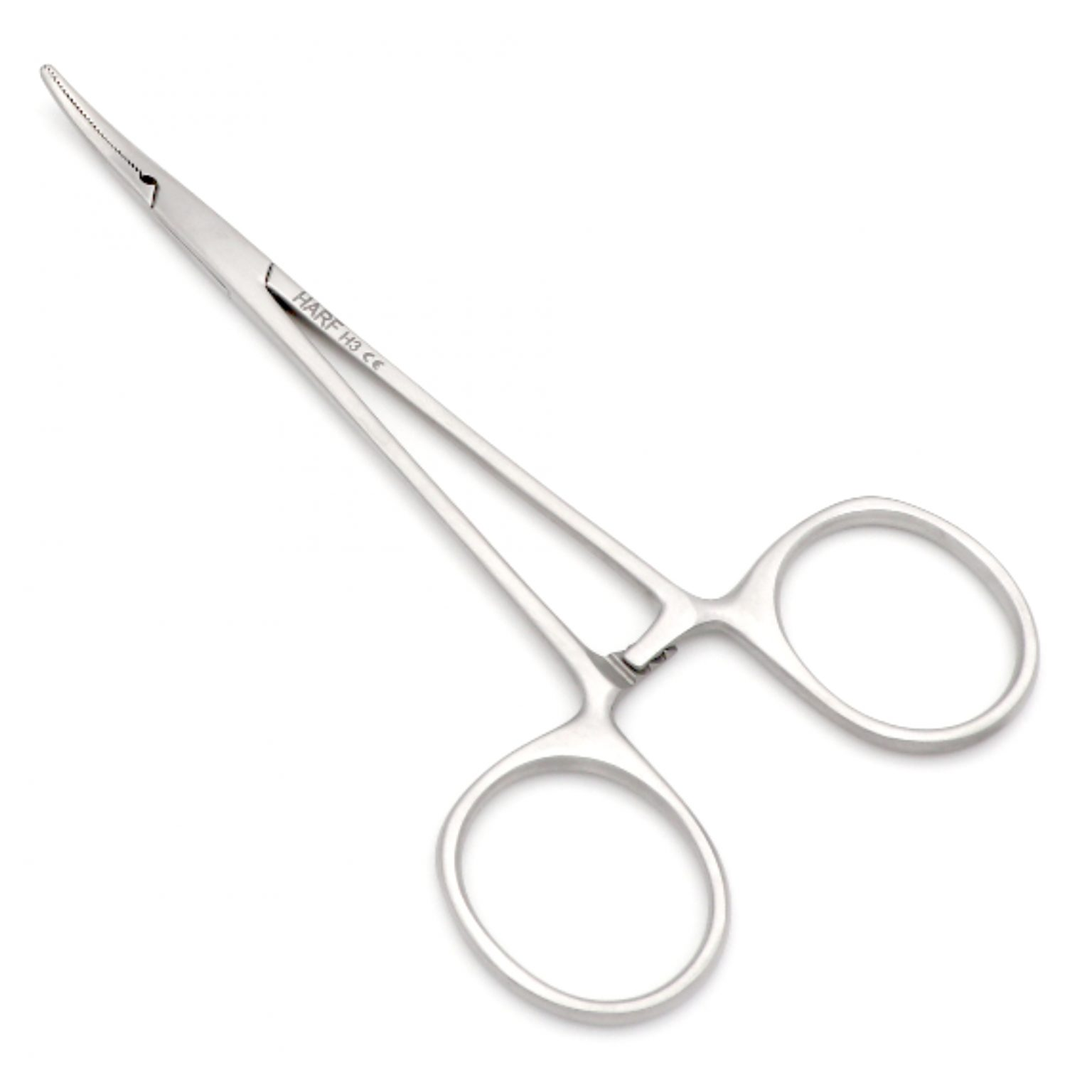
To prevent injury, it is best to use this tool when suturing the mouth:
A.) Arterial tube
B.) Hemostat
C.) Spring forceps
D.) Groove director
Hemostat
A full set of natural teeth must be present in order to use this method of mouth closure:
A.) Mandibular suture
B.) Needle injector
C.) Musculature suture
D.) Dental tie
Dental tie
The mouth is ___ in curvature from corner to corner:
A.) Concave
B.) Convex
C.) Lateral
D.) Medial
Convex
If a medical device poses a hazard or interferes with arterial embalming, when is it removed?
Before
(Or prior)
Implantable devices can be removed when?
Before or after embalming
Should you remove implantable devices with batteries in them when cremating?
Yes
(Example: Pacemakers)
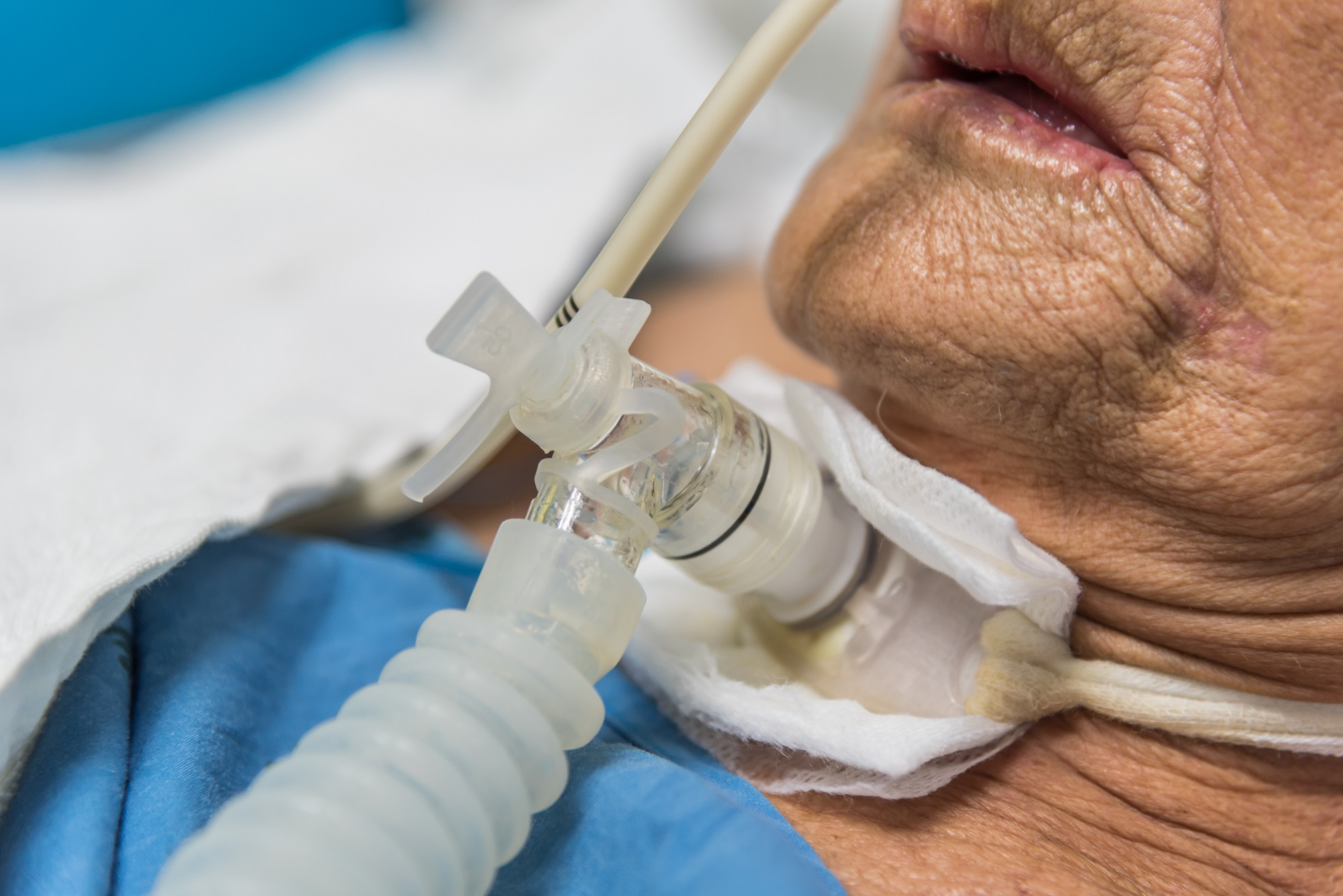
If the decedent has a mouth or nostril tube, should that be removed before or after embalming?
Before
If the decedent has a nasopharyngeal tube, should that be removed before or after embalming?
Before

If the decedent has a tracheostomy tube, should that be removed before or after embalming?
Before
If the decedent has an abdominal feeding tube, should that be removed before or after embalming?
It can be removed either before or after
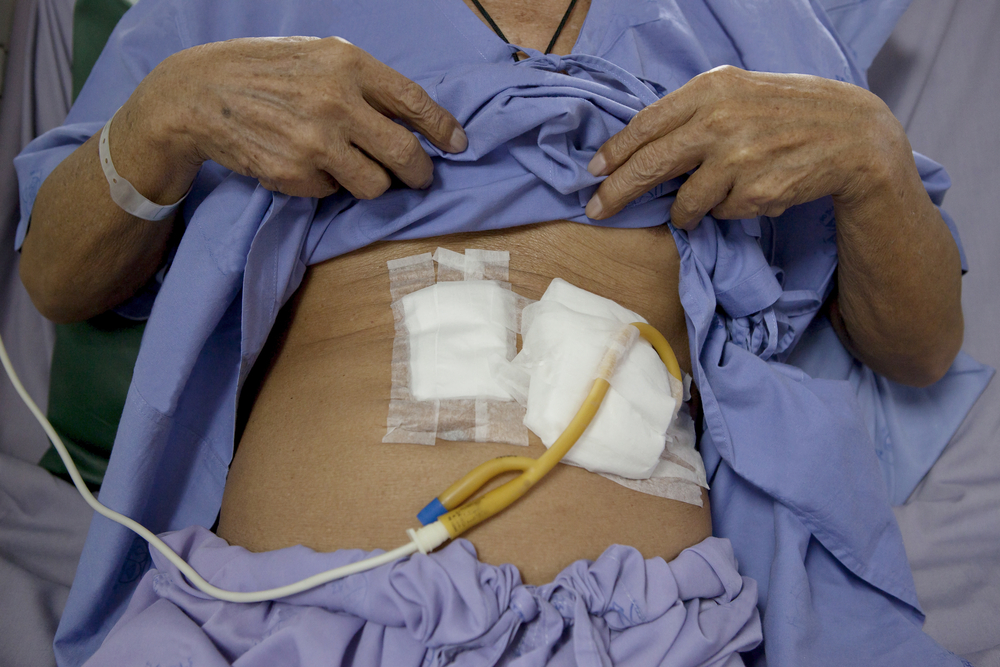
This is an opening in the human body, usually involved in a tracheostomy or a colostomy:
Stoma
If the decedent has a surgical drain, should that be removed before or after embalming?
It can be removed before or after
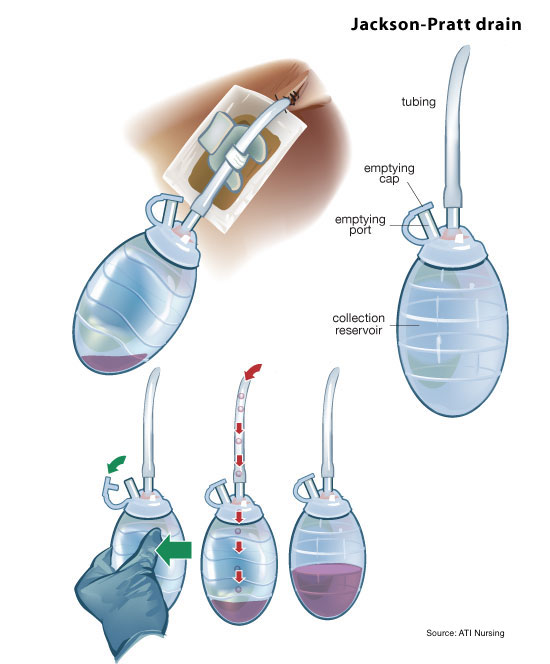
This is a surgical procedure that diverts a section of the colon to an opening in the abdominal wall:
Colostomy
If the decedent has a colostomy bag, should that be removed before or after embalming?
It can be removed before or after
When closing the stoma from a colostomy, what suture should be used?
Purse string
Intravenous catheters can remain in place until…
arterial embalming is completed
(they can also be removed after cavity embalming)
If the decedent has a cast, should that be removed before or after embalming?
before
The cleaning of the body and instruments at the time of embalming:
Concurrent disinfection
Those disinfection procedures carried out prior to embalming the body:
Primary disinfection
This is the cleaning and disinfection of the body, instruments, and the embalming room following embalming:
Terminal disinfection
This type of death causes closure of the carotid arteries and jugular veins causing cerebral hypoxia:
Hanging and strangulation
Which of these discolorations is caused by asphyxia?
A.) Carbon monoxide
B.) Jaundice
C.) Cyanosis
D.) Livor mortis
Cyanosis
What type of arterial injection is recommended hanging/strangulation cases?
Restricted cervical injection
This burn is superficial, only affecting the epidermal layer. Skin surface appears red:
1st degree burn

This type of burn is deep; it affects the posterior dermal layer. Skin blisters may develop:
2nd degree burn
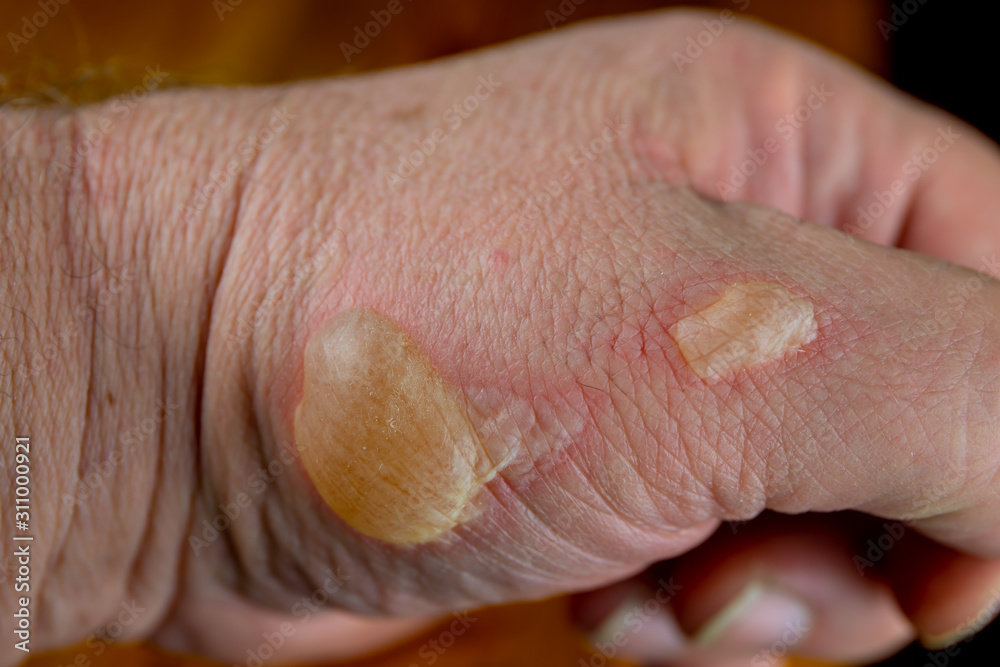
This burn is a full-thickness, there is destruction of both epidermal and dermal layers. Decedent may appear charred:
3rd degree burn
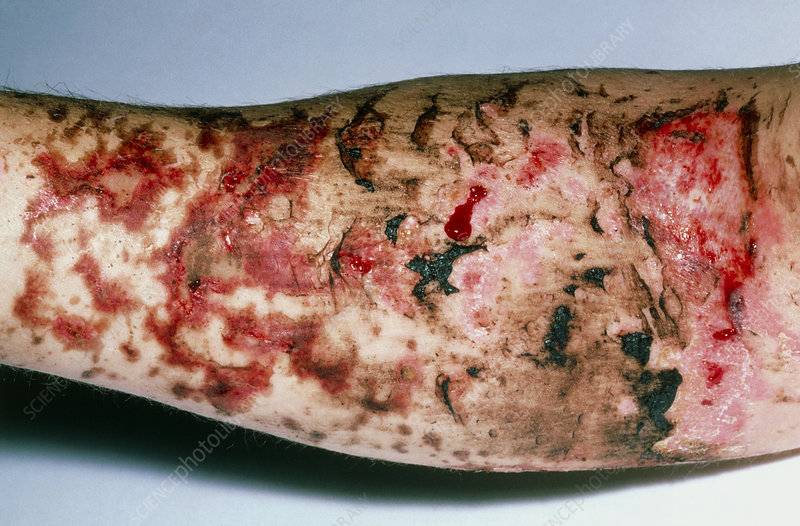
These are blisters beneath and within the epidermis:
A.) Embolus
B.) Vesicle
C.) Bullae
D.) Petechia
Bullae
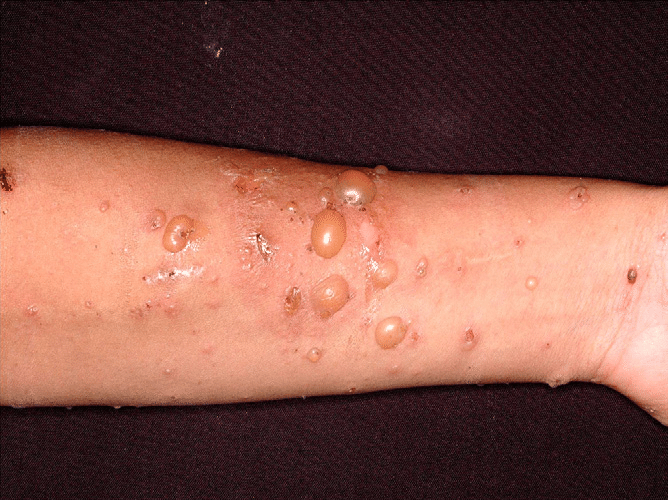
This type of burn is the most severe, it is complete destruction of all the skin layers and may even involve muscles and bones. Complete incineration:
4th degree burn
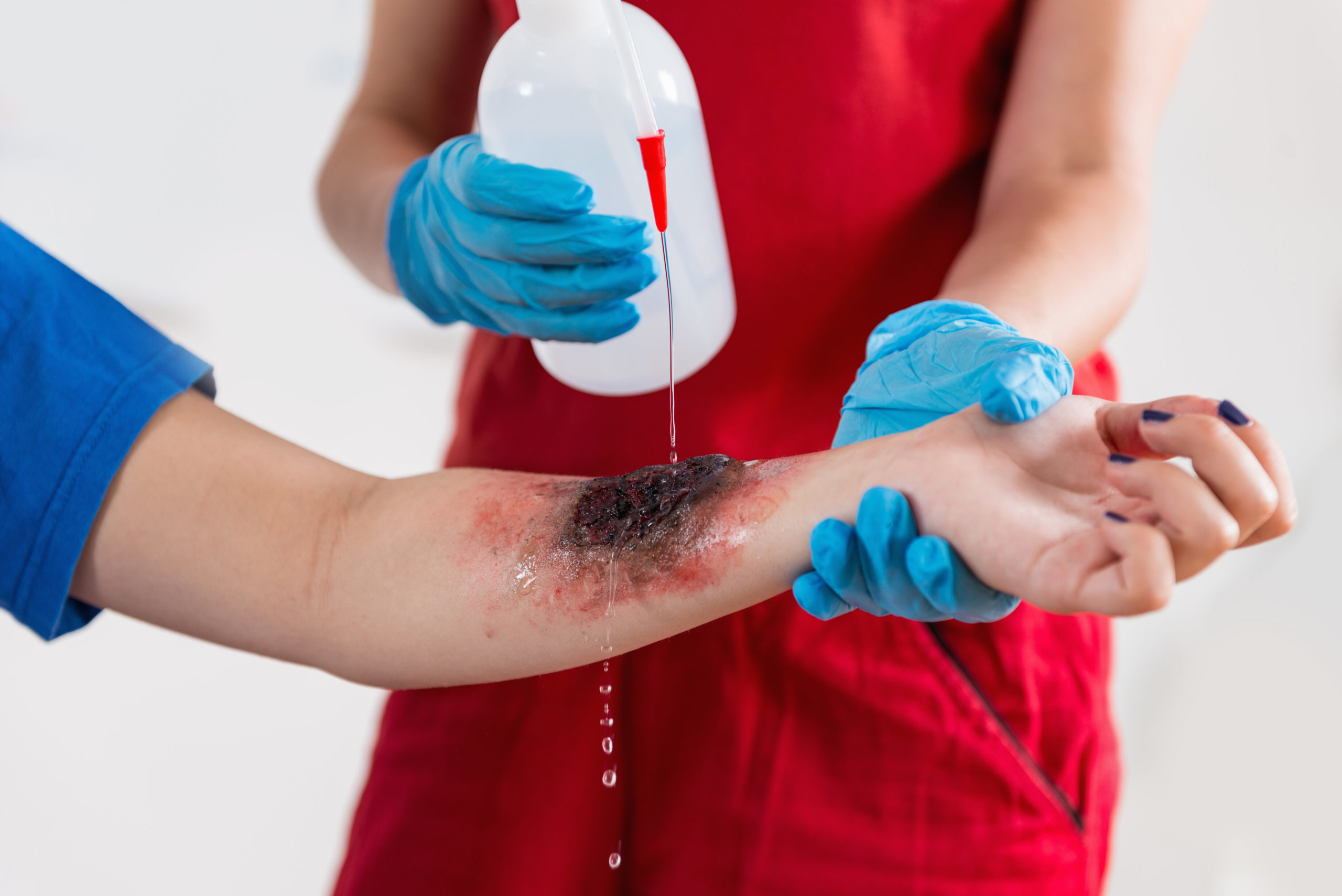
When dealing with a burned decedent, should you use autopsy gel?
Yes
When dealing with a burned decedent, which ppe is the best to use?
A.) Coveralls
B.) Unionall
C.) Capri pants
D.) Stockings
Unionall
Which suture may fit best for a burned decedent?
A.) Basketweave
B.) Baseball
C.) Worm
D.) Bridge
Worm
Note: Also called the inversion suture
What is another name for the worm suture?
Inversion suture
This is known as excessive blood loss to the point of death:
A.) Exacerbate
B.) Exsanguination
C.) Asphyxia
D.) Hypoxia
Exsanguination
What type of death may be characterized by a lack of color in the tissues?
A.) Death by exsanguination
B.) Death by asphyxia
C.) Death by electrocution
D.) Death by poisoning
Death by exsanguination
Lengthy refrigeration can cause…
A.) Excess moisture in tissues
B.) Loss of skin
C.) Mold growth
D.) Loss of hair
Mold growth
What environment may encourage mold growth?
Darkness and moisture
What is the best solution for mold?
1% phenol, 1% creosote
or
methyl alcohol and acetic acid
Which of the following are needle types?
1 - Half curved
2 - Double curved
3 - Luer lok
4 - Loopuypt
1, 2, 4
This suture aligns tissue margins and secures them in place until permanent sutures replace them:
Bridge suture
Note: Also called interrupted suture or individual suture
This suture is the most commonly used suture, it is considered the most secure.
Baseball
To make this suture, pass the needle and thread from beneath the incision up through the integument, and cross the needle from side to side with each stitch:
A.) Bridge
B.) Baseball
C.) Worm
D.) Double intradermal
Baseball
This suture continues thoughout the closure. A tight leak-proof closure is created:
Interlocking suture
This suture is made entirely within the dermal layer, traversing the needle side to side within the incision:
Single intradermal
This suture is knotted at each end, creating a greater holding strength than its single counterpart:
Double intradermal
This suture gathers and turns under excess tissues:
Worm suture
Note: Also called inversion suture
This is used to close lengthy incision, usually seen in an autopsy:
Whip suture
Note: Also called continuous suture