06 Spine
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
AP VIEW OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
TOWARDS C4 VERTEBRA (ADAM’S APPLE), 15-20 DEG CEPHALAD
view + central ray
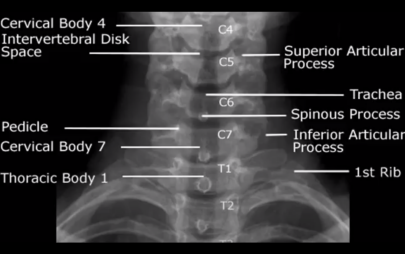
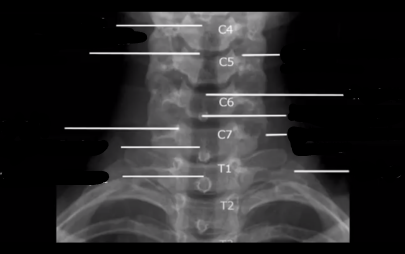
name the ff structures
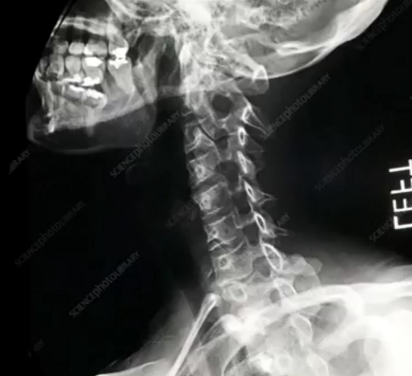
LAT VIEW OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
HORIZONTALLY TO THE CENTER OF THE C4 (LEVEL OF CHIN)
view + central ray
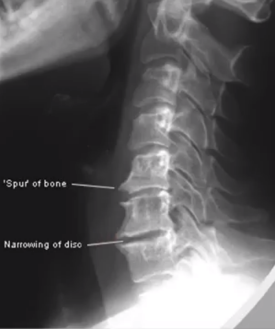
(TOP) BONE SPUR, (BOTTOM) NARROWING OF DISC
identify radiogaphic findings
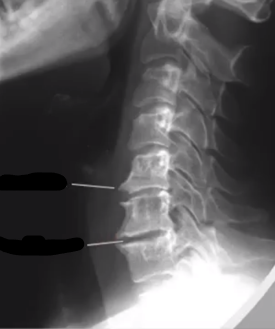
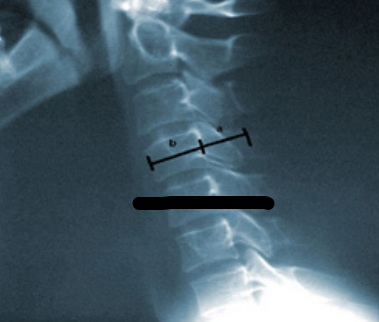
TORG-PAVLOV RATIO
ratio of the spinal canal diameter to the vertebral body diameter
OPEN OR ODONTOID “THROUGH-THE-MOUTH” VIEW
THROUGH THE OPEN MOUTH, 15 DEG TILTED TOWARDS THE HEAD AT A DISTANCE OF 40 IN
view + central ray
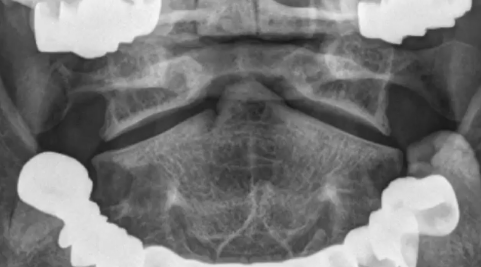
OPEN OR ODONTOID “THROUGH-THE-MOUTH” VIEW
In this view, atlanto-axial joint are seen to be best advantage
OBLIQUE VIEW
THROUGH THE C4 VERTEBRA, BODY IS 45 DEG ROT AND THE TUBE IS AT 15 DEG
view + central ray
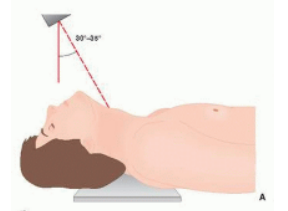
PILLAR VIEW
To evaluate the lateral masses of the cervical spin and facet joints
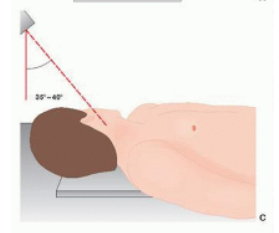
PILLAR VIEW
CENTER OF THE NECK AT THE THYROID CARTILAGE REGION, 30-45 DEG CAUDAL
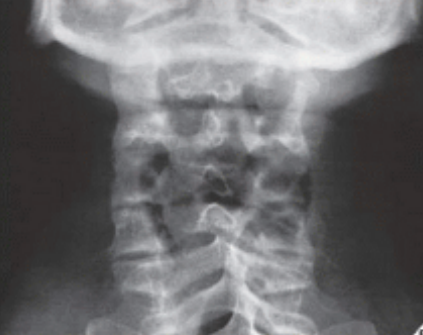
PILLAR VIEW
On the radiograph obtained in this projection, the "lateral masses" (or what we call pillars of the cervical vertebrae) are well demonstrated
OBLIQUE PILLAR VIEW
HYPEREXT NECK, HEAD ROTATED 45 DEG TOWARDS UNAFFECTED SIDE
what view + position of pt
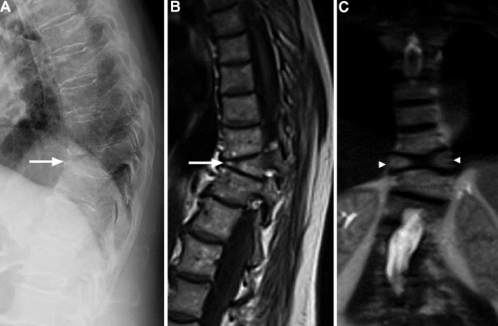
WEDGING
BAMBOO SPINE
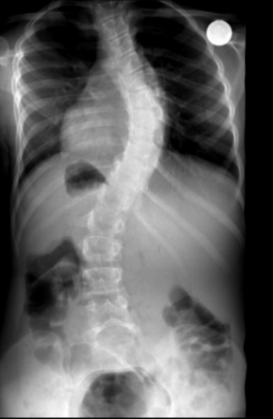
SCOLIOSIS
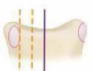
NASH-MOE METHOD
Spinous process rotates to concavity
NEUTRAL
identify nash-moe grade

GRADE: +
pedicle disappearing
GRADE: ++
pedicle disappears
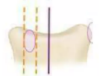
GRADE: +++
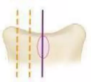
GRADE: ++++
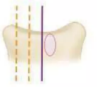
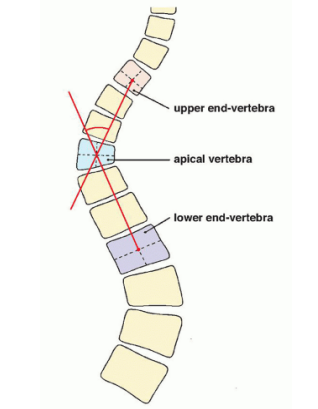
COBB METHOD
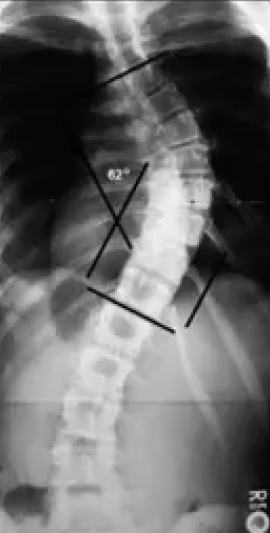
RISSER-FERGUSSON METHOD
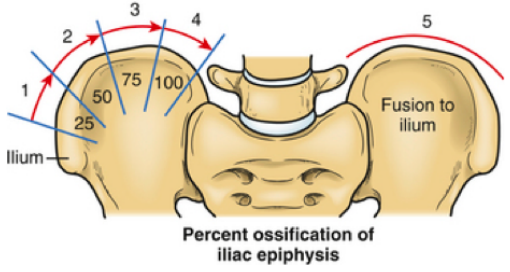
RISSER SIGN
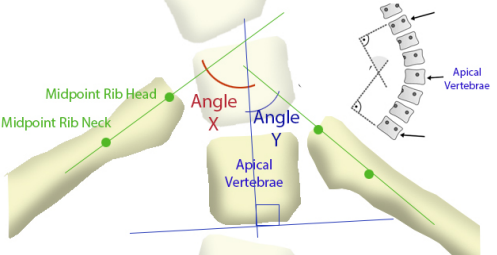
RIB VERTEBRAL ANGLE DIFFERENCE
SPONDYLOLISTHESIS
One of the vertebrae slips forward; can happen anywhere along the spine but commonly occurs at the lower back
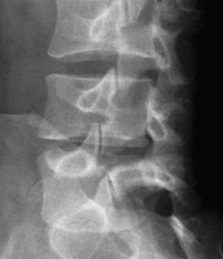
SPONDYLOLYSIS
Stress fx through the pars articularis of the lumbar vertebrae-a thin joint segment joining the two vertebrae-the most likely area affected by repetitive stress
SPONDYLOLYSIS
Transverse process
Pedicle
Superior articular process
Pars articularis/isthmus
Laminae
Inferior articular process
Spinous process
Interlaminar space
IV disc
findings + structures
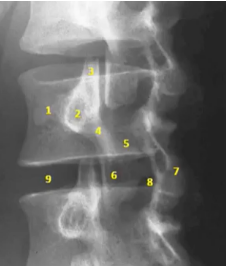
SPONDYLOLYSIS
Scottie dog sign
findings + structures
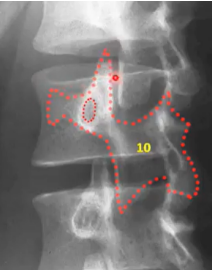
SCOTTY DOG FRACTURE
defect at pars interarticularis
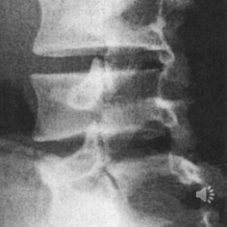
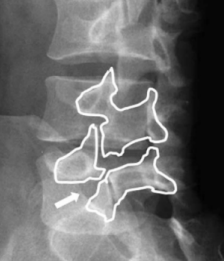
SCOTTY DOG FRACTURE
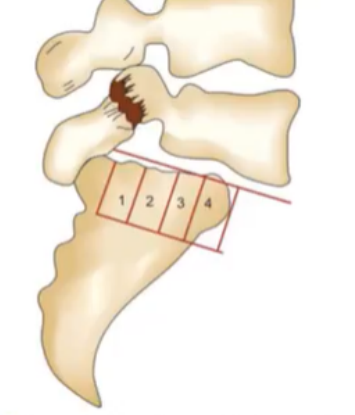
MEYERDING’S GRADING SYSTEM
This is a commonly adapted method of grading of spondyloptosis and it is based on the ratio of overhanging part of the superior vertebral body to the anteroposterior length of the adjacent inferior vertebral body.
GRADE 0 (NO SLIPPAGE)
identify grade
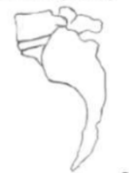
GRADE 1 (<25%)
identify grade
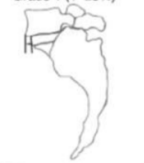
GRADE 2 (25-49%)
identify grade
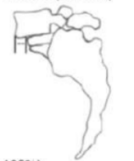
GRADE 3 (50-75%)
identify grade
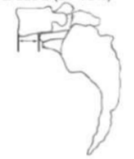
GRADE 4 (76-99%)
identify grade
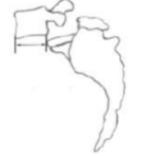
GRADE 5
> 100% SPONDYLOPTOSIS
MEYERDING’S GRADING SYSTEM
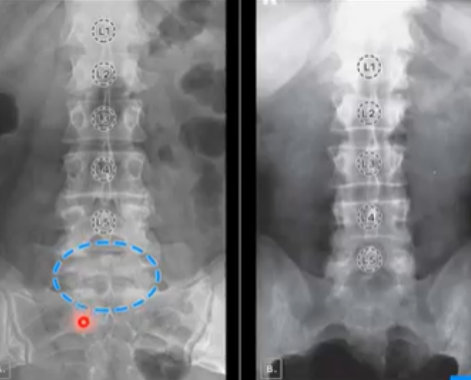
LUMBARIZATION OF S1
SACRALIZATION OF L5
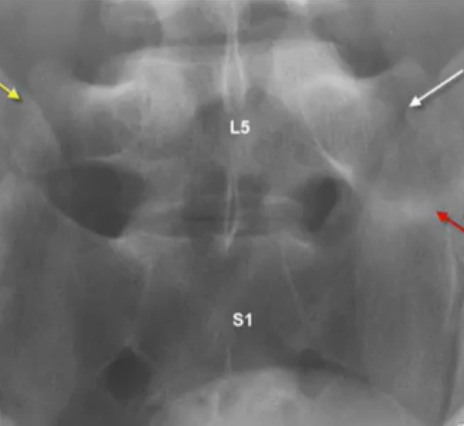
SACRALIZATION OF L5
Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae
TYPE 1 SACRALIZATION
a fusion of at least 19 millimeters in width of 1 or both sides
TYPE 2 SACRALIZATION
incomplete fusion with a pseudo joint created with 1 side or both sides
TYPE 3 SACRALIZATION
complete fusion at the L5 to the sacrum on one side or the other side
TYPE 4 SACRALIZATION
combination of type 2 and type 3
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA
Mildest type of Spina Bifida
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA
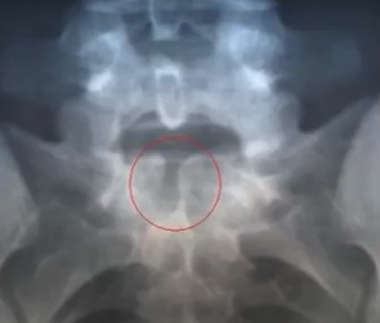
MENINGOCELE SPINA BIFIDA
When a sack that contains the spinal fluid, pushes through the gap in the spine
MYELOMENINGOCELE SPINA BIFIDA
When a sack that contains part of the spinal cord is covering and pushes through the spinal gap in the spine and in the skin; visible on the babies back
OSTEOPHYTES
are bone spurs that grow on any of the 7 vertebrae in the cervical spine; might elicit images of radiating spikes but bone spurs rounded end scalloped
WEDGING
This deformity occurs when the body of vertebra becomes fragmanted as in fracture crash or when the bone becomes sufficiently softened from pathologic processes, so that the body weight compresses the vertebra from above downwards
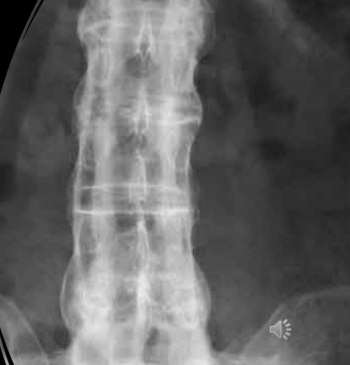
BAMBOO SPINE
occurs as a result of vertebral body fusion by margin syndesmophytes; often accompanied by fusion of posterior vertebral elements as well