psych 101 exam 2
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
what is sensation?
the detection of sensory information by a sensory detector
what are multiple senses?
vision, audition, olfaction, gustation, somatosensation, vestibular sense, proprioception, kinesthesia, nonciception, and thermoception
what is absolute threshold?
the minimum about of stimulus/stimulation a person can detect
what are subliminal messages?
messages presented below the absolute threshold for conscious awareness
what is difference threshold/just noticeable differences?
the minimum amount of change in a stimulation that can be detected
what is Weber’s Law?
the difference threshold is a constant fraction of the orignal stimulus
what is perception?
the process that organizes sensations into meaningful patterns
what is sensory adaptation?
failing to perceive some types of prolonged sensory stimulation
what is inattentional blindness?
failure to notice something that is completely visable becuase of lack of attention
what is bottom-up processing?
the idea that perceptions are builit from sensory information
what is top-down processing?
how we interept sensations influenced by our available knowledge and life experience.
what are visual illusions?
misperception of physical reality usually caused misapplication of visual cues
what is the Muller-Lyer illusion?
2 vertical lines drawn, the vertical line on the right appears longer then the one on the left. but both lines are equal in length.
what is frequency theory?
assumes the basilar membrane vibrates as a whole in direct proportion to the frequency of sound waves striking the eardrum
what is pitch?
frequency of sound waves
what is loudness?
amplitude and decibels
what is blindspot?
point on the retina through which the optic nerve penetrates
what is fovea?
the highest visual acuity
what are rods?
receptor cells on the retina that play a important role in night vision and peripheral vision
what are cones?
receptor cells on the retina that play a important role in day vision and color vision
what is optic chiasm?
crossing point of optic neurons disturbing half of the left and right visual fields to each half of the occipital lobe
what are olfactory receptors?
hair-like parts that extend from the olfactory bulb into the mucous membrane of the nacavity
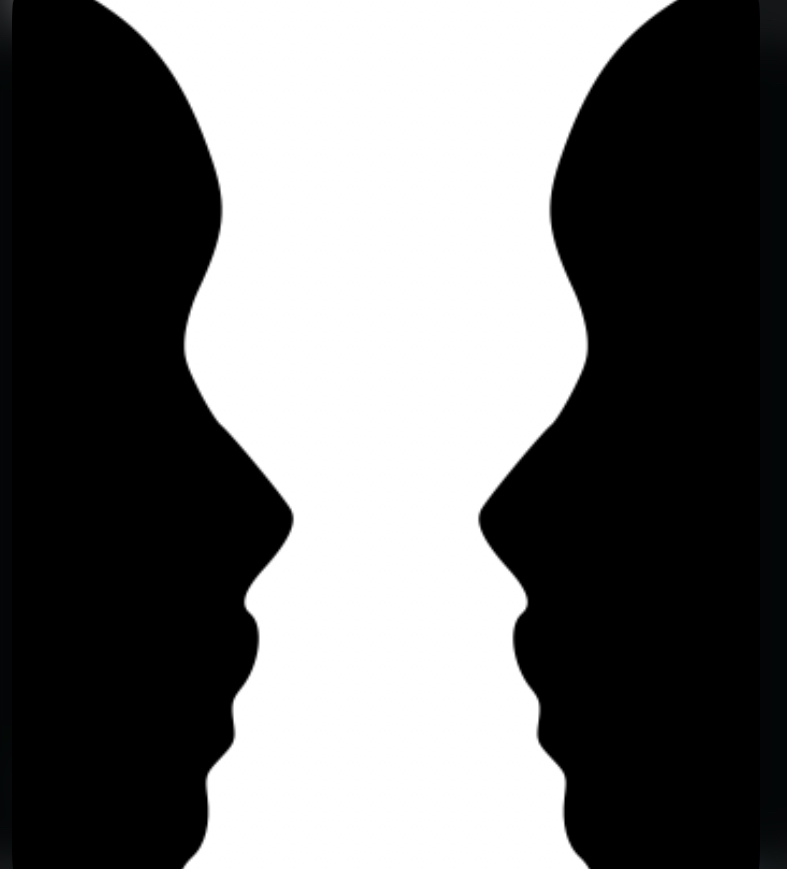
what is the figure ground relationship?
explains why this can be perceived either a vase or a pair of faces
what is extrasensory perception?
the alleged ability to perceive events without the use of sensory receptors
what is parapsychology?
the study of extrasensory perception, psychokinesis, and related phenomena
what is pseuoscience?
concepts and theories that are unsupported by empirical evidence and often masquerade as valid science
what is deja vu?
the ONLY studied and REAL phenomena
what is opponent-process theory?
color vision depends on red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white opponent processes in the brain
what is afterimage?
image that persists after the removal of visual stimulus
what is trichromatic theory?
argues that cones are individually responsive to only 3 colors (red, green, blue)
environmental factors that can lead to conductive hearing loss include…
regular exposure to loud music or construction
what is transduction?
taste molecules bind to receptors and cause chemical changes within the sensory cell
what are taste buds?
the number of individual taste receptors cells that transmit info to nerves
what are sensory receptors?
each attuned to specific touch-related stimuli
the major sensory organs of…
the vestibular system
where are the major sensory organs are located?
next to the cochlea inner ear
what does the principle of proximity suggest?
that you see one block of dots on the left side and three columns on the right side
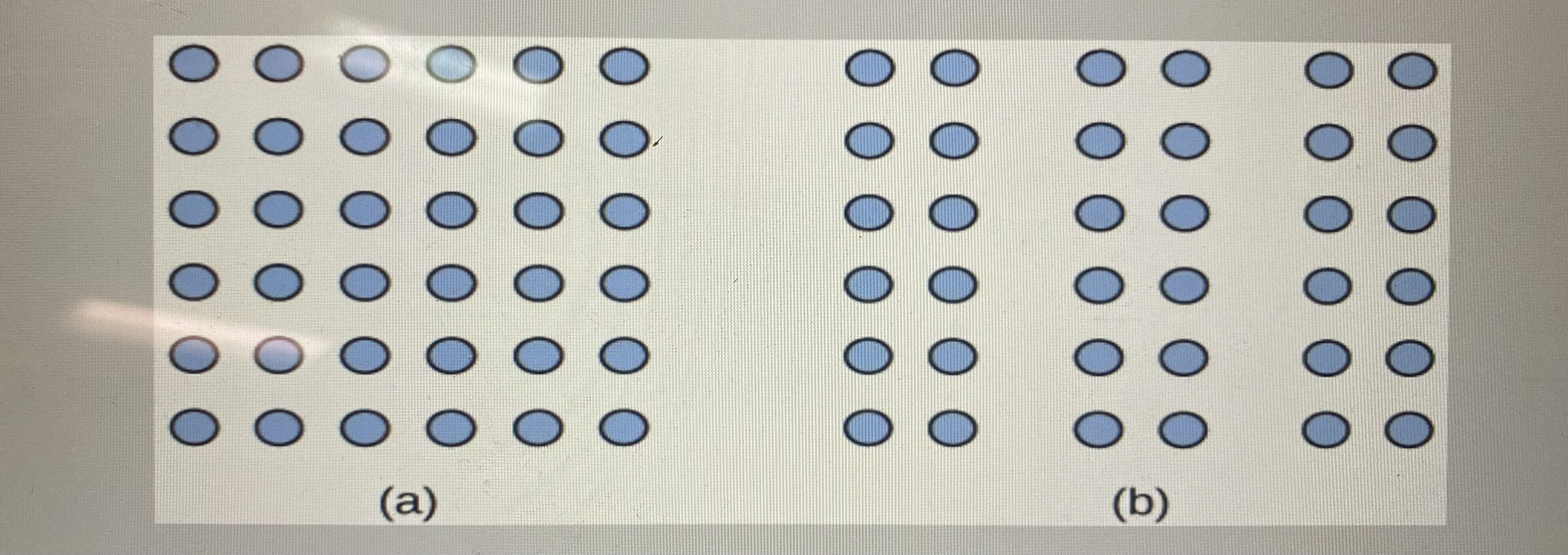
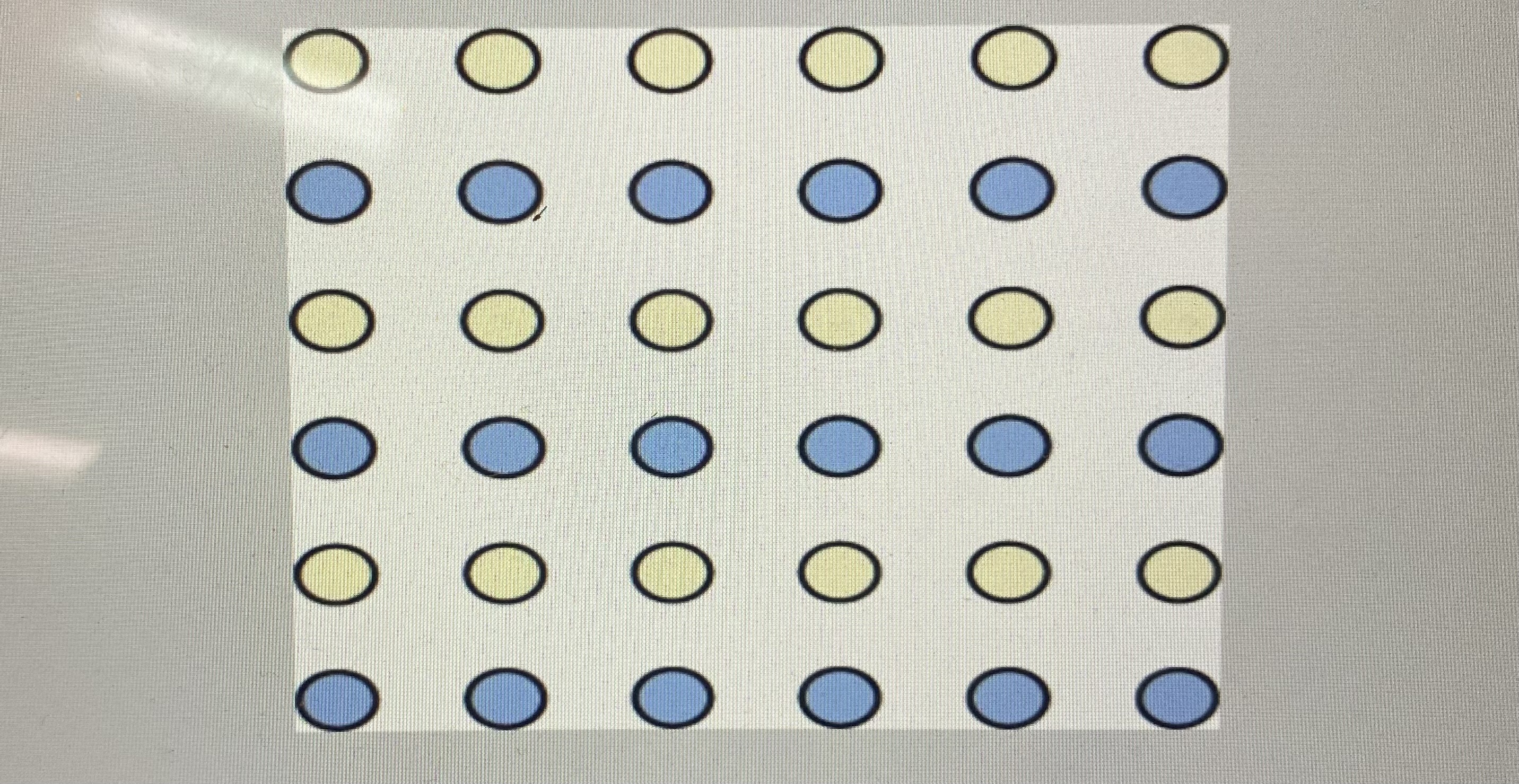
what is the principle of similarity?
when looking at a array of dots and perceiving alternating rows of colors

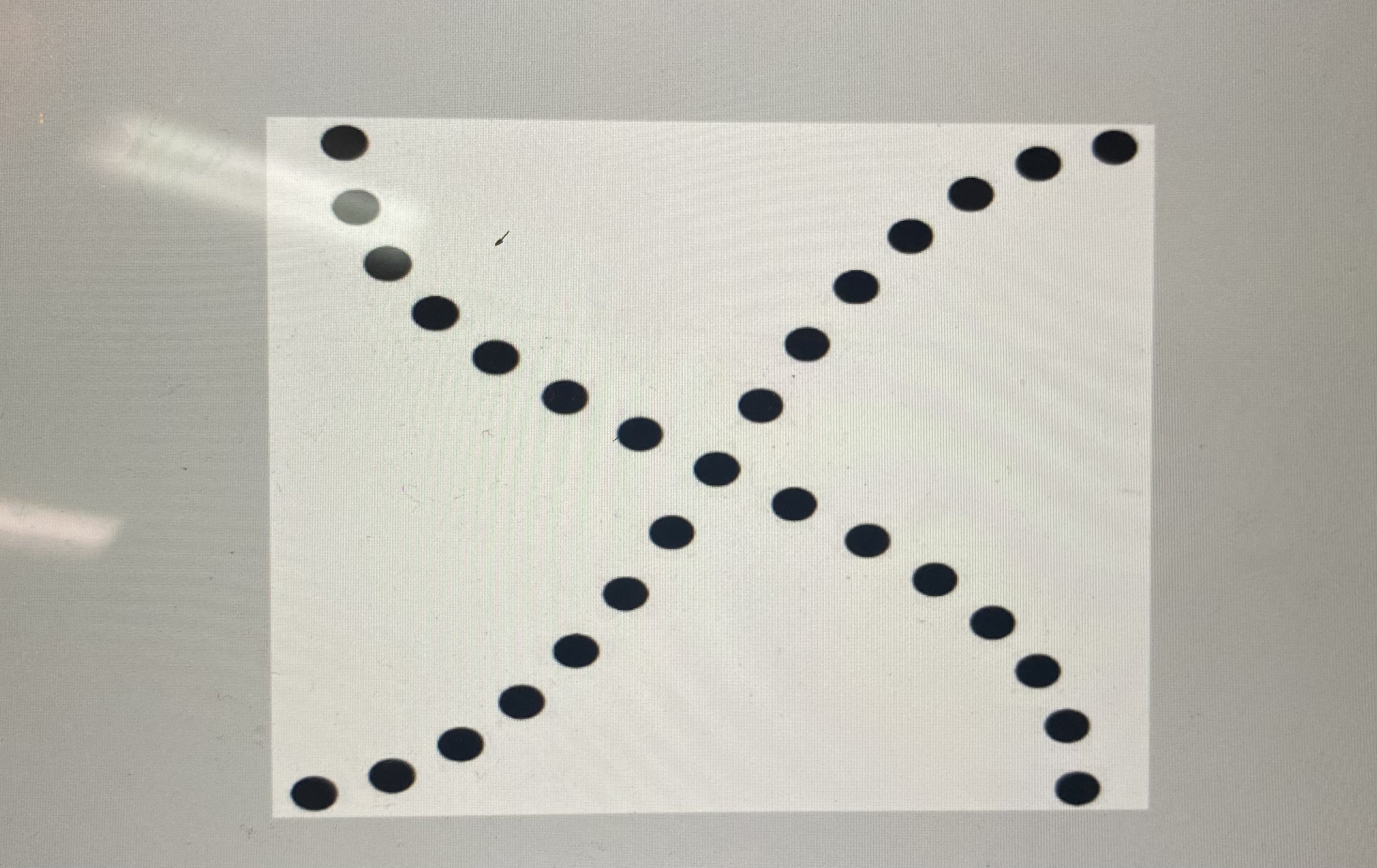
what is the principle of continuation?
when we are more likely to perceive two overlapping lines rather then 4 lines meeting in the center
what is the principle of closure?
we perceive a complete circle and rectangle, rather then a series of segments

what is consciousness?
awareness of one’s own cognitive actitvity including thoughts, feelings, and sensations
what is consciousness closely linked to?
the construct of memory
what is conscious also called?
a river or stream/altered streams
what is consciousness?
awareness of one’s own cognitive activity including thoughts, feelings, and sensations
consciousness is closely linked to…
the construct of memory
_____ and _____ of consciousness
streams and states
what are dreams?
story-like sequences of visual images
what are nightmares?
frightening dreams during REM sleep
what are night terrors?
frightening NREM experiences
what is attention?
makes us aware of certain stimuli while blocking out others
what is unconscious?
perception without awareness
what is sleep?
periodic, natural loss of consciousness
what is the circadian rhythm?
24 hour cycles of physiological changes; biological rhythms and sleep-wake cycle
what is the suprachiasmatic nucleus ?
serves as the brain's clock mechanism; the clock sets itself with light information received through projections from the retina
what brain structure is the suprachiasmatic nucleus sitting above?
the optic chiasm
what is one factor our sleep wake cycle is also regulated by?
the hormone melatonin
what is melatonin released by?
the pineal gland
what is sleep regulation?
brain's control of switching between sleep and wakefulness as well as coordinating this cycle with the outside world
what is a chronotype?
individual circadian pattern activity
what is season affective disorder (SAD)?
a person experiences depression during winter months and improved mood during spring
what are the functions of sleep?
physical restoration and adaptive inactivity
what is sleep-onset insomnia?
trouble falling asleep
what is sleep-maintenance?
falling asleep normally but find themselves awakening repeatly
dreaming is a by-product of _____ ?
random brain activity
what is activation-synthesis theory?
dreams are the by-products of the cortex’s attempt to make sense of spontaneous changes in physiological activity generated by the brain stem during REM
what is hypnosis?
an induced state of consciousness in which 1 person responds to suggestions by another person to alter perception, thinking, feelings, and behavior
what is hypermnesia?
memory enhancement
what is a effect from hypnosis?
moderate to large effect in relieving pain
hypnosis is a ______
dissociated state
what are depressants?
reduces arousal by inhibiting activity in central nervous system
what are examples of depressants?
alcohol, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and opiates
what are psychoactive drugs?
chemicals that induce changes in mood, thinkings perception, and behavior by affecting neuronal activity in the brain
what are stimulants?
act to increase arousal
what is substance abuse?
not satisfying the criteria for a substance use disorder, but involves irresponsible or hazardous use of substances
what is substance dependence?
tolerance and withdrawal; need for markedly increased amounts to achieve the desired effect
what is behavioral psychology?
study of how we learn; focus on observable phenomena to understand unconscious processes
what is behavioral psychology also called?
behaviorism
what is the “A” of behaviorism?
antecedents (before)
what is the “B” of behaviorism?
behavior
what is the “C” of behaviorism?
consequences (after)
what word is associated with Ivan Pavlov?
serendipity
what is systematic desensitization?
to alleviate anxiety based problems
fear is _________
rational
anxiety is ________
unrational
Pavlov is a ______
noble prize winner
neutral stimulus must ________
precede the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) closely in time
neutral stimulus will acquire _____
(from the unconditioned stimulus, UCS) the ability to elicit the UCR (at which point, it is a CR)
the process of acquisition is called _______
contiguity or more simply association
UCS (unconditioned stimulus) ——>
UCR (unconditioned response)
what is a unconditioned stimulus?
something that reflexively and unconsciously elicits a response
what is a unconditioned response?
the reflexive and unconscious result of a stimulus
what is a neutral stimulus?
something which doesn’t elicit a response on its own
what is a conditioned stimulus?
a once neutral stimulus that has been repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus
what is a conditioned response?
the result of classical conditioning where a once neutral stimulus now elicits the same response as the unconditioned stimulus with which it was repeatedly paired
what is positive reinforcement?
something pleasant that is added or given to encourage a desired behavior
what is negative reinforcement?
something unpleasant that is subtracted ot taken away to encourage a desire behavior
what is positive punishment?
something unpleasant that is added or given to discourage a undesired behavior
what is a negative punishment?
something pleasant that is subtracted or taken away to discourage a undesired behavior
what is a reinforcement?
used to increase behavior
what is punishment?
used to decrease behavior