respiration
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
why do organisms need to respire
produce ATP for
active transport against conc gradients ex. to absorb nutrients from s intestine/soil
metabolic reactions ex. form peptide bonds in protein synthesis
muscle contraction
releases heat energy for thermoregulation
structure of mitochondrion
double membrane bound organelle
folded inner membrane forms cristae: site of ETC
fluid matrix: contains mitochondrial DNA, respiratory enzymes, lipids, proteins
4 main stages of aerobic respiration + location
glycolysis: cytoplasm
link reaction: mitochondrial matrix
krebs cycle: mitochondrial matrix
oxidative phosphorylation: via ETC, membrane of cristae
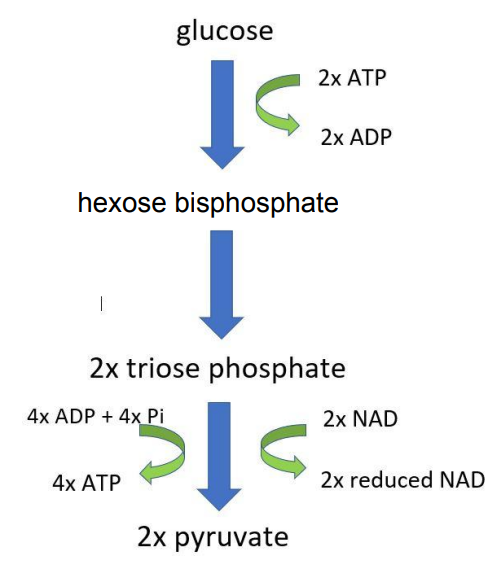
stages of glycolysis
glucose phosphorylated to hexose bisphosphate by 2 ATP
hexose bisphosphate splits into 2 triose phosphate
2 TP oxidised to 2 pyruvate
net gain of 2 reduced NAD, 2 ATP per glucose
how pyruvate from glycolysis enters mitochondria
active transport
stages of link reaction
oxidation of pyruvate to acetate
net gain of 1 CO2 (decarboxylation), 2 H atoms (used to reduce 1 NAD)
acetate combines w coenzyme A to form acetylcoenzyme A
summary equation for link reaction
Pyruvate + NAD + CoA → acetyl CoA + reduced NAD + CO2
stages of krebs cycle
series of redox reactions produces
ATP by substrate level phosphorylation
reduced coenzymes
CO2 from decarboxylation
begins when acetyl group from Acetyl CoA (2C) reacts with oxaloacetate (4C). cycle regenerates oxaloacetate
what is electron transfer chain (ETC)
series of carrier proteins embedded in membrane of cristae of mitochondria
produces ATP by oxidative phosphorylation via chemiosmosis during anaerobic respiration
what happens in electron transfer chain (ETC)
electrons released from reduced NAD + FAD undergo successive redox reactions
energy released is coupled to maintain proton gradient/released as heat
oxygen acts as final electron acceptor
how does chemiosmosis produce ATP during aerobic respiration
some energy released from ETC is coupled to active transport of protons from mitochondrial matrix to intermembrane space
protons move down conc gradient into mitochondrial matrix via channel protein ATP synthase
ATP synthase catalyses ADP + Pi → ATP
state role of oxygen in aerobic respiration
final electron acceptor in ETC
produces byproduct water
stages in respiration that produce ATP by substrate level phosphorylation
glycolysis (anaerobic)
krebs cycle (aerobic)
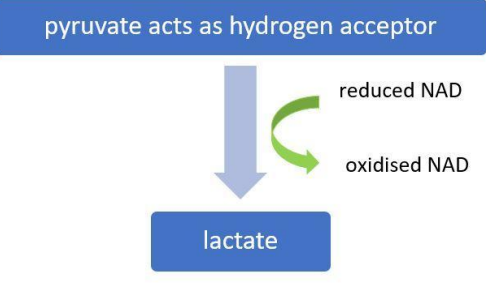
what happens during anaerobic respiration in mammals?
only glycolysis continues
reduced NAD + pyruvate → oxidised NAD (for further glycolysis) + lactate
what happens during anaerobic respiration in some microorganisms e.g. yeast and some plant cells
only glycolysis continues, so much less ATP produced compared to aerobic respiration
pyruvate decarboxylated to form ethanal
ethanal reduced to ethanol using reduced NAD to produce oxidised NAD for further glycolysis
benefits of being able to respire anaerobically
ATP production for vital metabolic processes continues
production of ethanol/lactate converts reduced NAD back into NAD so glycolysis can continue = max yield of ATP in conditions
suggest how student could investigate effect of named variable on rate of respiration of single celled organism
use respirometer - pressure changes in boiling tube cause drop of coloured liquid to move
use dye as terminal electron acceptor for ETC
purpose of sodium hydroxide solution in respirometer set up to measure rate of reaction
absorbs CO2 = net decrease in pressure as O2 is consumed
how could rate of respiration be calculated using respirometer
volume of O2 produced or CO2 consumes/time x mass of sample
volume = distance moved by coloured drop x (0.5 x capillary tube diameter)2 x pi
2 types of molecule that can be used as alternative respiratory substrates
(amino acids from) proteins
(glycerol and fatty acids from) lipids
what is the respiratory quotient (RQ)
RQ = carbon dioxide produced/oxygen consumed
can be used to determine
respiratory substrate being used (carbohydrates: 1.0, lipids: 0.8, proteins: 0.9)
if organism is anaerobically respiring (anaerobic values = larger)
why diff respiratory substrates have diff relative energy values
depends on number of hydrogens in structure which are oxidized to water ex. number of hydrogens is greater in fatty acids than carbohydrates