M03- chp. 5 questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:38 AM on 6/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
197 Terms
1
New cards
When did the first eukaryotic cells on earth appear?
Multiple choice question.
* 2 million years ago
* Just over 2,000 years ago
* 2 billion years ago
Multiple choice question.
* 2 million years ago
* Just over 2,000 years ago
* 2 billion years ago
2 billion years ago
2
New cards
Biologists believe that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotes through which process?
Multiple choice question.
* Endosymbiosis
* Endocytosis
* Parasitism
Multiple choice question.
* Endosymbiosis
* Endocytosis
* Parasitism
Endosymbiosis
3
New cards
The cell type that is believed to be the precursor to all three domains is referred to as the last common
ancestor
4
New cards
Which evidence supports the endosymbiont theory that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotes?
Multiple choice question.
* Mitochondrial DNA
* Nuclear DNA
* Cell wall structure
Multiple choice question.
* Mitochondrial DNA
* Nuclear DNA
* Cell wall structure
Mitochondrial DNA
5
New cards
A group of tissues that work together is called an ________.
Multiple choice question.
* organism
* organ
* organelle
Multiple choice question.
* organism
* organ
* organelle
organ
6
New cards
True or false: Eukaryotic life began on Earth about 200 million (200,000,000) years ago.
False
7
New cards
Which of the following organisms are eukaryotic?
Multiple select question.
* Archaea
* Bacteria
* Fungi
* Helminths
* Protozoa
* Algae
Multiple select question.
* Archaea
* Bacteria
* Fungi
* Helminths
* Protozoa
* Algae
Fungi
Helminths
Protozoa
Algae
Helminths
Protozoa
Algae
8
New cards
_____ is the term used to describe the origin of some eukaryotic organelles.
endosymbiosis
9
New cards
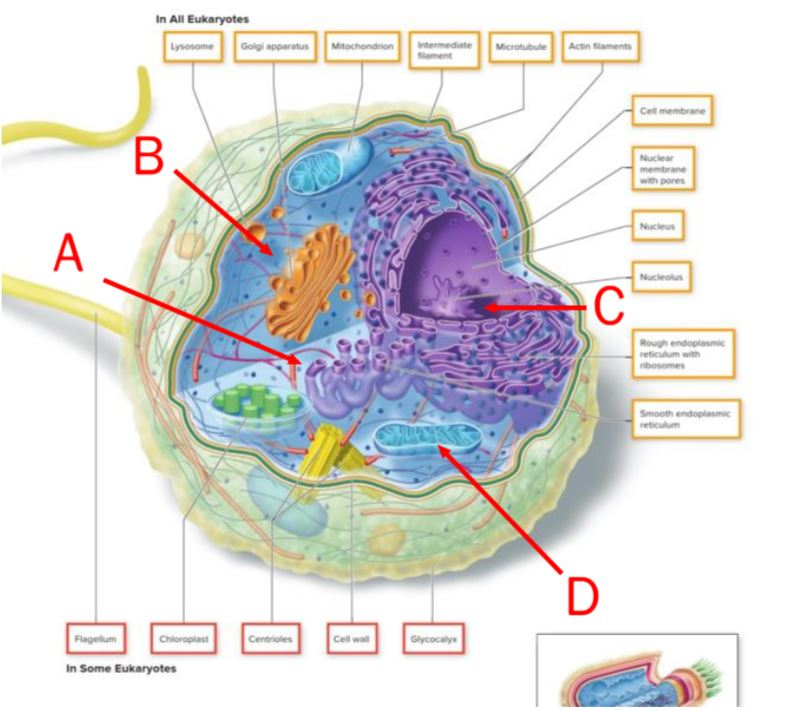
On this image of a cell, the letter indicating the site of energy generation is ______.
D
10
New cards
The last common ancestor refers to a cell type that gave rise to ______.
Multiple choice question.
* both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
* bacteria and archaea but not eukaryotes
* archaea and viruses
* eukaryotes and archaea but not bacteria
Multiple choice question.
* both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
* bacteria and archaea but not eukaryotes
* archaea and viruses
* eukaryotes and archaea but not bacteria
both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
11
New cards
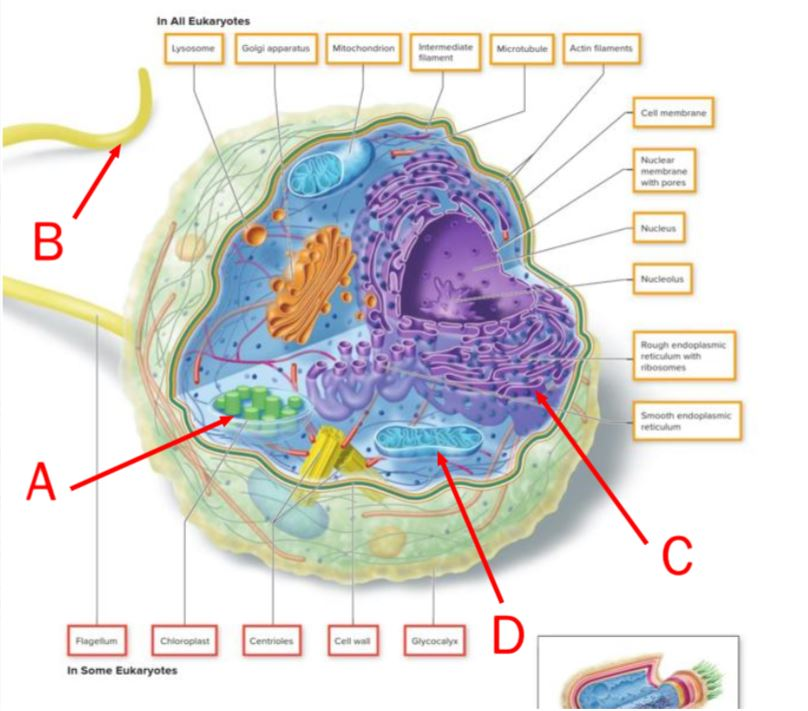
This image of a cell can be identified as photosynthetic on the basis of the presence of the structure marked by the letter ______.
A
12
New cards
The ribosomes in ATP-producing organelles called ______ are clearly bacterial in nature, providing evidence in support of endosymbiosis.
mitochondria
13
New cards
Which eukaryotic structures are NOT present in prokaryotic cells?
Multiple select question.
* Ribosomes
* Nucleus
* Plasma membrane
* Mitochondrion
* Golgi apparatus
* DNA
Multiple select question.
* Ribosomes
* Nucleus
* Plasma membrane
* Mitochondrion
* Golgi apparatus
* DNA
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
14
New cards
A(n) _____ is defined as a group of tissues.
organ
15
New cards
True or false: All eukaryotic organisms are microscopic.
False
16
New cards
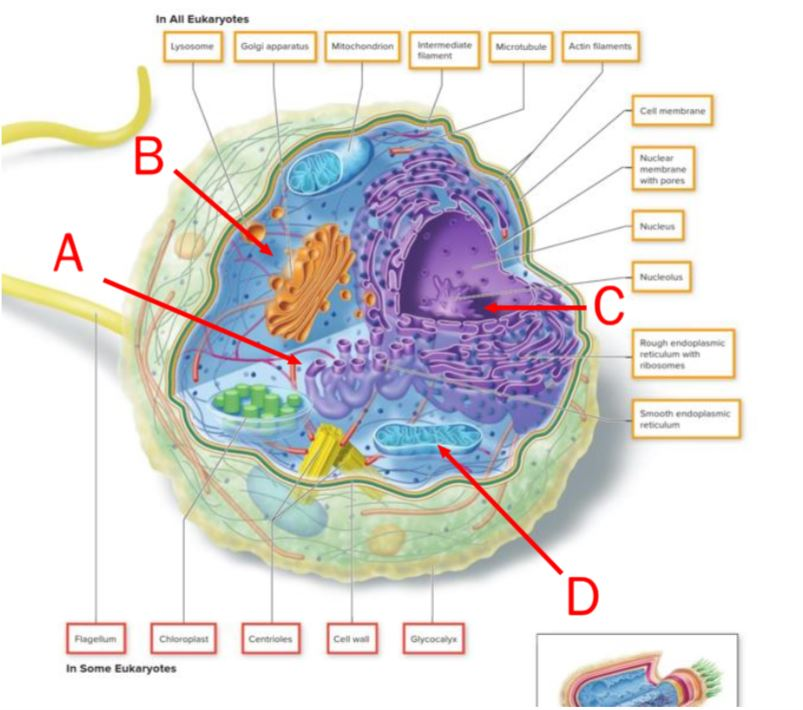
On this image of a cell, the letter indicating the site where proteins are modified and sent to their final destinations is ______.
B
17
New cards
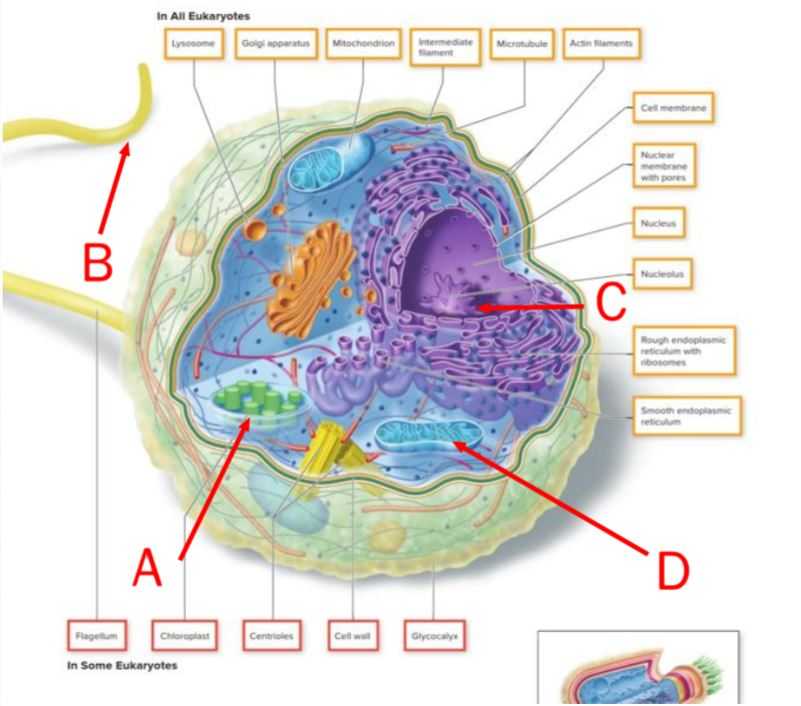
On this image of a cell, the nucleolus can be found in the region labeled by the letter ______.
C
18
New cards
In a eukaryotic cell propelled by a flagellum, the flagellum moves ______.
Multiple choice question.
* back and forth
* in a helical motion
* in a circular motion
Multiple choice question.
* back and forth
* in a helical motion
* in a circular motion
back and forth
19
New cards
Which components would be found in a eukaryotic cell but not in a prokaryotic cell?
Multiple select question.
* endoplasmic reticulum
* mitochondrion
* ribosomes
* DNA
* nucleus
* cell membrane
Multiple select question.
* endoplasmic reticulum
* mitochondrion
* ribosomes
* DNA
* nucleus
* cell membrane
endoplasmic reticulum
mitochondrion
nucleus
mitochondrion
nucleus
20
New cards
Which two of these terms are better applied to eukaryotic flagella than to bacterial flagella?
Multiple select question.
* Used for attachment to substrates
* Structurally complex
* Contains microtubules
* Thinner by a factor of 10
* Does not involve the cell membrane
Multiple select question.
* Used for attachment to substrates
* Structurally complex
* Contains microtubules
* Thinner by a factor of 10
* Does not involve the cell membrane
Structurally complex
Contains microtubules
Contains microtubules
21
New cards
True or false: Cilia can be found in both protozoa and bacteria.
False
22
New cards
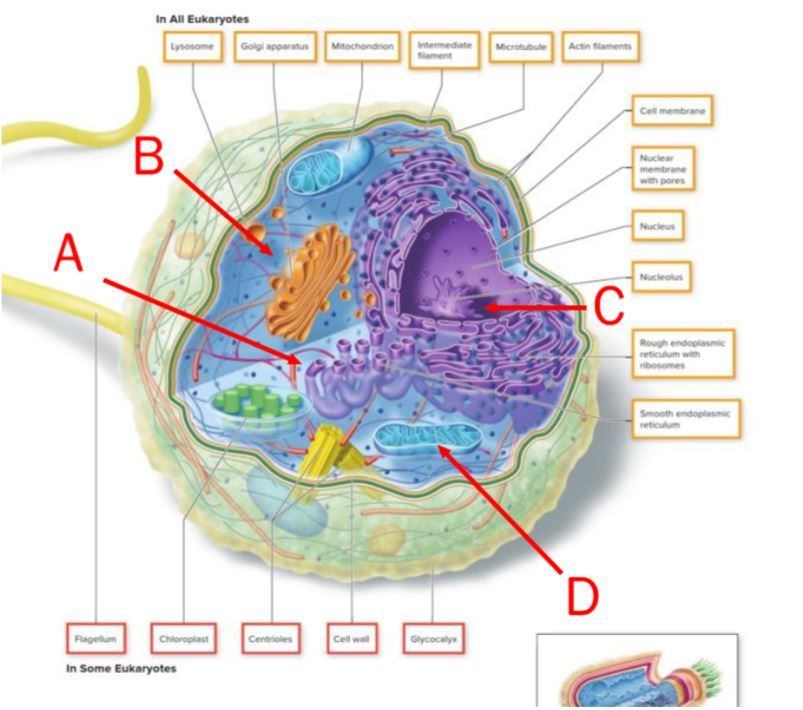
On this image of a cell, the letter indicating the site of energy generation is ______.
D
23
New cards
True or false: Many eukaryotic cells have a glycocalyx.
True
24
New cards
Of the eukaryotic subcellular structures listed below, which is the most external?
Multiple choice question.
* Glycocalyx
* Mitochondria
* Cell membrane
* Golgi
Multiple choice question.
* Glycocalyx
* Mitochondria
* Cell membrane
* Golgi
Glycocalyx
25
New cards
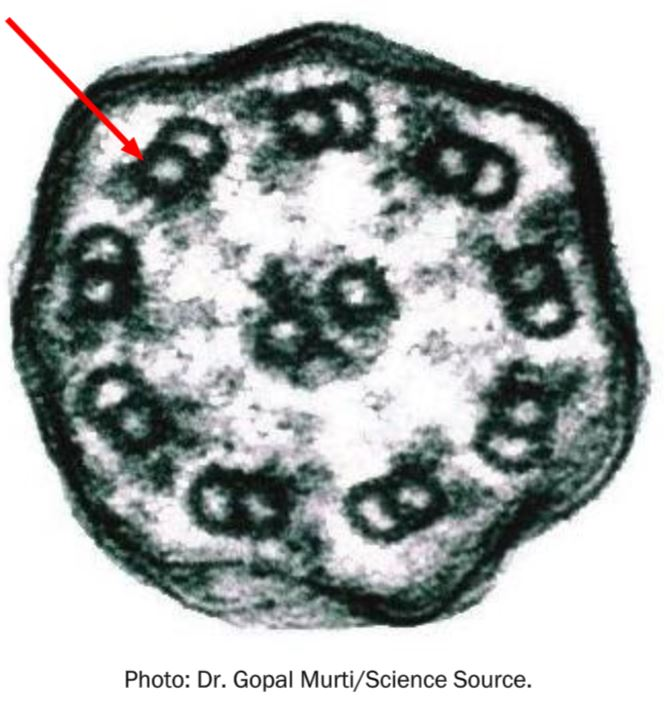
The structures illustrated here by the arrow represent _____ in a cross-section of a flagellum.
Multiple choice question.
* flagellin protein
* intermediate filaments
* microtubules
* glycocalyx
Multiple choice question.
* flagellin protein
* intermediate filaments
* microtubules
* glycocalyx
microtubules
26
New cards
Which is NOT a function of the eukaryotic glycocalyx?
Multiple choice question.
* Motility
* Adherence
* Protection
Multiple choice question.
* Motility
* Adherence
* Protection
Motility
27
New cards
The _____ flagellum is a long sheathed cylinder containing regularly spaced microtubules.
Multiple choice question.
* bacterial
* archaeal
* eukaryotic
Multiple choice question.
* bacterial
* archaeal
* eukaryotic
eukaryotic
28
New cards
Which of the following are considered to have relatively thick cell walls?
Multiple select question.
* Animals
* Fungi
* Protozoans
* Algae
Multiple select question.
* Animals
* Fungi
* Protozoans
* Algae
Fungi
Algae
Algae
29
New cards
Which of the following best describes the function of cilia and flagella?
Multiple choice question.
* Meiosis
* Cellular division
* Cell to cell communication
* Motility
Multiple choice question.
* Meiosis
* Cellular division
* Cell to cell communication
* Motility
Motility
30
New cards
Which of the following structures is principally composed of phospholipids?
Multiple choice question.
* Cell membrane
* Cytoskeleton
* DNA
* Ribosomes
Multiple choice question.
* Cell membrane
* Cytoskeleton
* DNA
* Ribosomes
Cell membrane
31
New cards
32
New cards
Which of the following compounds give rigidity (stability) to cell membranes?
Multiple choice question.
* Glycoproteins
* Phospholipids
* Porins
* Sterols
Multiple choice question.
* Glycoproteins
* Phospholipids
* Porins
* Sterols
Sterols
33
New cards
Unlike most bacteria, the cell membranes of eukaryotes contain _____ that stabilize the bilayer.
sterols
34
New cards
Identify various functions of the glycocalyx in eukaryotic cells.
Multiple select question.
* Adherence
* Protection
* Cell division
* Energy production (electron transport system)
* Motility
Multiple select question.
* Adherence
* Protection
* Cell division
* Energy production (electron transport system)
* Motility
Adherence
Protection
Protection
35
New cards
The cell membrane acts as a selectively ______ barrier between the cytoplasm and external cellular environment.
permeable
36
New cards
The cell membrane is a _____ bilayer with embedded proteins.
phospholipid
37
New cards
Which defines an intracellular, membrane-bound component of a eukaryotic cell?
Multiple choice question.
* Tissue
* Organelle
* Organ
Multiple choice question.
* Tissue
* Organelle
* Organ
Organelle
38
New cards
What is the main function of membrane sterols?
Multiple choice question.
* Act as molecular carriers
* Provide stability to the membrane
* Serve as membrane receptors
Multiple choice question.
* Act as molecular carriers
* Provide stability to the membrane
* Serve as membrane receptors
Provide stability to the membrane
39
New cards
The cell membranes of eukaryotes contain ______ that stabilize the bilayer.
Multiple choice question.
* proteins
* sterols
* phospholipids
* sugars
Multiple choice question.
* proteins
* sterols
* phospholipids
* sugars
sterols
40
New cards
Roughly 60-80% of a eukaryotic cell's total volume is made up of the various membrane-bound ______ found within the cytoplasm of this cell type.
organelles
41
New cards
The eukaryotic cell membrane acts as ______.
Multiple choice question.
* the location of photosynthesis
* a selectively permeable barrier
* the location for ribosomes to bind for protein synthesis
* an energy generator for the electron transport system
Multiple choice question.
* the location of photosynthesis
* a selectively permeable barrier
* the location for ribosomes to bind for protein synthesis
* an energy generator for the electron transport system
a selectively permeable barrier
42
New cards
True or false: Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
True
43
New cards
Which of the following structures separates DNA from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells?
Multiple choice question.
* Histones
* Nucleolus
* Nuclear envelope
* Cell membrane
* Ribosomes
Multiple choice question.
* Histones
* Nucleolus
* Nuclear envelope
* Cell membrane
* Ribosomes
Nuclear envelope
44
New cards
The nucleolus is found within the _____ of a eukaryotic cell.
Nucleus
45
New cards
Why does the nucleolus stain more intensely than surrounding cellular content?
Multiple choice question.
* RNA within the nucleolus absorbs dye
* DNA within the nucleolus absorbs dye
* Proteins absorb dye
Multiple choice question.
* RNA within the nucleolus absorbs dye
* DNA within the nucleolus absorbs dye
* Proteins absorb dye
RNA within the nucleolus absorbs dye
46
New cards
Which percentage of a eukaryotic cell's total volume is made up of organelles?
Multiple choice question.
* 30% to 40%
* 10% to 15%
* 60% to 80%
* 45% to 50%
Multiple choice question.
* 30% to 40%
* 10% to 15%
* 60% to 80%
* 45% to 50%
60% to 80%
47
New cards
The _____ is the small part of the nucleus where ribosomal subunit formation takes place.
nucleolus
48
New cards
The key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is the presence or absence of a(n) ______ and other membrane-bound organelles.
nucleus
49
New cards
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Multiple choice question.
* Protein synthesis
* Transcription of RNA
* Ribosomal subunit synthesis
Multiple choice question.
* Protein synthesis
* Transcription of RNA
* Ribosomal subunit synthesis
Ribosomal subunit synthesis
50
New cards
The nucleolus contains a large amount of_____, making it stain more intensely than surrounding structures in the nucleus.
RNA
51
New cards
Chromosomes in eukaryotic cells are made up of ______.
Multiple choice question.
* chromatin
* ribosomes
* cristae
* karyotypes
Multiple choice question.
* chromatin
* ribosomes
* cristae
* karyotypes
chromatin
52
New cards
Which biomolecules are found in chromatin?
Multiple select question.
* Carbohydrate
* Phospholipid
* Protein
* Nucleic acid
Multiple select question.
* Carbohydrate
* Phospholipid
* Protein
* Nucleic acid
Protein
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
53
New cards
A dense region found within the nucleus where ribosomal subunits are synthesized is called the ______.
nucleolus
54
New cards
In a eukaryotic chromosome, which type of protein is bound to the DNA?
Multiple choice question.
* histone
* nucleolar
* actin
Multiple choice question.
* histone
* nucleolar
* actin
histone
55
New cards
___ is the type of eukaryotic cell division that preserves the chromosome number.
mitosis
56
New cards
_____ are large, condensed units within the nucleus that contain the genetic information of eukaryotic cells.
chromosomes
57
New cards
Gametes, or sex cells, are produced by the type of cell division known as ____
meiosis
58
New cards
59
New cards
Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of dark fibers known as
chromatin
60
New cards
The ________ is a membrane-bound series of tubules that function in transport and storage.
endoplasmic reticulum
61
New cards
T/F: Chromatin is comprised predominantly of protein and RNA macromolecules.
False
62
New cards
Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of long, linear DNA molecules bound to ______ proteins.
histone
63
New cards
The cellular process in which the chromosomes of a eukaryotic cell are separated equally into daughter cells is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
* binary fission
* mitosis
* meiosis
Multiple choice question.
* binary fission
* mitosis
* meiosis
mitosis
64
New cards
Which term refers to the open spaces formed within the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Multiple choice question.
* Vesicles
* Cavitations
* Cristae
* Cisternae
Multiple choice question.
* Vesicles
* Cavitations
* Cristae
* Cisternae
Cisternae
65
New cards
Which of the following is used to describe the type of endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes associated with its membrane?
Multiple choice question.
* Ridged
* Smooth
* Rough
* Rippled
Multiple choice question.
* Ridged
* Smooth
* Rough
* Rippled
Rough
66
New cards
The cellular process in which diploid cells divide into haploid cells (sex cells) is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
* budding
* mitosis
* meiosis
* binary fission
Multiple choice question.
* budding
* mitosis
* meiosis
* binary fission
meiosis
67
New cards
The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound series of sacs and tubules that function in ___ production and __ storage
protein ; lipid
68
New cards
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) produces Blank______ while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) synthesizes Blank______.
Multiple choice question.
* lipids; proteins
* carbohydrates; lipids
* lipids; carbohydrates
* proteins; lipids
Multiple choice question.
* lipids; proteins
* carbohydrates; lipids
* lipids; carbohydrates
* proteins; lipids
proteins; lipids
69
New cards
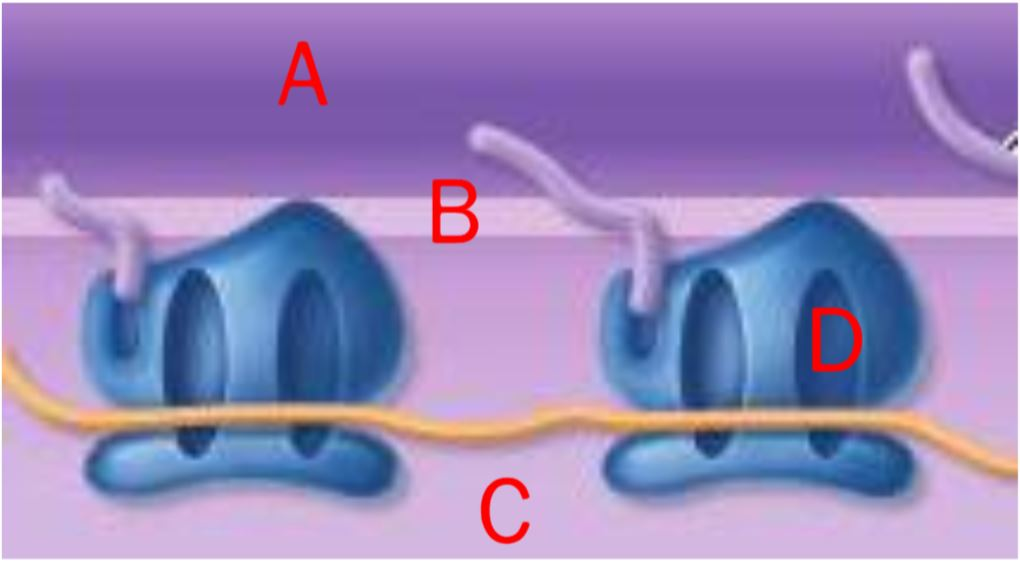
In this image of ribosomes synthesizing protein, which letter indicates the cistern of the RER?
A
70
New cards
Identify the functions of the Golgi Apparatus
protein modifications; secretion
71
New cards
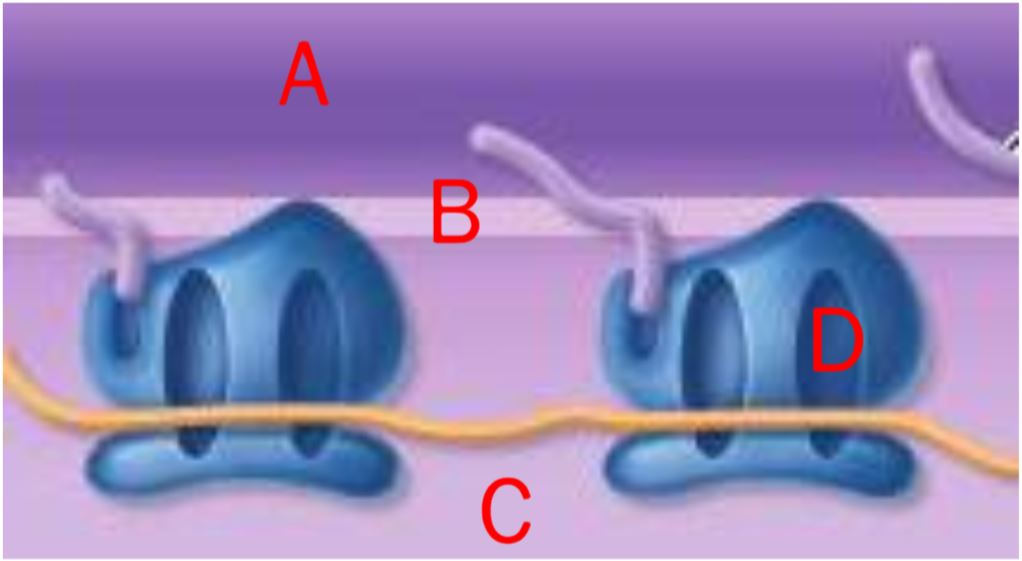
In this image of ribosomes synthesizing protein, which letter indicates the RER membrane?
B
72
New cards
Which structures are formed by the Golgi apparatus to transport products to lysosomes or the cell membrane for release through exocytosis?
Multiple choice question.
* Secretory vesicles
* Inclusion vesicles
* Transitional vesicles
* Condensing vesicles
Multiple choice question.
* Secretory vesicles
* Inclusion vesicles
* Transitional vesicles
* Condensing vesicles
Condensing vesicles
73
New cards
Where would a protein typically be synthesized if it was destined to leave the cell?
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi
* RER
* Mitochondrion
* SER
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi
* RER
* Mitochondrion
* SER
RER
74
New cards
From which organelle do lysosomes originate?
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi apparatus
* Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi apparatus
* Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
75
New cards
Membrane-bound packets that carry protein from the ER to the Golgi apparatus are called _____ vesicles.
transitional
76
New cards
Membrane-bound packets that carry modified proteins and pinch off from the Golgi apparatus are called ______ vesicles.
condensing
77
New cards
Place the following locations for protein exocytosis in order, placing the location for the first step at the top of the list.
\
Nucleus (mRNA synthesis)
Golgi Apparatus
Cell Membrane
RER (Protein synthesis)
\
Nucleus (mRNA synthesis)
Golgi Apparatus
Cell Membrane
RER (Protein synthesis)
1. Nucleus (mRNA synthesis)
2. RER (protein synthesis)
3. Golgi apparatus
4. Cell membrane
78
New cards
Which of the following is a membrane-bound organelle that contains digestive enzymes?
Multiple choice question.
* Ribosome
* Peroxisome
* Chloroplast
* Lysosome
Multiple choice question.
* Ribosome
* Peroxisome
* Chloroplast
* Lysosome
Lysosome
79
New cards
Lysosomes are produced by
golgi apparatus
80
New cards
A membrane-bound _____ is a vesicle that may contain many different types of solid or liquid particles.
vacuole
81
New cards
Which type of vesicles bud from the endoplasmic reticulum and fuse with the forming face of the Golgi apparatus?
Multiple choice question.
* Secretory
* Transitional
* Condensing
* Reticulating
Multiple choice question.
* Secretory
* Transitional
* Condensing
* Reticulating
Transitional
82
New cards
83
New cards
Which of the following organelles is immediately involved in phagocytic function by white blood cells?
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi complex
* Lysosome
* Endospore
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi complex
* Lysosome
* Endospore
lysosome
84
New cards
Which term listed below is used to describe the many different types membrane-bound sacs containing fluids or solid particles found within cells?
Multiple choice question.
* Peroxisomes
* Vacuoles
* Lysosomes
* Phagosomes
Multiple choice question.
* Peroxisomes
* Vacuoles
* Lysosomes
* Phagosomes
Vacuoles
85
New cards
Membrane-bound packets that carry protein from the ER to the Golgi apparatus are called _____ vesicles.
transport
86
New cards
Which structure helps regulate osmotic pressure in protozoan cells which live in hypotonic environments?
Multiple choice question.
* Contractile vacuole
* Mitochondrion
* Lysosome
* Phagosome
* Peroxisome
Multiple choice question.
* Contractile vacuole
* Mitochondrion
* Lysosome
* Phagosome
* Peroxisome
Contractile vacuole
87
New cards
The _______ is an organelle which merges with a vacuole to allow digestion of engulfed structures from phagocytosis.
lysosome
88
New cards
A phagosome is the fusion of ______.
Multiple choice question.
* the nucleus and a lysosome
* a food vacuole and the nucleus
* a lysosome and a food vacuole
* a food vacuole and the Golgi apparatus
Multiple choice question.
* the nucleus and a lysosome
* a food vacuole and the nucleus
* a lysosome and a food vacuole
* a food vacuole and the Golgi apparatus
a lysosome and a food vacuole
89
New cards
Which is NOT a function of a vacuole?
Multiple choice question.
* Glycogen storage
* Water removal
* Digestion
* Lipid synthesis
Multiple choice question.
* Glycogen storage
* Water removal
* Digestion
* Lipid synthesis
Lipid synthesis
90
New cards
Which of the following organelles has both an inner and an outer membrane?
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi
* Mitochondrion
* Endoplasmic reticulum
* Lysosome
Multiple choice question.
* Golgi
* Mitochondrion
* Endoplasmic reticulum
* Lysosome
Mitochondrion
91
New cards
The ______ vacuole helps regulate osmotic pressure by expelling excess water that has diffused into a protozoan cell.
Multiple choice question.
* lysosomal
* ribosome
* peroxide
* contractile
Multiple choice question.
* lysosomal
* ribosome
* peroxide
* contractile
contractile
92
New cards
\
Order the steps in phagocytosis, putting the first step at the top of the list.
* Merger of lysosome and phagosome
* Formation of food vacuole
* Digestion
* Engulfment of food
Order the steps in phagocytosis, putting the first step at the top of the list.
* Merger of lysosome and phagosome
* Formation of food vacuole
* Digestion
* Engulfment of food
1. Engulfment of food
2. Formation of food vacuole
3. Merger of lysosome and phagosome
4. Digestion
93
New cards
94
New cards
What name is given to the tubular, finger-like internal membrane structures of the mitochondrion?
Multiple choice question.
* Outer membrane
* Microtubules
* Cristae
* Matrix
Multiple choice question.
* Outer membrane
* Microtubules
* Cristae
* Matrix
Cristae
95
New cards
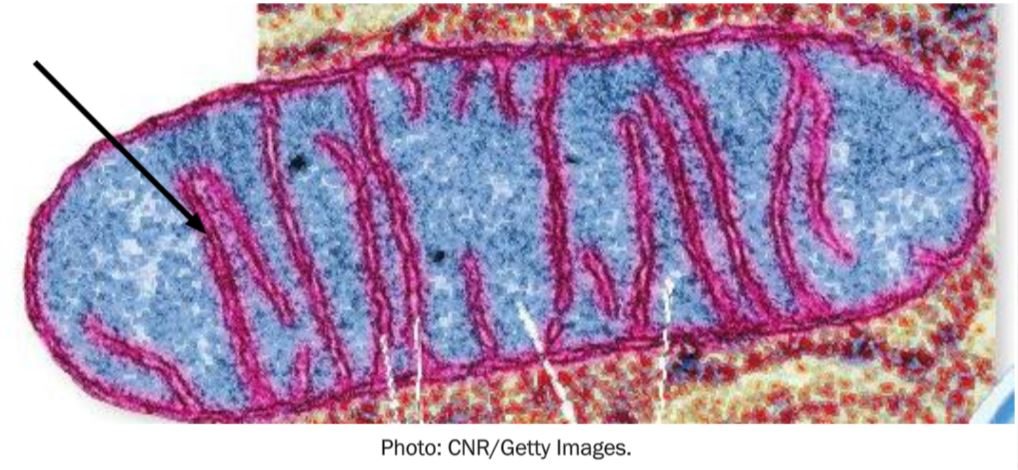
The name for the folded membrane within the mitochondrion indicated by the arrow is a(n)
cristae
96
New cards
What is the principal function of mitochondria?
Multiple choice question.
* Motility
* Secretion
* Protein synthesis
* DNA synthesis
* ATP production
Multiple choice question.
* Motility
* Secretion
* Protein synthesis
* DNA synthesis
* ATP production
ATP production
97
New cards
Which region of the mitochondrion contains fluid, ribosomes and is the location for the metabolic cycle?
Multiple choice question.
* Matrix
* Ribosome
* Outer membrane
* Cristae
Multiple choice question.
* Matrix
* Ribosome
* Outer membrane
* Cristae
Matrix
98
New cards
Often called the "powerhouse" of cells, the ______ is the organelle where ATP is synthesized for cellular energy use.
mitochondria
99
New cards
Mitochondrial DNA is ______.
Multiple choice question.
* circular
* linear
Multiple choice question.
* circular
* linear
circular
100
New cards