Field Methods Research
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FM LAB
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Field methods research
Practical application of research techniques outside controlled laboratory settings
Benefits
High ecological validity
Real behavior in natural context
Limitations
Less control over variables
Ethical and logistical constraints
Research
Systematic process of colleting, analyzing, and interpreting data
Involves empirical investigations, controlled and critical methods, and hypothetical propositions
Research = experience + reasoning
Importance of Research
Human advancement relies on the creation and application of new theories and knowledge which is achieved through systematic research
Research integrates methodology, strategy, and critical inquiry
Objectives of research
To develop or to support theory
To create new knowledge
Theory
Set of statements explaining phenomena and relationships
Knowledge
Information and understanding gained by study or experience
Two pathways of knowledge
Experience
Reasoning
Experience
Acquired through living, observation, and interactionR
Reasoning
Reaching conclusion through logic and argument
Research Methodology/ Approach
Overarching philosophical and methodological orientation or the big picture
Qualitative, Quantitative, Mixed Methods
Research Design
Overall strategy or blueprint for conducting research
Descriptive, Correlational
What and How the research will be conducted
Re
Research Methods
Specific techniques or procedures used to gather and analyze data
Interviews, surveys, observation
How exactly data will be collected, measured, and analyzed
Res
Types of research design
Experimental
Correlational
Descriptive
Phenomenology
Explanatory Sequential
Exploratory Sequential
Convergent Parallel
Experimental
Manipulates variables to test causal relationships
Correlational
Examines relationships between variables
Descriptive
Describes characteristics or behaviors
Phenomenology
Explores lived experiences or social phenomena deeply
Explanatory Sequential
Quantitative —> Qualitative; qualitative data is used to explain the quantitative data
Used to answer why and how; topic is known
Exploratory Sequential
Qualitative —> Quantitative; Qualitative data is used to explore and identify important themes, then quantitative data is used to test or measure them with a larger group
Used to discover; topic is new
Convergent Parallel
Collect quantitative (numbers) and qualitative (stories) data at the same time
Analyze each separately, then compare to see if they match, conflict, or complement
used to confirm, validate, or complement results
comprehensive and time-efficient (both types collected together)
Researchers must be skilled in both methods; integration can be tricky if results disagree
Example of Convergent Parallel
“Understanding Test Anxiety Among Senior High School Students”
a. Quantitative: Survey 150 students to measure anxiety levels.
b. Qualitative: Interview 8–10 students to hear personal experiences.
c. compare results for consistency and deeper understanding.
Research Methods
Survey/Questionnaires
Interviews
Observation
Experiments
Focus Groups
Surveys/Questionnaires
Collecting structured responses from many respondents
Interviews
In-depth understanding of individual perspectives
Observation
Watching behaviors in natural and controlled settings
Experiments
Testing hypothesis with variable manipulation
Focus groups
Interactive group discussions for exploring perspectives
Cornerstone of Research
Concept
Theory
Model
Construct
Variable
Proposition
Hypothesis
Concept
General idea or understanding of a phenomenon
Provides the basic unit of meaning in a study
Clear conceptualization ensures reader interprets your research correctly
Thoery
Set of principles intended to explain facts or events
Explain why something happens
Provides a framework for analyzing and interpreting findings
Model
A representation of a problem, system, or process
Explain why something happens
Provides framework for analyzing and interpreting findings
Construct
Abstract idea created for research purposes, often not directly observable
Central in psychological research since it operationalizes intangible concepts
Variable
Measurable component of a construct or concept
Types of Variable
Independent - cause
Dependent - effect
Mediating - explains
Moderating - changes the form or intensity
Control - constant
Mediating
explains
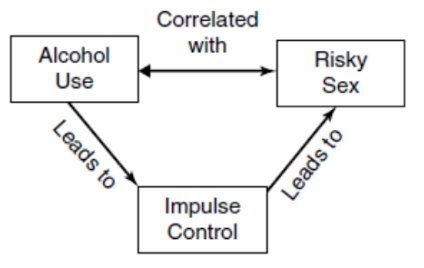
Moderating
changes the form or intensity
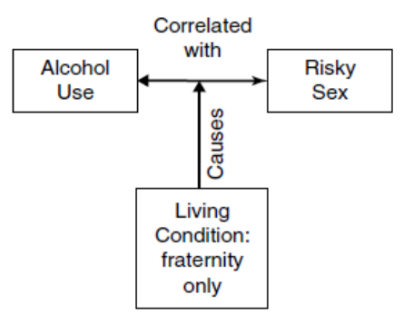
Proposition
Statement that proposes a relationship between two or more concepts of variables
Tentative explanation that can be tested and potentially lead to a hypothesis
Often derived from existing theories or observations
“Empathy influences altruistic behavior among young adults”
Hypothesis
Testable prediction about the relationship between variables
Provides a specific direction for analysis
"Filipino undergraduate students with higher empathy scores will have higher altruism scores”