17. Non-covalent bonds
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Are non covalent bonds stronger or weaker than covalent?
Weaker.
What is bonding strength measured in?
Kj/mol
Non-covalent bonds are…
Weak, distance dependant, have a varying degree of directionality and convey shape.
Give examples of when noncovalent bonds are important in bio:
DNA strands built by covalent interactions and held together by H bonds to allow unzipping
Hydrophobic interactions ensure membranes don’t break apart but remain fluid and flexible
Proteins must remain structured yet flexible to interact with other molecules
Extended structure of cellulose to allow extensive H bonding
Why are non-covalent bonds so important in biology?
individually weak
Collectively strong
Give flexibility
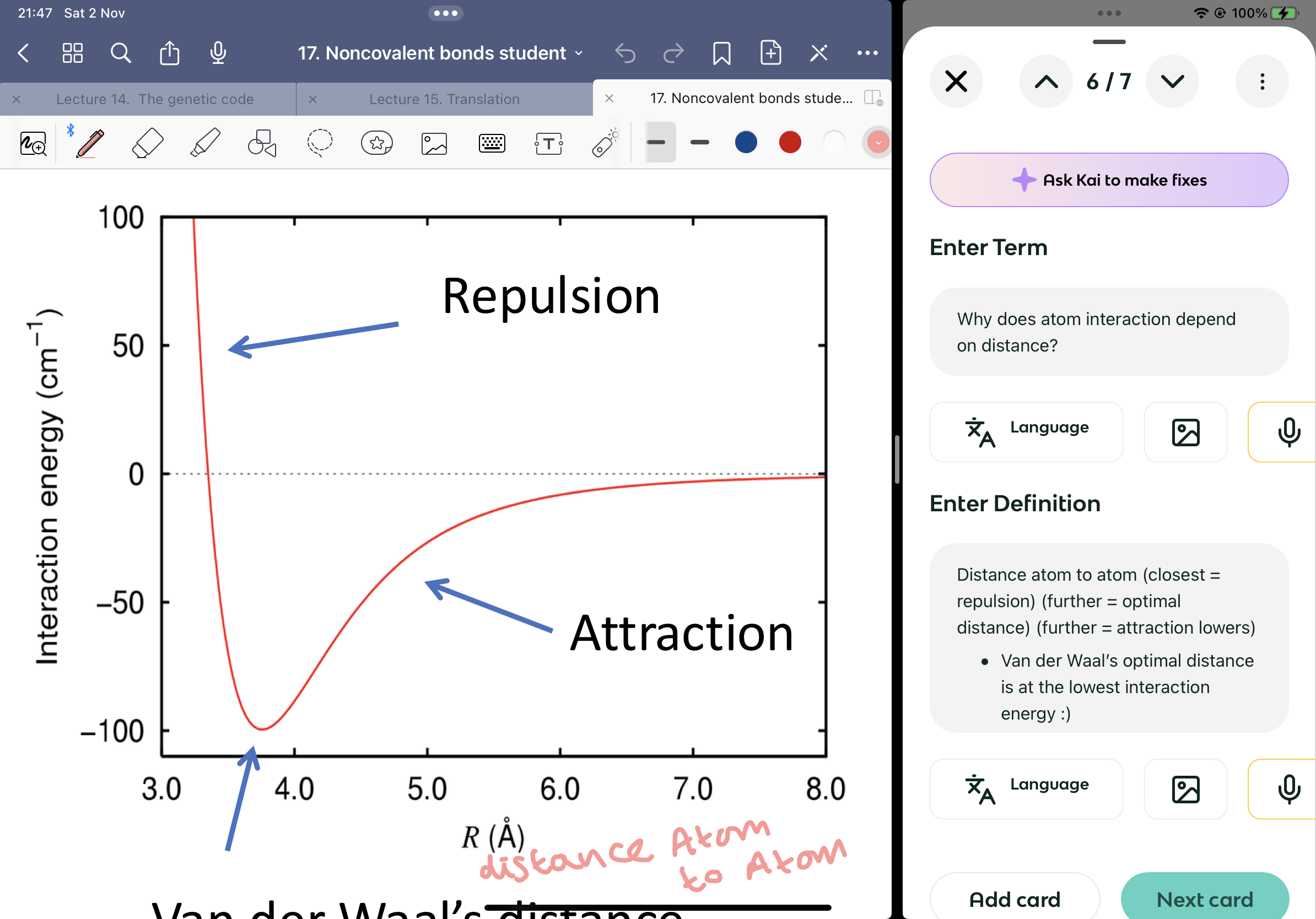
Why does atom interaction depend on distance?
Distance atom to atom (closest = repulsion) (further = optimal distance) (further = attraction lowers)
Van der Waal’s optimal distance is at the lowest interaction energy :)
What are Van der Waals?
An umbrella term for several non-covalent interactions. Eg. Gecko feet having extended surfaces that make van de waal’s interactions with walls.
How much more stable is the native form of a protein (folded) compared to the denatured form?
The stability is equivalent to the energy of a couple of hydrogen bonds.
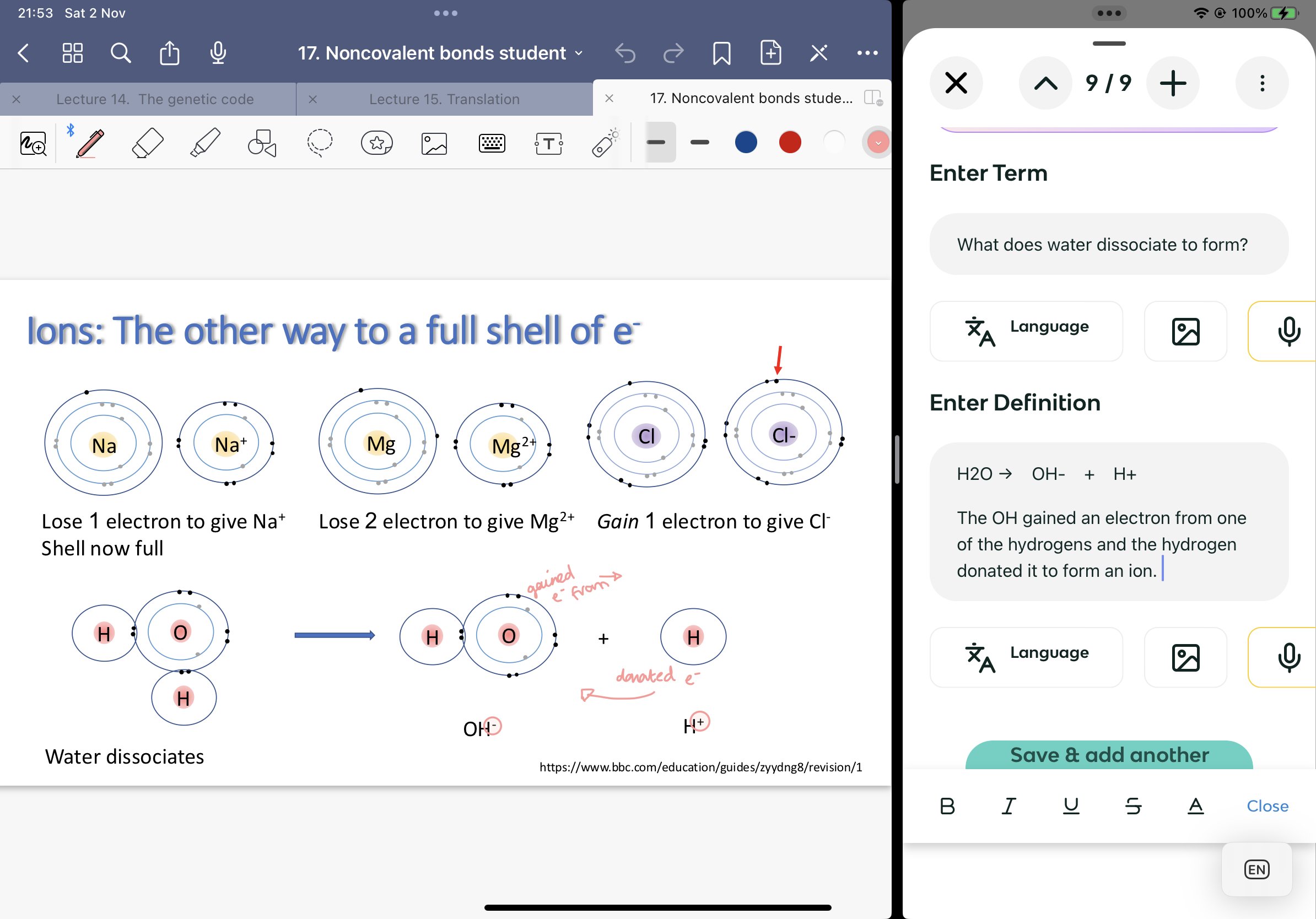
What does water dissociate to form?
H2O → OH- + H+
The OH gained an electron from one of the hydrogens and the hydrogen donated it to form an ion.
What are lone pairs?
Electron pairs not engaging in the covalent bond.
Why are metal ions important?
They often are part of proteins. They bind to charge and polar parts of the proteins.
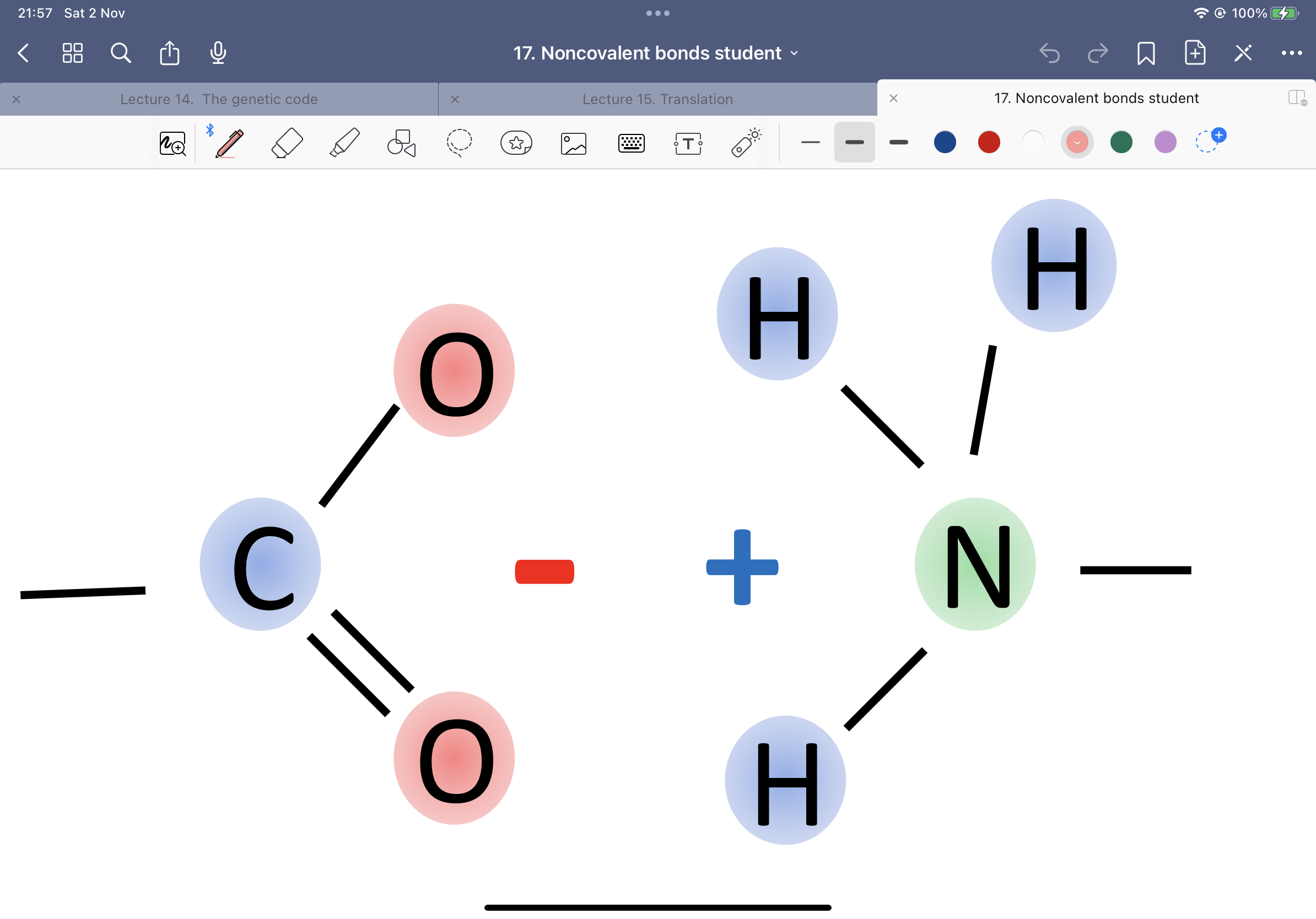
What is this an example of?
Carboxyl and amino group forming a salt bridge. (Weak).
Are ionic bonds strong?
In solids such as NaCl crystals. Very strong (often stronger than covalent bonds)
Oxygen holds onto the electrons tighter than the hydrogens in water, meaning…
The O is slightly negatively charged and the Hs positive.
List elements in their order of electronegativity (the power they have to attract electrons to themselves):
highest
fluorine - 4
Oxygen - 3.5
Nitrogen - 3.0
Sulfur - 2.5
Carbon - 2.5
Hydrogen - 2.1
Lowest
Show a dipole dipole interaction:
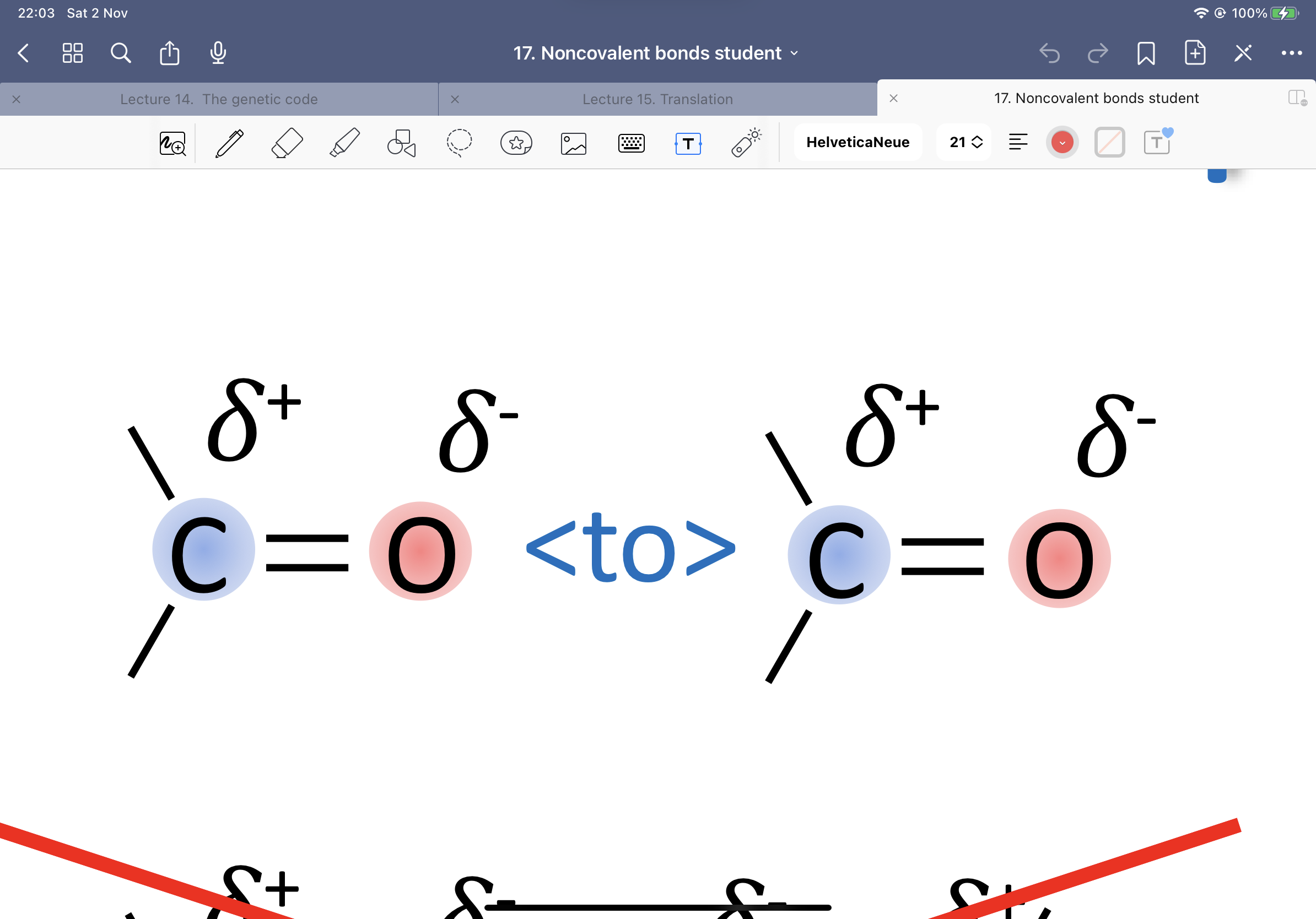
Show a dipole to ion interaction:
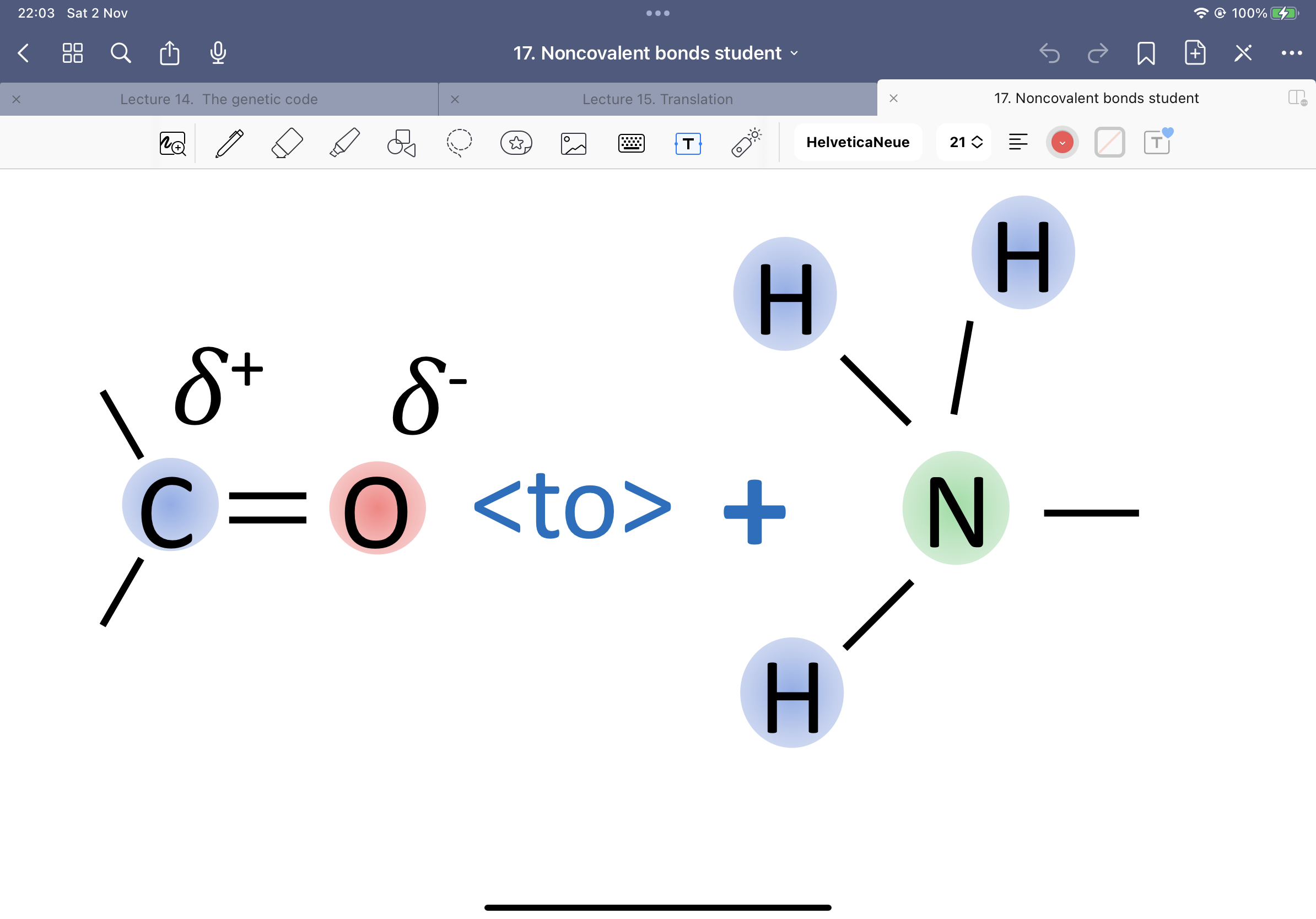
Hydrogens can be donors or acceptors. Give an example of both:
Donor - polar covalent bond between hydrogen and nitrogen or oxygen
Acceptor - oxygen and nitrogen
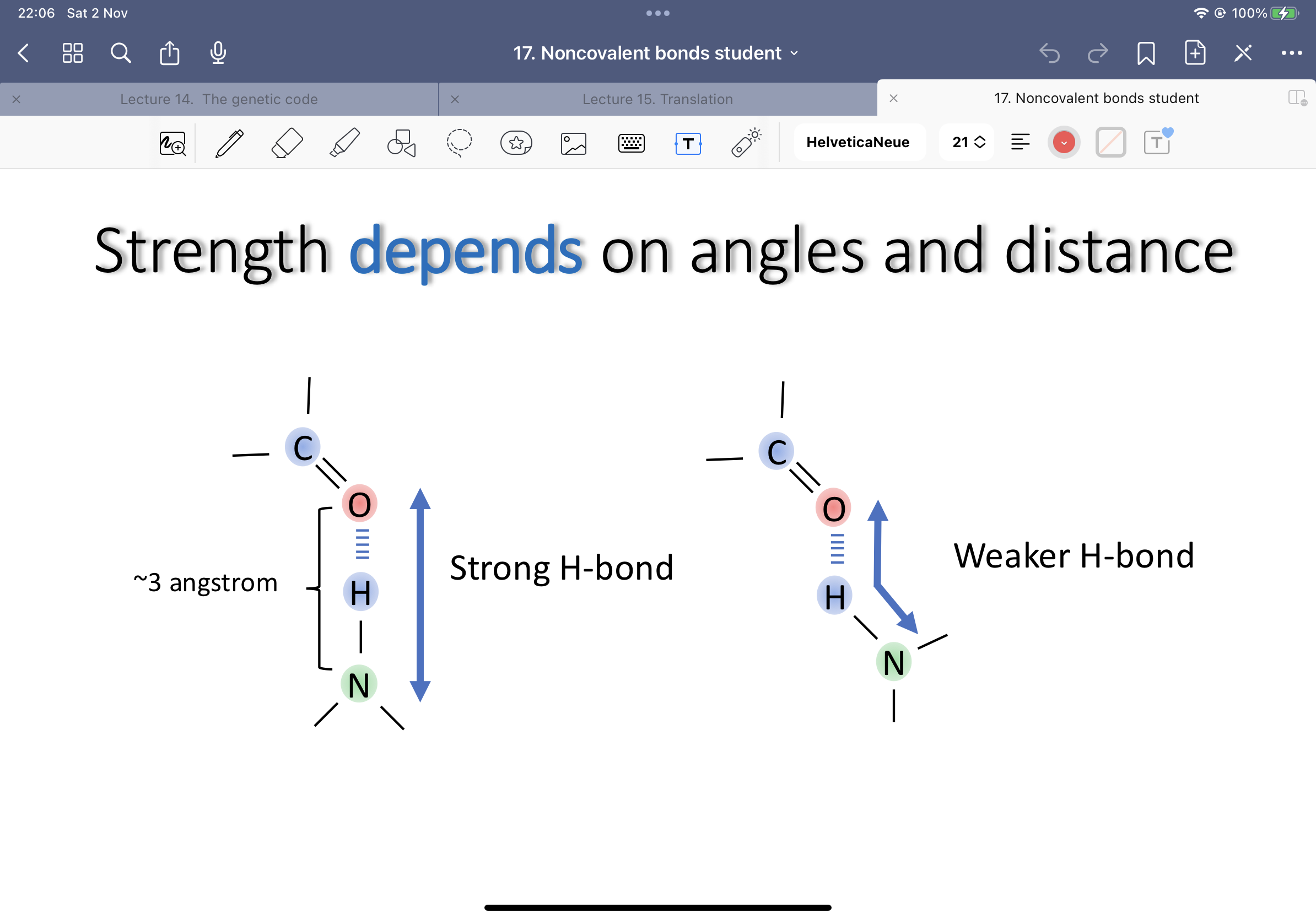
Show how strength of the bonds depends on angles and distance:
What are dispersion forces?
Interaction between temporary dipoles induced by proximity. Weak electrostatic interactions. Interaction between atoms in close space. Important in macro molecular structures.
Why is water highly unusual? Properties:
The solid form floats. There are three forms of it.
excellent solvent
Cause of hydrophobic interaction
High heat capacity
High vaporisation heat
Freezes from the top downwards
Strong cohesion and adhesion
Describe water (molecular):
electronegative
2 lone pairs
Polar bonds
Makes 4 hydrogen bonds
Not volatile
Higher melting and boiling point than expected (due to many non-covalent bonds that need breaking)
Water is an excellent solvent for __ molecules.
Hydrophilic
What happens differently with hydrophobic molecules?
An ordered lattice like structure forms round them. This is energy costly.