The Multi-store model of memory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Multi-store model
A representation of how memory works in terms of 3 stores.
Sensory register
Short term memory
Long term memory
Also describes how information is transferred from one store to another, what makes some memories last and others disappear.
Sensory register
The memory stores for each of our 5 senses like vision (iconic) and hearing (echoic).
Coding in the iconic sensory register is visual and in the echoic sensory register is acoustic. The capacity of SRs is huge. Information lasts for around 0.05 seconds for iconic but up to 3 seconds for echoic memory
Atkinson and Shiffrin
Made the multi-store model.
Describes how information flows through the memory system
Suggests memory is made of 3 stores (boxes) linked by processing (arrows)
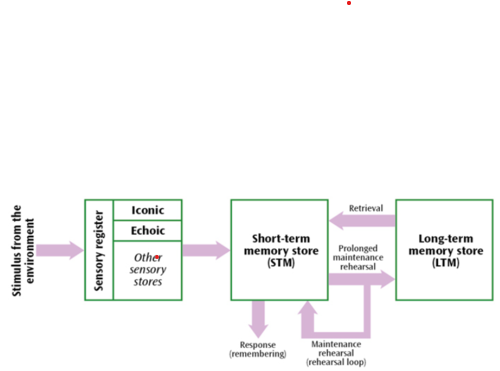
Pathway of information to long-term memory
Environmental input and senses receive it. Gets put in the sensory registers
Passes onto STM when attention paid to information.
Held in STM if information is rehearsed.
Transfer to LTM when rehearsed elaboratively.
Goes back into STM through retrieval.
Information can leave STM or LTM through forgetting it
STM in the multi-store model
Mainly encoded acoustically and lasts about 18 seconds unless rehearsed. Temporary store.
Limited capacity as it can hold a certain number of things before you forget it. 5-9 items
Maintenance rehearsal
We repeat materials to ourselves over and over again. We keep the information in STM if we rehearse it.
Passes into LTM if we rehearse it long enough
LTM in multi-store model
Permanent memory store for info that has been rehearsed.
Encoded semantically. Duration up to a lifetime.
Retrieval
Transfer from LTM to STM
Murdock 1962
Gave participants 20 words to remember. Each word flashed up for a second before next word was shown.
Write as many as they can after the last word
Highest % recall at the start and end
U-shaped graph
Primacy effect
First words heard so they can be rehearsed so we can recall them from our LTM
Recency effect
Most recently heard words so we can recall them as they are still in our STM
Squire 2009 - Separate stores
Reviewed neuroimaging studies that compared brain areas associated with STM and LTM.
Showed the prefrontal cortex is active during tasks involving STM.
The hippocampus was associated with the reorganisation of memories during LTM.
Suggest that STM and LTM are separate stores, supports the MSM
Contradiction to Squire
Ranganath and Blumenfield 2005
Pointed out that there is an overlap and interaction between the brain regions that support STM and LTM.
Hippocampus also involved in STM tasks, particularly with new or complex information.
The evidence for separation of STM and LTM isn’t as strong.
Craik and Watkins 1973
Found that the type of rehearsal is more important than the amount.
Elaborative rehearsal is needed - Linking information to your existing knowledge or you think about what it means.
Information can be transferred to LTM without maintenance rehearsal
Suggests that MSM doesn’t fully explain how long term storage is achieved.
Tulving 1985
Proposed that LTM could be subdivided into different types of LTM.
Semantic and Episodic - Knowledge about the world and memories for events in your life.
Cognitive psychology focuses on different types of memory and ignores the MSM
Wixted 2024
Argues that psychologists misunderstood the MSM.
Never intended as a specific theory but as a framework for incorporating our changing understandings of how memory works.
Shallice and Warrington
Reduced STM after a motorbike accident
Only recall 1 or 2 digits from STM but LTM was fine.
K.F.’s deficit only for verbal information but visual information was normal
Concluded there may be more than 1 type of STM and it isn’t explained by the MSM.
Contradicts the MSM model as it suggests all information goes through STM to get to LTM
Clive Wearing
Contracted a brain infection in 1985 - damaged parts of his brain including the hippocampus.
Left with some LTM like knowing he is married
No episodic memory
Inability to form new memories and can’t transfer information into LTM. Limited to STM
Bill Scoville 1953
Tried an experimental technique to cure someone’s epilepsy.
Cut a hole in HM’s head and sucked out part of his brain including the hippocampus.
Lost the ability to encode new memories and was stuck in the past and present.
Normal STM but incapable of transferring to LTM.