Hearing Healthcare context and ICF
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Prevalence of hearing loss
1.5 billion people globally
increases with degree of hearing loss
increases with age
HA uptake in high income countries
Between 14-30%
Sonova share of HA market
31%
retail outlets they own in NZ are Triton Hearing and Blamey Saunders
Demant share of HA market
30%
retail outlets in NZ are Audika and Hearing Life
WS Audiology share of HA market
19%
retail outlet in NZ is Bloom
GN Nord Store share of HA market
15%
doesn’t have retail outlet
Non-manufacturer Retail Outlets
Amplifon - Bay Audiology and Dilworth Hearing (largest retail outlet for HAs in NZ)
Specsavers
Independent audiology clinics in canterbury
Bishopdale Hearing
Hearing Excellence
Bellbird Hearing
Sincock & Till Audiology
Hear Again
New Zealand Hearing
Vera Setz Hearing
Resonate
Who provides HA funding and to whom?
Ministry of Health provides hearing aid subsidy to permanent residents and citizens
subsidy provides $511.11 per hearing aid every 6 years
HA funding for children and some eligible adults
Ministry of Health covers entire cost of HAs and HA fitting
HA funding for HL due to injury
ACC funds HAs
HA funding for veterans
Veteran’s Support Act provides funding for HAs for eligible veterans with service-connected HL
ICF
biopsychosocial model that combines biological, psychological, and social elements into a single model
disability and functions seen as outcomes of the interactions between a person’s health condition and contextual factors
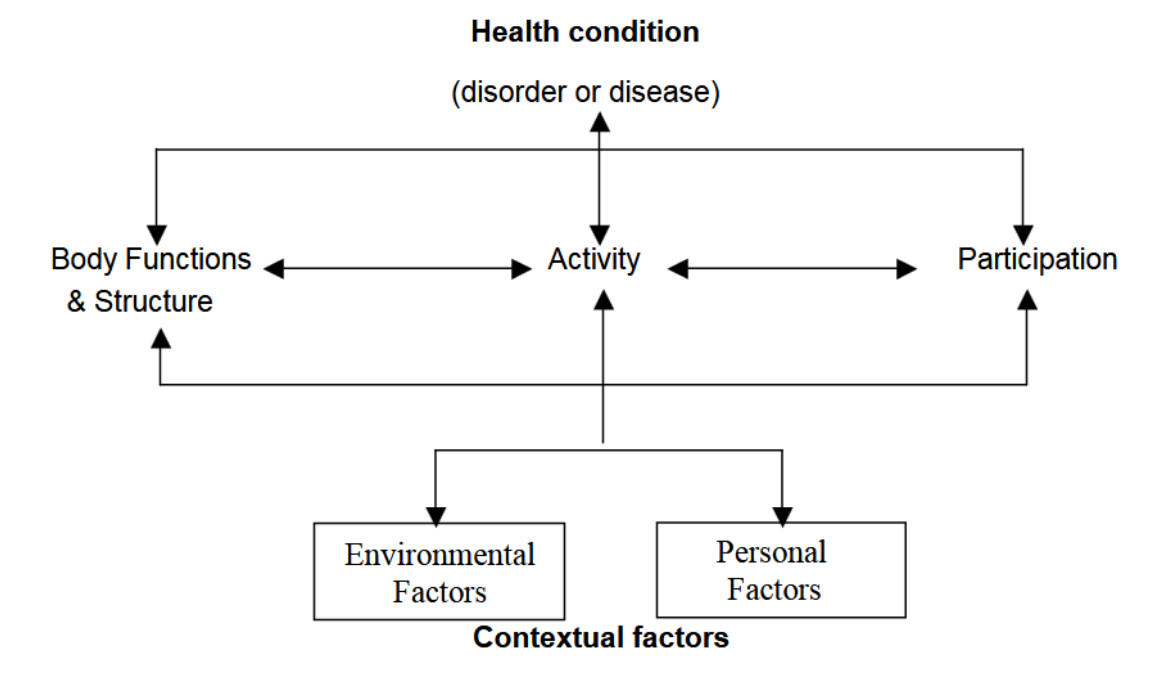
Health condition
label that you put on the person’s health e.g. presbycusis
can be a disease (e.g., diabetes) or a disorder (e.g., depression)
impacts functioning, but also impacted by functioning
Bodily functions and structures
aspects of the person’s body that are affected by the health condition
Impairment
negative expression of body fxns and structures
problems w/ body structures and/or fxns
e.g. mild sloping to moderate SNHL (degree, type and configuration of HL)
Activity
Something the person would like to do
e.g. hear GP and understand their instructions
Activity limitations
something the person would like to do but can’t because of their impairment
negative expression of activity
e.g.
can’t hear phone ring
can’t hear soft speech
can’t understand what people are saying in noise
can’t understand dialogue on TV
Participation
being involved in life events - it’s social
e.g. socialising with friends at the cafe
Participation restrictions
not being able to engage socially in life events
negative expression of participation
e.g.
miss out on chatting with friends on phone
don’t participate in small group activities in classroom
don’t go to the pub with friends
don’t watch TV as a family
Environmental factors
relate to anything in the environment (external to person with health condition)
can be physical, social, or attitudinal
Environmental facilitator
things in environment which can improve or enhance functioning
positive expression of environmental factor
e.g. supportive family, hearing aids etc
Environmental barriers
things in the environment that make functioning more difficult
negative expression of environmental factors
e.g. being in noisy group setting, bullying from peers about wearing HAs
Personal factors
anything about that person that either improves or hinders their functioning
e.g. age, gender, financial resources, psychological resources, personality, coping style, education, profession, past and current experience, and behaviour patterns
Third Party Disability
effect of others without the health condition
e.g. don’t go to pub because of partner’s participation restriction, don’t enjoy watching TV as a family