Psychological Theories and Treatment Methods
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Therapy
treatment methods aimed at making people feel better and function more effectively.
Psychotherapy
therapy for mental disorders in which a person with a problem talks with a psychological professional.
Insight therapies
psychotherapies in which the main goal is helping people to gain insight with respect to their behavior, thoughts, and feelings.
Action therapy
psychotherapy in which the main goal is to change disordered or inappropriate behavior directly.
Biomedical therapy
therapy for mental disorders in which a person with a problem is treated with biological or medical methods to relieve symptoms.
Psychoanalysis
an insight therapy based on the theory of Freud, emphasizing the revealing of unconscious conflicts.
Dream interpretation
the process of analyzing the content of dreams to uncover hidden meanings.
Manifest content
the actual content of one's dream.
Latent content
the symbolic or hidden meaning of dreams.
Free association
Freudian technique in which a patient was encouraged to talk about anything that came to mind without fear of negative evaluations.
Resistance
occurring when a patient becomes reluctant to talk about a certain topic, either changing the subject or becoming silent.
Transference
in psychoanalysis, the tendency for a patient or client to project positive or negative feelings for important people from the past onto the therapist.
Psychodynamic therapy
a newer and more general term for therapies based on psychoanalysis, with an emphasis on transference, shorter treatment times, and a more direct therapeutic approach.
Directive
therapy in which the therapist actively gives interpretations of a client's statements and may suggest certain behavior or actions.
Nondirective
therapy style in which the therapist remains relatively neutral and does not interpret or take direct actions with regard to the client, instead remaining a calm, nonjudgmental listener while the client talks.
Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
form of therapy for depression which incorporates multiple approaches and focuses on interpersonal problems.
Person-centered therapy
a nondirective insight therapy based on the work of Carl Rogers in which the client does all the talking and the therapist listens.
Reflection
therapy technique in which the therapist restates what the client says rather than interpreting those statements.
Unconditional positive regard
referring to the warmth, respect, and accepting atmosphere created by the therapist for the client in person-centered therapy.
Empathy
the ability of the therapist to understand the feelings of the client.
Authenticity
the genuine, open, and honest response of the therapist to the client.
Motivational Interviewing
In contrast to client-centered, MI has specific goals, to reduce ambivalence about change and to increase intrinsic motivation to bring that change about.
Gestalt therapy
form of directive insight therapy in which the therapist helps clients to accept all parts of their feelings and subjective experiences, using leading questions and planned experiences such as role-playing.
Humanistic therapies
are not based in experimental research and work best with intelligent, highly verbal persons.
Behavior therapies
action therapies based on the principles of classical and operant conditioning and aimed at changing disordered behavior without concern for the original causes of such behavior.
Behavior modification or applied behavior analysis
the use of learning techniques to modify or change undesirable behavior and increase desirable behavior.
Systematic desensitization
behavior technique used to treat phobias, in which a client is asked to make a list of ordered fears and taught to relax while concentrating on those fears.
Counterconditioning
replacing an old conditioned response with a new one by changing the unconditioned stimulus.
Aversion therapy
form of behavioral therapy in which an undesirable behavior is paired with an aversive stimulus to reduce the frequency of the behavior.
Exposure Therapy
Behavioral techniques that introduce the client to situations, under carefully controlled conditions, which are related to their anxieties or fears.
Flooding
technique for treating phobias and other stress disorders in which the person is rapidly and intensely exposed to the fear-provoking situation or object and prevented from making the usual avoidance or escape response.
Eye-movement desensitization reprocessing (EMDR)
controversial form of therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder and similar anxiety problems in which the client is directed to move the eyes rapidly back and forth while thinking of a disturbing memory.
Modeling
learning through the observation and imitation of others.
Participant modeling
technique in which a model demonstrates the desired behavior in a step-by-step, gradual process while the client is encouraged to imitate the model.
Reinforcement
the strengthening of a response by following it with a pleasurable consequence or the removal of an unpleasant stimulus.
Token economy
the use of objects called tokens to reinforce behavior in which the tokens can be accumulated and exchanged for desired items or privileges.
Contingency contract
A formal, written agreement between the therapist and client (or teacher and student) in which goals for behavioral change, reinforcements, and penalties are clearly stated.
Extinction
The removal of a reinforcer to reduce the frequency of a behavior.
Time-out
An extinction process in which a person is removed from the situation that provides reinforcement for undesirable behavior, usually by being placed in a quiet corner or room away from possible attention and reinforcement opportunities.
Behavior therapies
Can be effective in treating specific problems, such as bedwetting, drug addictions, and phobias. Can help improve some of the more troubling behavioral symptoms associated with more severe disorders.
Cognitive therapy
Therapy in which the focus is on helping clients recognize distortions in their thinking and replace distorted, unrealistic beliefs with more realistic, helpful thoughts.
Arbitrary inference
Distortion of thinking in which a person draws a conclusion that is not based on any evidence.
Selective thinking
Distortion of thinking in which a person focuses on only one aspect of a situation while ignoring all other relevant aspects.
Overgeneralization
Distortion of thinking in which a person draws sweeping conclusions based on only one incident or event and applies those conclusions to events that are unrelated to the original.
Magnification and minimization
Distortions of thinking in which a person blows a negative event out of proportion to its importance (magnification) while ignoring relevant positive events (minimization).
Personalization
Distortion of thinking in which a person takes responsibility or blame for events that are unconnected to the person.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
Action therapy in which the goal is to help clients overcome problems by learning to think more rationally and logically.
Goals of cognitive-behavioral therapy
Relieve the symptoms and solve the problems. To develop strategies for solving future problems. To help change irrational, distorted thinking.
Rational-emotive behavior therapy (REBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy in which clients are directly challenged in their irrational beliefs and helped to restructure their thinking into more rational belief statements.
Success of CBT
CBT has seemed successful in treating depression, stress disorders, and anxiety. Criticized for focusing on the symptoms and not the causes of disordered behavior.
Family counseling (family therapy)
A form of group therapy in which family members meet together with a counselor or therapist to resolve problems that affect the entire family.
Self-help groups (support groups)
A group composed of people who have similar problems and who meet together without a therapist or counselor for the purpose of discussion, problem solving, and social and emotional support.
When is Group Therapy Useful?
Group therapy is most useful to persons who cannot afford individual therapy and who may obtain a great deal of social and emotional support from other group members.
Advantages of Group Therapy
Low cost. Exposure to other people with similar problems, social interaction with others. Social and emotional support from people with similar disorders or problems.
Disadvantages of Group Therapy
Need to share the therapist's time with others in the group. Lack of a private setting in which to reveal concerns.
Effectiveness of Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is more effective than no treatment at all. From 75 to 90 percent of people who receive therapy improve, the longer a person stays in therapy the better the improvement, and psychotherapy works as well alone as with drugs.
Types of Psychotherapy
Some types of psychotherapy are more effective for certain types of problems, and no one psychotherapy method is effective for all problems.
Effective Therapy
Effective therapy should be matched to the particular client and the particular problem.
Eclectic Therapies
Eclectic therapies - therapy style that results from combining elements of several different therapy techniques.
Therapeutic Alliance
Therapeutic alliance - the relationship between therapist and client that develops as a warm, caring, accepting relationship characterized by empathy, mutual respect, and understanding.
Common Factors Approach
Common factors approach. Opportunity for catharsis. Learning and practicing new behaviors. Positive experiences.
Cultural Barriers in Psychotherapy
When the culture, ethnic group, or gender of the therapist and the client differs, misunderstandings and misinterpretations can occur.
Barriers to Effective Psychotherapy
Four barriers to effective psychotherapy that exist when the backgrounds of client and therapist differ are language, cultural-bound values, class-bound values, and nonverbal communication.
Cybertherapy
Cybertherapy - psychotherapy that is offered on the Internet. Also called online, Internet, or Web therapy or counseling.
Advantages of Cybertherapy
Offers the advantages of anonymity and therapy for people who cannot otherwise get to a therapist.
Biomedical Therapies
Biomedical therapies - therapies that directly affect the biological functioning of the body and brain.
Psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology - the use of drugs to control or relieve the symptoms of psychological disorders.
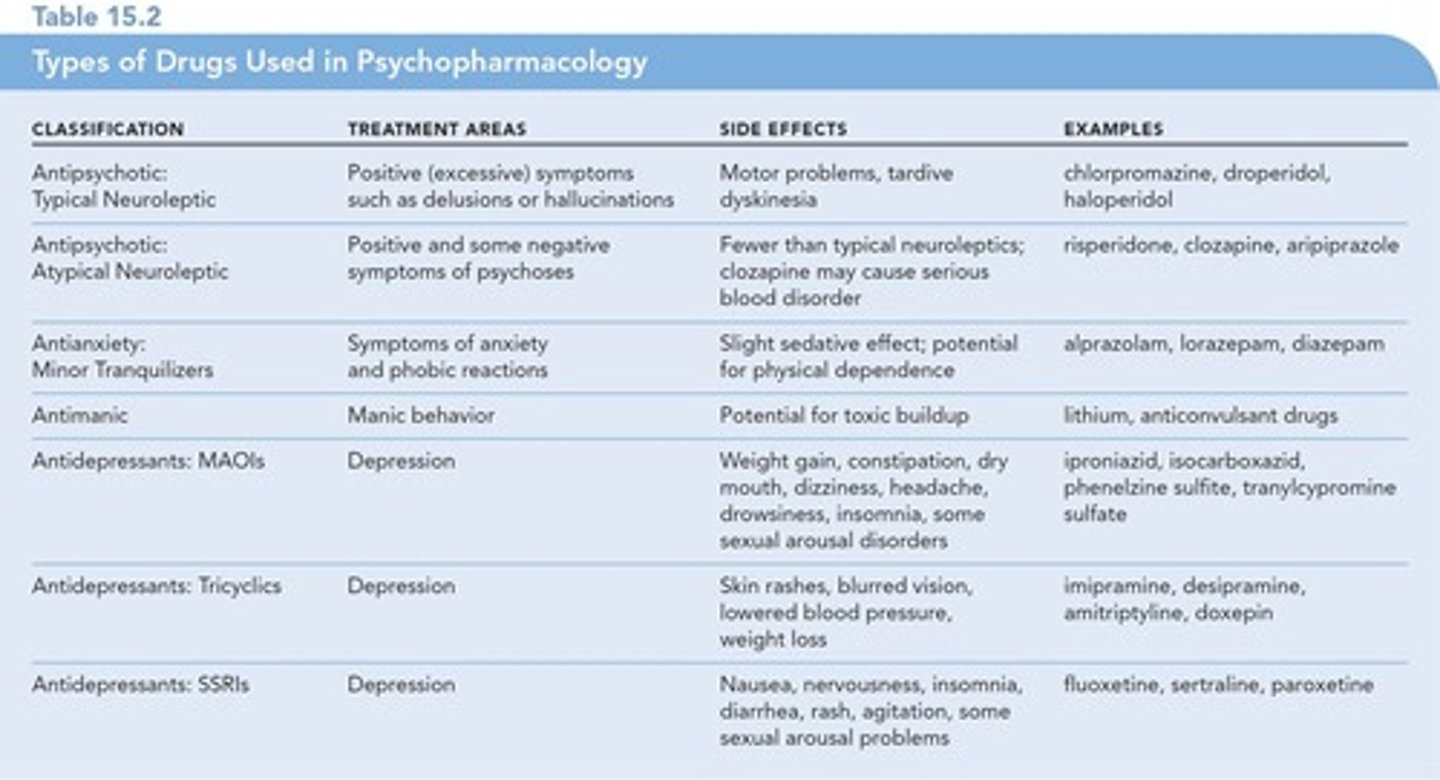
Antipsychotic Drugs
Antipsychotic drugs - drugs used to treat psychotic symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, and other bizarre behavior.
Antianxiety Drugs
Antianxiety drugs - drugs used to treat and calm anxiety reactions, typically minor tranquilizers.
Antimanic Drugs
Antimanic drugs - used to treat bipolar disorder and include lithium and certain anticonvulsant drugs.
Antidepressant Drugs
Antidepressant drugs - drugs used to treat depression and anxiety.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) - form of biomedical therapy to treat severe depression in which electrodes are placed on either one or both sides of a person's head and an electric current is passed through the electrodes that is strong enough to cause a seizure or convulsion.
Psychosurgery
Psychosurgery - surgery performed on brain tissue to relieve or control severe psychological disorders.
Prefrontal Lobotomy
Prefrontal lobotomy - psychosurgery in which the connections of the prefrontal lobes of the brain to the rear portions are severed.
Bilateral Anterior Cingulotomy
Bilateral anterior cingulotomy - psychosurgical technique in which an electrode wire is inserted into the anterior cingulated gyrus area of the brain with the guidance of a magnetic resonance imaging machine for the purpose of destroying that area of brain tissue with an electric current.
Emerging Techniques in Psychosurgery
Emerging techniques - repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), where magnetic pulses are applied to the cortex and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which uses scalp electrodes to pass very low amplitude direct currents to the brain.
Virtual Reality in Psychotherapy
Virtual reality - is a software generated three-dimensional simulated environment which can be used in the treatment of PTSD.