Lecture 6 -- Forelimb Anatomy and Nerve Supply Flashcards
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
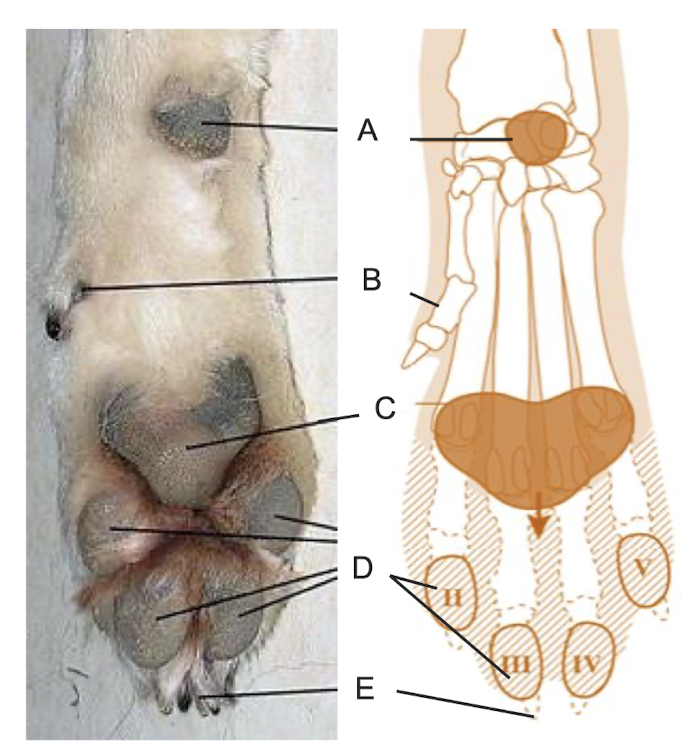
Describes the labelling features.
A: Carpal pad
Protect accessory carpal bone
B: Dew clew
C: Metacarpal pad
Overlies metacarpo-phalangeal joint
D:Digital pad
Overlies distal interphalangeal joint
E: Claw
What is the function of the carpal pad specifically?
Protects the accessory carpal bone
What are the functions of footpads?
Resistance to trauma/wear and tear
Traction = Prevent slipping
Anti-concussive 防震
Protection of deep structures
Support of the digit → Allow weight bearing over DP, MP, PP and MCP joints
What are the modifications to the epidermis of the footpad for trauma resistance?
Increased skin thickness
Increased turnover of cells (Active germinative layer = Stratum basale)
Deposition of keratin (Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium)
Rough surface
Sweat glands
Variable amounts of pigmentation
Hairless, thick skin.
What are the components of a footpad?
Skin
Epidermis
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale = Germinative layer
Dermis
Superficial fascia
Digital cushion
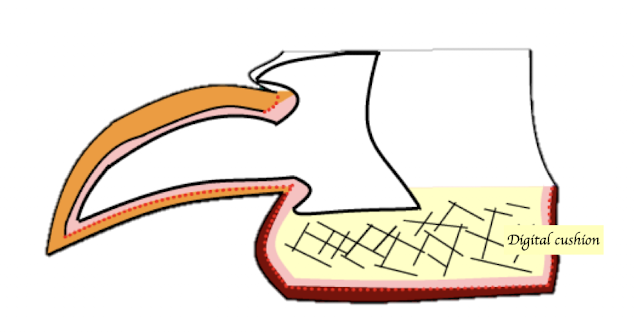
What is the function of the digital cushion in the footpad?
Vacular supply and Shock absorption
What clinical consideration of footpad?
Damage of DDFT → Stubbed toes (Hyperextension of digits)
Careful with bandaging → Sweat gland around footpad
Wounds (Contain excessive vascular channels)
Describe the normal position of a claw.
How is the normal claw position maintained?
Tip touches ground.
Extensor tendons, dorsal elastic ligament, balanced by DDFT, continuous growth where the tip wears naturally.
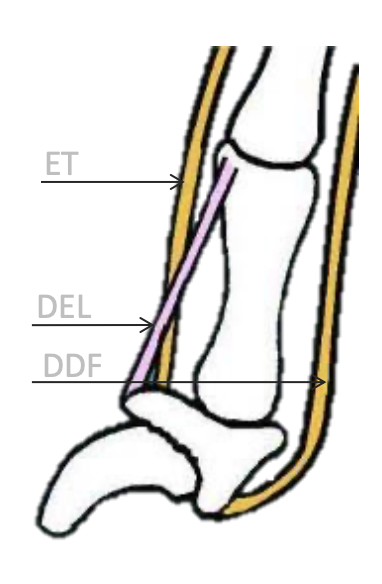
What are the two germinative area in claws?
Horn (Epidermis that is heavily keratinised) grows over dorsal and lateral surfaces of ungual process
Horn overs palmar surface
What happens to the dermis of the claw?
It fuses directly to periosteum of unfurl process of digital phalanx
As the claw continues to grow, the tip wears naturally. What factors may reduce the wearing?
Not walking
Walking on soft ground
Dew claw
DDFT damage = Subbed toe
Which part of the claw can be cut, and which cannot?
Horn = Epidermis = Insensitive = Can cut
BUT dermis → Contain blood and nerve supply = Cannot cut
What are the similarities and difference between the claws of cats and dogs?
Similarities:
Same number of pads and claws
Same components and function
Difference:
Cat claws are retractable by adding more pressure on DDFT, while dog claws are not
Cat claws tend to be sharper.
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Filters lymph
Prevents contaminants from reaching systemic circulation
Contains defense cells → Removes invading organisms
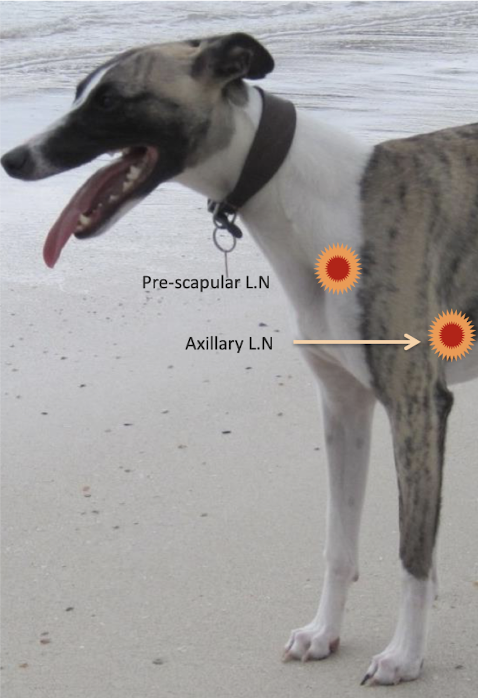
What are the forelimb lymph nodes?
Prescapular (Located at the cranial aspect of scapular - In front of the should joint)
Axillary lymph nodes (Located under the axilla)
Which selected extrinsic muscles does the brachial plexus supply?
Pectoral muscles, latissimus dorsi, and serratus ventralis.
Which intrinsic muscles nerves does the brachial plexus supply?
Subscapular, suprascapular, musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, and ulnar nerves.
What type of nerve is the subscapular nerve (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscle does it supply?
Motor nerves only
Located at the medial aspect
Supply subscapularis muscle
What type of nerve is the suprascapular nerve (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscle does it supply?
Motor nerve only
Located at the lateral aspect
Supplies supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
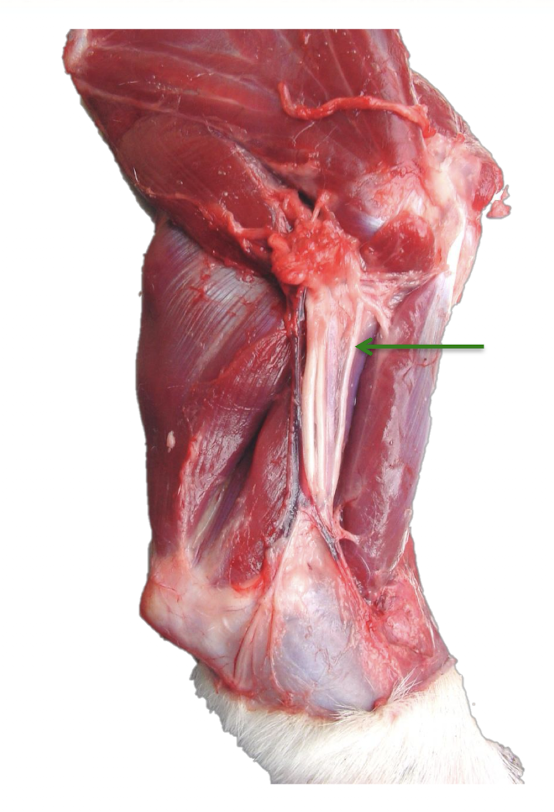
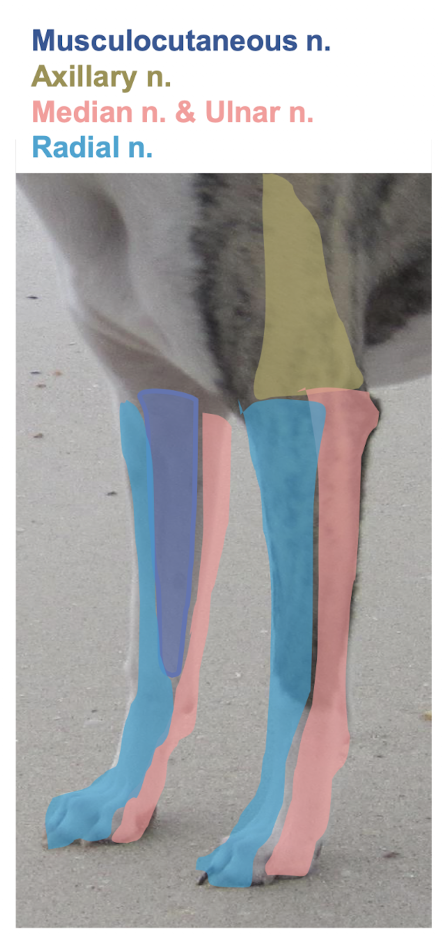
Which nerve is shown in this picture?
Musculocutaneous nerve
What type of nerve is the musculocutaneous nerve (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscles does it supply, and how do they function?
Sensory:
Cranial & medial aspect of elbow
Medial aspect of antebrachium.
Motor:
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
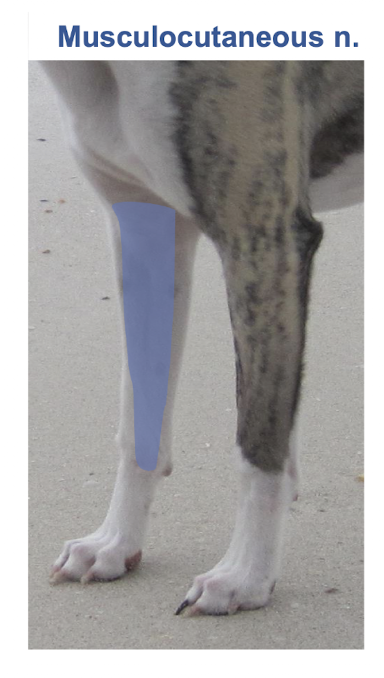
What happens if there is damage to the musculocutaneous nerve? Is there any compensation?
No compensation → Loss of elbow flexion
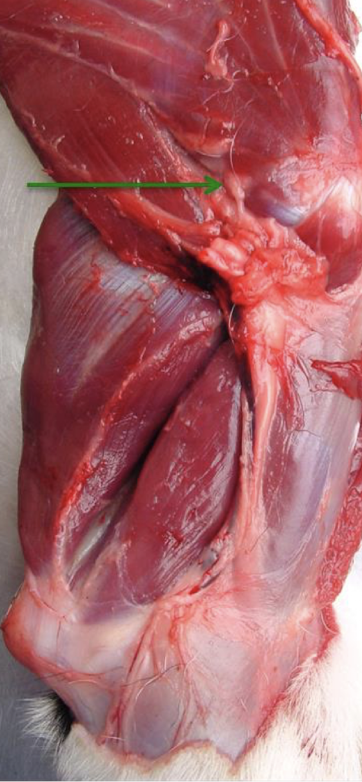
Which nerve is shown in this picture?
Axillary nerve
Located between teres major and subscapularis
Where else can the axillary nerve be found besides the teres major?
Deep to the deltoid muscle
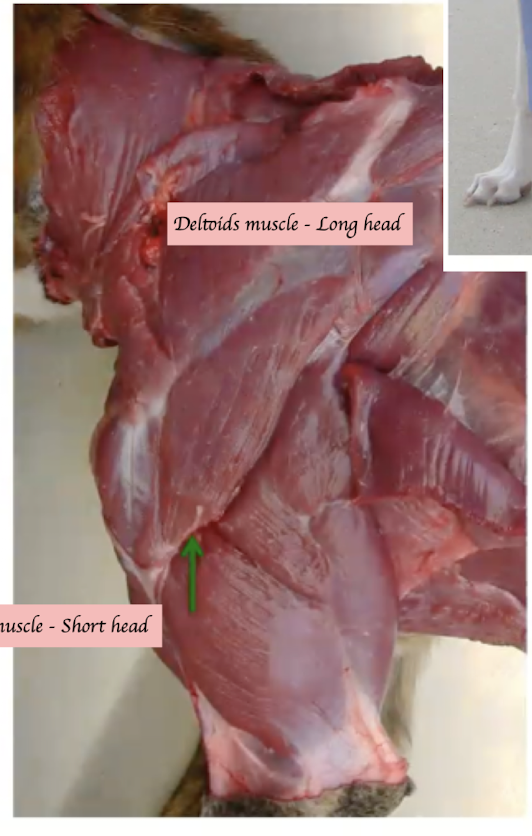
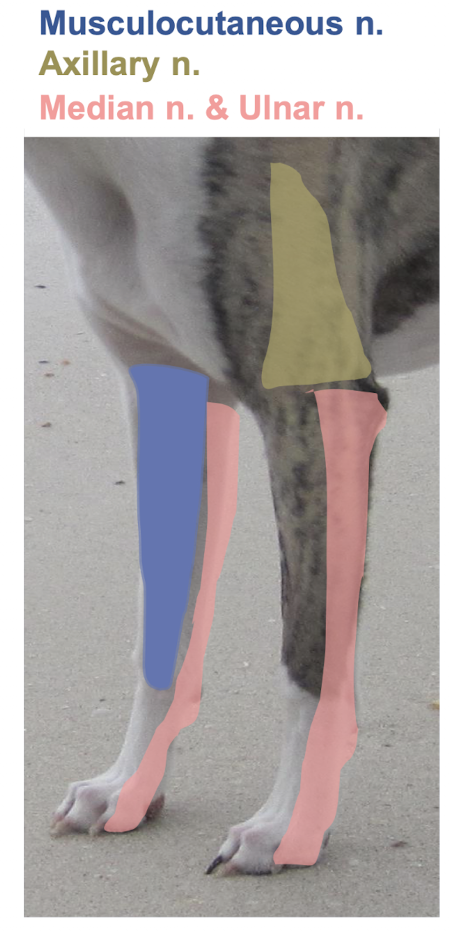
What type of nerve is the axillary nerve (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscles does it supply, and how do they function?
Sensory:
Lateral aspect of shoulder and brachium
Motor:
Deltoid
Teres major

What happens if there is damage to the musculocutaneous nerve? Is there any compensation?
Yes
Should flexor can be compensated by latissimus doors and long head triceps
= !! Even axillary nerve is damaged, the shoulder of animals can still be fixed !!
What type of nerve is the median and ulnar (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscles does it supply, and how do they function?
Sensory:
Caudal & palmar aspect limb
Dorsal aspect 5th digit
Motor:
All carpal & digital flexor

What happens if there is damage to the median and ulnar nerve? Is there any compensation?
No compensation → Loss of distal limb flexion
How does the radial nerve run?
The radial nerve originates from the medial aspect of the scapula → Passes caudal to the shoulder → Follows the musculospiral groove of the humerus → Passes through the triceps
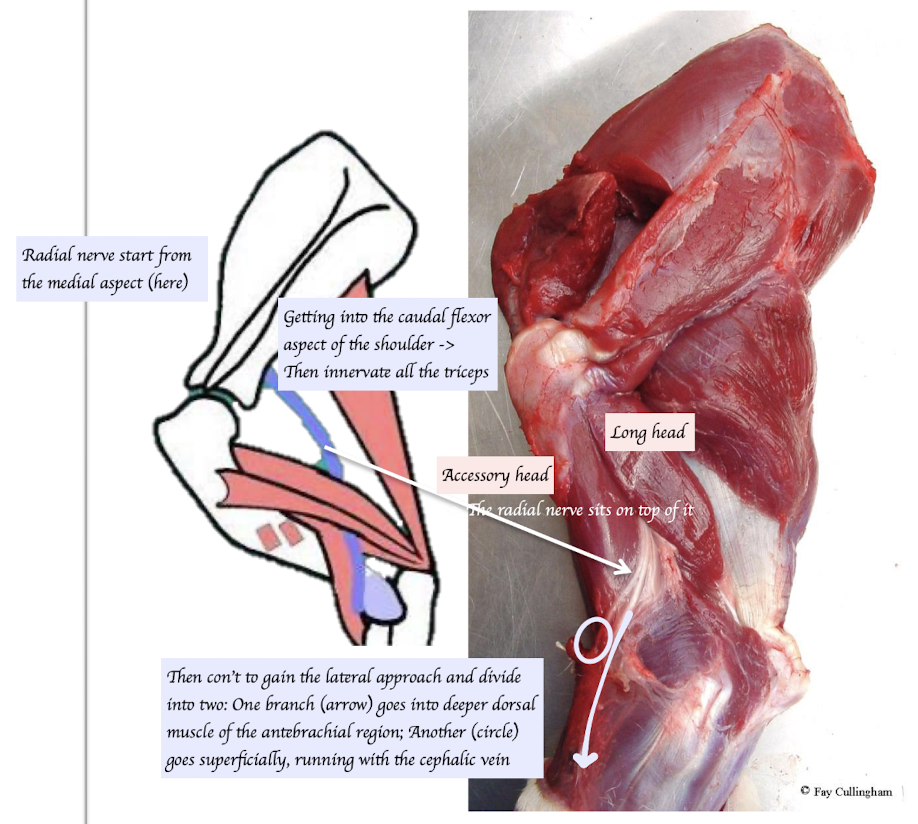
What type of nerve is the radial (sensory, motor, or both)? Where is it located, and which muscles does it supply, and how do they function?
Sensory;
Dorsal & cranial aspect limb, except dorsal aspect 5th digit
Motor:
All extensor of carpus and digits
Triceps
What happen if the proximal level of radial nerve damage?
Motor:
All extensor muscles affected → Cannot extend elbow, carpus and digits
Sensory:
Sensory losses of dorsal + cranial aspect of limb, except 5th digit
What happen if the distal level of radial nerve damage?
Motor:
Triceps intact → Can still extend elbow
Extensor of carpus and digits affected → Cannot extend the carpus and digits
Sensory:
Sensory losses of dorsal + cranial aspect of limb, except 5th digit
What happen if brachial plexus damage?
Motor:
Trapezius, Rhomboideus and Brachiocephalius are not supplied by the brachial plexus → Can still protract and abduct the limb
Cannot retract/ adduct/ extend/ flex limb + weight bearing
Sensory:
No cutaneous sensation on limb or lateral thorax to level of 3rd intercostal space