Starting a Project
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
research quesiton
a specific, open-ended question that guides the investigation into the human past through the study of material remains and cultural practices
CRM based projects
research mandated by law and conducted to comply with historic preservation regulations
problem-oreintated research
a systematic method that begins with a specific, well defined question or hypothesis
previous research
nominal data
descriptive categories
ex:
cats and dogs
vase and jar

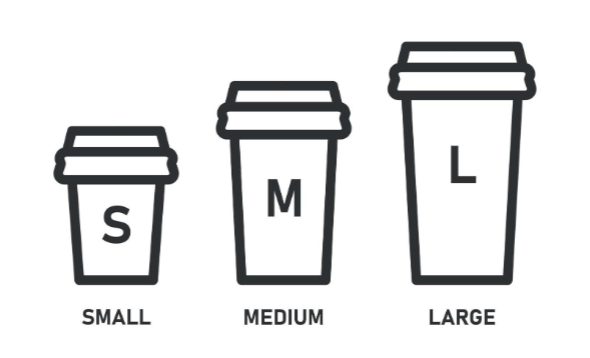
ordinal data
ranked data
not continuous, there are specific categories
ex:
small, medium, large
interval data
continuous data without a “true zero“
numbers
no minimum
not limited from the lower bound
no actual 0 to stop you
ex:
numbers
ratio data
continuous data with a “true zero“
numbers
have a starting point
there is an actual 0
go up as high as you want
ex:
height (you can’t have 0 height)

population
(in most unavailable for social sciences)
variable
a measurable characteristic of the population
sample
a portion of elements to make inferences about the population
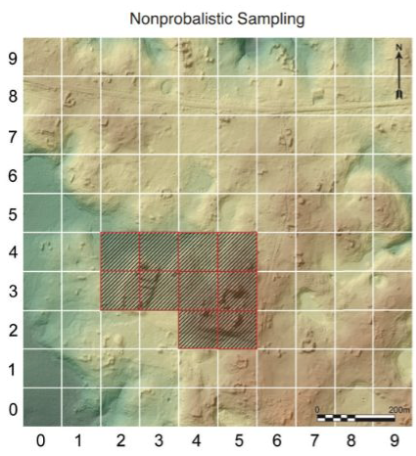
non-probablistic sampling
using prior information to guide the selection process
judgemental sampling

probablistic sampling
sampling based on statistical criteria that enables archaeologists to evaluate how close a sample represents the larger population of artifacts or features at a site
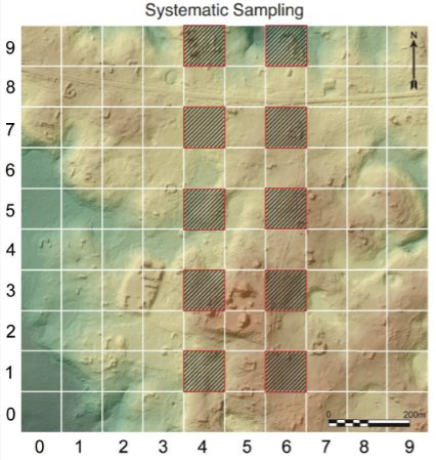
systematic sampling
establish a pattern of sampling
areas of sampling are evenly. distributed thorghout overall sampling universse
sampling areas are selected according to pattern
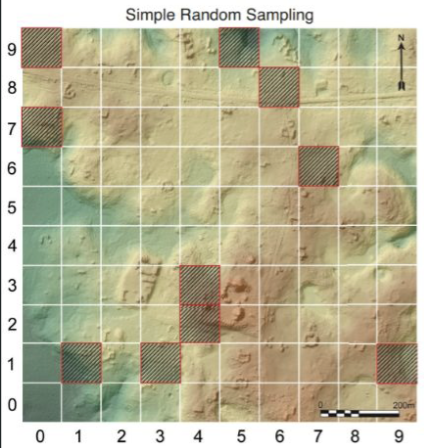
simple random sampling
completely random
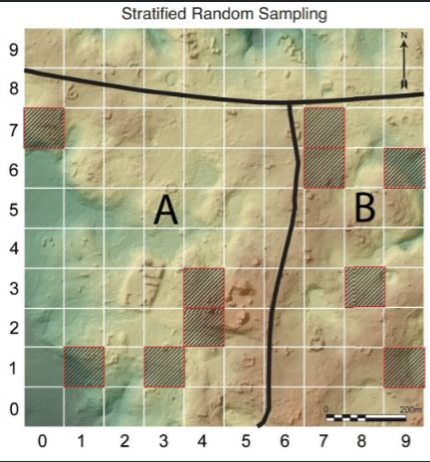
stratified random sampling
divides area into natural zones, then utilizes simple, random method to sample each area independently
each zone is tested at a predetermined percentage
the area tested is proportional to the zones overall area
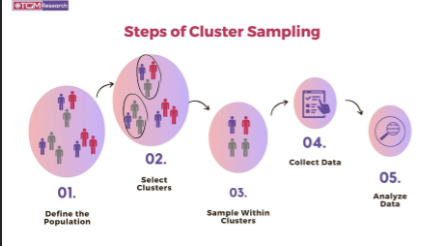
cluster sampling
divides data into groups then utilizes simple random method to sample within groups
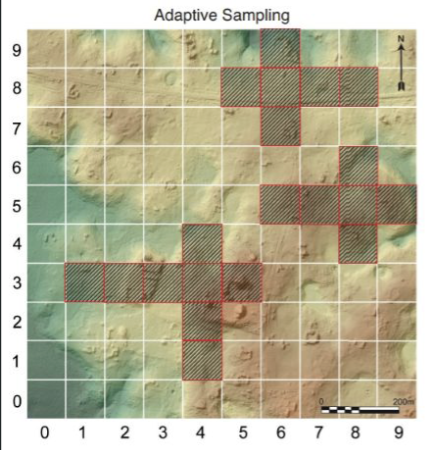
adaptive sampling
begins with another sampling method (simple random, systematic, or stratified) to find a starting location
sampling areas are modified according to data obtained during the study
assembling the team
director
field director (crew chief)
field archaeologist
technical experts
students
workers
other needs for the team
camp
provisions
logistics
permits
political relations
the study of power dynamics in both past and present societies, the use of historical artifacts to shape national identity, and the political implications of archaeological sites and discoveries
social relations
focus on understanding how past and present societies are, or were, structured and how people interacted through their material culture and social practices
community relations
the practice of collaborative partnerships with stakeholders, including descendant communities, local residents, and civic officials, to involve them in research from project design to dissemination
artifact
portable objects created or modified by humans
ecofact
unmodified remains of biological materials
feature
non-portable archaeological remains that were constructed by humans = hearths, burials, storage pins, roads, dams
region
beyond the limit of a single site
defined by both natural and cultural factors
site
a spatial cluster of artifacts, ecofacts, feature, and/or structure
non-random sampling
a method of selecting participants for a study where not every member of the population has an equal chance of being chosen