BIOL 304 - Chapter 15 Metabolism
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the advantage of having enzymes organized in complexes for metabolic pathways?
increases speed and efficiency
allows efficient processing of unstable or toxic intermediates
catabolism
reactions that break down complex molecules into simpler ones to capture energy in useful forms
anabolism
reactions that construct a more complex molecule from simpler molecules by using energy
Recognize how coupling of reactions allows for unfavorable reactions to proceed
Overall free-energy change for a chemically coupled series of reactions equals the sum of the free energy changes of the individual steps.
allows for the coupling of thermodynamically unfavorable and favorable reactions in enzyme active sites
structure of ATP
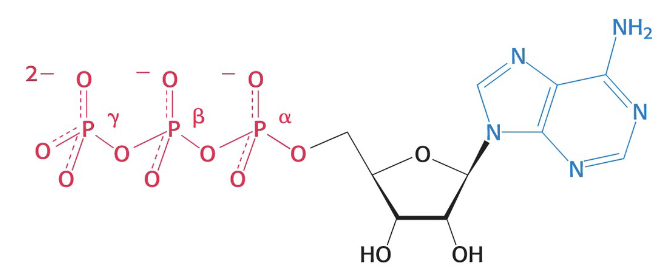
why is phosphoryl transfer favorable?
ATP acts as the free-energy donor in most energy-requiring processes
ATP hydrolysis is exergonic
what does ATP hydrolysis power?
release of free energy
What are the structural features of ATP that give it high phosphoryl transfer potential?
orthophosphate (Pi) has greater resonance stabilization than any of the ATP phosphoryl groups
electrostatic repulsion of the triphosphate unit
the entropy of the products of ATP hydrolysis is greater
ADP and Pi are stabilized due to hydration
How do the sources of energy change in exercising muscle?
ATP in muscle sustains contractile activity for < 1 second
How does creatine factor into ATP production?
creatine kinase = catalyzes the regeneration of ATP from creatine phosphate and ADP
How proton gradients power the synthesis of ATP?
The oxidation of fuel molecules or phototrophy produces electrochemical potentials of ion gradients across membranes
90% of ATP is generated when the energy of a proton gradient is coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation)
Stage 1 of extraction of energy from whole food
large molecules in food are broken down into smaller units
Stage 2 of extraction of energy from whole food
small molecules are degraded to a few simple units that play a central role in metabolism
Stage 3 of extraction of energy from whole food
ATP is produced from the complete oxidation of the acetyl unit of acetyl CoA
activated carriers
small molecules to which a chemical group or electrons have been added, which can then be donated to another molecule
NAD+
accepts a proton and two electrons in the oxidation of a substrate to form NADH
FAD
accepts two protons and two electrons in the oxidation of a substrate to form FADH2
coenzyme A
a carrier of acyl groups that is derived from vitamin B5 (pantothenate)
Acetyl CoA
Acetyl linked to CoA is called acetyl CoA
Electrons of the C=O bond cannot form resonance structures with the C—S bond that are as stable as
those that they can form with the C—O bond
oxidation-reduction reaction
electron transfer
Useful energy is often derived from the oxidation of carbon compounds
group transfer reaction
Transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
used to synthesize ATP and in signaling pathways, among others
hydrolytic reaction
Cleavage of bonds by the addition of water
commonly used to degrade large molecules
Carbon bond cleavage by means other than hydrolysis or oxidation
Two substrates yielding one product or vice versa. When H2O or CO2 are a product, a double bond is formed
isomerization
Rearrangement of atoms to form isomers
typically to prepare the molecule for a subsequent reaction
Ligation requiring ATP cleavage
Formation of covalent bonds (i.e., carbon–carbon bonds)
forms bonds using free energy from ATP hydrolysis
metabolism regulated by
altering the amount of enzymes
restricting the accessibility of substrates
regulating the catalytic activity of enzymes internally or externally
energy charge
proportional to the mole fraction of ATP plus half the mole fraction of ADP
ATP-generating pathways are inhibited, and ATP-utilizing pathways are stimulated under conditions of high-energy charge