Skeletal Muscles Contractions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Requirements for Muscle Contractions to occur
Muscle must be stimulated by the nervous system
Without any innervation from nerves, paralysis occurs, leading to the eventual shrinkage of muscles due to strophy
Nerve innervation of Muscles
One axon of a nerve branches off into many axon terminals to connect to multiple myofibrils at once.
One axon can range from stimulating a few myofibrils, to thousands
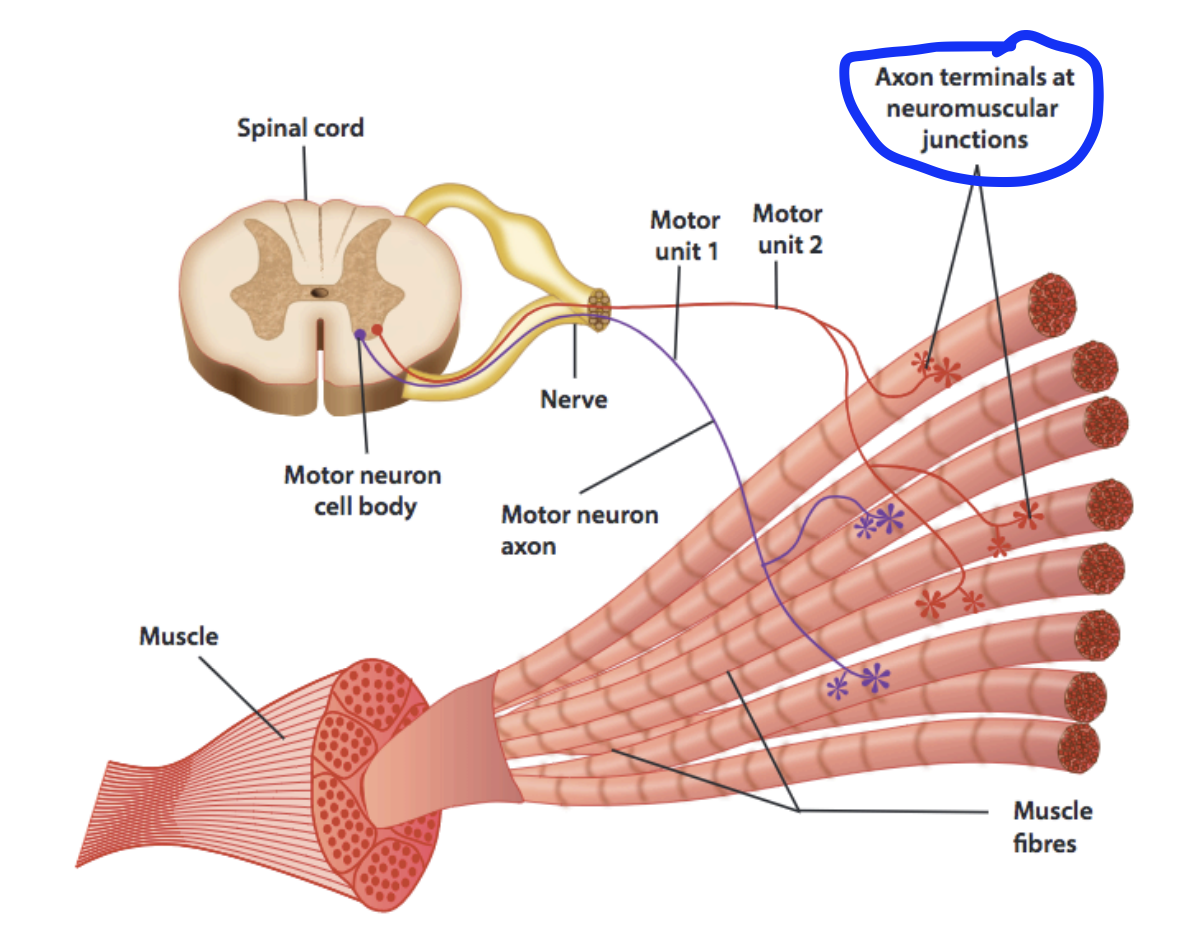
Motor unit
A unit of an axon and all the muscle fibres it stimulates
Size of motor units vary. One axon can range from stimulating a few myofibrils, to thousands
The variation of motor unit size allows a spectrum of movements from gross to fine.
Smaller motor units are for fine movements, and have a lower threshold. Thus, they are stimulated much more easily.
Neuromuscular junction Location
The synapse between the axon terminal and a specialised area in the muscle called the motor end-plate
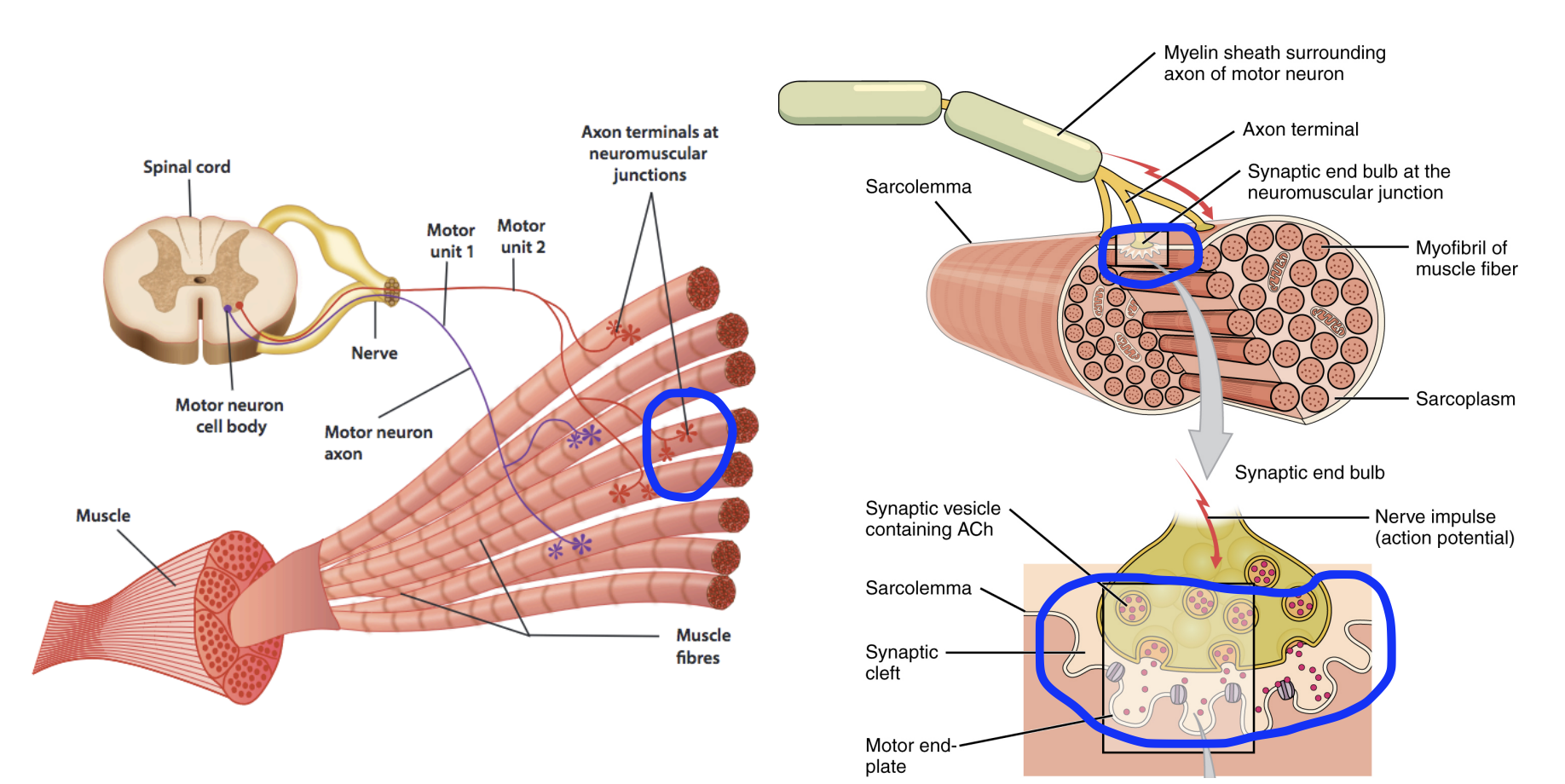
Neuromuscular junction Function
To continue the impulse and signal from the neuron to the muscle.
Electrical impulse (Neuron) → Chemical response (neurotransmitters) → Electrical impulse (inside muscle)
Process of synaptic transmission from Neuron to Muscle
Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter.
Initially is waiting stored within vesicles at the axon terminal of nerves.
Waiting for the stimulus of an action potential
Receiving an action potential triggers the opening of calcium channels, causing calcium to enter the neuron.
In response to the presence of calcium in the neuron, the vesicles containing ACh combine with the cell membrane at the axon terminal, opening up and releasing ACh out from the axon terminal
ACh binds onto the ACh receptor found on the motor end-plate (muscle), which in of itself is a Na+ channel protein
Na+ rushes into the muscle cell through the opened channels. Depolarisation begins within the muscle, from the sarcolemma, triggering another action potential inside the muscle.
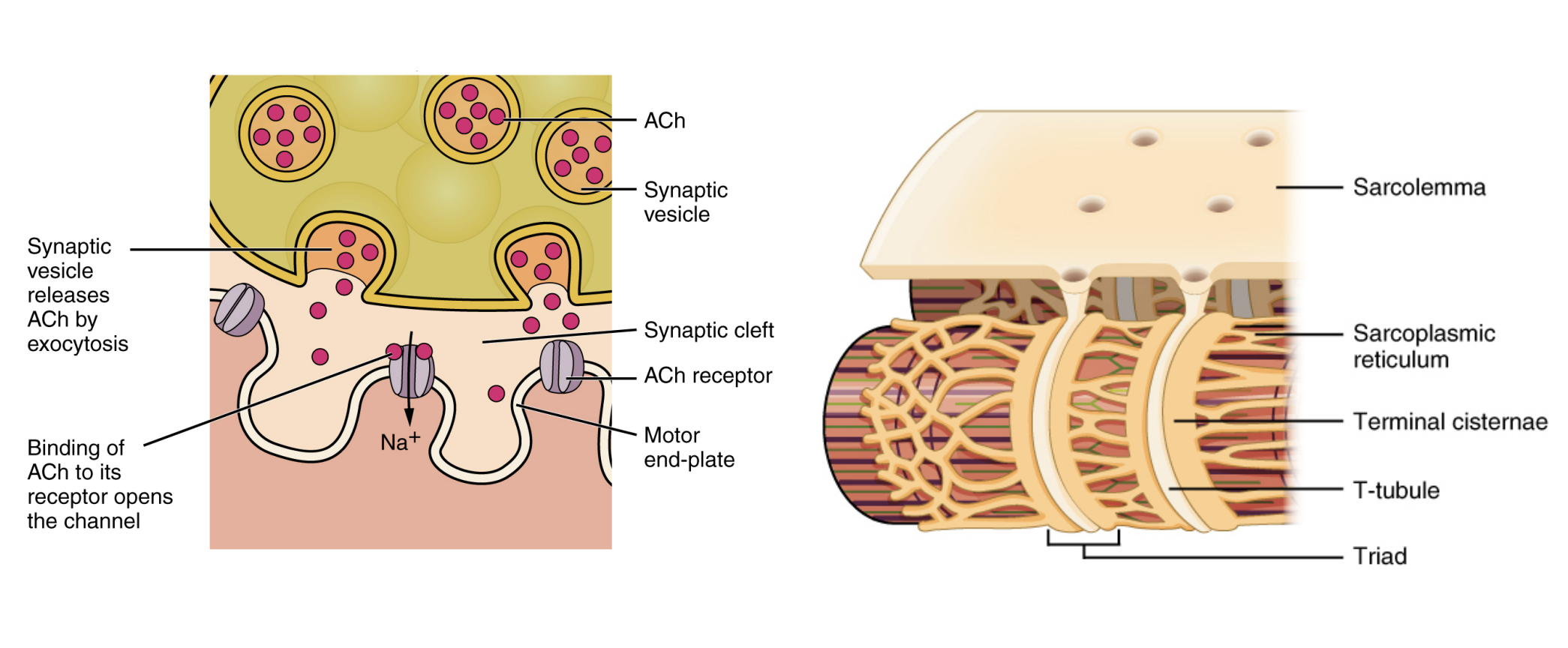
T-tubule (Transverse tubules)
Perforations found on the sarcolemma (cell membrane of myofibrils), through which the action potential travels
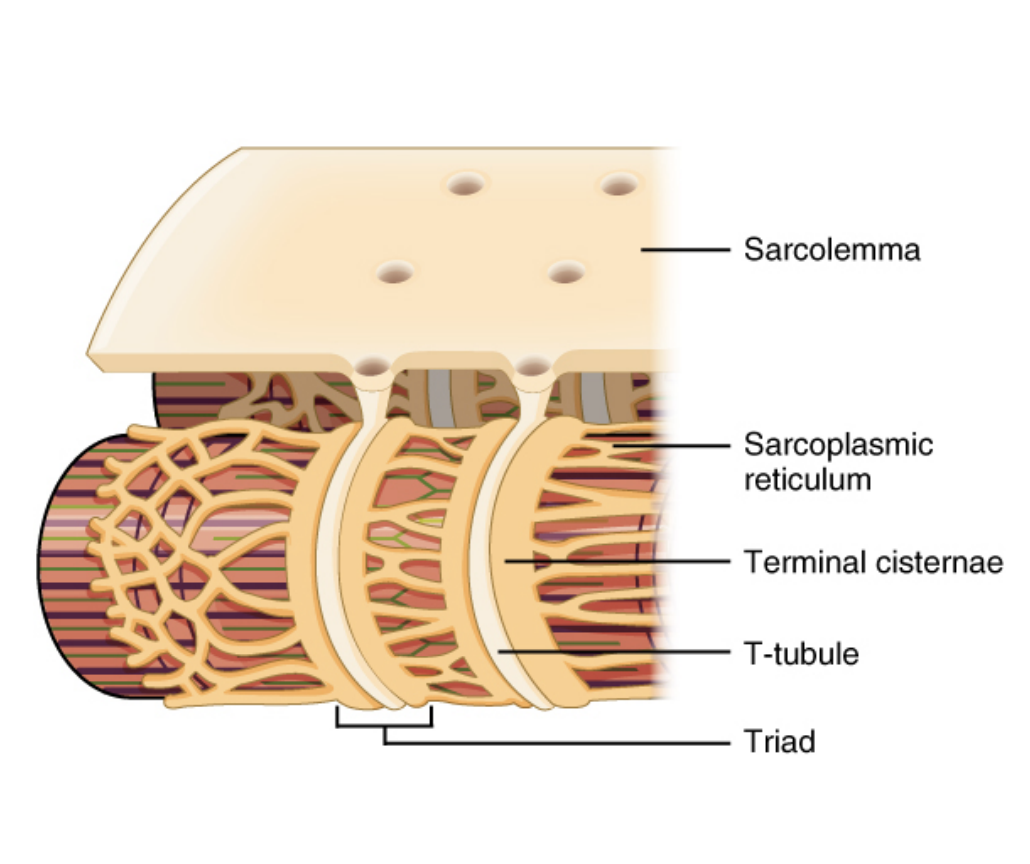
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
A derivative of the endoplasmic reticulum found sitting next to the bottom of T-tubules.
Stores calcium
The signal from the action potential causes the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Calcium rushes out to the sarcomere
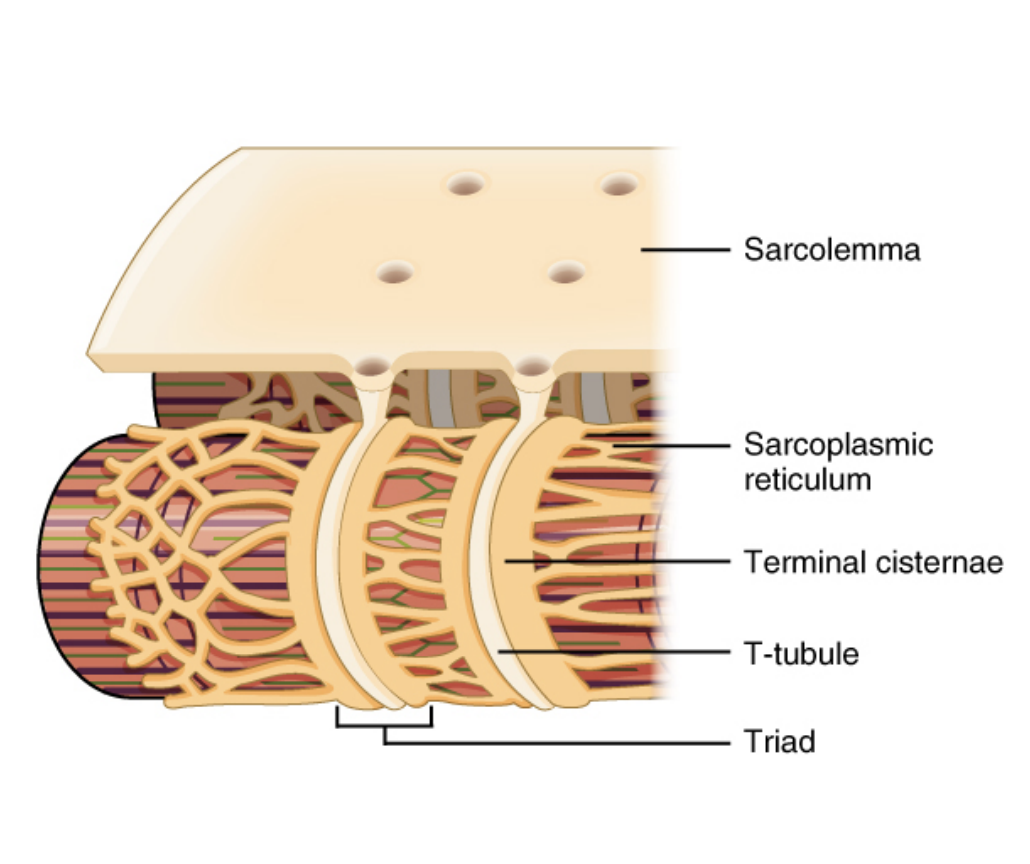
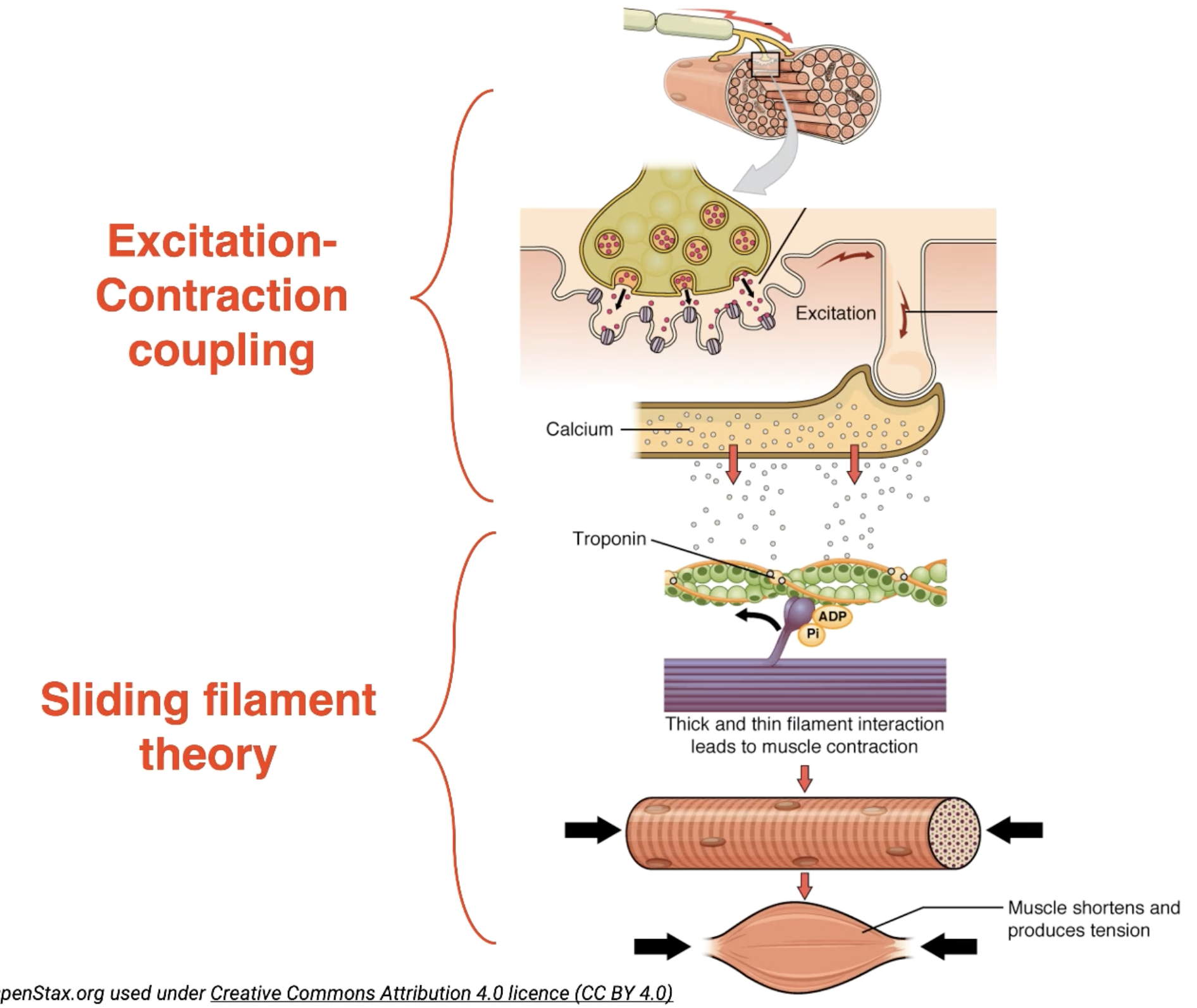
Excitation-Contraction coupling
When the action potential travels from the motor-endplate, down to the bottom of T-tubules, the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels is triggered on the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Calcium rushes out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, to the actin myofilaments.
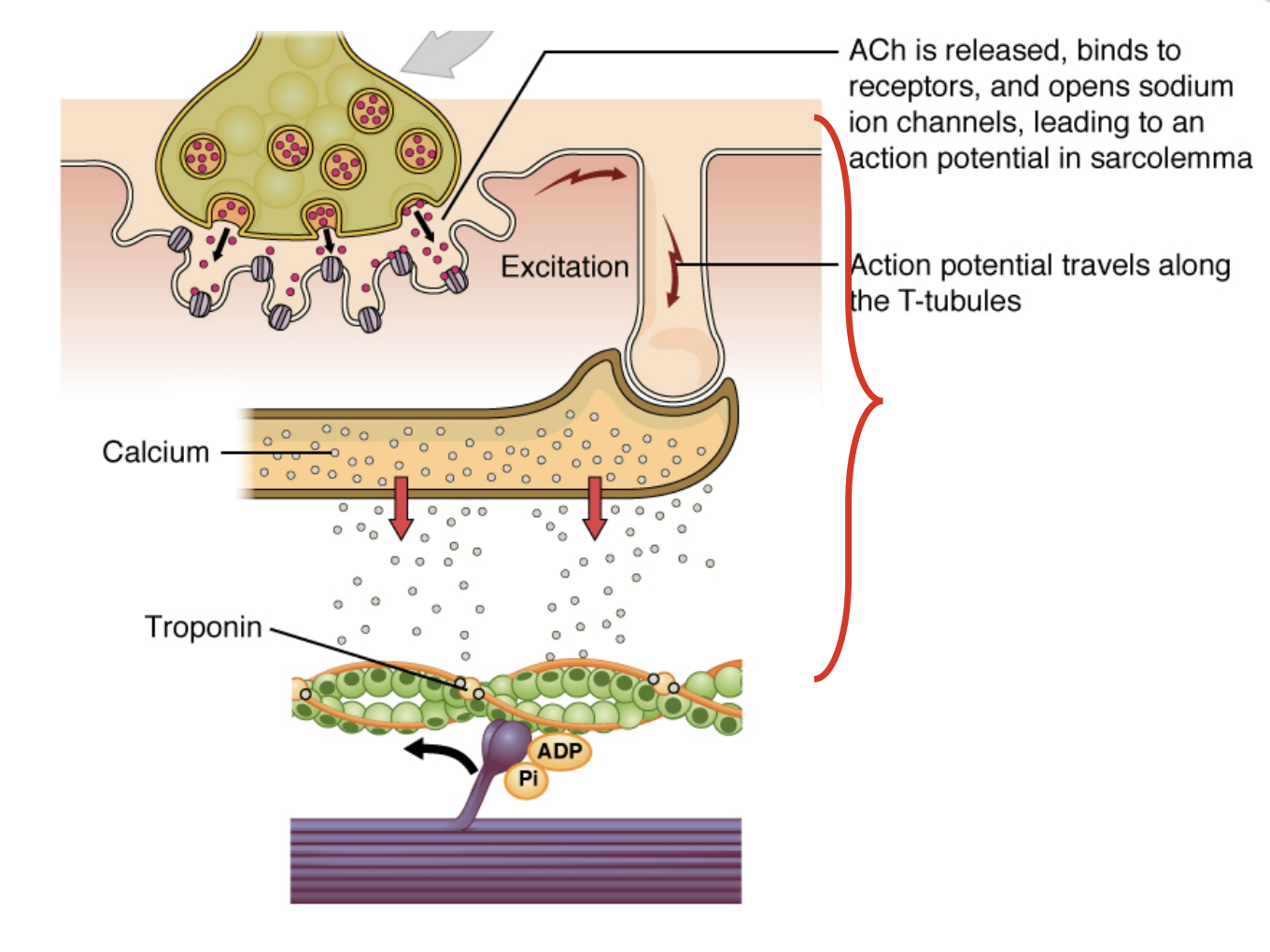
Resting Actin-Myosin Filaments (Resting Sarcomere)
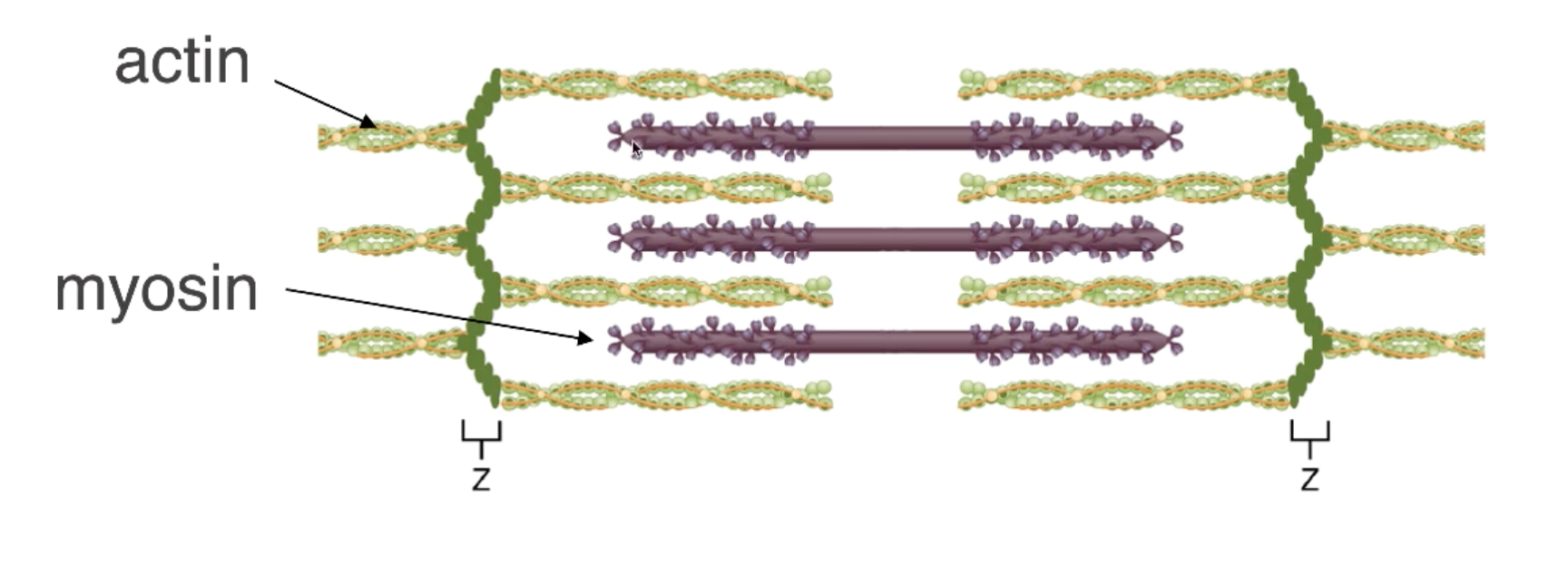
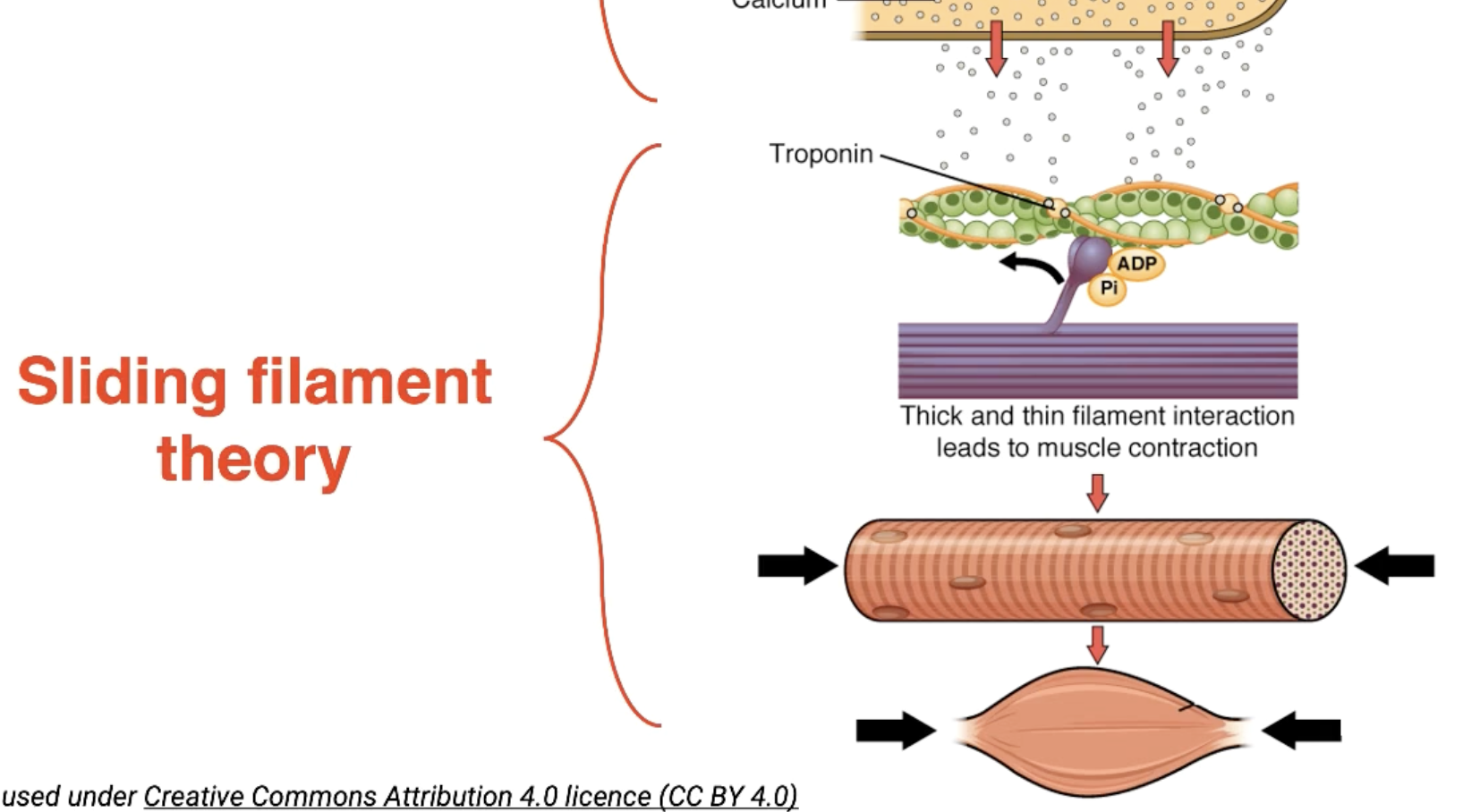
Sliding Filament Theory Phase 1
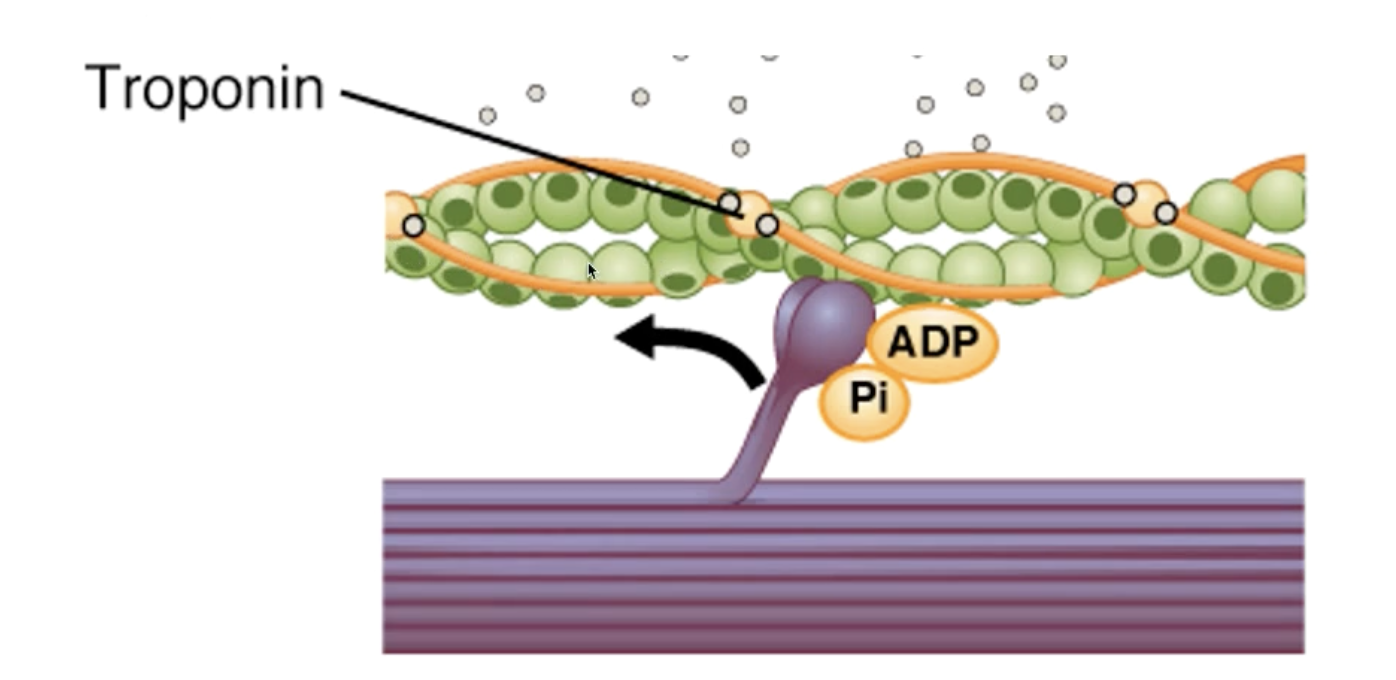
Calcium that rushed out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to troponin located on the actin myofilament.
Myosin binding sites on actin myofilaments are exposed (dark green spots)
Myosin heads attach to the actin myofilament (only in the presence of ATP)
In the presence of ATP, movement of the myosin head can occur, and actin myofilaments move past (referred to as a power stroke).
Shortened Actin-Myosin Filaments (Contracted Sarcomere)
Shortening only one cycle contracts only 1% of the muscle.
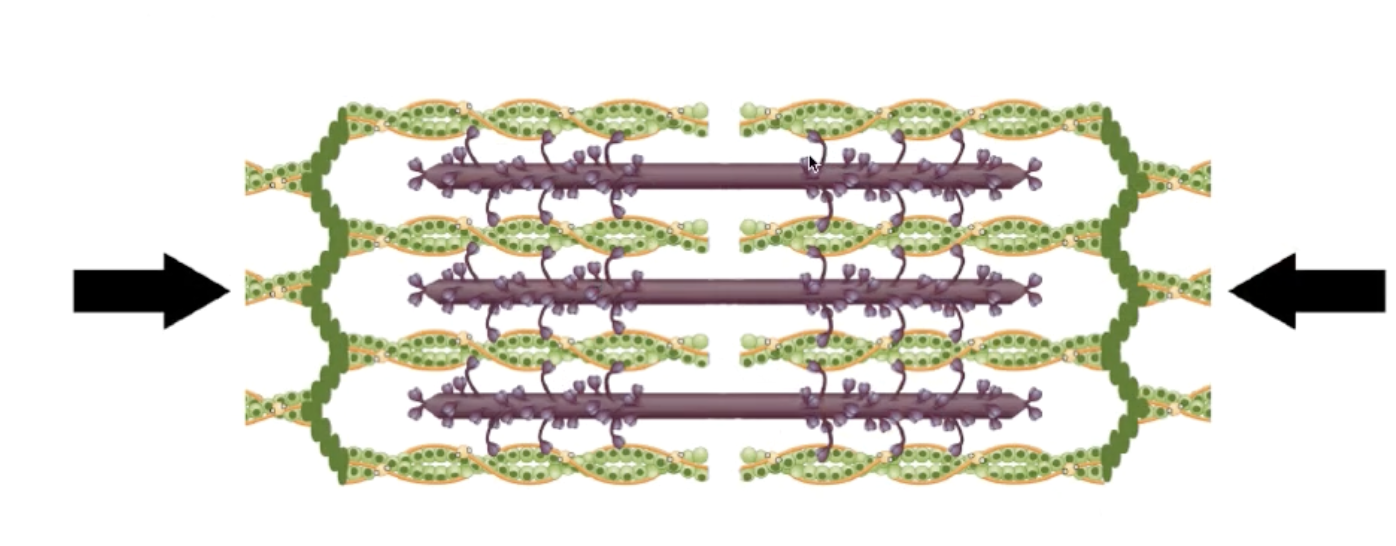
Cross-bridge cycling:
Overall shortening of the sarcomere occurs over and over (Myosin heads drag the actin closer like in a canoe) until the anatomical limit.
Sliding Filament Theory Phase 2
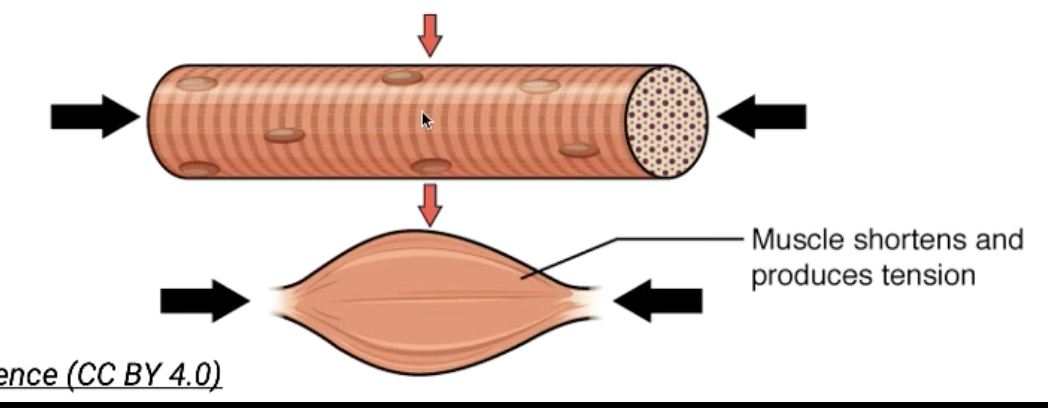
Cross-bridge cycling causes the overall length of the muscle to shorten.
Sliding Filament Theory Overall
Overall Muscular contraction
How are muscles relaxed?
The signal (action potential) is inhibited to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, preventing calcium from being released from the voltage-gated calcium channels.