Period 3 - Modern Era (1750-1900) - Part 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force (empire-building)

hegemony
dominance, especially by one country or social group over others

Social Darwinism
The application of Darwinian ideas about evolution ("survival of the fittest") to human societies & races -- as a justification for imperialist expansion

Paternalism
A policy of treating subject people as if they were children, providing for their needs but not giving them rights
colony
A group of people in one place who are directly ruled by a parent country elsewhere (ex: India became a British colony in 1858)
Protectorate
A territory with its own local government, but under the indirect control & "protection" of an outside power (ex: Puerto Rico as a territory of the US)
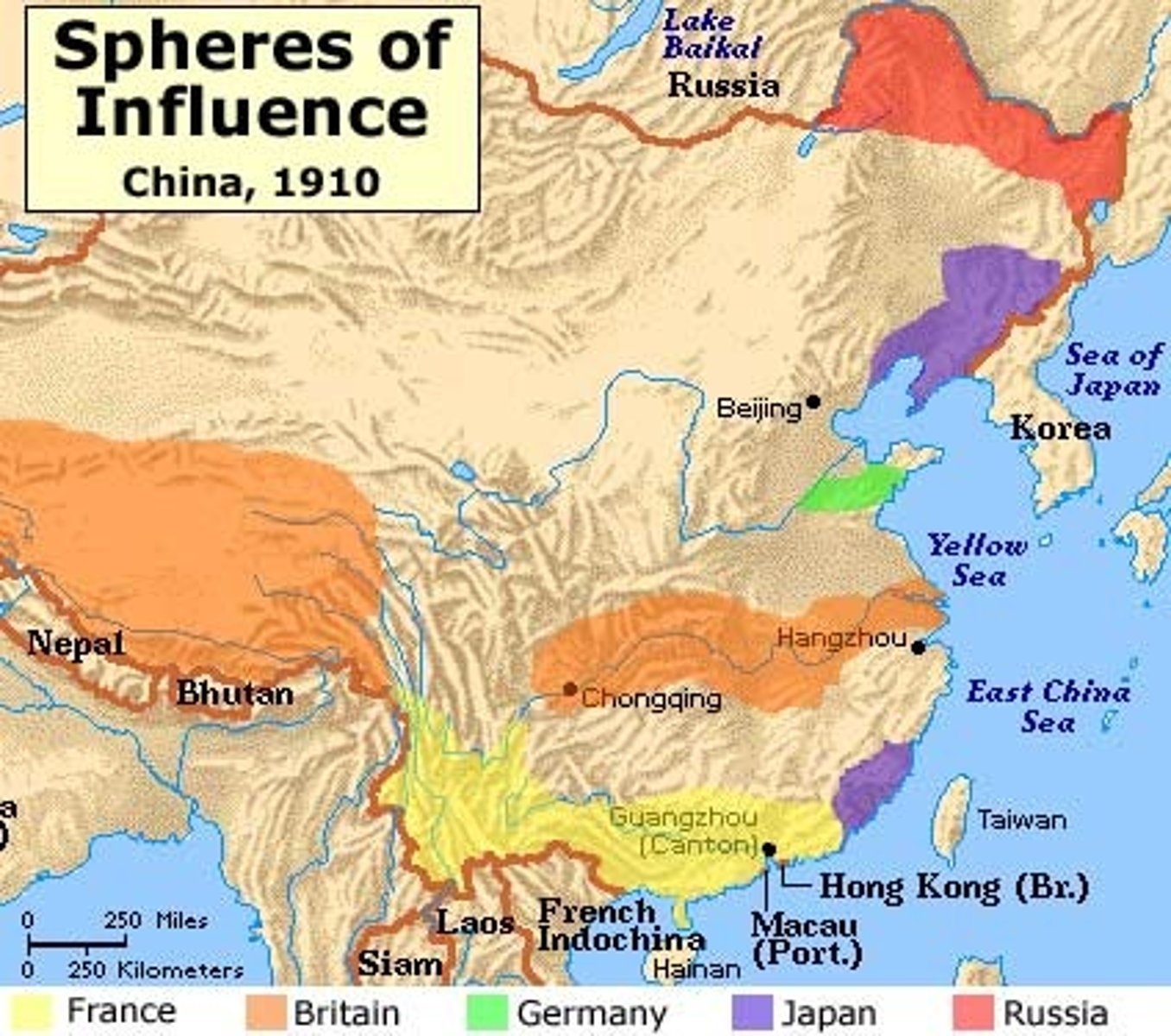
Sphere of Influence
A region in which a foreign nation has exclusive trading rights & control over economic activities (ex: competing European "spheres of influence" in 19th c. Qing China)
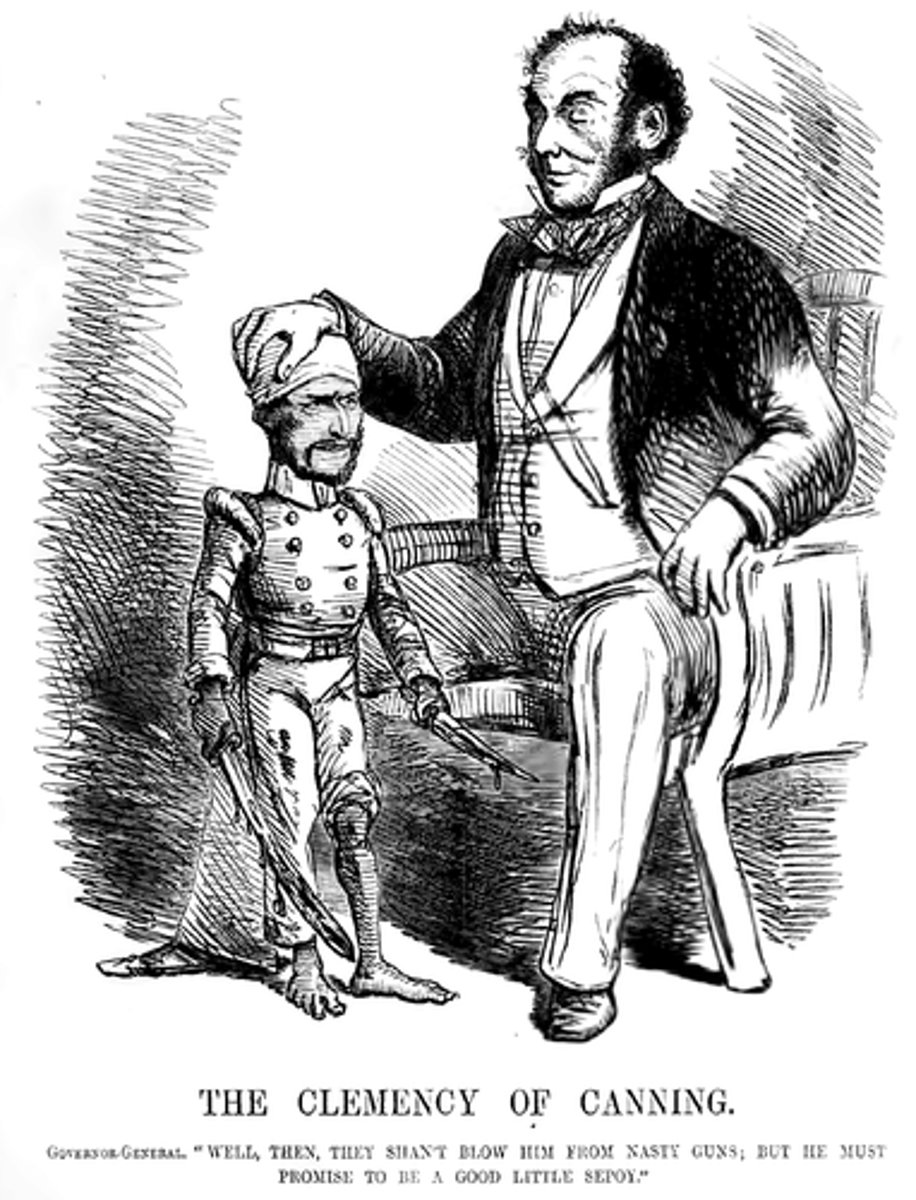
Sepoy Mutiny
1857 rebellion of Hindu & Muslim hired mercenary soldiers (called sepoys) against their British East India Company officers across northern India

Indian National Congress (INC)
Nationalist movement & political party est. in 1885 to demand greater Indian (particularly Hindu) participation in the government under British rule

Viceroy
a governor who ruled as a representative of a foreign monarch

Congo Free State
large area in Central Africa created & controlled by Leopold II of Belgium in the mid-19th c., for the purpose of controlling the rubber trade there (NOT really "free"...)

Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
Meeting in Berlin, Germany, where representatives of European nation-states agreed upon rules for the partition of Africa into European colonies (no African leaders were invited)
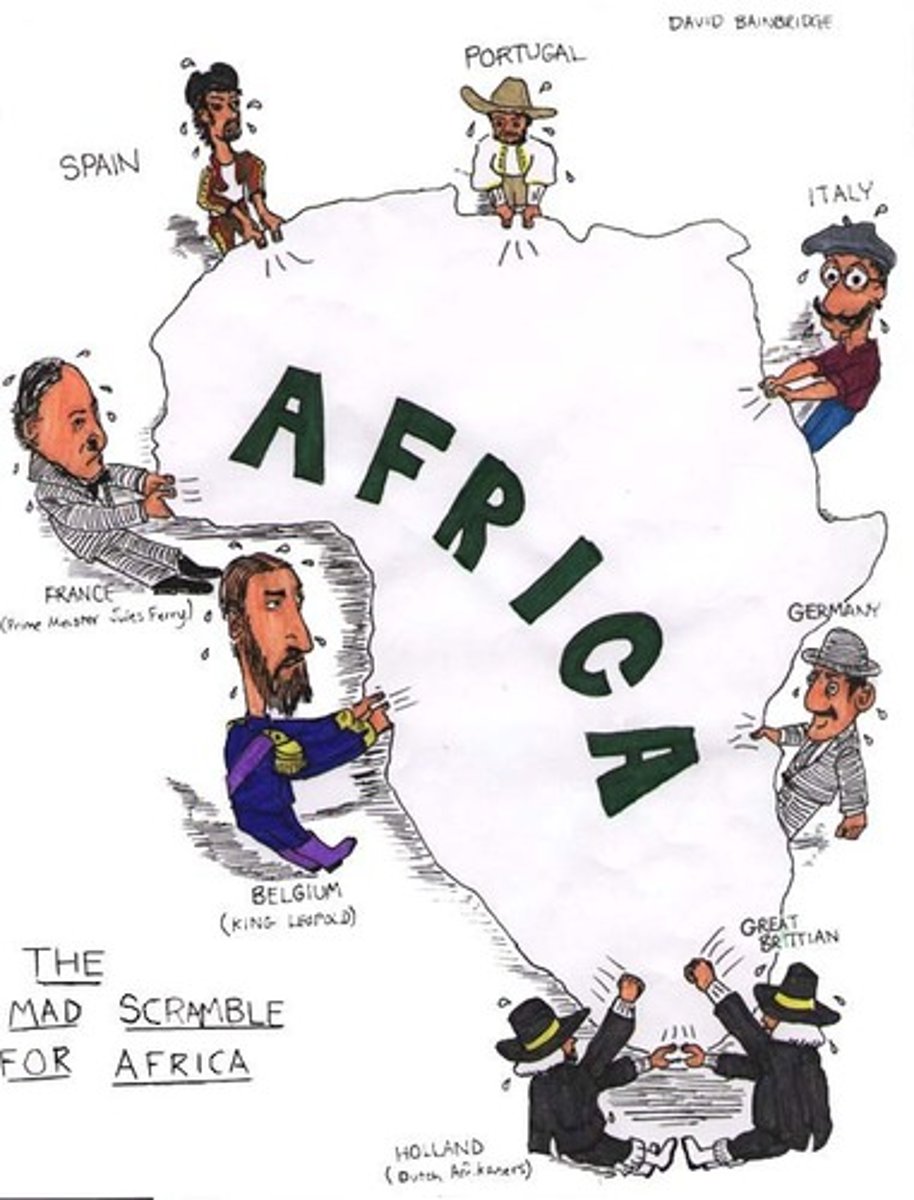
"Cape to Cairo"
Cecil Rhodes's idea of a trans-African railroad that would stretch from Cape Town, South Africa to Cairo, Egypt -- bringing "civilization" to Africa (& allowing the British to capitalize on shipping of raw materials and gemstones out of southern Africa)

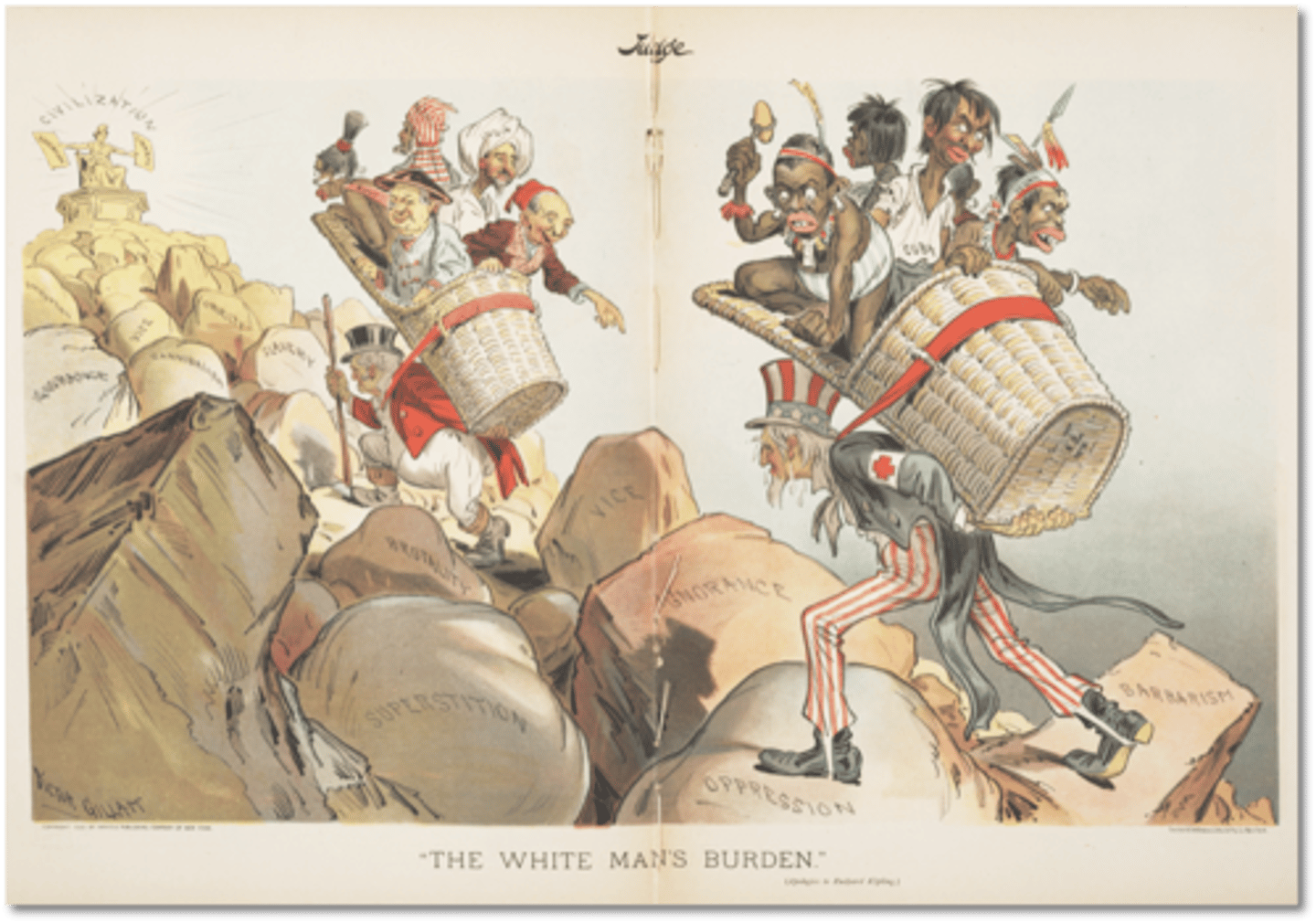
"White Man's Burden" (1899)
Poem by British poet Rudyard Kipling about the "burdens" to be faced by American imperialists in the Philippines (after the US won the territory in the Spanish-American War)

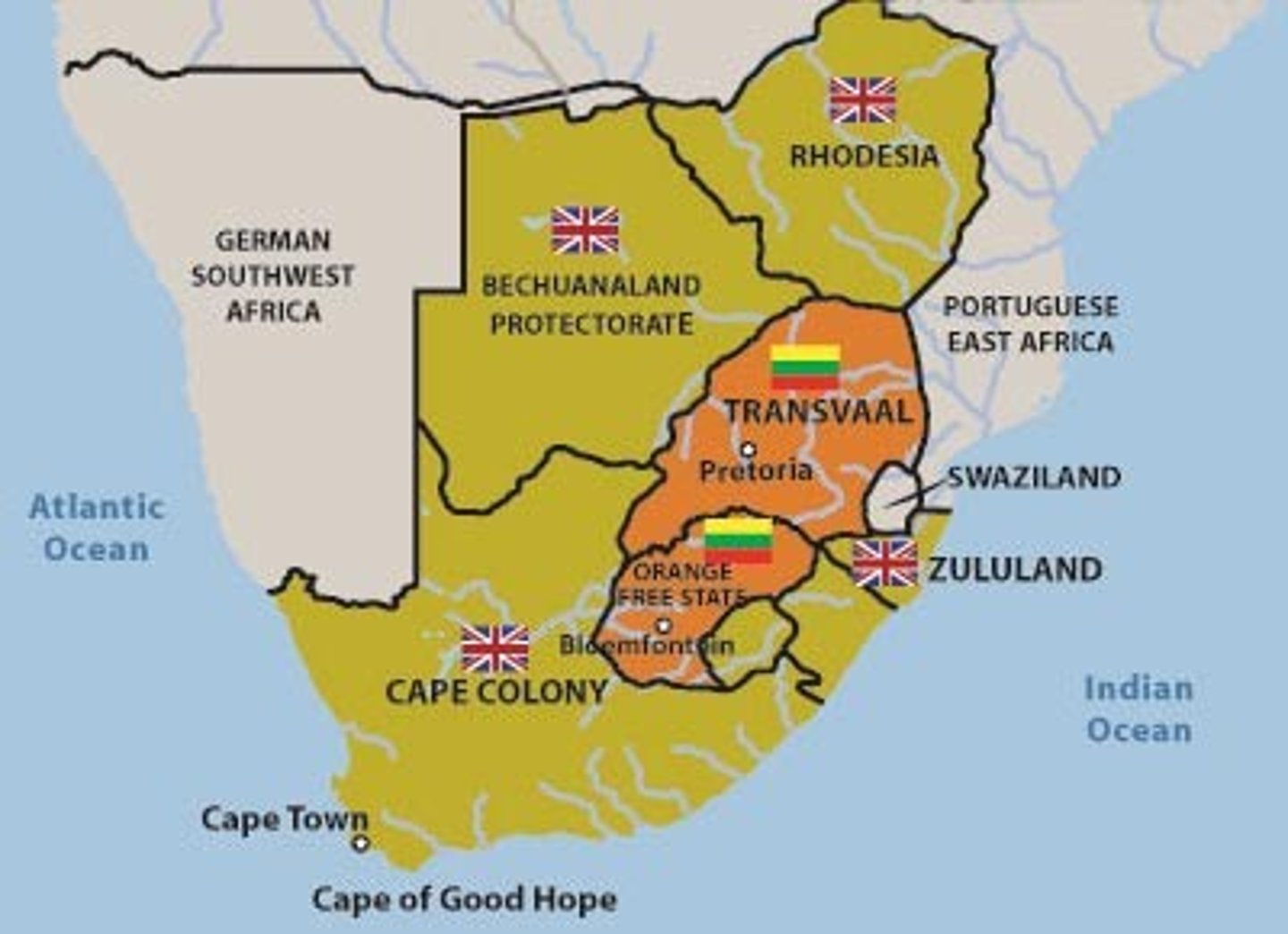
Boer War (1899-1902)
fought between the British and Afrikaners (Dutch settlers, aka "Boers") over land & mineral rights; British victory and post-war policies left native Africans (driven to the interior) under Afrikaner control
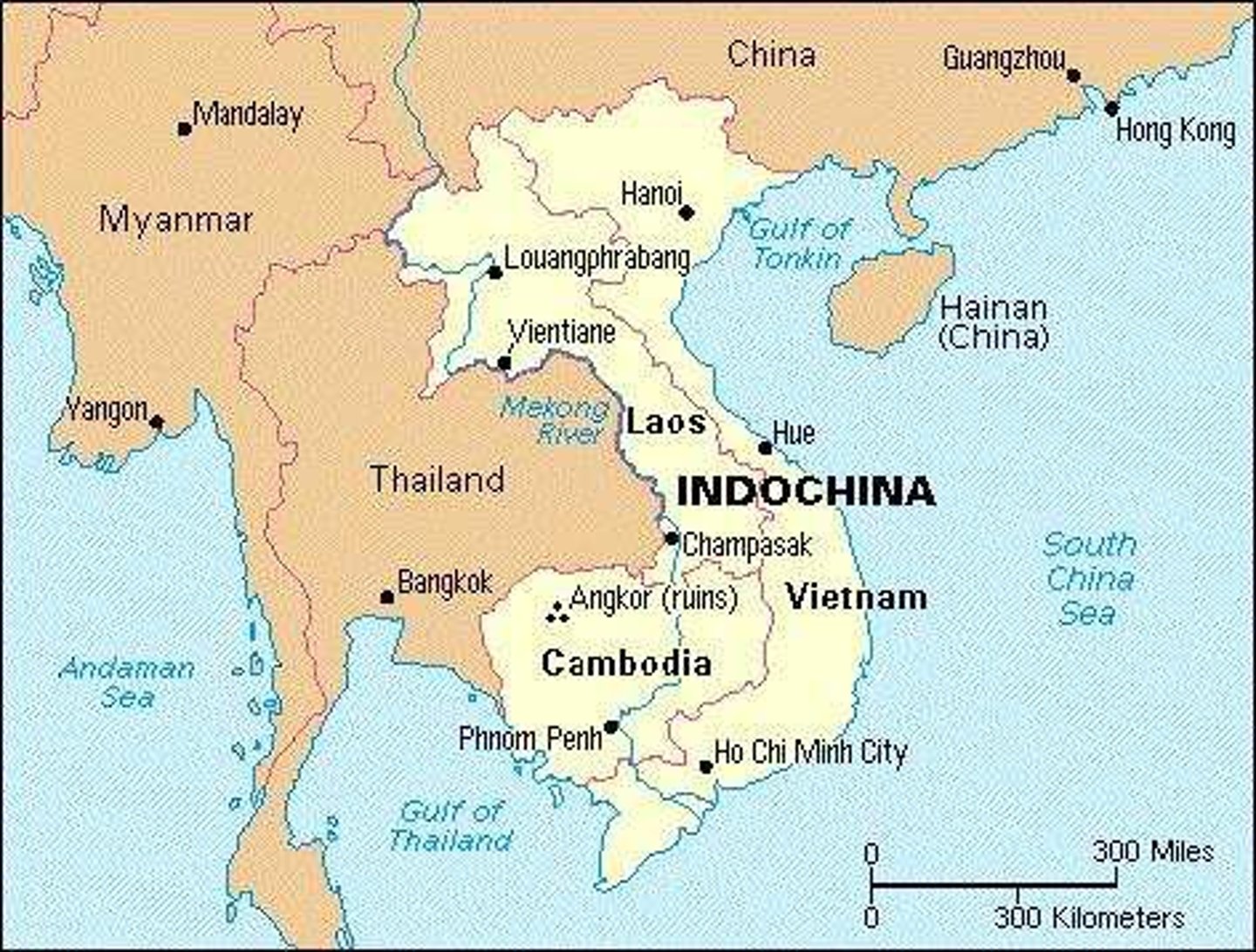
French Indochina
Area of SE Asia controlled by France starting in the late 19th c.--includes Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam
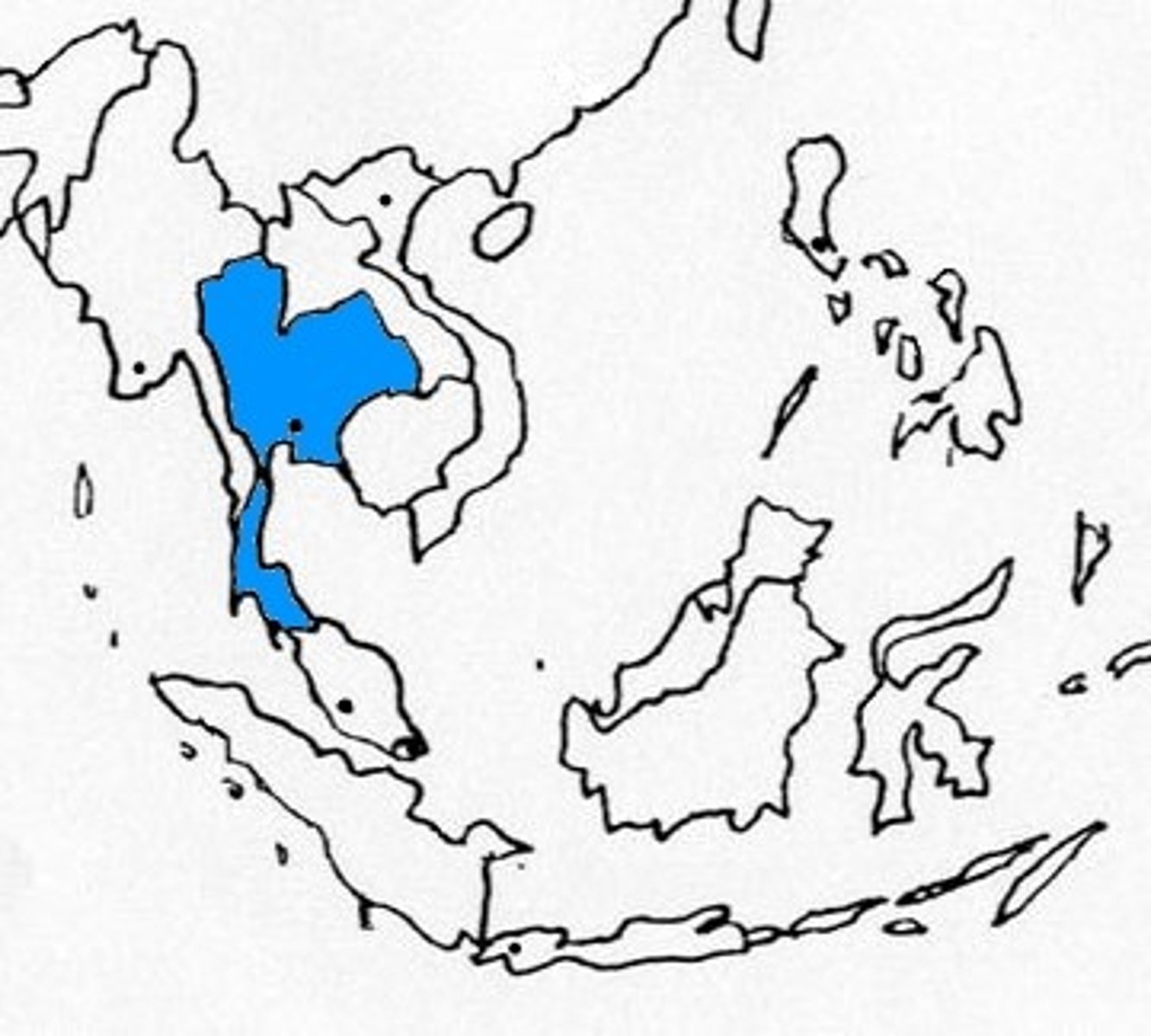
Siam
today known as Thailand; remained relatively independent during the 19th c., because it served as a buffer zone between British & French colonies in Indochina
Maoris
native New Zealanders whose traditions and population were threatened by British colonial rule

Indentured Servitude
contract labor to an employer for a fixed period of time (5-7 years), in exchange for overseas passage, food, clothing, lodging and necessities -- used by British & Dutch in late 19th-early 20th c. as a replacement of slave labor (after abolitionist movement)

Panama Canal
a ship canal 40 miles long across the Isthmus of Panama built by the United States (1904-1914)
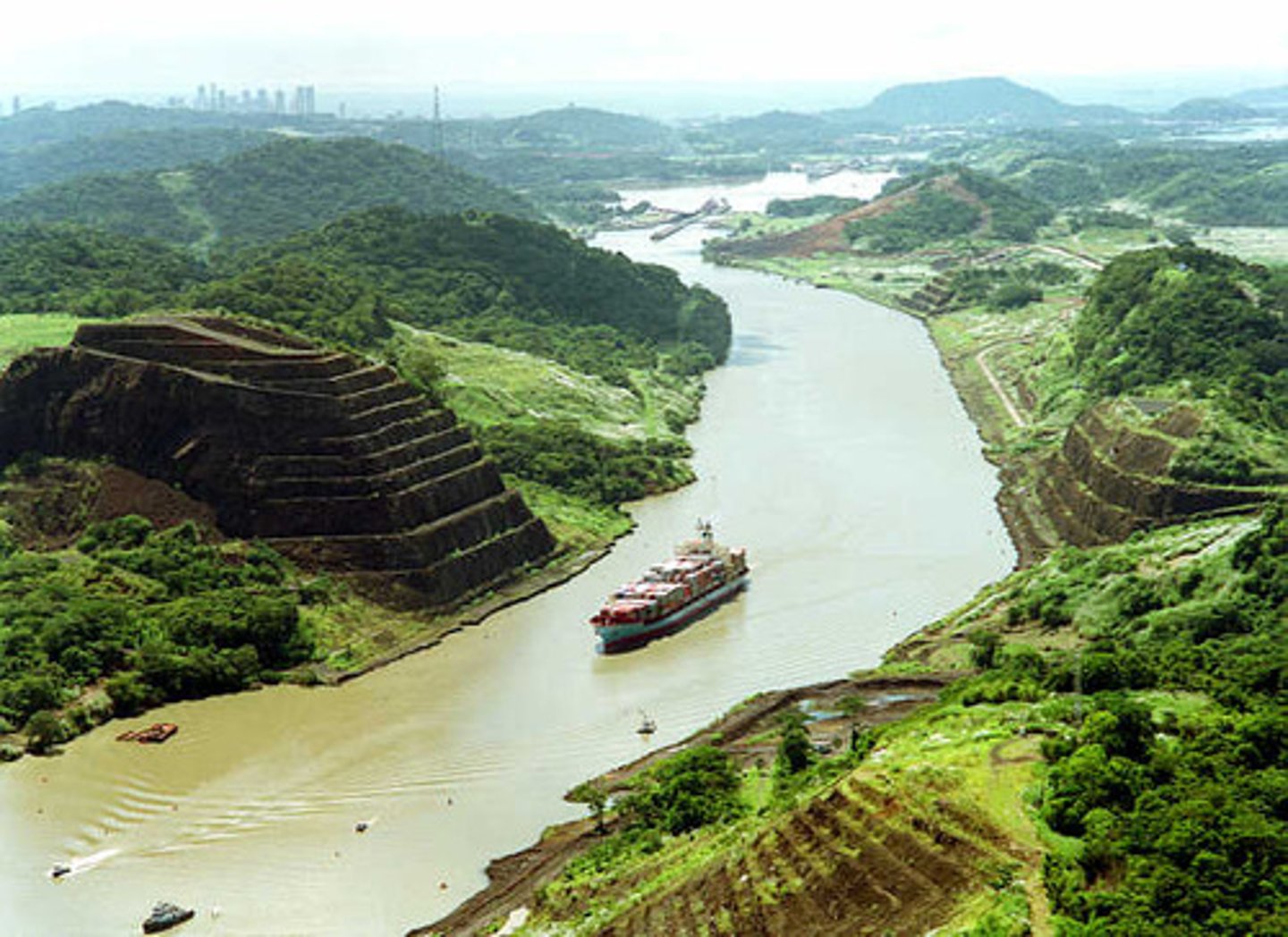

Suez Canal
Ship canal dug across the isthmus of Suez in Egypt; opened in 1869, and shortened the shipping route between Europe and Asia. Its strategic importance led to the British conquest of Egypt in 1882.
Janissaries
Infantry, originally of slave origin, constituting the elite of the Ottoman army from the fifteenth century until the corps was abolished in 1826

Tanzimat Reforms
Series of reforms in the Ottoman Empire that est. Western-style universities, a postal system, railways, extensive legal reforms & a new constitution in 1876
Young Turks
Group favoring liberal reform in the Ottoman Empire; they were against the sultan's monarchy and instead favored a liberal constitution with goals of creating a modern secular republic

Emancipation
the act of setting free (ex: freeing of slaves; freeing of Russia's serfs in 1861, etc.)

Witte System
Program est. by Sergei Witte (finance minister of Russia) to promote state-sponsored industrialization; led to rapid construction of railroads (& eventually the Trans-Siberian RR)

Trans-Siberian Railroad
a railroad construction project that would eventually link Moscow to the Pacific port of Vladivostok; completed by 1904
Duma
Russian Parliament, established by Czar Nicholas II (in the October Manifesto) as a response to the 1905 revolution

Soviets
local councils in Russia, consisting of workers, peasants, and soldiers (like labor unions)

Pogroms
Government supported mob attacks against Jews in imperial Russia, from the late 19th-early 20th c.
Cohong System
a system of trade in which specially licensed Chinese firms (cohongs) were under strict government regulation in trading with foreigners

Opium War (1839-1842)
War between Qing Dynasty & Great Britain over sale of opium in China and opening ports for trade; British naval superiority forcefully opened Hong Kong to British control and gave the British extraterritorial rights in China

Treaty of Nanking (Nanjing)
peace treaty signed ending the Opium War; greatly restricted Chinese control over their own trade with western countries
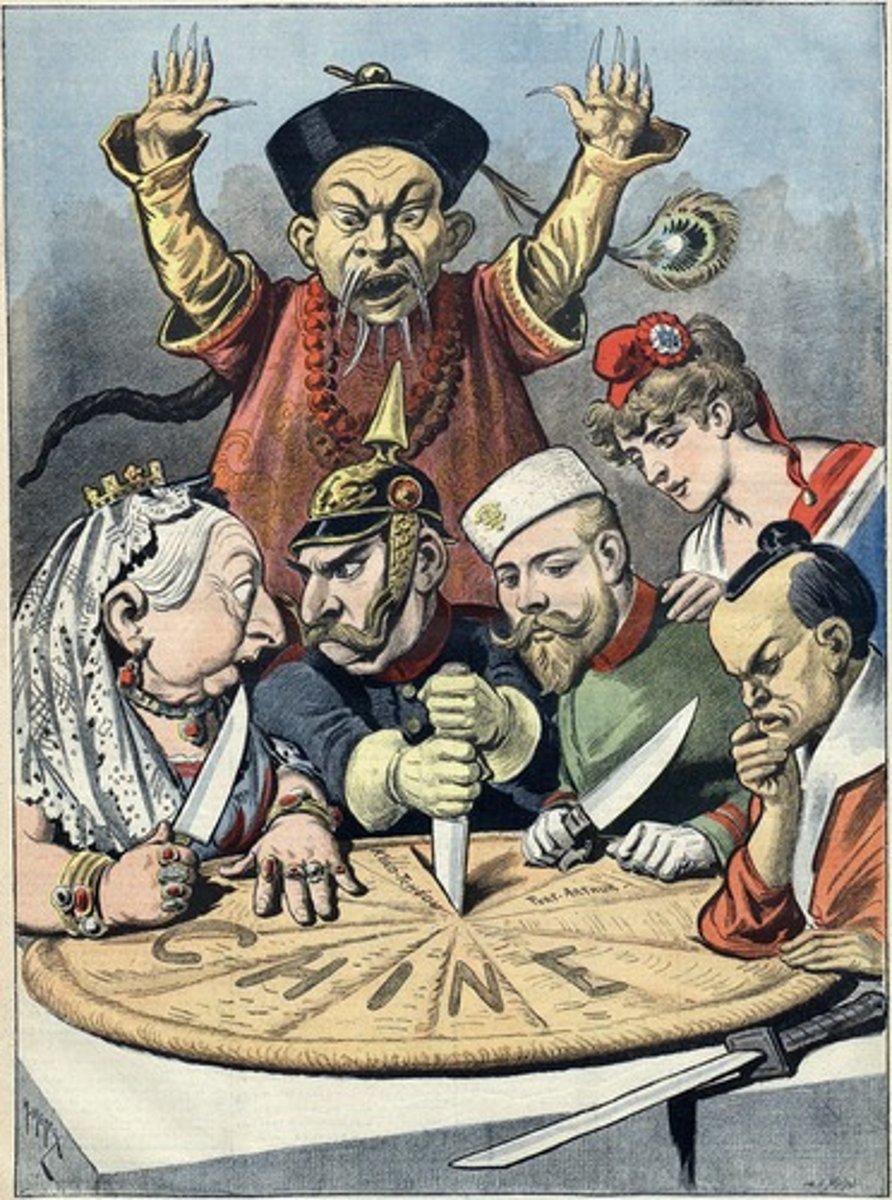

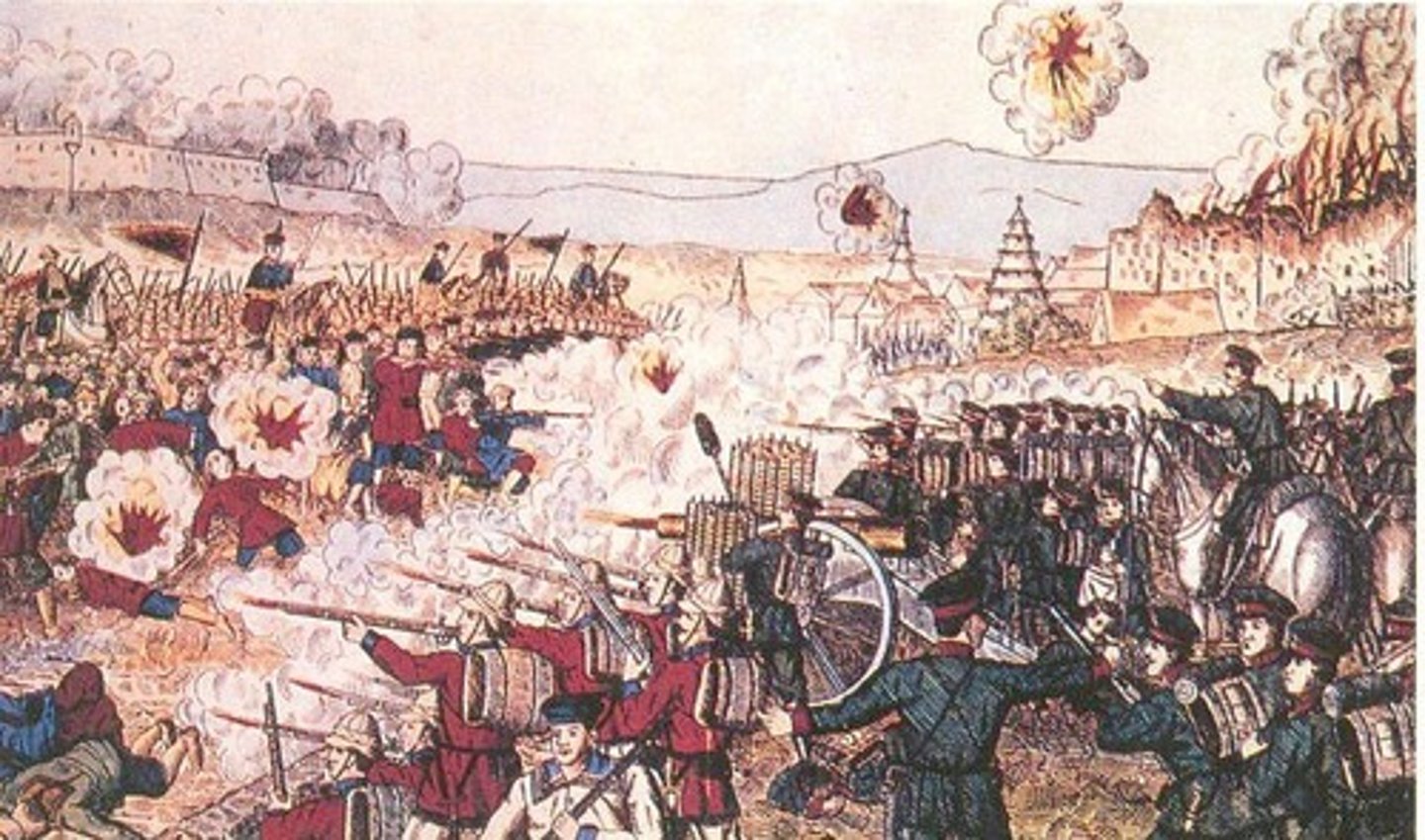
Taiping Rebellion (1850-1864)
a mid-19th c. peasant rebellion against the Qing Dynasty, led by village school teacher & mystic Hong Xiuquan; was suppressed, but only after massive amounts of casualties and damage

Self-Strengthening Movement
Qing Dynasty's program of internal reform in the 1860s-1870s, based on vigorous application of Confucian principles and limited borrowing from the West

Boxer Rebellion (1899-1900)
Uprising of Chinese militants whose goal was to drive the "foreign devils" out of China; it was suppressed by an international force of soldiers, including several thousand Americans; paved the way for the revolution of 1911 & fall of the Qing

Bakufu
military-style government of the Japanese shogun

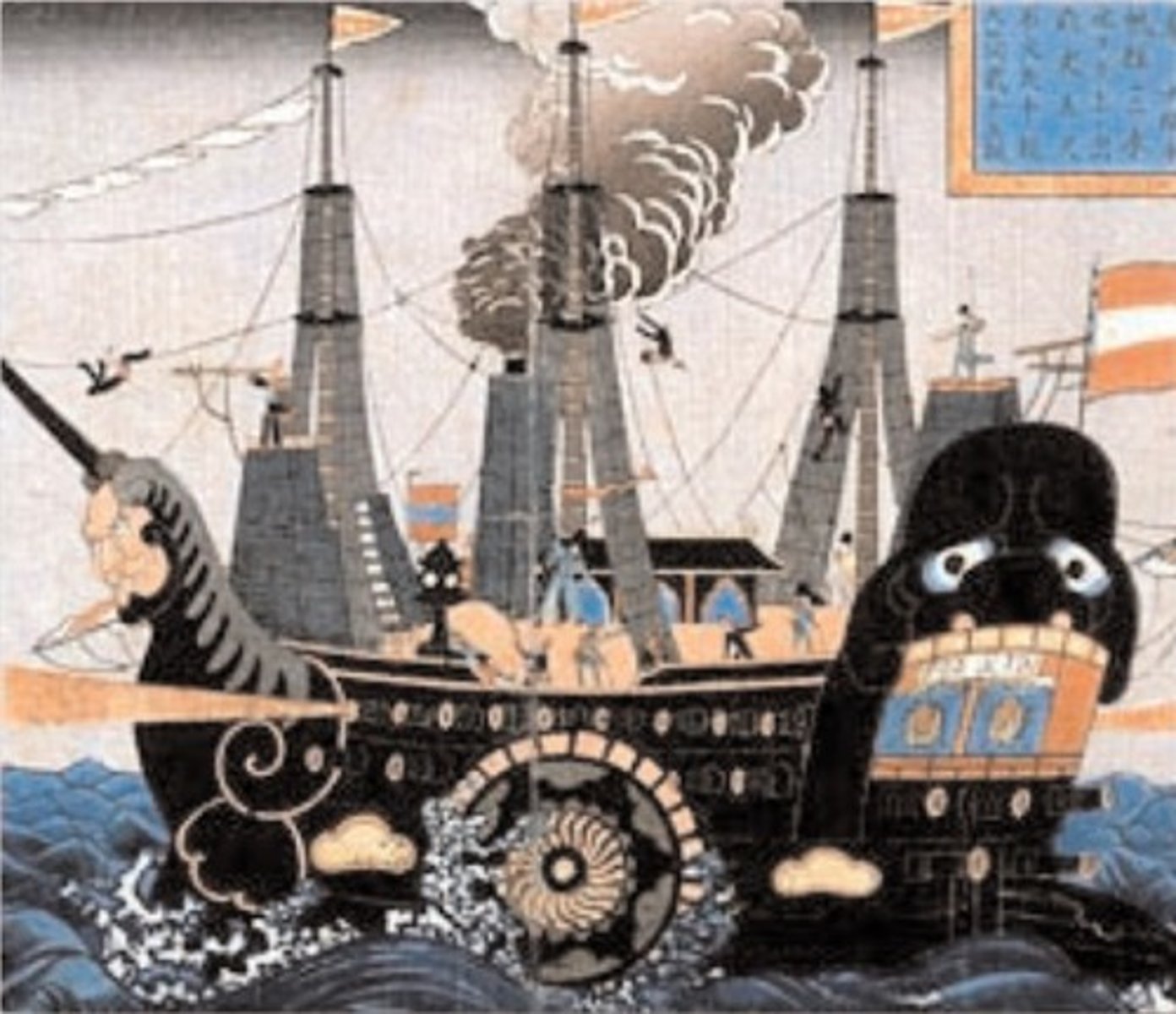
Treaty of Kangawa (1854)
Treaty that was negotiated between the US and Tokugawa Japan to open 2 ports to trade w/ the US

Zaibatsu
The large family-controlled banking and industrial groups that owned many companies in Japan from the Meiji Restoration through World War II.

Meiji Restoration
Political reforms that followed the end of the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1868; set Japan on the path of modernization, industrialization, and imperialism.

Imperial Diet
the highest representative assembly in an empire (refers to Japan's new parliament est. in the Meiji era)
