thyroid eye disease, tumors, lesions and surgeries of the orbit
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
hypothyroidism
decreased production of thyroid hormones
can be structurally or functionally induced
most common cause of hypothyroidism
hashimotos thyroiditis autoimmune mediated attack of the thyroid gland
iodine deficiencies in developing countries
signs/symptoms of hypothyroidism
cold intolerance
fatigue
weight gain
dry skin
course hair
diagnostic testing for hypothyroidism
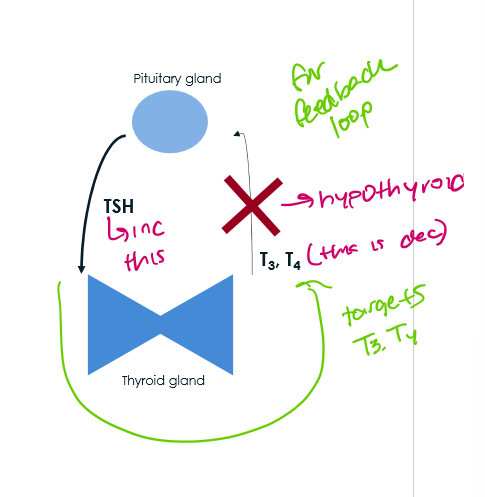
increased TSH
decreased T4, T3, antithyroid antibodies
bio of hypothyroidism
inc TSH from pituitary
thyroid gland doesnt make as mucuh T3, T4
hyperthoidism most common caus e
graves disease - autoimmune disease of TSH autoantibodies constantly stimulating thyroid gland
FEMALE predilection
signs of hyperthyroidism include
heart palpitations
weight loss
heat intolerance
hair loss
diagnostic testing foro hyperthyroidism
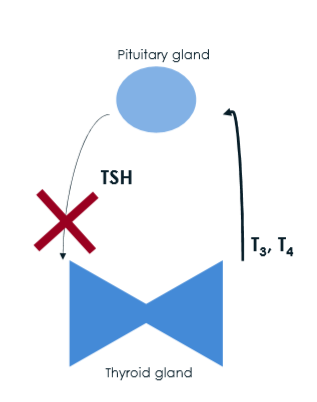
decreased TSH
increased T4, T3, anti-thyroid antibodies
hyperthyroidism biology
no TSH fro pituitary
increased T3, T4 from thyroid
thyroid eye disease cause
autoimmune process that mostly affects pt w graves disease
can occur w other autoimmune diseases of the thyroid
who gets TED
middle aged women
when men get it tho its more severe
whats the controlable risk for TED
smokers
(severe presentation)
what is TED the most common cause of
unilateral or bilateral proptosis in adults
pathophys of TED
autoimmune process affecting fibroblasts of the orbit found on orbital fat and EOM
orbital fibroblasts trigger inflammation
stimulation of T and B lymphocytes
production of pro inflammatory ccytokines
accumulation of GAGs
—> orbital fat expansion of EOM enlargement
—> proptosis/diplopia
what are the general 4 clinical signs of TED
eyelid disorders
ocular surface disorders
EOM disorders
ONH disorders
whats the progression of TED
NOSPECS
no ocular signs or symptoms
only signs, no symptoms
soft tissue swelling
proptosis
EOM involved
Corneal involvement
sight loss form ON head involvement
what does TED eyelid disorders include
eyelid retraction
eyelid edema
reduced blinking
lid lag (von grafe sign)
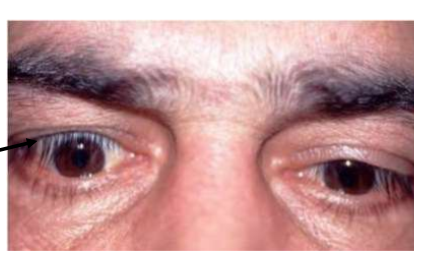
eyelid retraction sign TED
upper eyelid is too high and lower eyelid is too low
Dalyramples sign - retraction of the upper lid on primary gaze
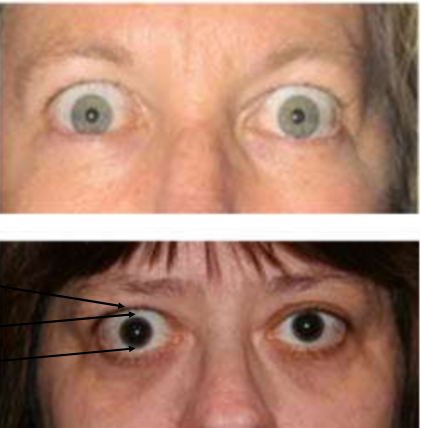
eyelid edema/reduced blinking sign TED
Enroth’s sign - lid puffines
eyelid edema: upper>lower lid
Stellwig’s sign - infrequent blinking
lid lag sign TED
Von grafe sign - lid lag on inferior gaze
ocular surface disorders TED
superficial keratopathy
conjuntival injection
superior limbic keratoconjunctivits
proptosis
superficial keratopathy in TEd
exposure keratopathy
can lead to corneal ulceration, pannus, or perforation if not treaed
due to the increased surface area of eye exposed to air —> bc lids are retracted
also called SPK, PEE (loss of ep cells
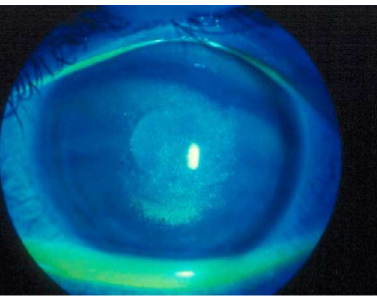
conjunctival injection in TED cause
dryness of ocualr surface causes inflammation of the conj
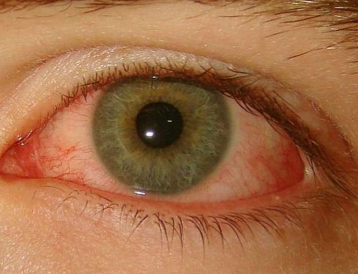
superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis TED cause
thouguht to arise from constant friction btw the superior bulbar conj adn the tarsal conj
what are the norms for whites exophthalmometry range
12-22 mm
what are the norms for black exophthalmometry range
12-24 mm
what are the norms for asian exophthalmometry range
12-18 mm
what asymmetry in exophthalmometry is abnormal
3 mm
what are the EOM disorders of TED
eom restriction
resistance to retropulsion of the globe
whats the order that the EOMs get affected in TED
IM So Lazy
IR, MR, SR, LR
if theres movement in forced duction
negative force duction
if theres not movement in forced duction
positive force duction
EYE WILL NOT MOVE IN DIRECTION OF ACTION
mechanical obstruction (TED)
what are ONH disorders w TED
decreased VA
decrease color vision
positive RAPD
visual field defects
MOST SEVERE W POTENTIAL FOR IRREVERSIBLE VISION LOSS
what are TED symptoms
asymptomatic to decreased vision (depensd on severity)
red eye
foreign body sensation
tearing
bulging eyes
retracted eyelids
diplopia
decreased vision
dyschormatopsia
clincial exam of TED
medial histroy
histroy of throid, autoimmune, or cancer
ask about symptoms of hyper/hypo thyroidism
ask if they smoke
entrance testing
obtain VF tests - will be helpful if it progresses to involve ON
what labs/tests do we do for TED
TSH
T3,T4
thyroid autoantibodies
obrital CT scan w contrast
EOM enlargement w sparing of the tendons
IM So Lazy
when we see what in CT scans we think TED
Coke bottle EOM
what do we do to manage TED
can’t do irrecersible interventions until a 6 mo stable interval is recorded
exception is Optic neuropathy or extreme proptosis causing severe exposure keratopathy or corneal ulceration
sx intervention after a 6 mo quiesent interval
first: posterior sx
second: anterior sx
underlying disease is managed by endocrinolofy
smoking cessation education
what do we do for TED eyelid retraction
sx eyelid recession after 6 mo interval of stable incerval
refer to oculoplastics
how do we manage TED ocular surface issues
corneal protection
topical lubrication (PF-AT) q1hr-PRN
gels/ointments at bedtime
topical immunomodulator
restasis 1 drop BID-6x OU a day
Xiidra 1 drop BID OU
Cequa 1 drop BID OU
lid taping
punctal occlusion
sew part of eyelid closed
how do we treat proptosis/diplopia in TED
systemic steroids
Topezza - IV - q3 weeks x 8 cycles
fresnel prisms
strabismus sx - only after 6 mo stable interval and orbital sx is done
how do we treat compressive optic neuropathy in TED
systemic steroids
orbital decompression sx - refer to oculoplastics
whats Topezza side effect
ototoxicity
what are the 2 tumors and lesions of the orbit
orbital cavernous hemagioma
rhabdomyosarcoma
cause of orbital cavernous hemagioma
most common neoplasm in adults
presents around age 20-40
more in women
presentation of orbital cavernous hemagioma
slow progressive vascular neoplasm of endothelial lined spaces by a fibrous capsule
Main location - wi common tendinous ring
proptosis
signs of orbital cavernous hemagioma
motility defects
proptosis
ONH swelling
symptoms of orbital cavernous hemagioma
painless progressive proptosis
as the tumor grows it may involve EOM and ON
how are orbital cavernous hemagioma managed/treated
for small asymptomatic lesions - monitor every 6 mo w eye exam and imaging
MRI TRICKS
sx excision for large - symptomatic lesions
rhabdomyosarcoma epi
most common childhood primary orbital malignancy
presents wi first decade of life
males more likely to develop
presentation of rhabdomyosarcoma
history of nosebleesd
rapidly progressie proptosis that may mimic an inflamatory procss
rhabdomyosarcoma signs
palpable mass and ptosis ocur 1/3 the time
swelling and injection over the skin develop - but the skin is not warm
what do lab studies and images shoaw of rhabdomyosarcoma
Ct scans - homogenous density usually adjacent to bony structure
systemic investigation - to rule out metastasis — lung and bone
whats the differential diagnosis for rhabdomyosarcoma
orbital cellulitis
treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma
radiation adn chemo
sx excision is for rare recurrent or radioactive resistant tumors
cure rate is 95% if in orbit only
what are the orbital sx
enucleation
evisceration
exenteration
enucleation
detach the EOM and remove the entire eyeball - intraocular contents adn scleral shell
keep EOM
spherical implant to maintain volume - eoms atach to it
after sx a conformer is placed into socket so there can be a prosthetic in the future
if not there could be adhesion of palpebral and bulbar conj
why is enucleation done
intraocular malignancy
trauma
body attacking eye - sympathetic ophthalmia
microophthalmos
EYE IS BLIND AND PAINFUL
who makes an eye prosthetic
ocularist
evisceration
removes intraocular contents but keeps the scleral shella dn EOMs
spherical implant wi the scleral shell
conformer
prosthetic
why woudl you do evisceration
endoophtalmitis
penetrating ocular injury
blind painful eye
why is evisceration better than enucleation
shorter sx
less complex sx
more cost efficient
less disruption of orbital tissues
improved mobility
less change of spread of infection to nervous system
less painful
disadvantages of evisceration over enucleation
risk of sympathetic opthalmia
attacks good eye
risk of dissemination of intraocular tunors
exenteration
removes eyeball and surrounding tissues (lids, nerves, fatty tissue, muscles)
reasons for exenteration
malignant tumor which involves eyelids or structures beding the eye
to prevent metastatic spread of tumor via blood stream
cosmetic sticker possible