Marketing week 5 - products (goods and services)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
products
can be physical goods, services, or experiences.
is what a business provides to satisfy customer needs
composed of core and supplementary features
importance of getting the core product right
if the core product is not good enough, changing the marketing mix will not make it good.
if the core product is good, but other parts of the product package aren’t, then it will let the product down.
most products we buy are a mix
most physical products nowadays come with services (intangible).
e.g., car rentals (tangible) + car insurance (intangible)
product vs brand
product is what your band offers, while the brand exists out in the market place.
does name of brand matter
no. many brands were not well researched, rather named after someone or something. however, you must follow a criteria to aid its marketability.
how to name your brand
consider:
descriptive of benefits
short and memorable
able to be registered
suggest authority and trust
easy to pronounce, read, and spell
translatable
a brand’s distinctive assets
along with brand name, distinctive assets also identify the brand.
colours
logo
labels and packaging
taglines
symbols or characters
celebrities
advertising styles
jingles
if you educate people that your distinctive asset belongs to your brand, your company will be at advantage as it allows it to be noticed in buying situations.
role of labels and packaging
labels identify and promote the brand. packaging protect and promote.
product categories
consumer - buy and use themselves - B2C
industrial - buy and use themselves or use to produce products - B2B
combined - start in one area and move to the other.
new products - three types
continuous innovations - small changes to existing products
discontinuous innovations - new technology in an existing product, but does not require learning new behaviour.
dynamically continuous innovations - significant changes in a product that require consumer learning.
how brands get new products
develop their own
copy
license
buy a patent
buy a company
product category life cycle aka PLC
The product category life cycle, or PLC, refers to the stages a product category goes through from introduction to growth, maturity, and decline. This cycle helps marketers understand how to manage product categories over time.
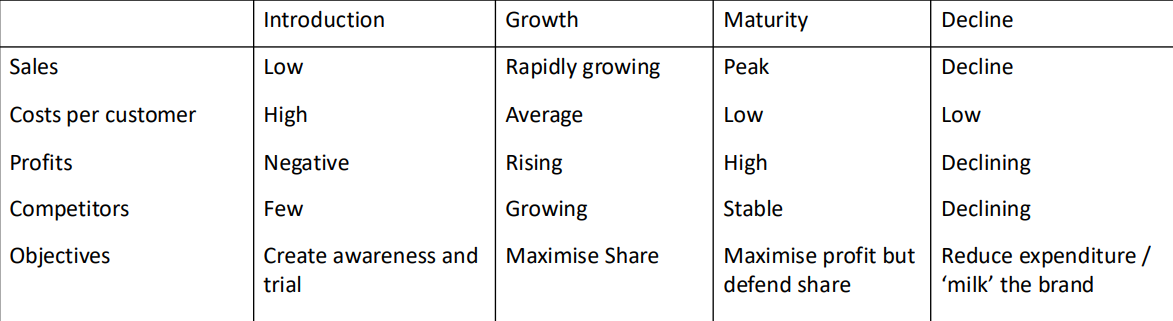
characteristics of services
intangible - cannot be seen, sampled or tested before purchase
perishable - a service like booking a flight is perishable.
inseparable - production and consumption take place simultaneously.
heterogenous - people aka service providers are variable in their performance
key dimensions of quality service delivery
reliability—performing the promised service properly
• assurance—competence, courtesy, credibility and security
• tangibles—physical appearance • empathy—communication and understanding the customer
• responsiveness—timely service
• recovery—the ability of an organisation to rectify aspects of their services (and products) that have caused dissatisfaction to customers.