Bio 124 Chapter 1
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From the actual online textbook, need to add anatomy of viruses and bacteria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Scientists believe that the first forms of life on Earth were _____
microorganisms that existed for billions of years in the ocean before plants and animals appeared
What is biology?
the study of living organisms and their interactions with one another and their environments, so far life is restricted to Earth
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria is/does what?
normal residents of our digestive tracts that aid in absorbing vitamin K and other nutrients, virulent strains are sometimes responsible for disease outbreaks
Hypothesis:
a suggested explanation for an event, which one can test
The diversity of scientific fields includes ________
astronomy, biology, computer science, geology, logic, physics, chemistry, mathematics, and many other fields
Science can be defined as ________
knowledge that covers general truths or the operation of general laws, especially when acquired and tested by the scientific method
The scientific method is a method of ______
research with defined steps that include experiments and careful observation
Cyanobacteria:
blue-green algae, some of Earth’s oldest life forms
What are stromatolites?
ancient structures formed by the layering of cyanobacteria in shallow waters
Who was Sir Francis Bacon?
the first to define the scientific method, 1561-1626
How are science and biology restricted?
natural explanations
Inductive reasoning:
a form of logical thinking that uses related observations/evidence to arrive at a general conclusion
Deductive reasoning:
a form of logical thinking that uses a general principle or law to forecast specific results
Example of inductive reasoning:
members of a species are not all the same, individuals compete for resources, species are generally adapted to their environment
Example of deductive reasoning:
individuals more adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on their traits to the next generation
The scientific method:
consists of a series of well-defined steps, if a hypothesis is not supported by experimental data, a new hypothesis can be proposed
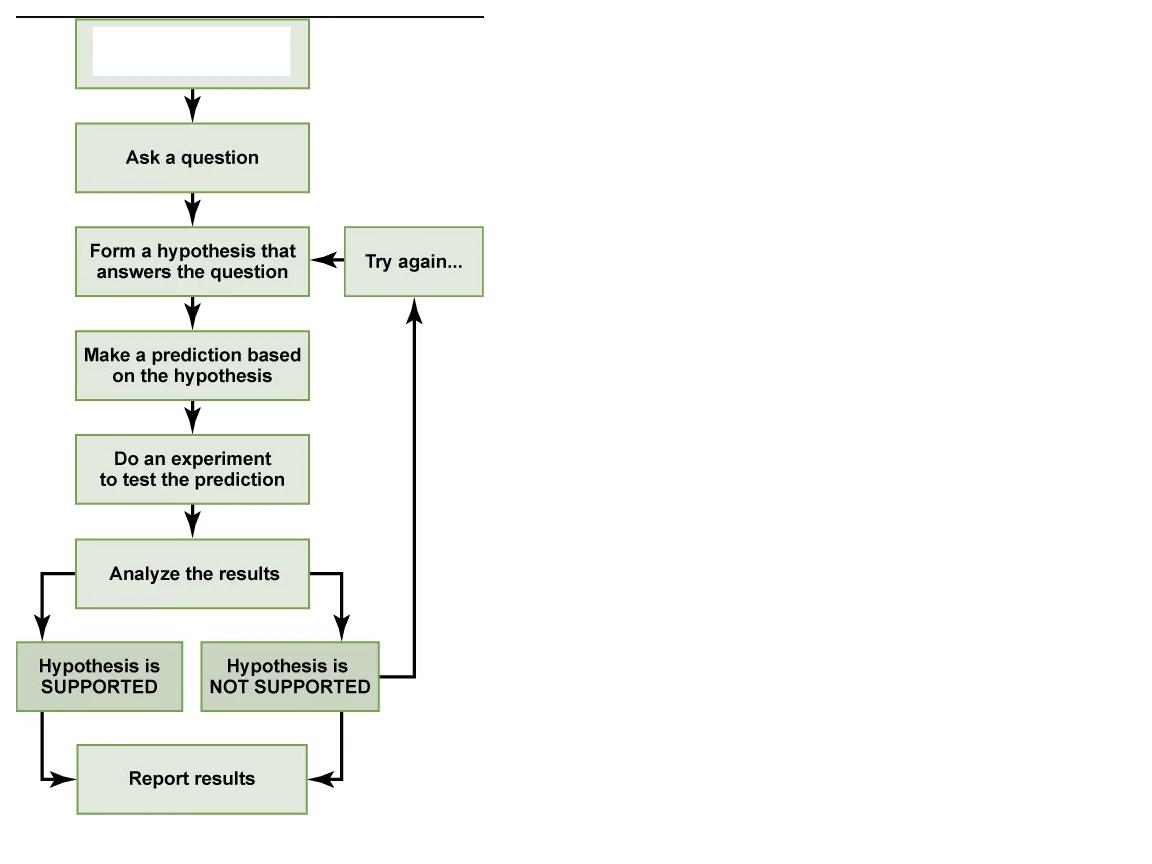
What step is this in the scientific method?
make an observation
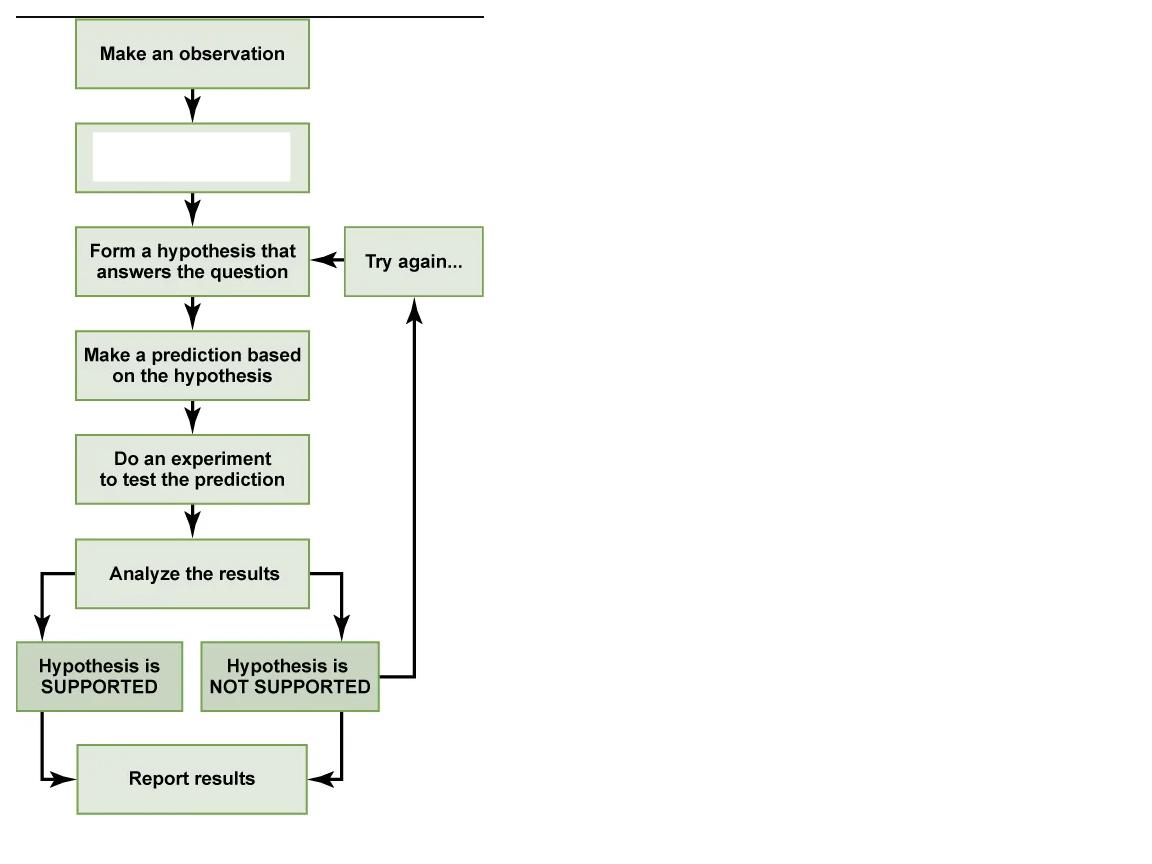
What step is this in the scientific method?
ask a question
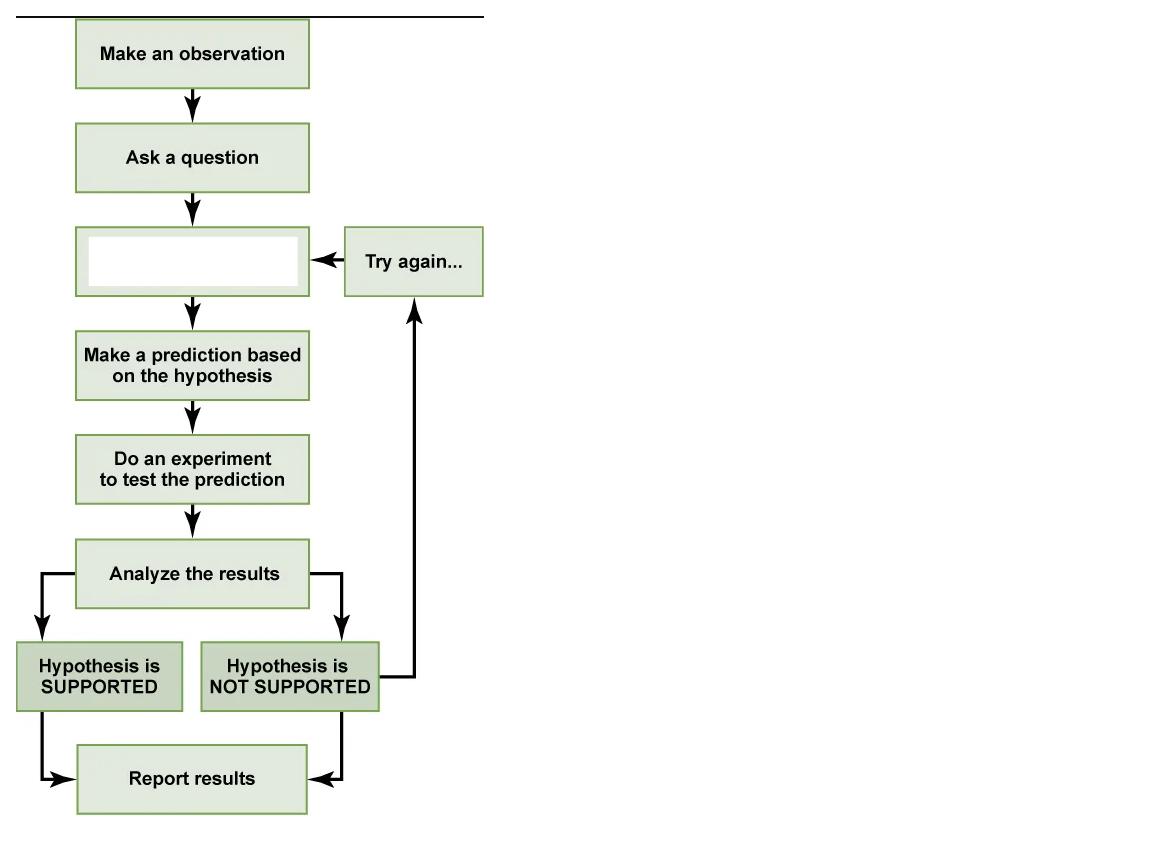
What step is this in the scientific method?
form a hypothesis that answers the question
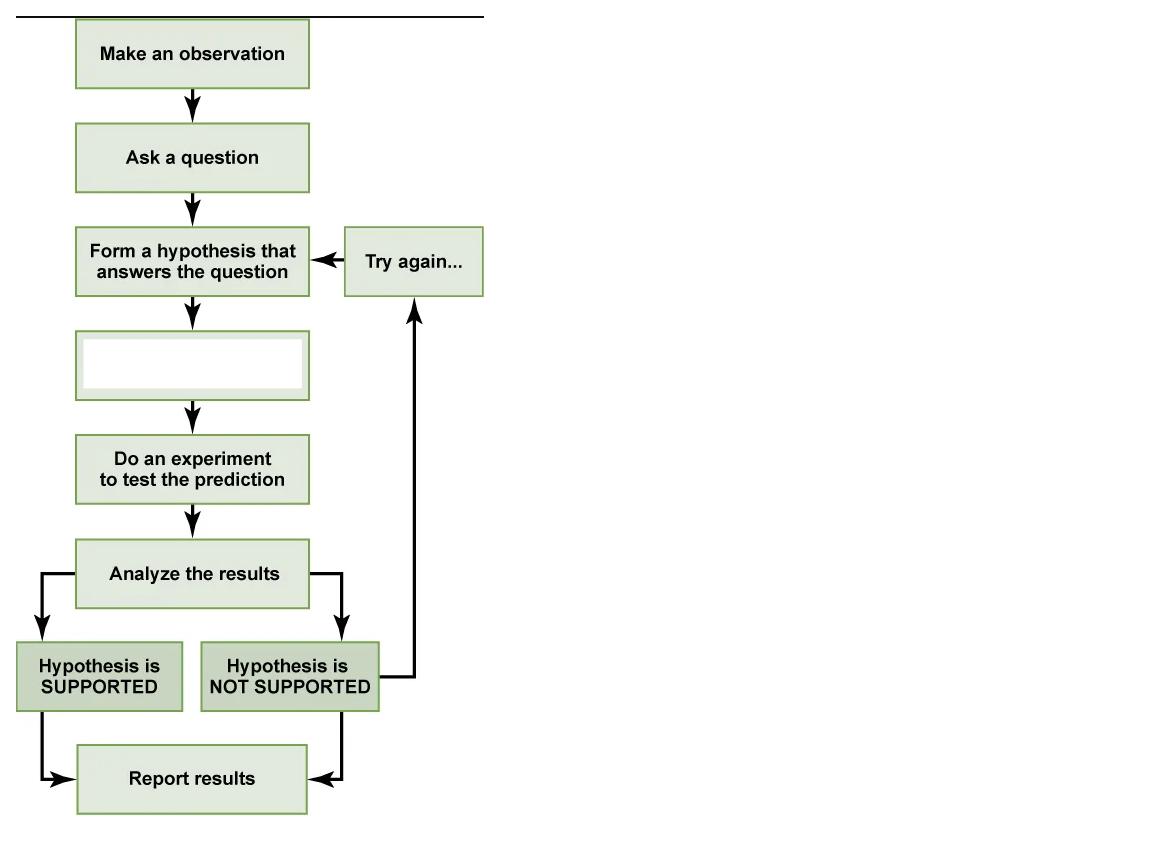
What step is this in the scientific method?
make a prediction based on the hypothesis
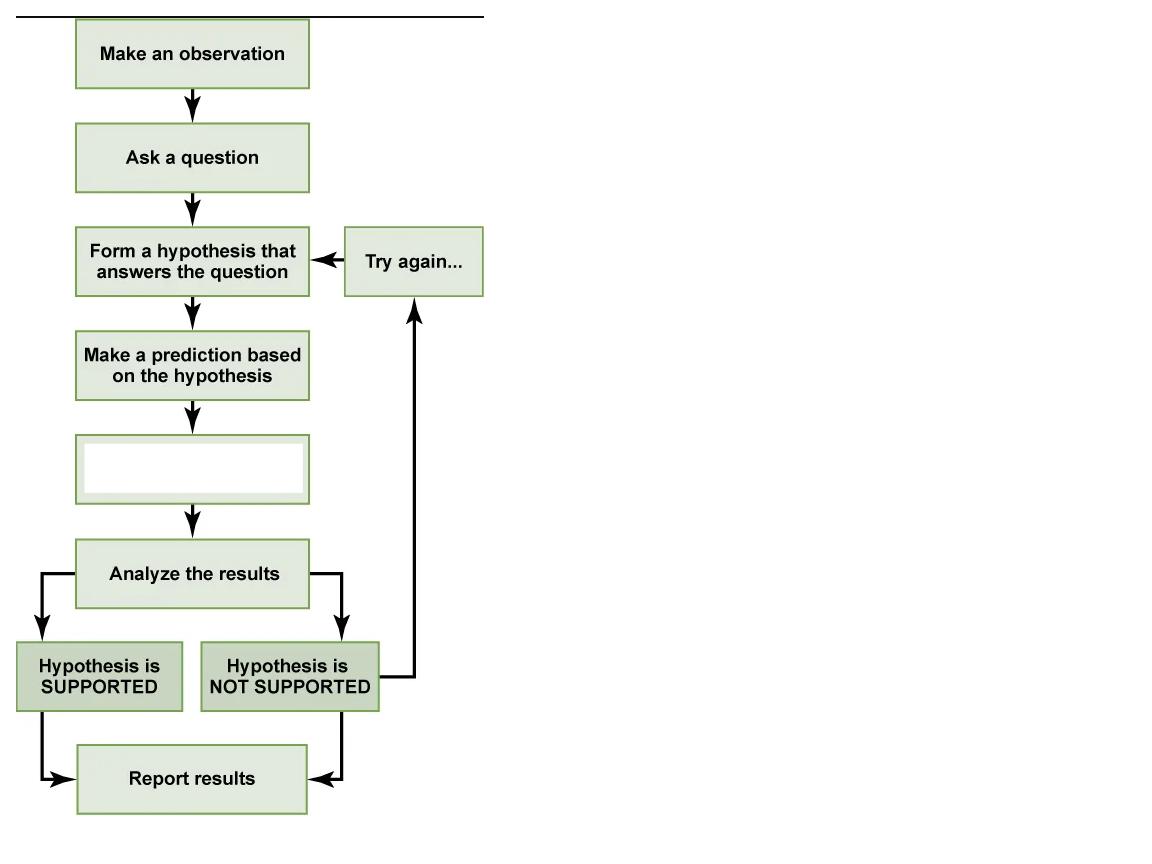
What step is this in the scientific method?
do an experiment to test the prediction
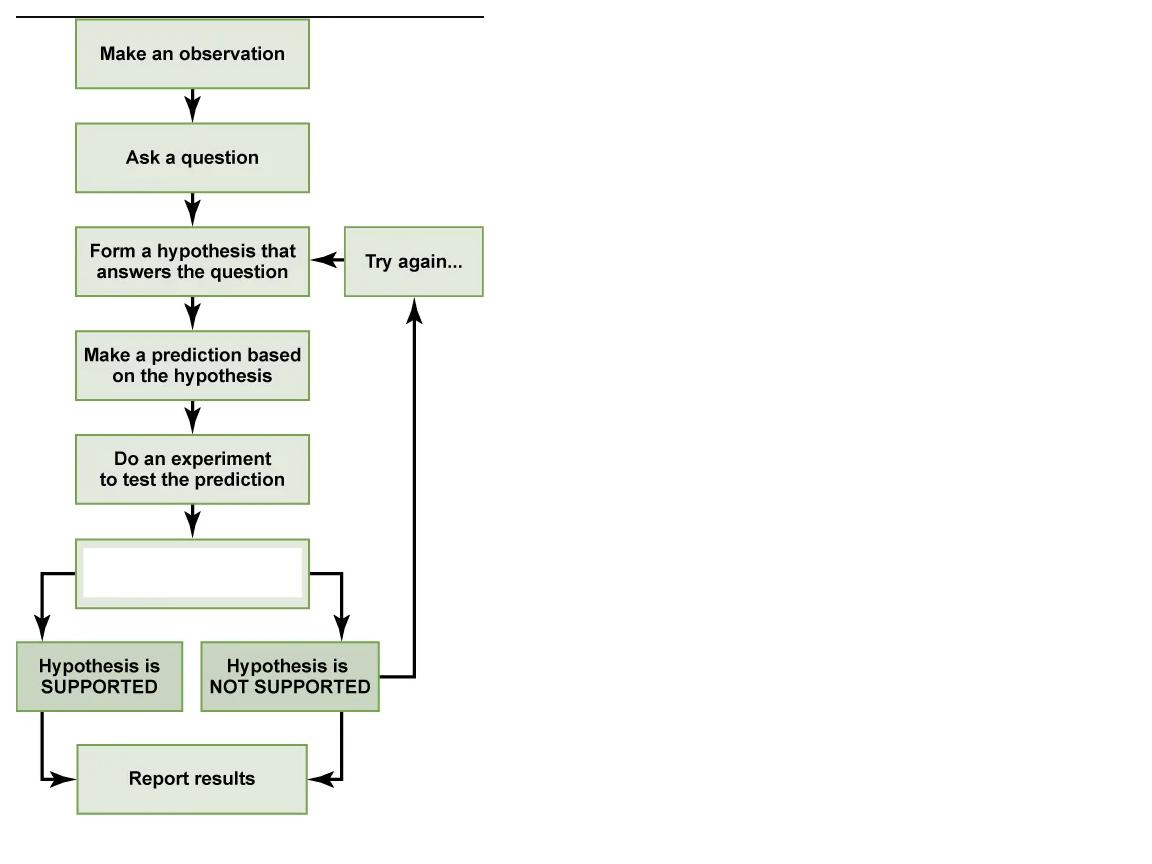
What step is this in the scientific method?
analyze the results
Basic/pure science:
seeks to expand knowledge regardless of the short-term application of that knowledge
Applied science:
aims to use science to solve immediate problems, problems as defined by the researcher
Scientific progress is typically made through _____
the publication of peer-reviewed literature
Peer review involves _______
a blind process whereby scientists submit the details of their experiments, results and interpretations, and reviewers determine the veracity and merit of that work for publication
Properties of life include ____
order, sensitivity or response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, regulation, homeostasis, and energy processing
Example of order:
a toad represents highly organized structure consisting of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems
Example of response to stimuli:
the leaves of this sensitive plant, mimosa pudica, will instantly droop and fold when touched, after a few minutes, the plant returns to normal
All molecules are composed _____
of atoms including DNA
Example of reproduction:
single-celled organisms reproduce by first duplicating their DNA, and then dividing it equally as the cell prepares to divide to form two new cells
Example of adaption:
heat-resistant archaea that live in boiling hot springs to the tongue length of a nectar-feeding moth that matches the size of the flower from which it feeds
Homeostasis:
the relatively stable internal environment required to maintain life
Example of homeostasis:
polar bears living in ice-covered regions maintain their body temperature by generating heat and reducing heat loss through thick fur and a dense layer of fat under their skin
Example of energy processing:
the californian condor uses chemical energy derived from food to power flight
Levels of structural organization of the human body is ____
discussed in terms of six distinct levels of increasing complexity, from the smallest chemical building blocks to a unique human organism
Levels of organization:
atoms, molecules macromolecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems, organisms, populations, and communities, ecosystems and biosphere
Biological levels of organization:
organelles, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems, organisms, populations, and communities, ecosystems, the biosphere
Prokaryotes:
single-celled organisms lacking intracellular organelles, lacks organelles and does not have nuclei surrounded by a nuclear membrane
Bacteria and Archaea are ______
prokaryotes
What are the domains of life?
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
What domains are humans in?
eukarya
Bacteriology:
the study of bacteria
Bacteria is ____
prokaryotic
Bacteria have ____
all the characteristics of living things, the greatest percentage of the biomass on Earth
Cell:
smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living things
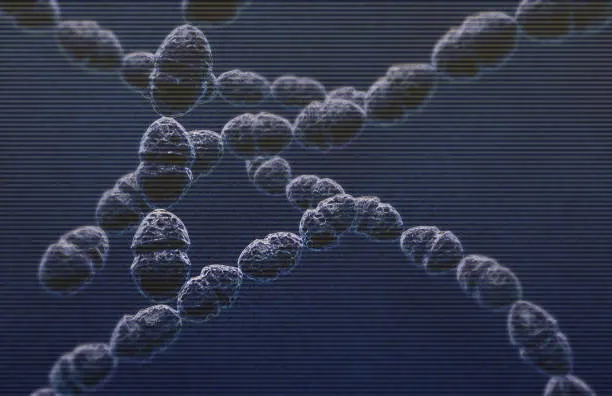
What bacteria shape is this?
spherical(cocci)
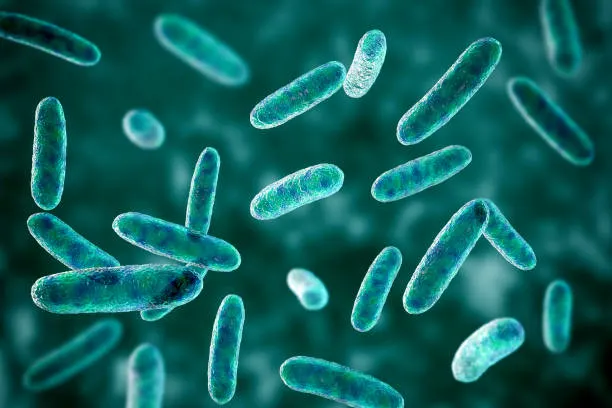
What bacteria shape is this?
rod-shaped(bacilli)
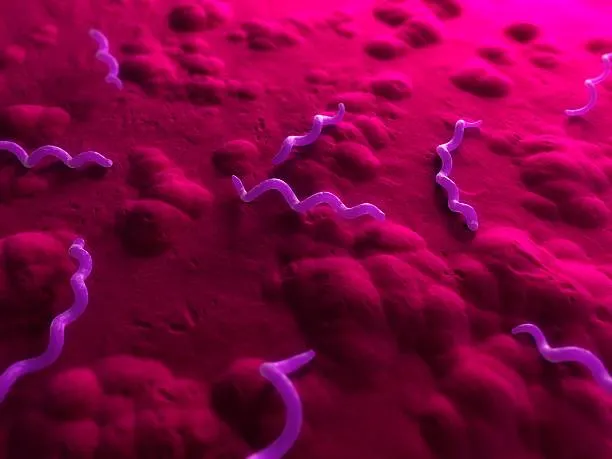
What bacteria shape is this?
spiral(spirilla)
Bacteria help make what?
buttermilk, yogurt, cheese, sauerkraut, pickles, and olives
Bacteria does what?
decomposes organic matter, and chemically changes nitrogen gas into ammonia
What does bacteria do with humans?
location on skin helps prevent infection and bacteria in gut helps digest food and make vitamins
Biotechnology:
used to make antibiotics, insulin, human growth hormone, vitamins, and other drugs
How does pathogenic bacteria work?
they use cells for food by breaking down healthy cells for food which destroys tissue, releases poisonous protein into bloodstream where it can travel throughout the body which disrupts normality and damages tissue
Virology:
the study of viruses
Viruses contain either _____
DNA or RNA that require another cell to survive
Are viruses living?
they have some but not all characteristics of life so no, they exist only to make more
Bacteriophage:
viruses that infect bacteria
Capsid:
protective coat over a virus that contains either RNA or DNA
Viruses need a host cell in order to do what?
to replicate and make copies of itself, any living cell can become a host cell including animals, plants, and bacterial cells
Specific viruses will only infect what?
specific cells, an example would be HIV which will only infect human T cells, a part of your immune system
What disease can a virus cause?
common cold, hepatitis A,B,C, herpes, mononucleosis, warts, chickenpox, polio, influenza, mumps, measles, viral meningitis, AIDS
Antibiotics can only be used to ____
treat bacterial infections
What do vaccines do?
trick the immune system to make antibodies that destroy foreign bodies like bacteria and viruses, the body remembers how to make these antibodies when the real thing invades
What does a vaccine come from?
made from a weakened virus, inactivated virus, or by using only part of the virus/bacteria itself
What is a eukaryote?
organism with cells that have nuclei and membrane-bound organelles
Hypothesis-based-science:
form of science that begins with a specific question and potential testable answers
Macromolecule:
large molecule, typically formed by the joining of smaller molecules
Microbiology:
study of the structure and function of microorganisms
Molecule:
chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by one or more chemical bonds
Neurobiology:
study of the biology of the nervous system
Organ:
collection of related tissues grouped together performing a common function
Tissue:
group of similar cells carrying out related functions
The first forms of life on Earth were ________
microorganisms
A suggested and testable explanation for an event is called a _______
hypothesis
Which of the following sciences is not considered a natural science?
computer science
The type of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion is called ________
inductive reasoning
The process of ________ helps to ensure that a scientist’s research is original, significant, logical, and thorough
peer review
A person notices that her houseplants that are regularly exposed to music seem to grow more quickly than those in rooms with no music. As a result, she determines that plants grow better when exposed to music. This example most closely resembles which type of reasoning?
inductive reasoning
The smallest unit of biological structure that meets the functional requirements of “living” is the ________
cell
Viruses are not considered living because they ________
cannot naturally reproduce
The presence of a membrane-enclosed nucleus is a characteristic of ________
eukaryotic cells
A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area is called a _______
population
Which of the following sequences represents the hierarchy of biological organization from the most inclusive to the least complex level?
biosphere, ecosystem, community, population, organism
Where in a phylogenetic tree would you expect to find the organism that had evolved most recently?
at the branch tips
Give an example of how applied science has had a direct effect on your daily life.
the use of vaccines
Name two topics that are likely to be studied by biologists, and two areas of scientific study that would fall outside the realm of biology.
diseases affecting humans, pollution affecting species habitat but not calculating the surface area of a rectangular ground, functioning of planetary orbitals
Although the scientific method is used by most of the sciences, it can also be applied to everyday situations. Think about a problem that you may have at home, at school, or with your car, and apply the scientific method to solve it.
my car wont start, why won’t it start, ask someone who knows about cars, I think it won’t start because the battery is dead, I charge the car battery, the car started after charging
Consider the levels of organization of the biological world, and place each of these items in order from smallest level of organization to most encompassing: skin cell, elephant, water molecule, planet Earth, tropical rainforest, hydrogen atom, wolf pack, liver.
hydrogen atom, water molecule, skin cell, liver, elephant, wolf pack, tropical rainforest, and planet Earth
Using examples, explain how biology can be studied from a microscopic approach to a global approach.
an ecologist may be able to research about the population of people, the population's community, and the community's ecosystem, and as well as the ecosystem's part in the biosphere