structure and bonding
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Trigonal planar
120
Bent
104.5 2 lone pairs
Linear
180
Tetrahedral
109.5
Pyramidal
107 one lone pair
Octahedral
90
Trigonal bipyramidal
120 90
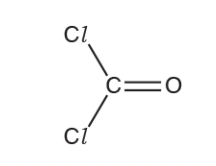
Name the shape of a phosgene molecule and explain why it has this shape
trigonal planar
3 bonding regions/3 bonded pairs and no lone pairs
electron pair repulsion — bonded pairs repel each other equally
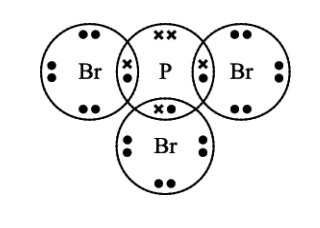
Name the shape of this molecule and explain why the molecule has this shape.
pyramidal
3 bonded pairs and 1 lone pair
the lone pair repels the bonded pairs more greatly than they repel each other so will give a pyramidal shape overall
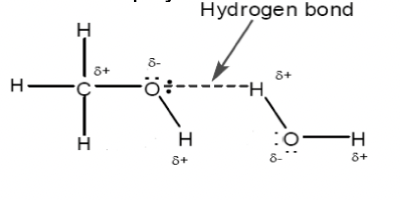
Use a labelled diagram to explain why methanol is soluble in water.
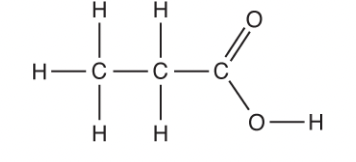
State the shape and bond angle around a carbon atom in the alkyl group of propanoic acid. Explain the shape.
tetrahedral
109.5
four bonded pairs repel each other equally
Suggest a value for the C–O–H bond angle in propanoic acid.
104.5
State what is meant by the term ionic bond.
electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
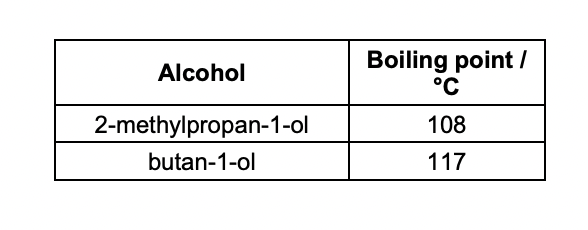
Explain why the boiling points are different.
2-methylpropan-1-ol has less surface contact
weaker london forces
therefore less energy required to break london forces
This question is about halogens. Solid chlorine and solid bromine have a similar structure. Name this structure.
simple molecular lattice
The shape around the oxygen atom in butan-2-ol is non-linear. Predict the C−O−H bond angle and explain this shape
104.5
2 bonded pairs and 2 lone pairs
the lone pairs repels the bonded pairs more greatly than they repel each other
Explain the differences in the melting points of phosphorus and chlorine
phosphorous has more electrons
stronger london forces
more energy required to break the london forces
Explain the different boiling points of NH3, F2 and Br2.
NH3 has hydrogen bonding
F2 and Br2 have london forces
there are forces between molecules in ammonia and fluorine and bromine
the london force in br2 are greater than in f2 because bromine has more electrons than flourine
the london forces in br2 are greater than hydrogen bonding in NH3 but the hydrogen bonding in NH3 is stronger than the london forces in F2
Explain what is meant by the term electronegativity.
the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
Draw a 3-D diagram of a molecule of CH2Cl2. Use partial charges to indicate polar bonds.
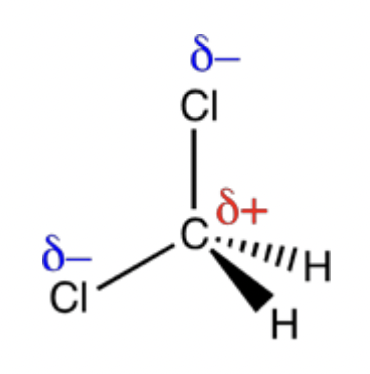
Explain why a CH2Cl2 molecule is polar.
the dipoles do not cancel out because the molecule is asymmetrical
Describe what is meant by the term ionic lattice, in terms of the type and arrangement of particles present.
repeating pattern of oppositely charged ions
What is meant by the term covalent bond?
the electrostatic attraction between 2 nuclei and a shared pair of electrons
Complete the diagram below to show hydrogen bonding between the H2O molecule shown and one other H2O molecule.
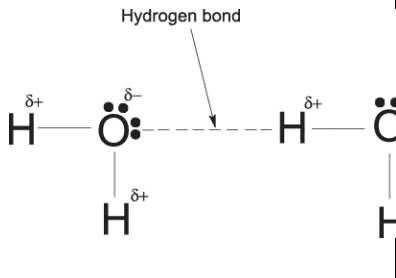
State and explain two anomalous properties of ice caused by hydrogen bonding.
ice is less dense than water
the molecules in ice are held apart by hydrogen bonds and ice has an open lattice
ice has a relatively high melting point
hydrogen bonds are relatively strong and more energy needed to overcome it
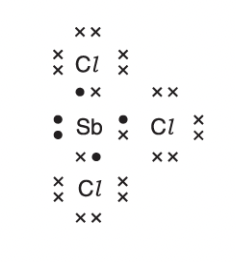
Predict the shape of a molecule of SbCl3.
pyramidal
3 bonded pairs and one lone pair of electrons
the lone pair repels the bonded pairs more greatly than the bonded pairs repel each other
SbCl3 molecules are polar. explain why
there is a difference in electronegativities and so bonds are polar
the molecule is not symmetrical and the dipoles do not cancel
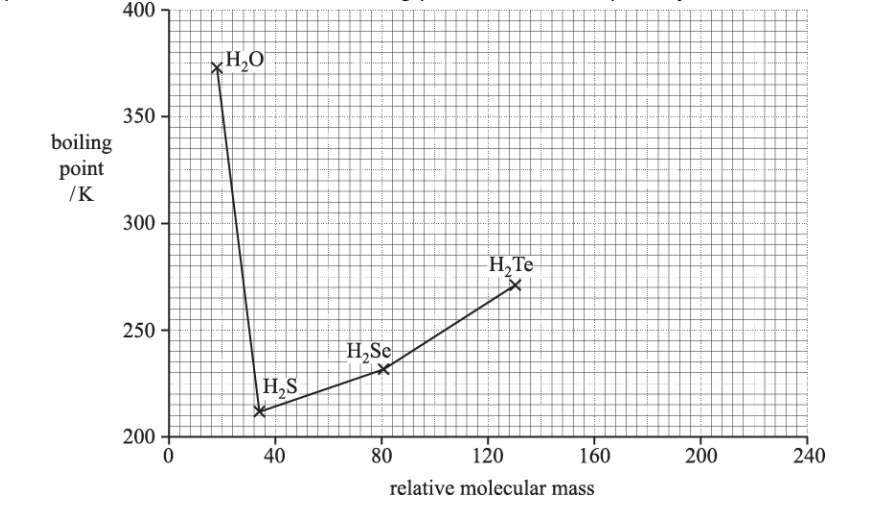
The variation in boiling point can be explained by intermolecular bonding. Explain why H2S has a lower boiling point than H2O and H2Se.
h2o has hydrogen bonding
hydrogen bonding is stronger and requires more energy to overcome
london forces in h2s are weaker as it has fewer electrons
less energy the overcome london forces
Predict the type of structure and bonding of SO2 and MgO and explain the difference in their melting points.
MgO = giant ionic
SO2 = simple molecular
ionic bonds in mgo are stronger than intermolecular bonds
ionic bonds need more energy to overcome
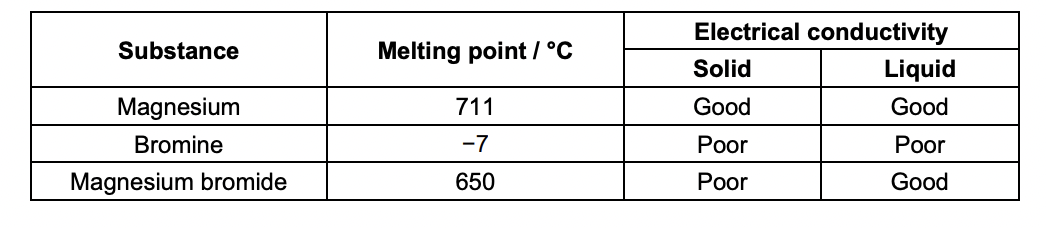
Explain the physical properties shown in Table 16.1 using your knowledge of structure and bonding.
MAGNESIUM
giant lattice
metallic bonding
delocalised electrons
bromine
simple molecular
london forces between molecules
magnesium bromide
giant lattice
ionic bonding between oppositely charged ions
metallic and ionic bonds are stronger than london forces
magnesium conducts due to delocalised electrons that cna move
magnesium bromide = solids ions cannot move but in solution ions can move
bromine does nto conduct as no mobile charge carriers
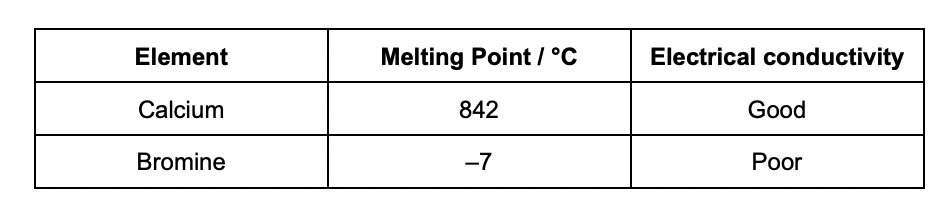
Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain the properties in the table
calcium = metallic bonding and is a giant lattice
electrons are delocalised
metallic bonds are strong need large amount of energy
br2 = simple molecular and has london forces between molecules
charge carriers are not mobile
london forces are weak and need little energy
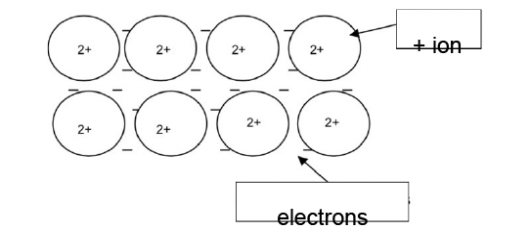
Explain these physical properties of strontium, in terms of bonding and structure. Include a labelled diagram in your answer.
melting point high
very good electrical conductivity
metallic bond strong and require a lot of energy to break — high mp
strong attraction between electrons and positive ions
delocalised electrons can move — good conductivity
Solid SiO2 melts at 2156 °C. Solid CO2 melts at −56 °C. Suggest the type of lattice structure in solid SiO2 and in solid CO2 and explain the difference in melting points in terms of the types of force within each lattice structure.
sio2 = giant covalent
covalent bonds
co2 = simple molecular
london forces
covalent bonds are stronger than london forces so more energy to break bonds in sio2 than london forces in co2
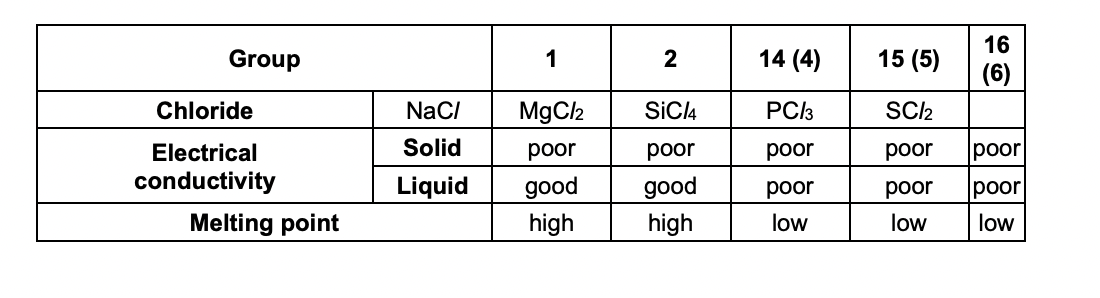
Explain the properties shown in Table 1.1 in terms of bonding and structure.
mgcl2 = giant ionic lattice
ions are mobile in liquid state
sicl4/pcl3/scl2 = simple molecular
london forces
ionic bonds are stronger than london forces
Explain the differences in the melting points of sodium and magnesium, using the model of metallic bonding.
magnesium has more outer electrons
magnesium ions have a greater positive charge
magnesium has a greater attraction between ions and delocalised electrons
Magnesium and silicon have different types of giant structures. Describe the bonding in magnesium and in silicon
magnesium has metallic bonds, positive ions and delocalised electrons
silicon has covalent bonds between atoms
Describe and explain the electrical conductivity of sodium oxide, Na2O, and sodium in their solid and molten states.
sodium conducts in solid and molten states
sodium has delocalised electrons
na2o conducts when molten and not when solid
molten na2o has ions which are mobile
sold na2o has ions which are fixed in an ionic lattice
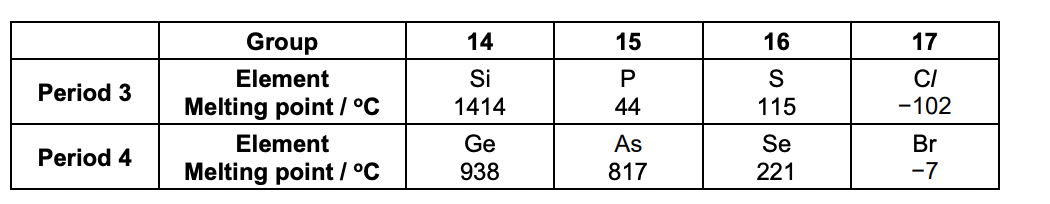
Explain the trend in melting point from Si to Cl across Period 3. • Comment, with reasons, on the similarities and differences in the trends across Period 3 and Period 4.
si = giant covalent, covalent bonding and atoms
p,s,cl = simple molecular, london forces, molecules
covalent bonds in si are much stronger than london forces
london forces greater with larger molecules as there are more electrons
the stronger the force the higher the melting point
period 4 = ge, se, br similar trend
as has much higher mp suggesting giant structure
ge has low mp suggesting weaker covalent bonds