Glycogen Metabolism
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the five utilization of Glucose? What are the three sources?
Utilization of Glucose
glycolysis (energy production)
glycogen synthesis (storage mainly in liver and skeletal muscle)
complex carbohydrate (glycosaminoglycans, oligosaccharides)
Pentose-phosphate pathway (NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate production)
conversion of sorbitol (fructose synthesis, mainly in seminal vesicles)
Sources of glucose:
Diet
glycogen degradation
gluconeogenesis (DE NOVO in Kidney and Liver Only)
What organ uses glycogen the most? What is glycogen important for? Where are most of the glycogen stores in the body?
Muscles. Glycogen is important for cells that almost exclusively rely on glucose as an energy source. Most of the glycogen stores in the body is the liver and muscles
What tissues preferentially use glucose?
brain (fatty acids can’t get pass the blood-brain barrier)
Red Blood cells (no mitochondria)
testes, medulla of kidneys, cornea of eyes, lens (poor in mitochondria)
exercising muscles (short term high intensity exercise requires glucose)
what pathway is used in short-term fasting? in long term fasting.
short term = glycogenlysis by liver
Long term = gluconeogenesis by liver
Describe the differences in glycogen degradation in the liver and muscle.
why can’t muscle provide glucose to the blood stream?
in liver:
when glycogen degradation is activated, glycolysis is inhibited
provides glucose for maintaining blood glucose level
in muscle:
glycolysis and glycogen are induced at the same time to produce ATP
provides energy to the excercising muscle
Muscle can’t provide glucose to blood stream by GNG because it is missing glucose-6-phosphatase
describe the role of liver glycogen in Newsborn.
What happens when the mother is malnourish during pregnancy?
During pregnancy: mother provides glucose to newborn
during last 10 weeks of pregnancy: baby build up glycogen stores (due to high insulin level)
after birth: glucose from mother stops
after birth: baby degrades glycogen to help with glucose levels (initiated by glugagon and insulin)
if mother is malnourish, baby presents hypoglycemia due to low glycogen stores
Where is glycogen stored in the cell?
What is in the center of every glycogen core? What does it do?
Explain glycogen’s chemical structure? Describe the different bonds in glycogen
glycogen is stored in the cytoplasm of cell
at the center, there is a glycogenin protein; it binds glycogen covalently via tyrosine residue
it is an alph-D- glucose polymere;
It has two type of bonds
alpha(1-4) glycosidic bond: most of glucose in glycogen is stored this way
alpha (1-6) glysoidic bond : these are how the glycosidic branches occur; every 8-10 glucose molecule
Draw out the general metabolism of glycogen in the liver
everything non-reversible
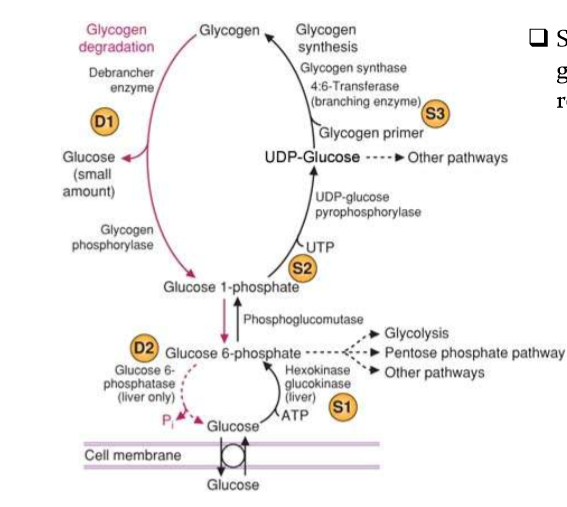
Why do we must make glucose-UDP before attaching it to the growing chain of glycogen? What enzyme catalyze this?
because in order for monosaccharides to be built to oligo or polysacharides, it must be nucleotide-activated
this is catalyzed by UDP-glucose-phosphorylase
Describe glycogen synthesis starting at the formation of UDP-glucose
Glucose with UDP-Glucose-Phosphorylatse—>Glucose-UDP
There, it can elongate the chain via Glycogen Synthase (makes 1-4 bonds)
or
can make new branches via branching enzyme (4:6 transferase) (makes 1-6 bonds)
describe how glycogen degradation occur? During this process, what occurs every 9th glucose generated? What happens in the lysosome?
degradation occurs in the cytoplasm via glycogen phosphorylase —→ this produces glucose-1- phosphate; G1P has to be isomerized to G6P for use in GNG to make glucose
at every 9th glucose created; debranching enzyme ( which has alpha(1-6) glucosidase activity and a transferase activity). This result in a FREE GLUCOSE
in the lysosome: degradation occurs by acid a-glucosidase (lysosomal a(1-4)-glucosidase). Glucose comes off as a FREE GLUCOSE
what are the three isoforms of glycogen phosphorylase
liver (LL)
muscle (MM)
Brain (BB)
what enzyme catalyzie isomerization of G1P to G6P?
phosphoglucomutase
How does the liver provide the glucose produced from glycogenolysis to the rest of the body?
G1P —> G6P via phosphoglucomutase
G6P is translocated from the cytoplasm to the ER by glucose-6-P translocase.
In the ER, G6P is converted to Glucose via glucose-6-phosphatase
Glucose is then transported out of ER by Glut-7
Glucose then is secreted to circulation via Glut-2
what is Von Gierke Disease and its consequences?

Describe the deficiency, organs involved, blood metabolites and other information for type 0 —> type VI glycogen storage disease
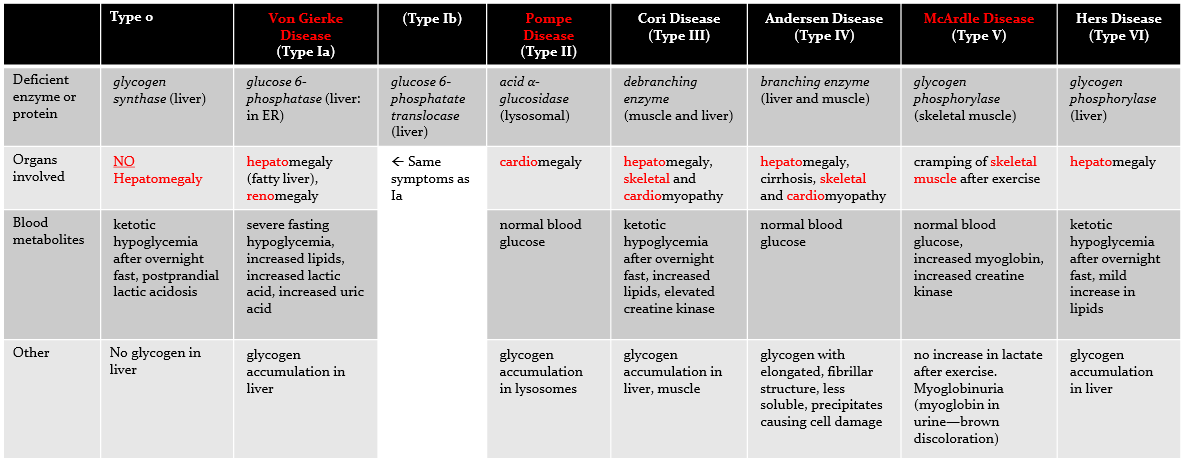
how is glycogen accumulation detected?
via periodic acid - Schiff (PAS) stain
What is the relationship between Lactic Acidosis and Hyperuricemia? How does Uric Acid cause gout?
Lactic Acidosis causes uric acid absorption in the kidneys
This is done via URAT1 which couples Lactic excretion with Uric Acid absorption
Uric Acid is a purine degradation product associated with gout.
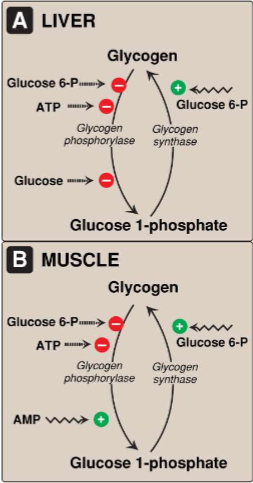
Describe the allosteric regulation of Glycogen Metabolism in the Liver and the Muscle
Describe the hormonal regulation of glycogen metabolism
Glycogen degradation is activated by Phosphorylation
Glycogen synthesis is activated by Dephosphorylation
Glucagon/epinepherin phosphorylates Glycogen phosphorylase —> glycogen degradation
Insulin dephosphorylates glycogen synthesis —> Glycogen synthesis occurs
Describe the pathway in which glucagon regulates glycogen metabolism
Glucagon binds to glucagon Receptor (GPCR) —> activates adenyl cyclse and protein kinase A —> phosphorylates phosphorylase kinase (activate) and glycogen synthase (inactive) —>phosphorylase kinase phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase (active) —> glycogen is degraded
how does epinepherine regulates glycogen metabolism?
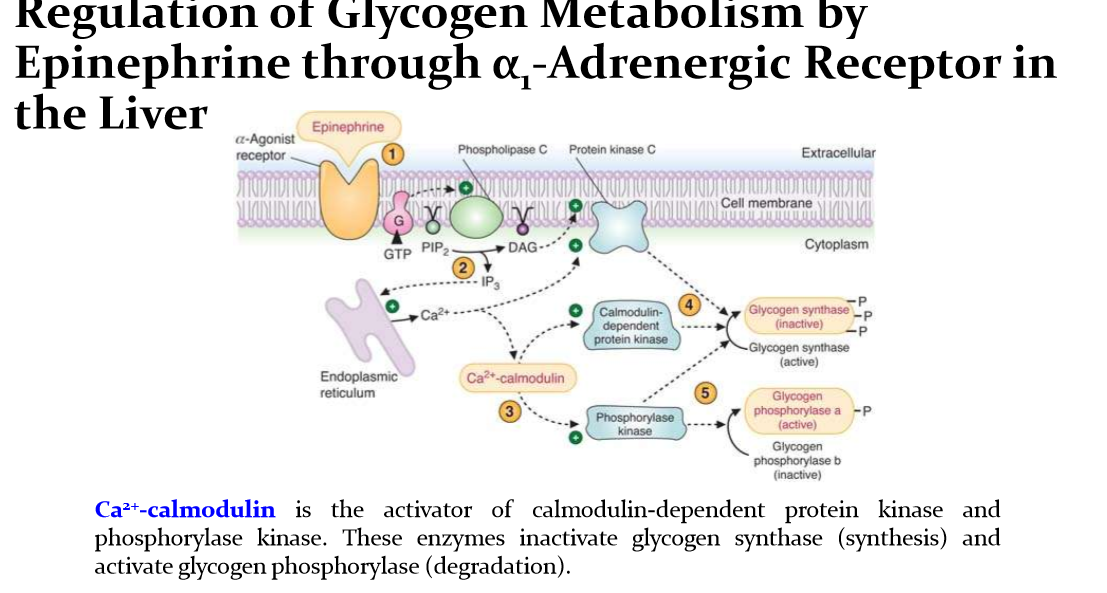
what two receptors can epinepherin bind to for glycogen metabolism
B2 adrenergic receptor (same pathway as glucagon)
A1 adrenergic receptor
How does insulin regulate glycogen metaolism
activates protein phosphatases —> dephosphorylate glycogen phosphorylase (inactivates) and glycogen synthesis (activates)
Can also activate phosphodiesterase which destroys cAMP (secondary messenger for glucagon regulation pathway of glycogen metabolism)
describe the regulation of glycogen breakdown in muscle
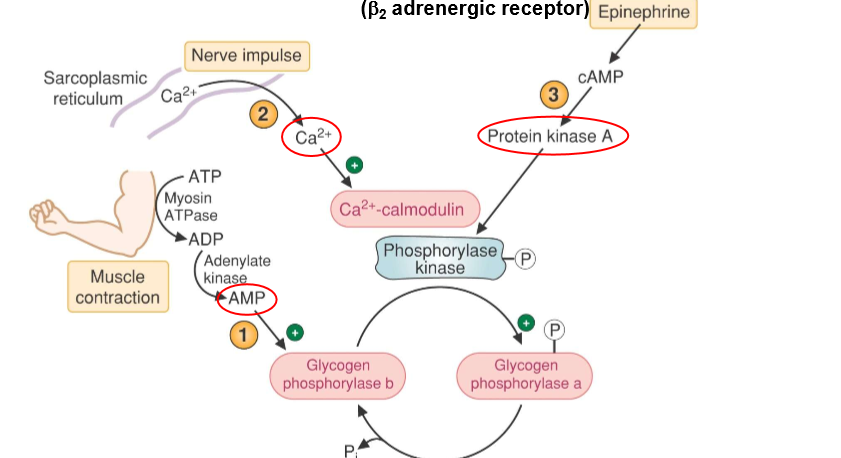
what is the difference between regulation of glycogen metabolism in the liver and the muscle?
glycogen phosphorylase from both are genetically different from each other
muscle glycogen phosphorylase is allosterically activated by AMP (produced during high intensity excercise)
glucagon is not an inhibitor of muscle glycogen phosphorylase
glucose is not an allosteric inhibor of muscle glycogen phosphorylase
glucagon has no effect on muscle glycogen metabolism
excercise stimulates release of Ca2+ which induces glycogen degradation via ca2+ calmodulim