1 introduction to cattle lameness
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1. lose status of dominance
2. inc. interval between calving and conception
3. more time laying down in a single event, less time down in a day
How can we tell cows are lame by their activity in the herd?
Losses from DISEASE not treatment:
lower milk production, lower fertility rates, higher culling rates, discarded milk, management practices to care for lame cows
How does lameness in cows cause economic loss?
1. lameness
2. mastitis
3. retained placenta
4. displaced abomasum
What are the most costly clinical diseases of dairy cattle?
1. repro problems
2. mastitis
3. lameness
What are the most common causes of culling or premature removal from the herd for cattle?
1. floors that are abrasive, wet, and hard
2. less time laying down
3. prolonged feet exposure to wet slurry
4. rations to encourage ruminal acidosis
5. slippery floors
6. systemic disease
7. improper trimming
Name some of the MANY factors that determine cattle lameness
90% originate in foot, 90% involve rear foot, and 90% involve lateral claw (and typically axial location of lateral claw)
What is the most COMMON PLACE for lameness in cows?
1: stands and walks normally with level back and confident strides
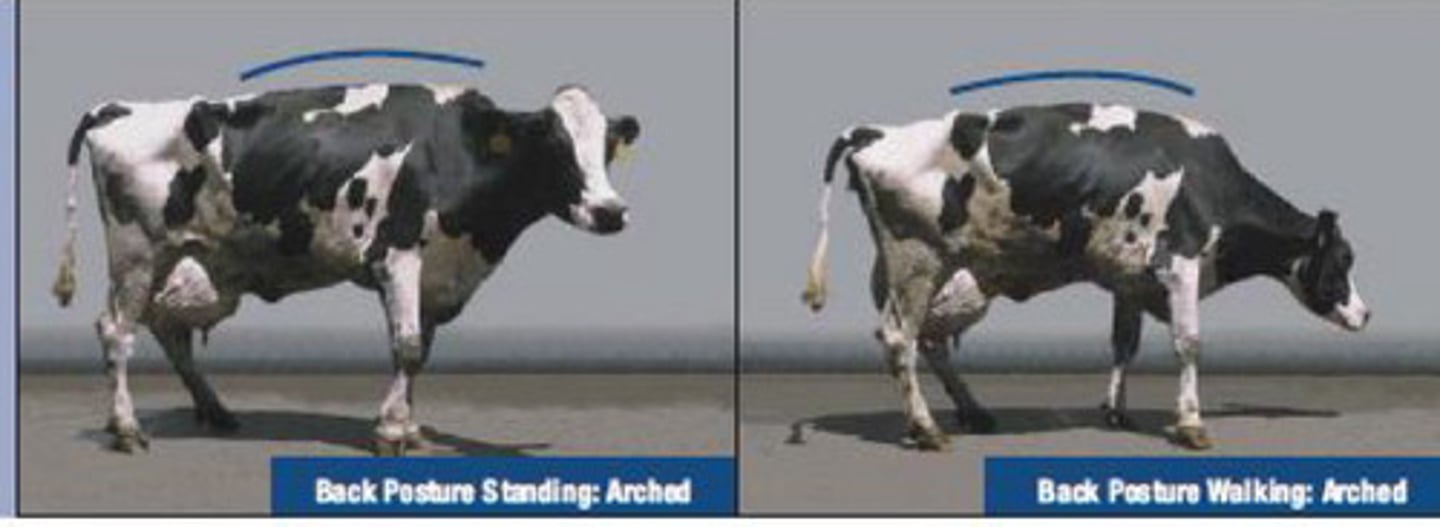
2. stands with flat back, arches when walking, slightly abnormal gait
3. arched back standing and walking, short stride
4. arches back standing and walking, can still bear some weight
5. pronounced arching of back, reluctance to move and toe touching
Name the stages of locomotion score in cattle
1
This cow stands and walks normally with a level back and long confident strides. What is the locomotion score?
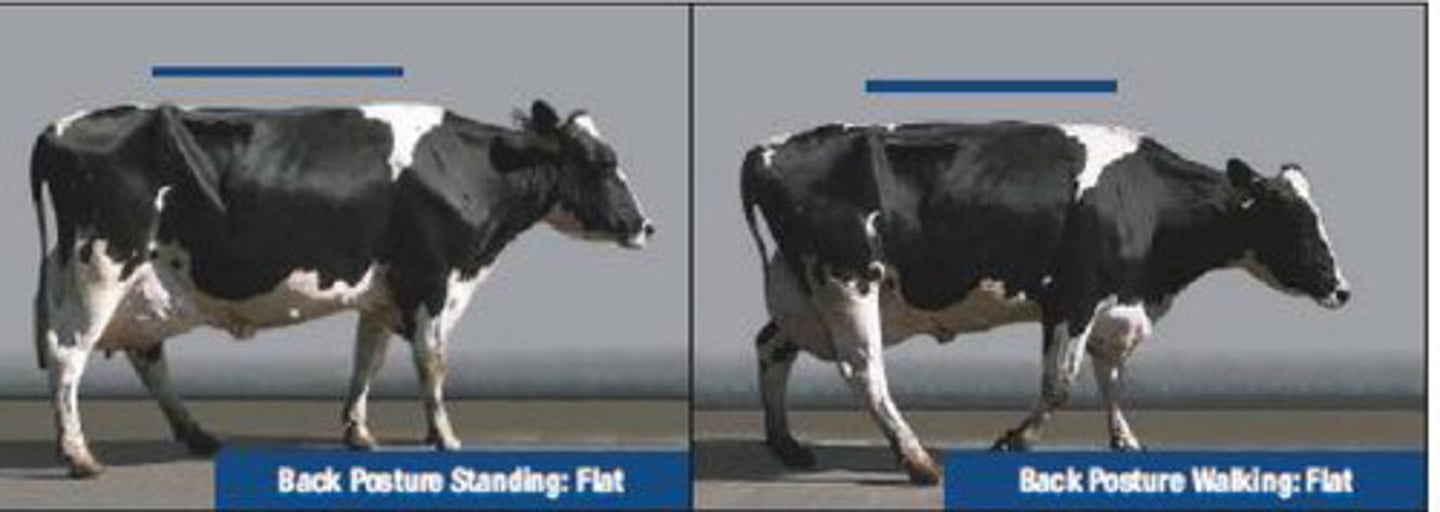

2
This cow stands with a flat back, arching when walking. It is only mildly lame with a slightly abnormal gait. What is the locomotion score?
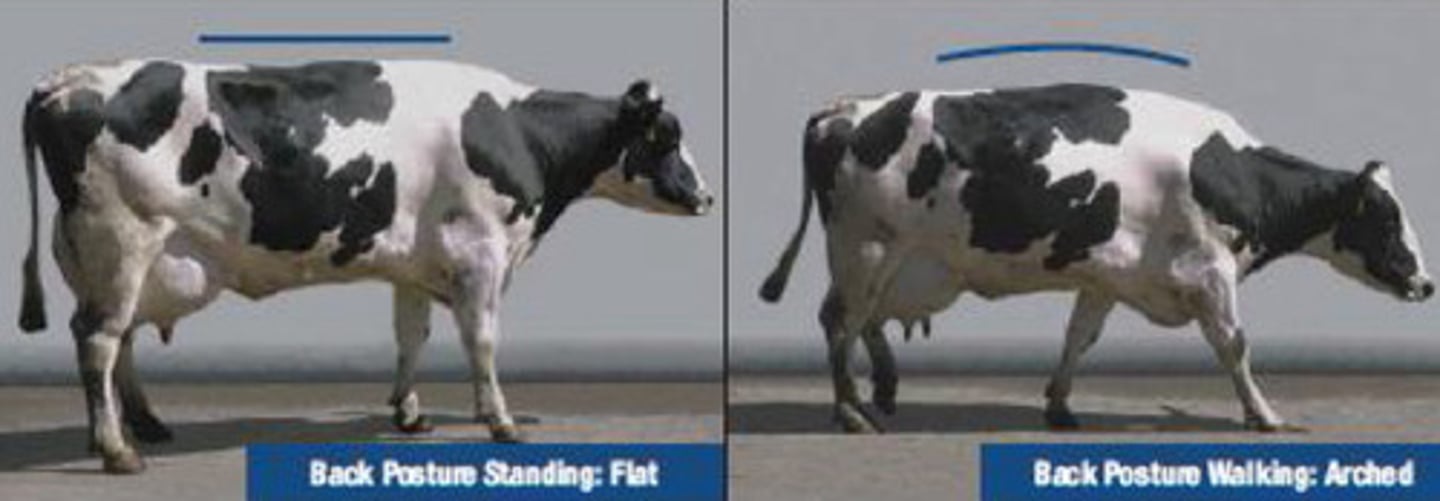

3
This cow has an arched back when standing and walking. It is moderately lame with a short stride. What is the locomotion score?
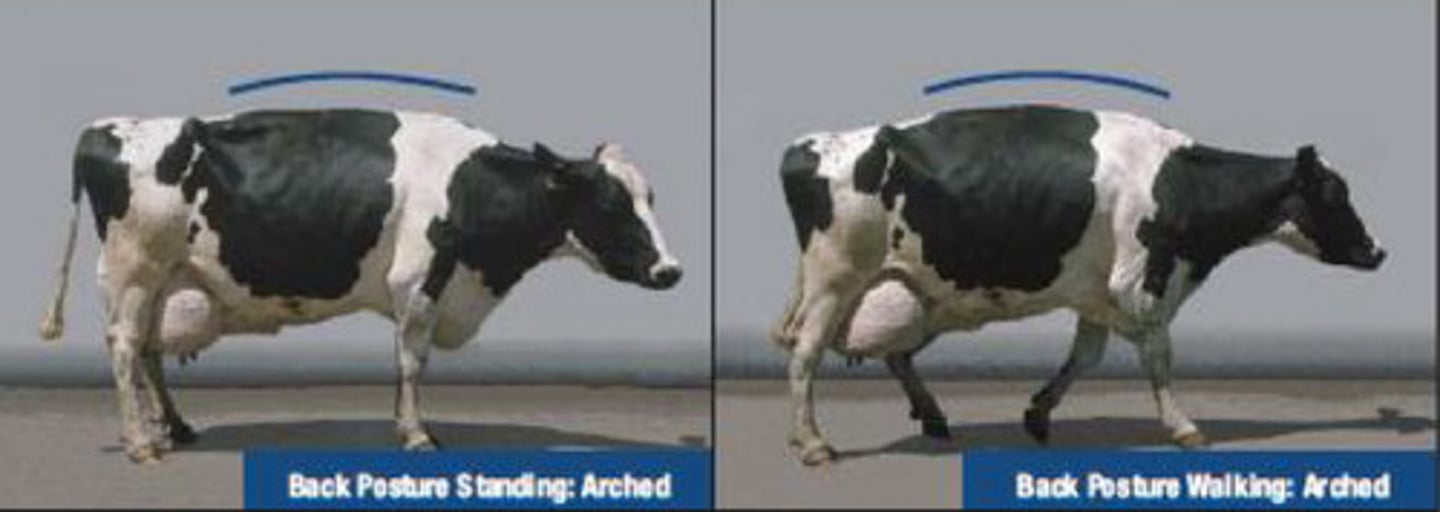

4
This cow has an arched back when standing and walking. It is positively lame but can still bear some weight. What is the locomotion score?
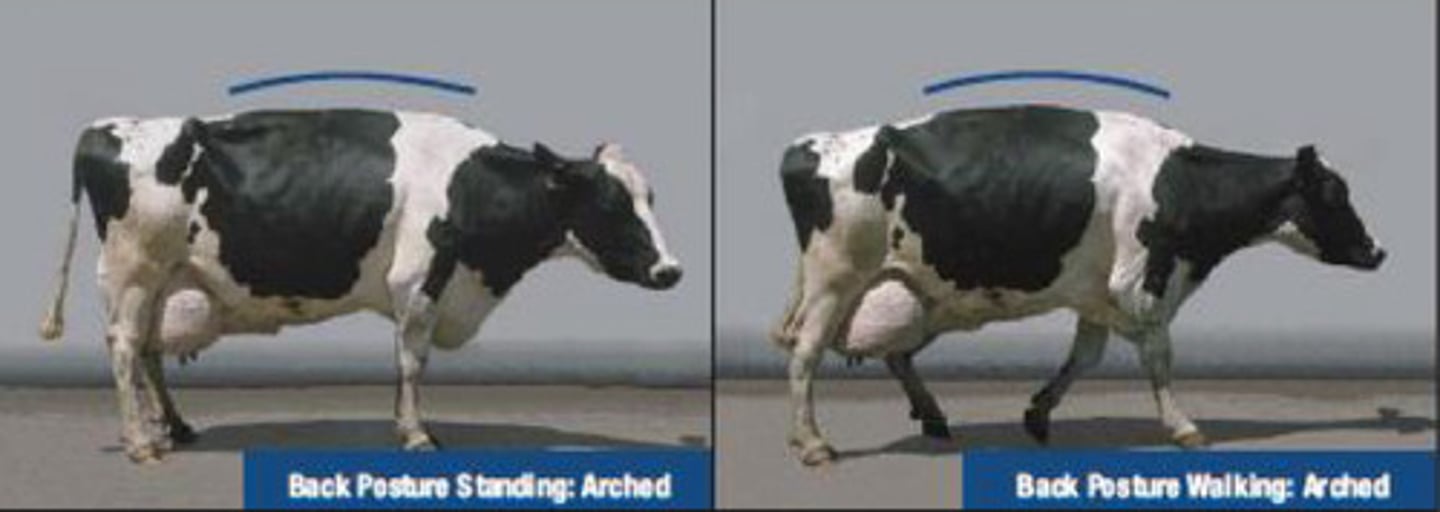

5
This cow has pronounced arching of the back and is reluctant to move and toe touching. It is severely lame. What is the locomotion score?

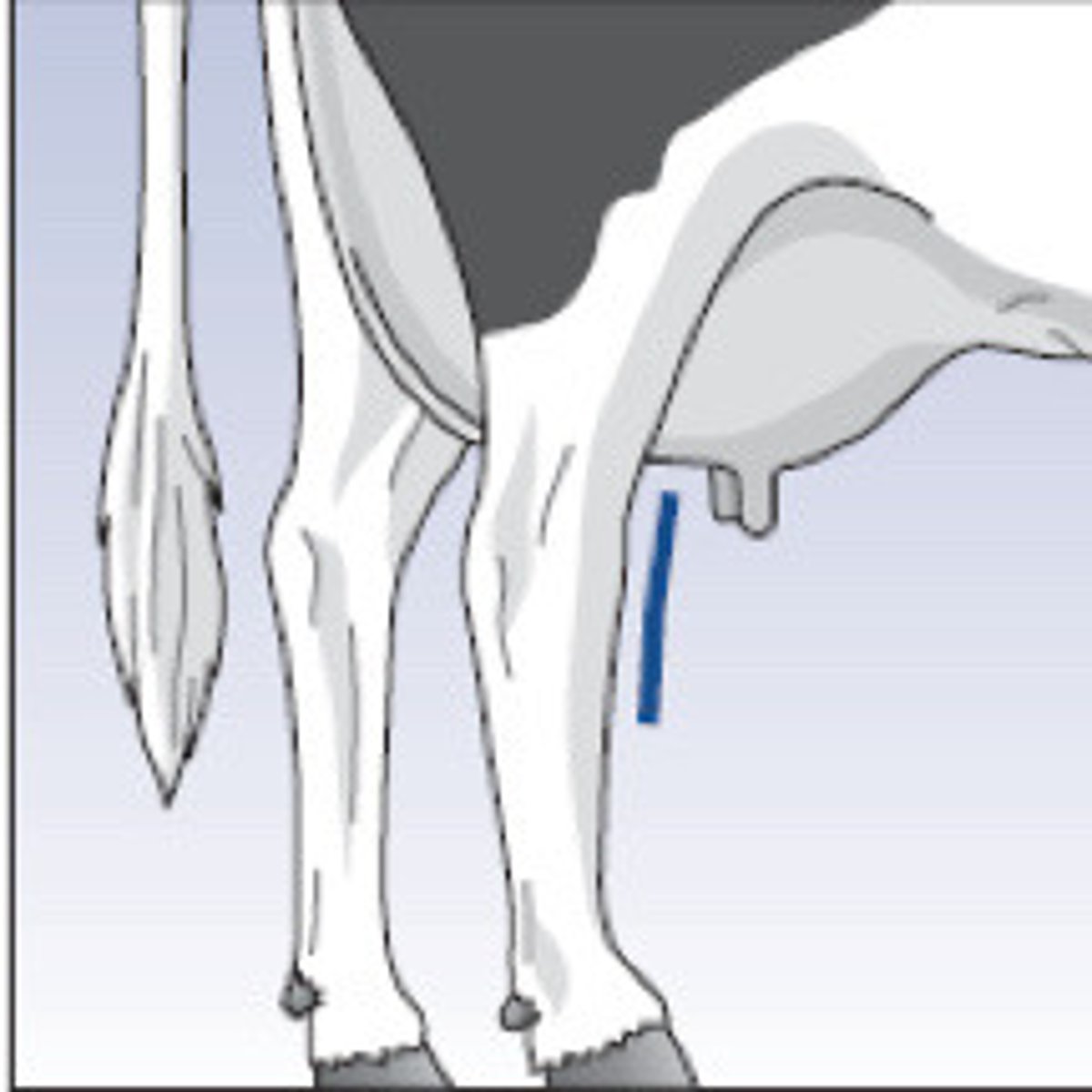
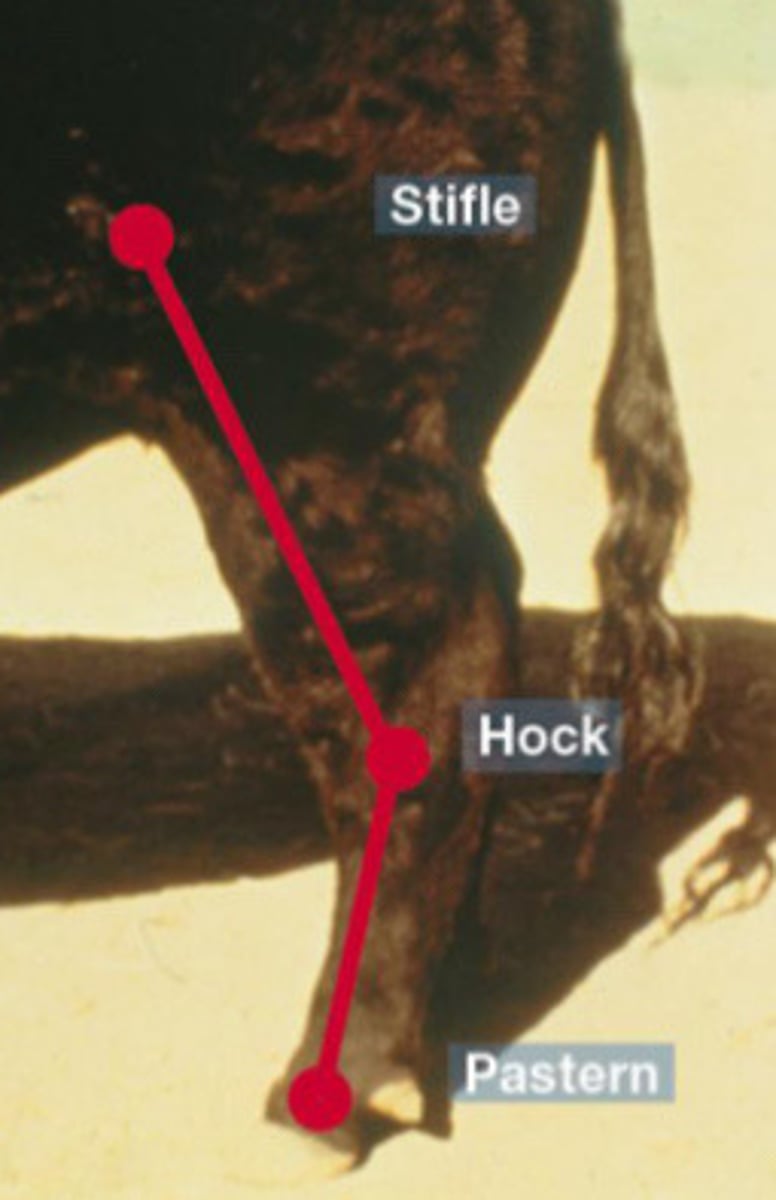
Straight, post legged (160 degrees)
What is the term for this hock angle?
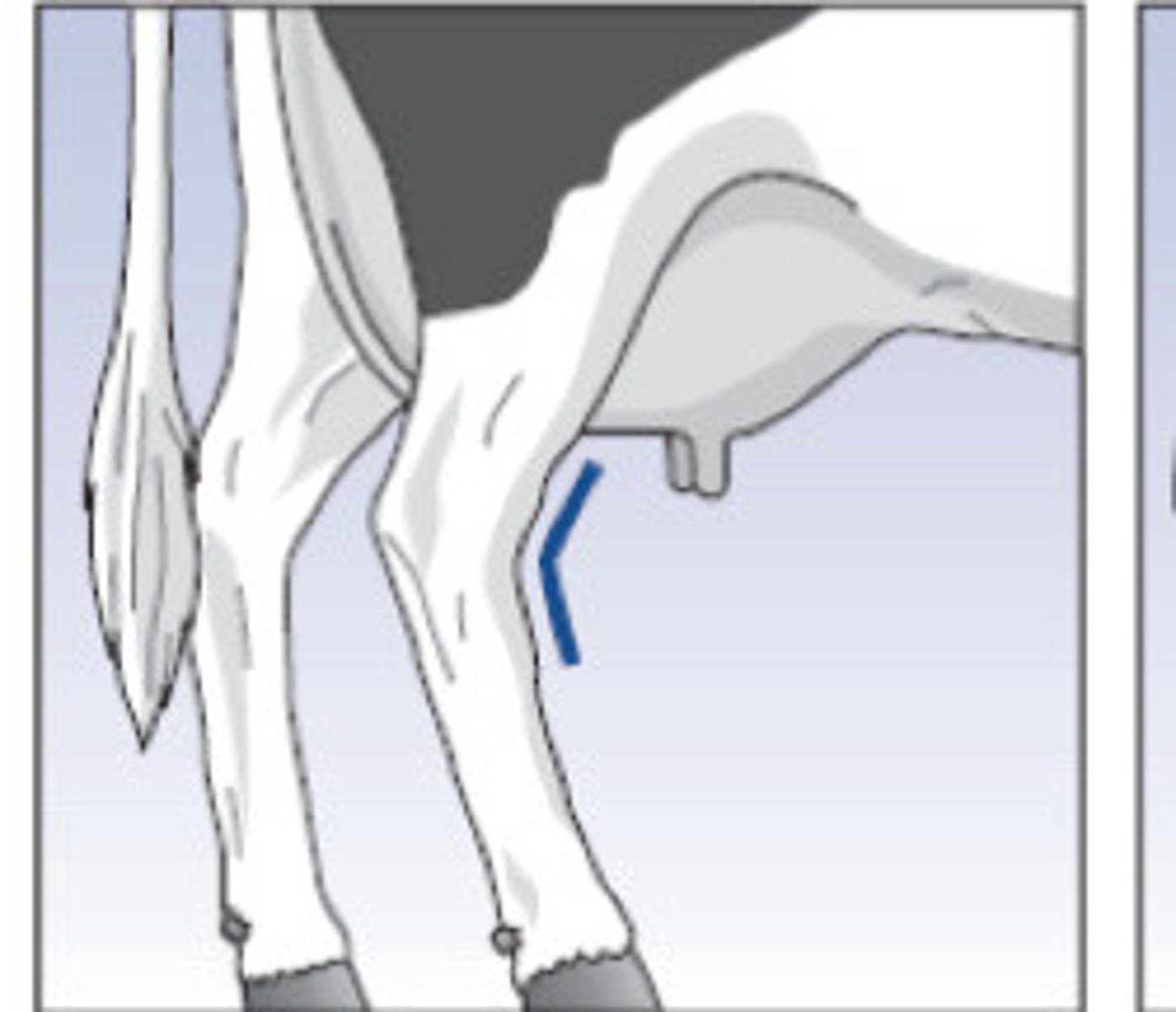
Intermediate (147 degrees)
What is the term for this hock angle?
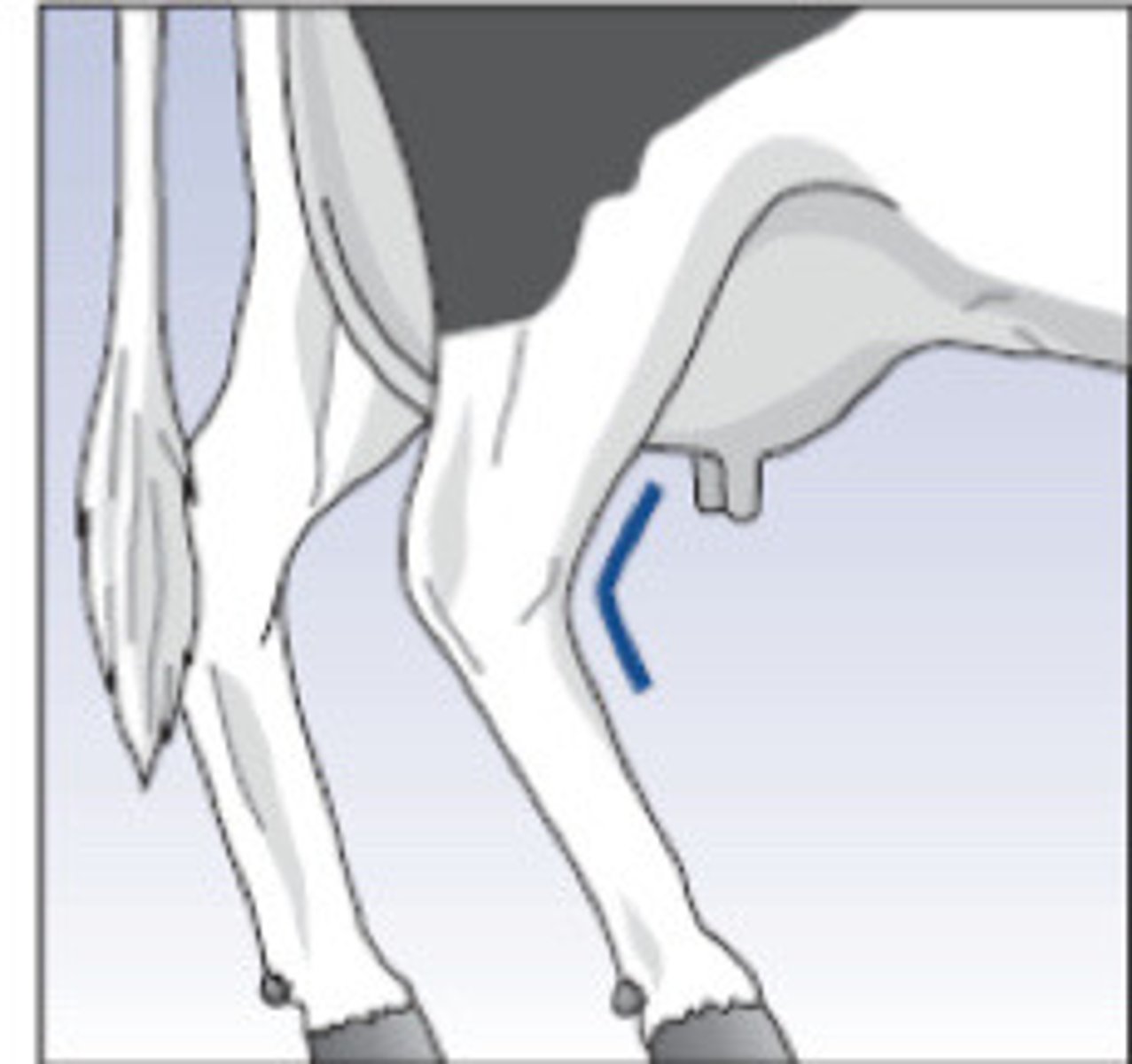
Sickle (134 degrees)
What is the term for this hock angle?
Sickle hock
What is the term for this hock angle?

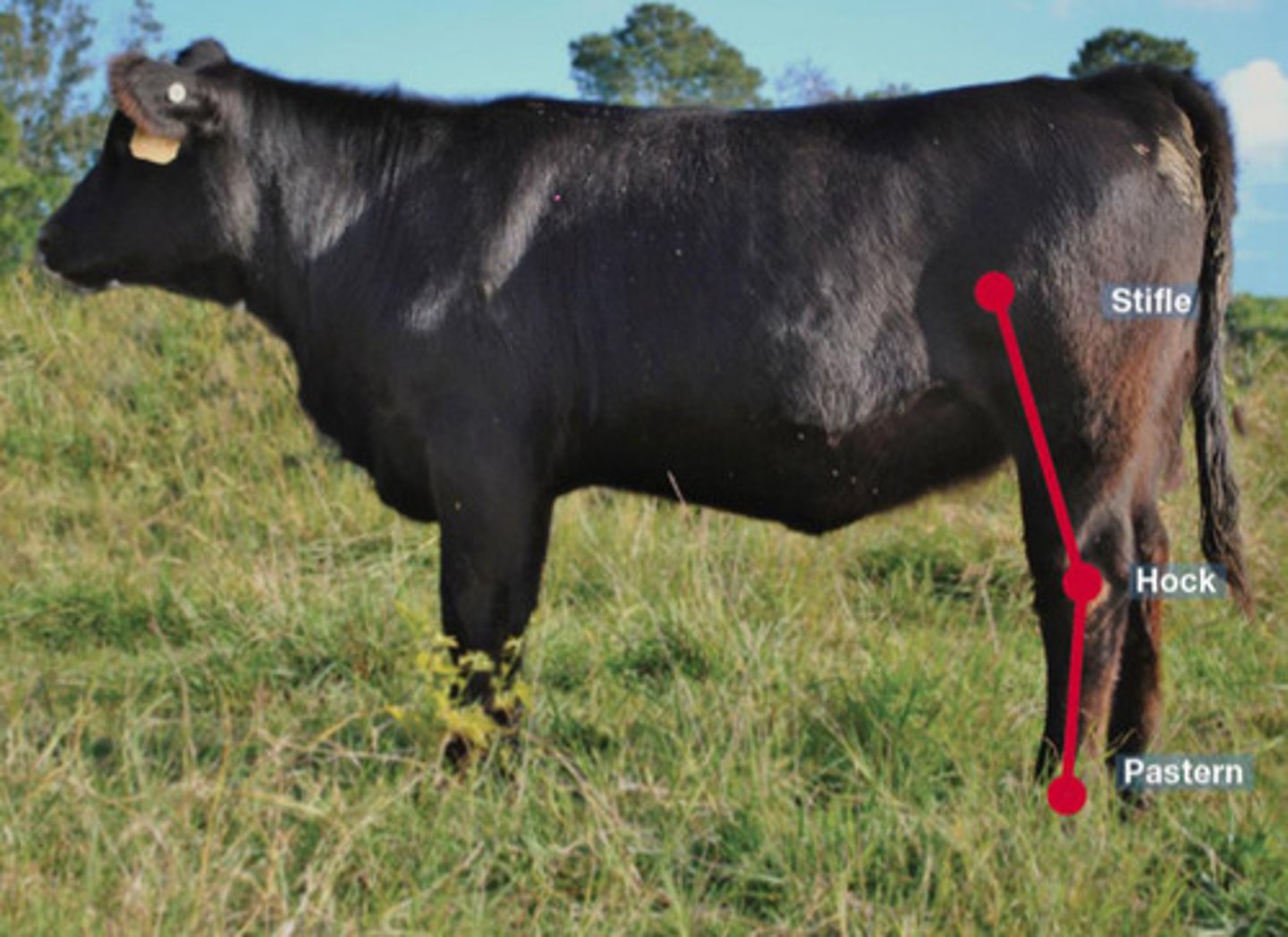
Post legged
What is the term for this hock angle?

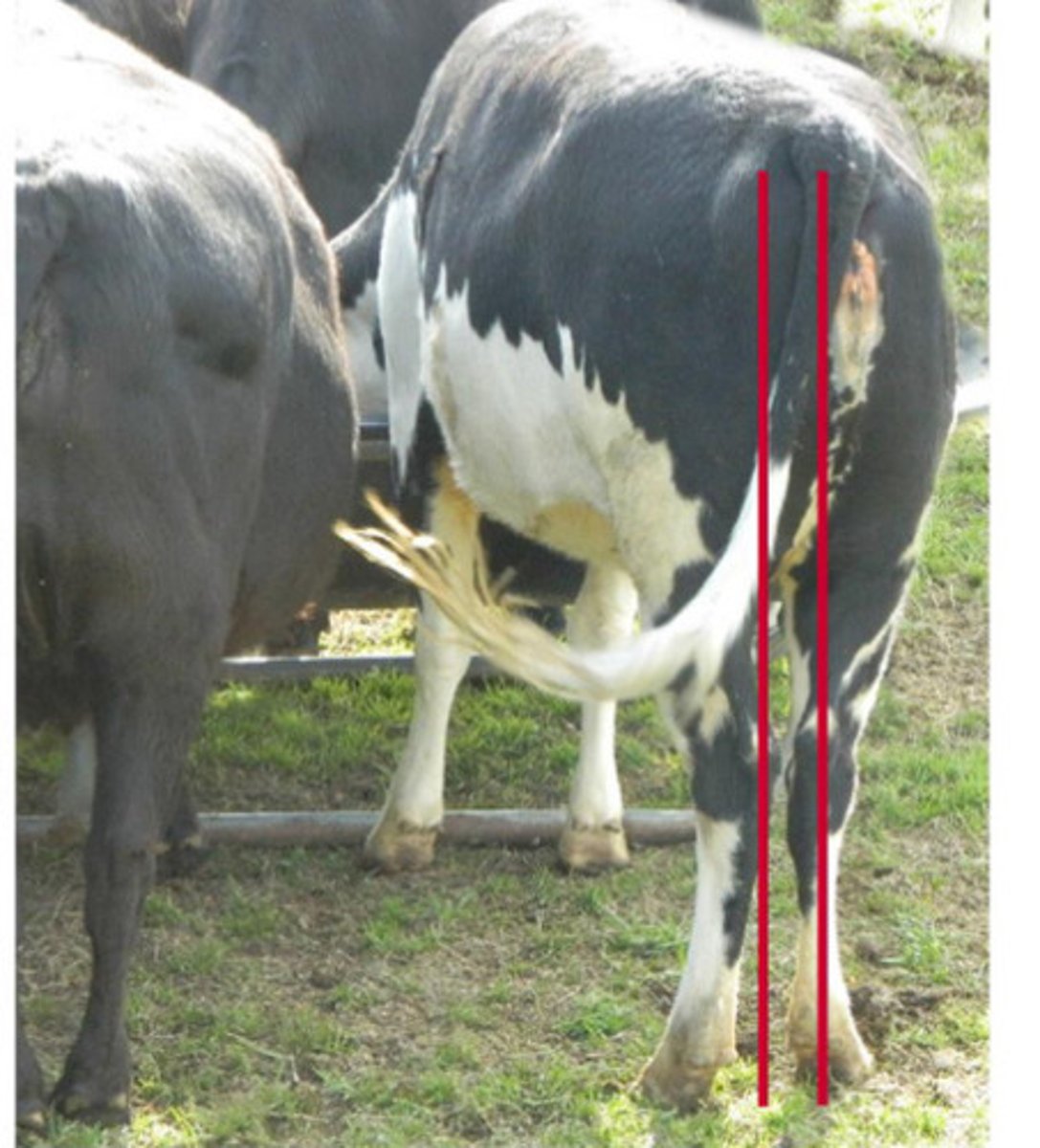
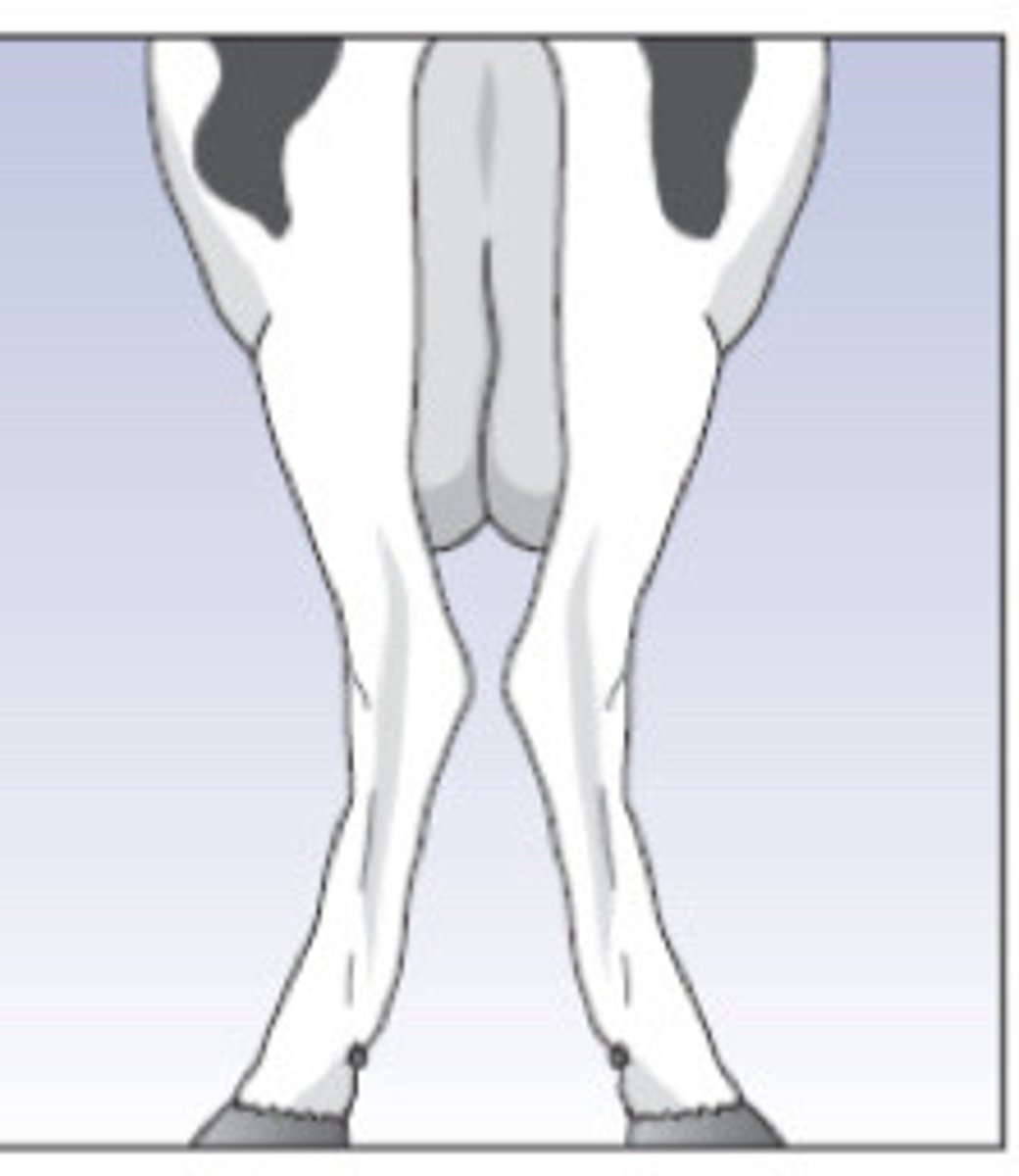
Cow hocked, light muscled cow (hocks point inward, feet point outward)
Describe what you are seeing

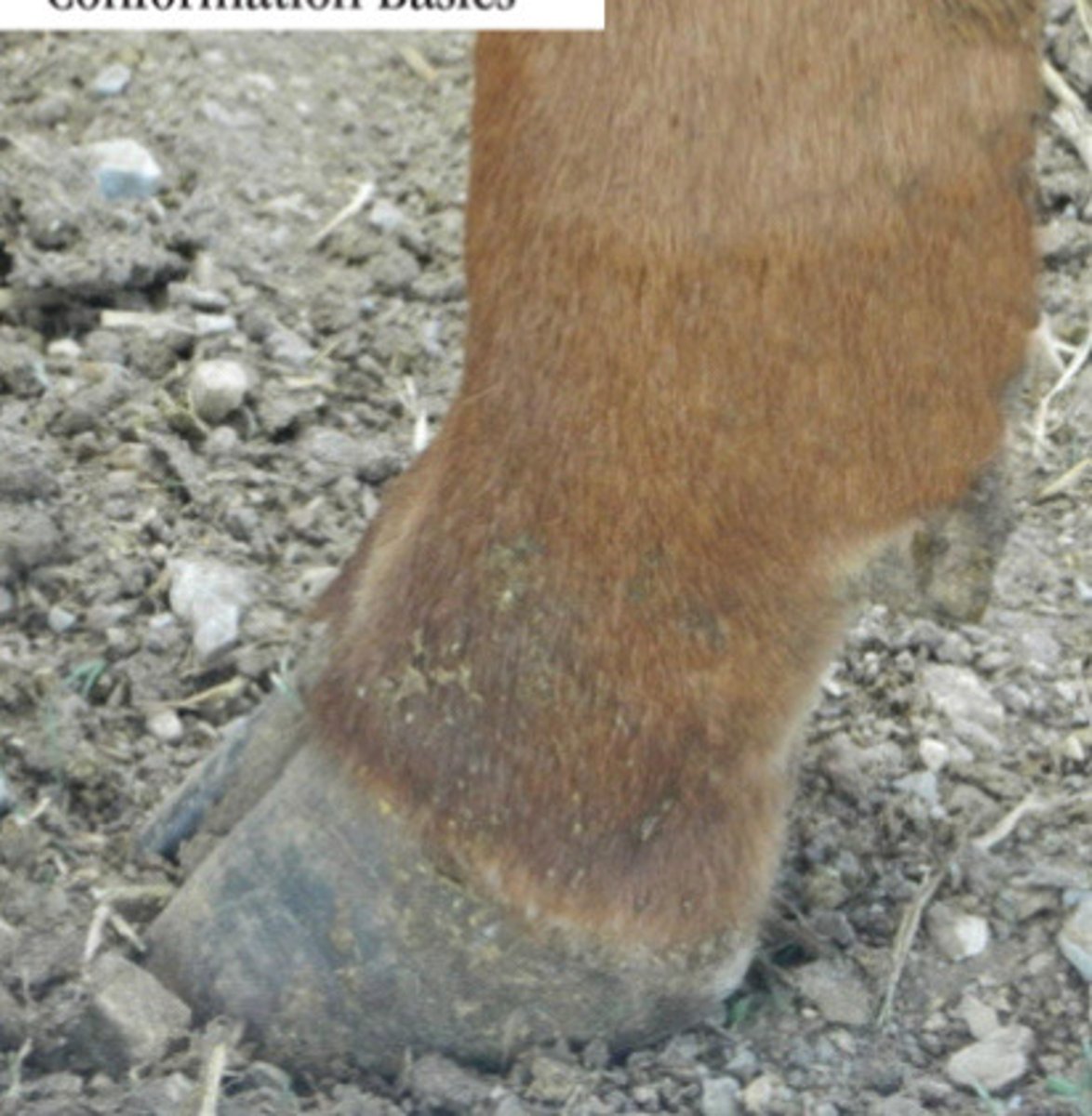
Appropriate angle of pastern
Describe what you are seeing?

Post legged is worse = short inefficient strides
Which is worse, sickle hock or post legged cows? Why?
Extreme toe out
Describe the conformation here
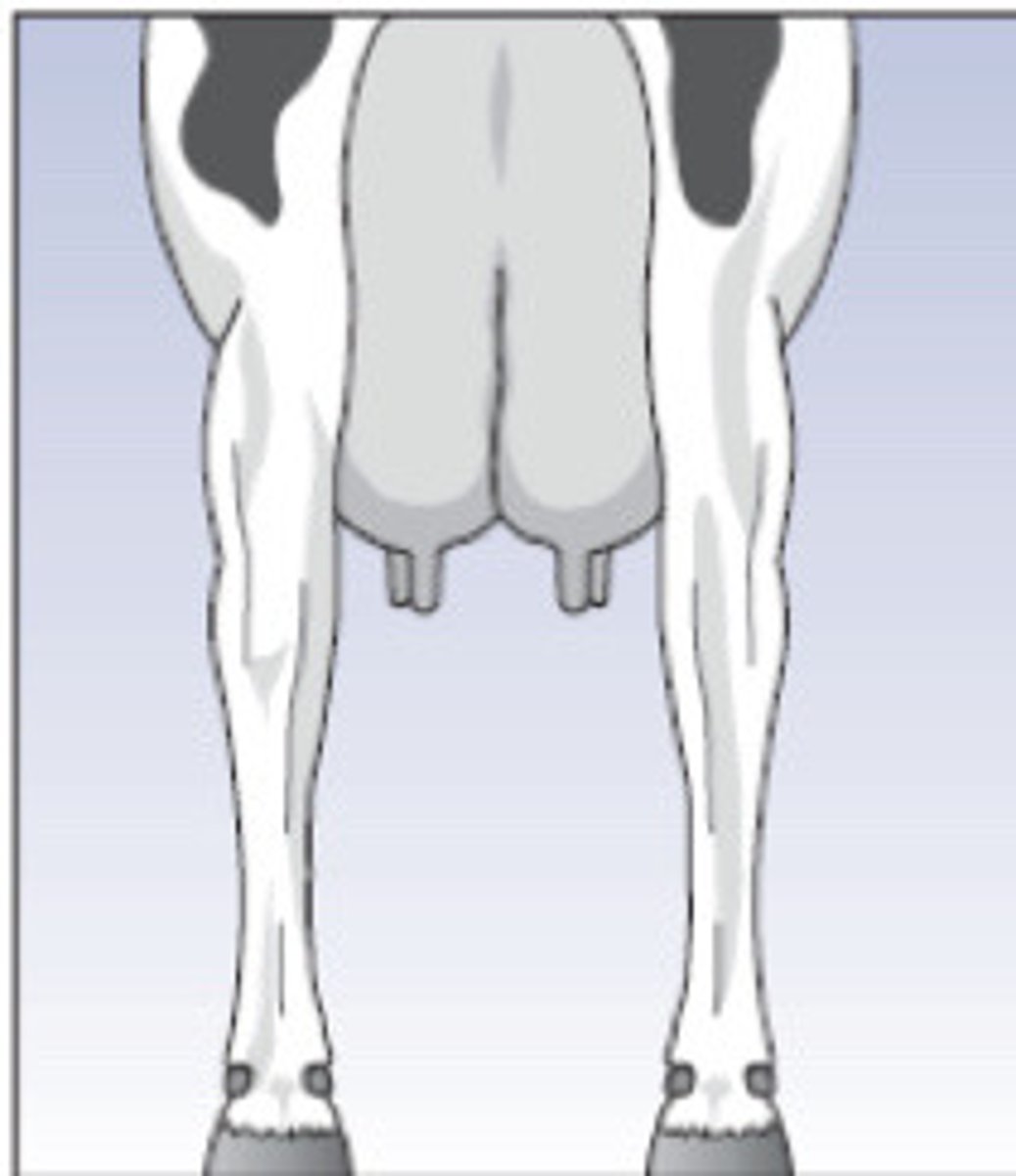
Slight toe out
Describe the conformation here
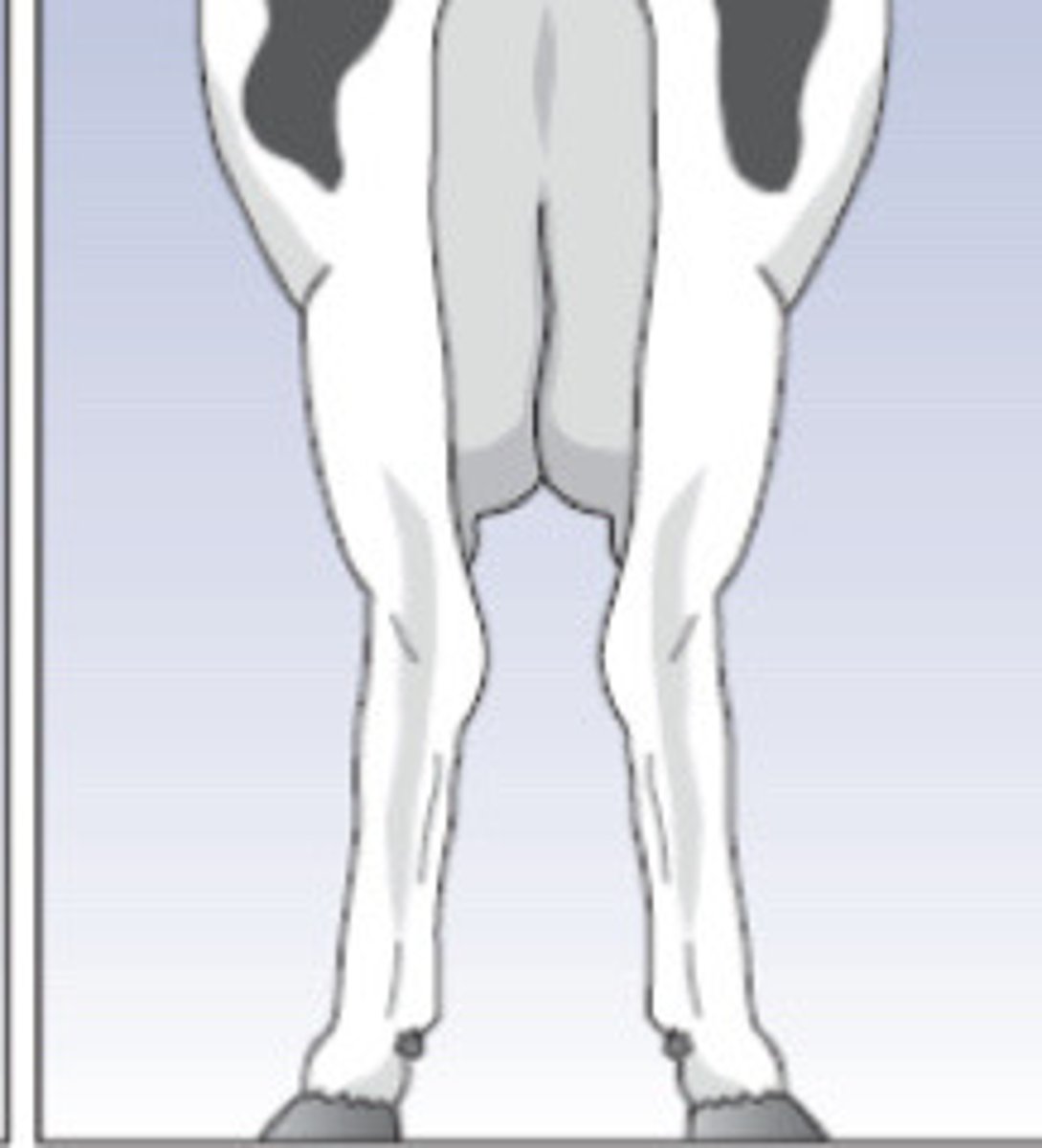
Parallel feet
Describe the conformation here
1. Pack barn = lower investment, hard to keep clean
2. freestall = reduce time standing
3. tie stall barn = each cow has own stall, labor intensive
Compare the housing modalities for dairy cattle
Most common = concrete floors. Grooved smooth concrete preferred. Rubber belts if walking long distance
Whats wrong = excessive wear and abrasive. Cows need to be off concrete for 10-12 hours per day
What is the most common type of flooring in dairies? What is preferred? What is wrong with this type of flooring?
5-5.5 hrs eating
12-14 hours resting (lay down about 13 times per day, 6 of these hrs are ruminating)
4 hours ruminating while standing
30 mins drinking
30 mins grooming and interactions
What is a dairy cow's day like?
Cows will sacrifice eating over resting (they prioritize rest even if it means they eat less)
What will cows typically sacrifice if there is not enough time in their day?
Pressure inside claw capsule increases --> blood in claw dec. --> ischemia and hypoxia
Additionally, if they stand more, the claw is more exposed to slurry = softer = more prone to injury
More standing = dec. blood perfusion to mammary gland = dec. milk production
What is the problem if a cow stands for prolonged periods of time?
Perching
This means a cow stands with front feet in the stall in hind feet in the alley. Often associated with shorter stalls or low/restrictive neck rails
Stall standing index
This is the percent of cows touching a stall that are standing 2 hours before AM milking, where if the number is over 20%, then standing time is too long
Cow comfort index
This is the percent of cows using their stalls 1 hour after AM milking
Foot baths
What treatment protocol can you use to help control digital dermatitis and foot rot?
Trim every 6 months
When should dairy cattle have their feet trimmed? How often?
They are unfit for transport and should not leave the farm of origin. Either treat and allow sufficient time for recovery or euthanize. Do NOT use electric prods on these animals
What does it mean if cattle/calves are "non ambulatory"
Digital dermatitis, interdigital dermatitis, interdigital fibroma (corns), foot rot, foot abscess
What are some infectious causes of lameness in the digit in cattle?
Laminitis, screw claw, white line disease, thin sole, hoof wall cracks
What are some noninfectious causes of lameness in the digit in cattle?
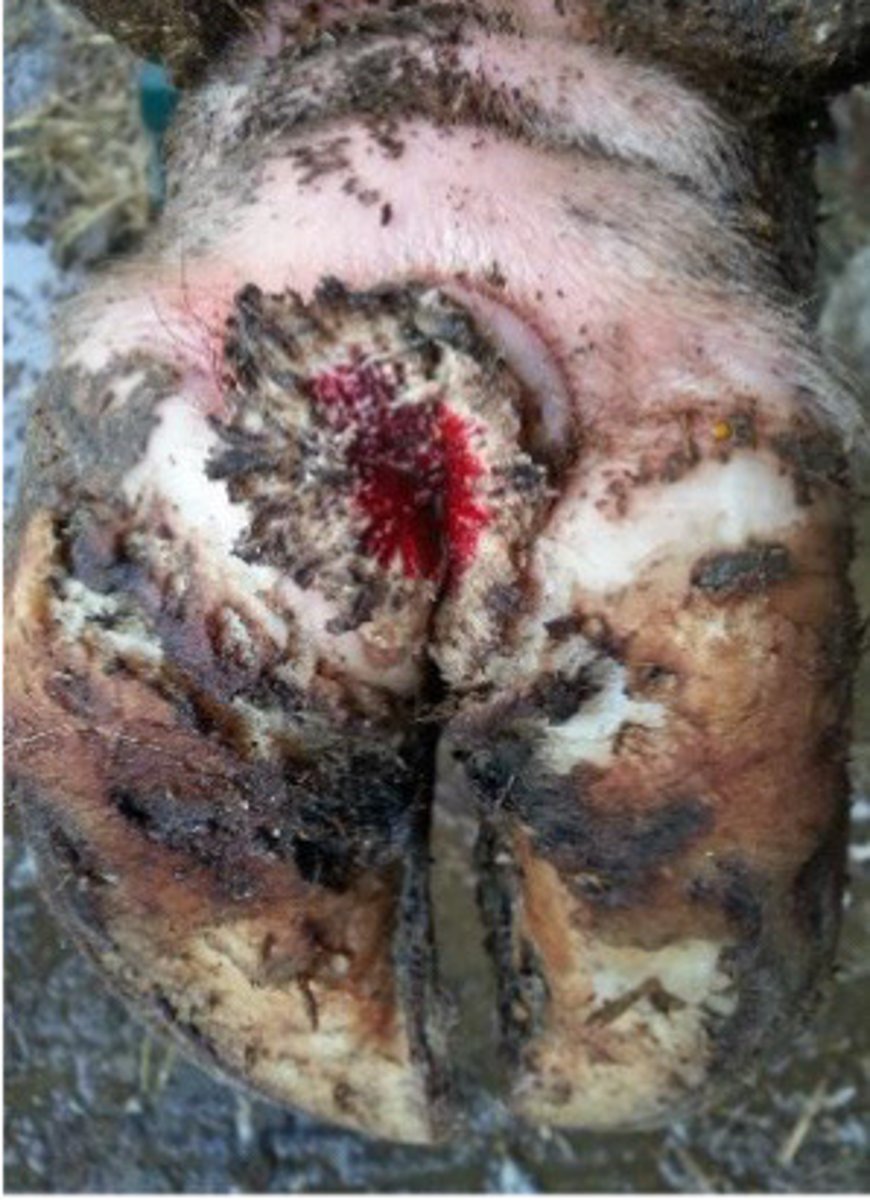
Digital dermatitis
What is happening here?
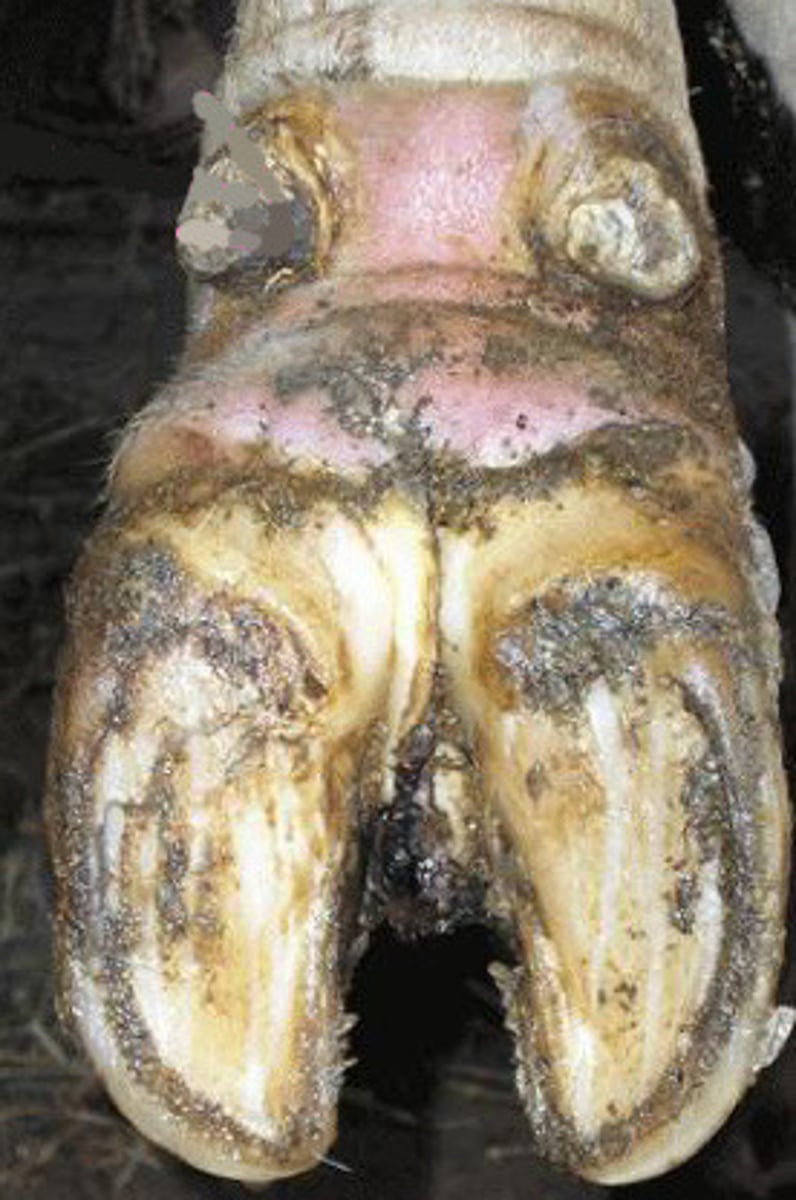
Foot rot
What is happening here?
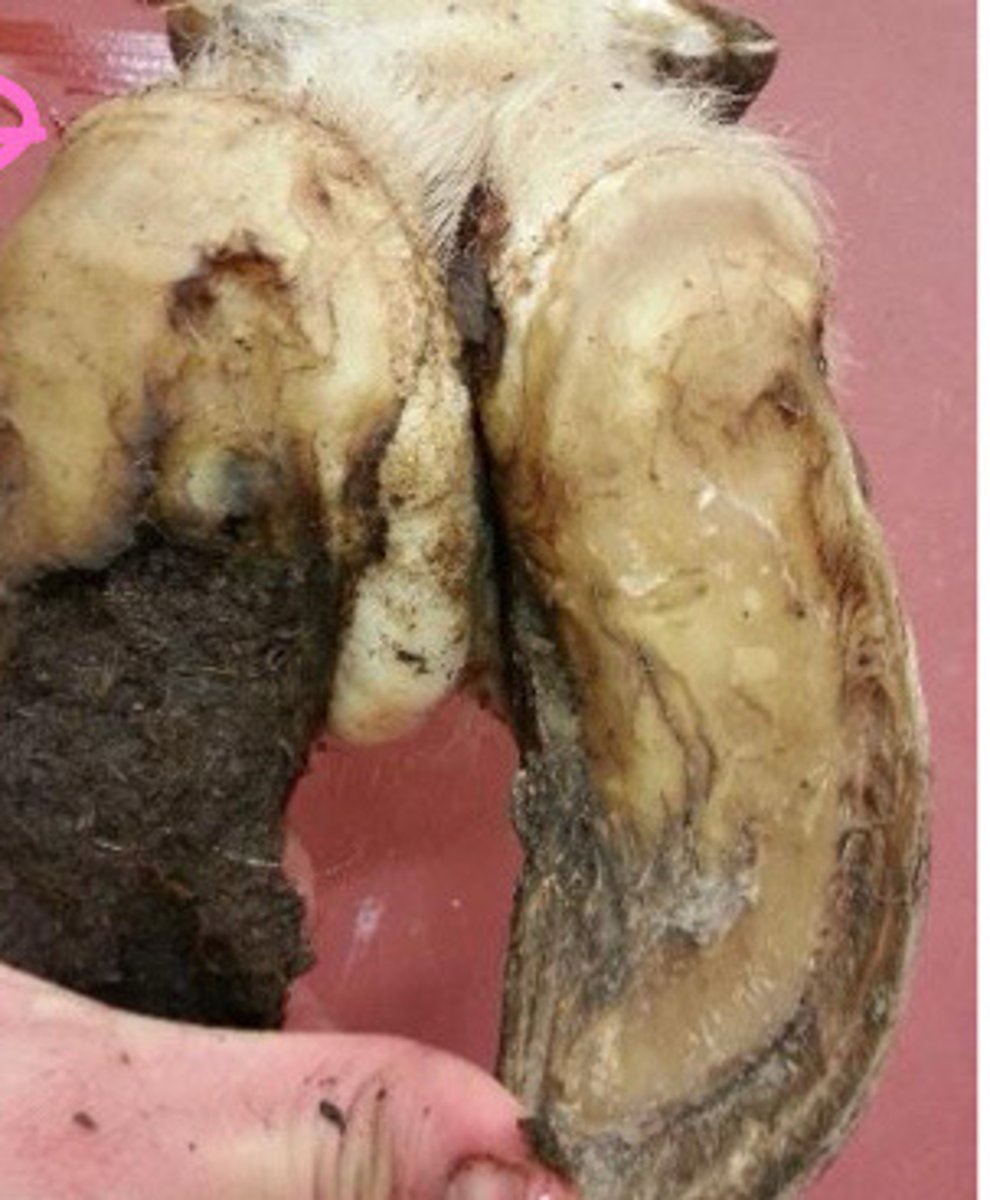
Interdigital fibroma or corns
What is happening here?
Dairy cattle = more common and more common in the digits
Beef cattle = incidence is low because they are on grass, more commonly have upper leg problems
What is the difference between lameness in beef cattle versus dairy cattle?
Lameness
What accounts for 70% of all sales of non performing feedlot beef cattle?
Salvage value of lame animals is about 50% of original purchase price
How does lameness affect purchase price of feedlot beef?
1. loop below fetlock
2. loop through a ring high up
3. loop around leg (over hock from inside first)
4. lift leg, take up slack
5. halter tie free end
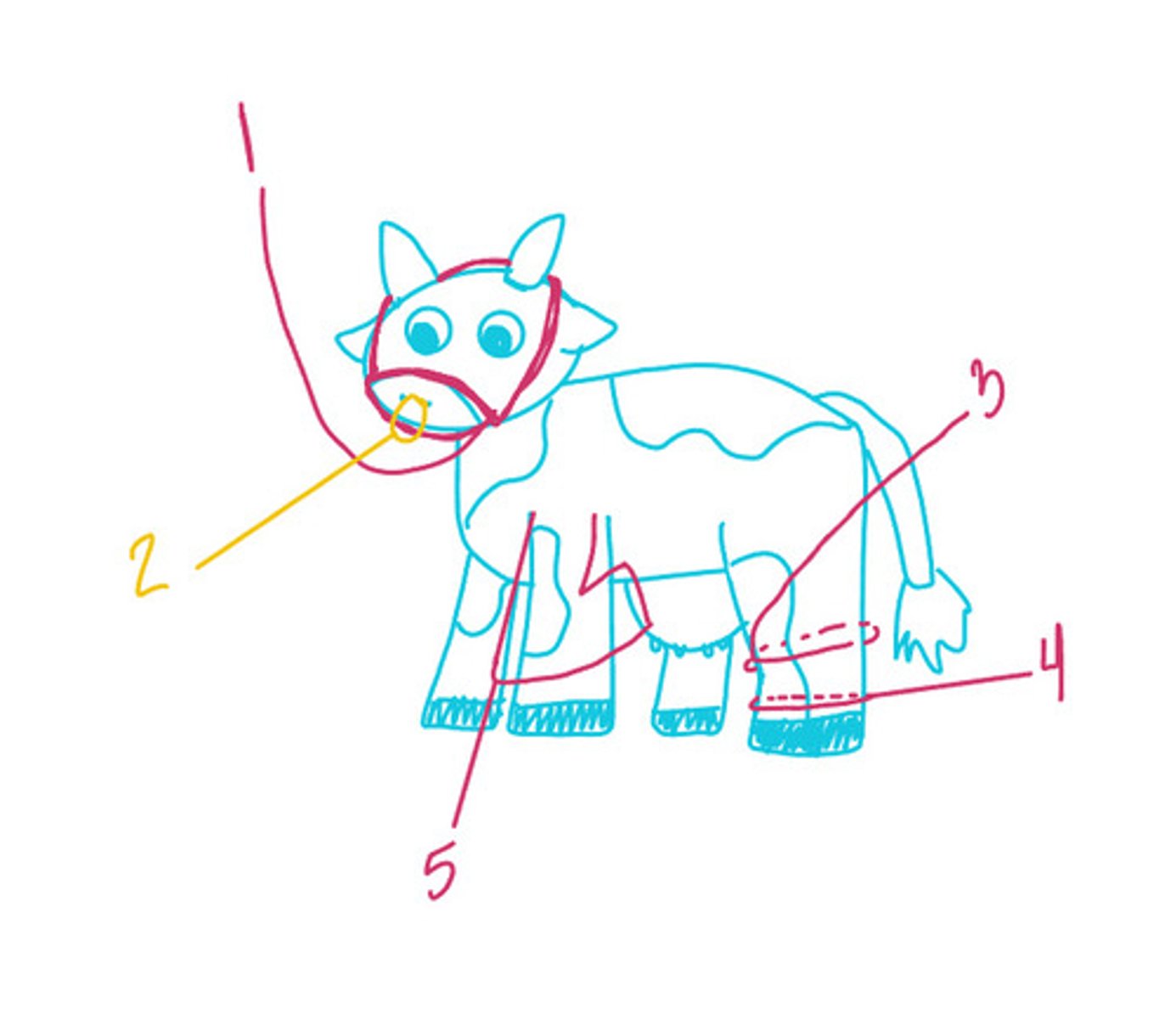
Name some ways to restrain cattle
1. standing (manual and hydraulic) = more common, faster
2. horizontal (manual and hydraulic) = easier to assess front feet
What are the types of chutes for cattle restraint?
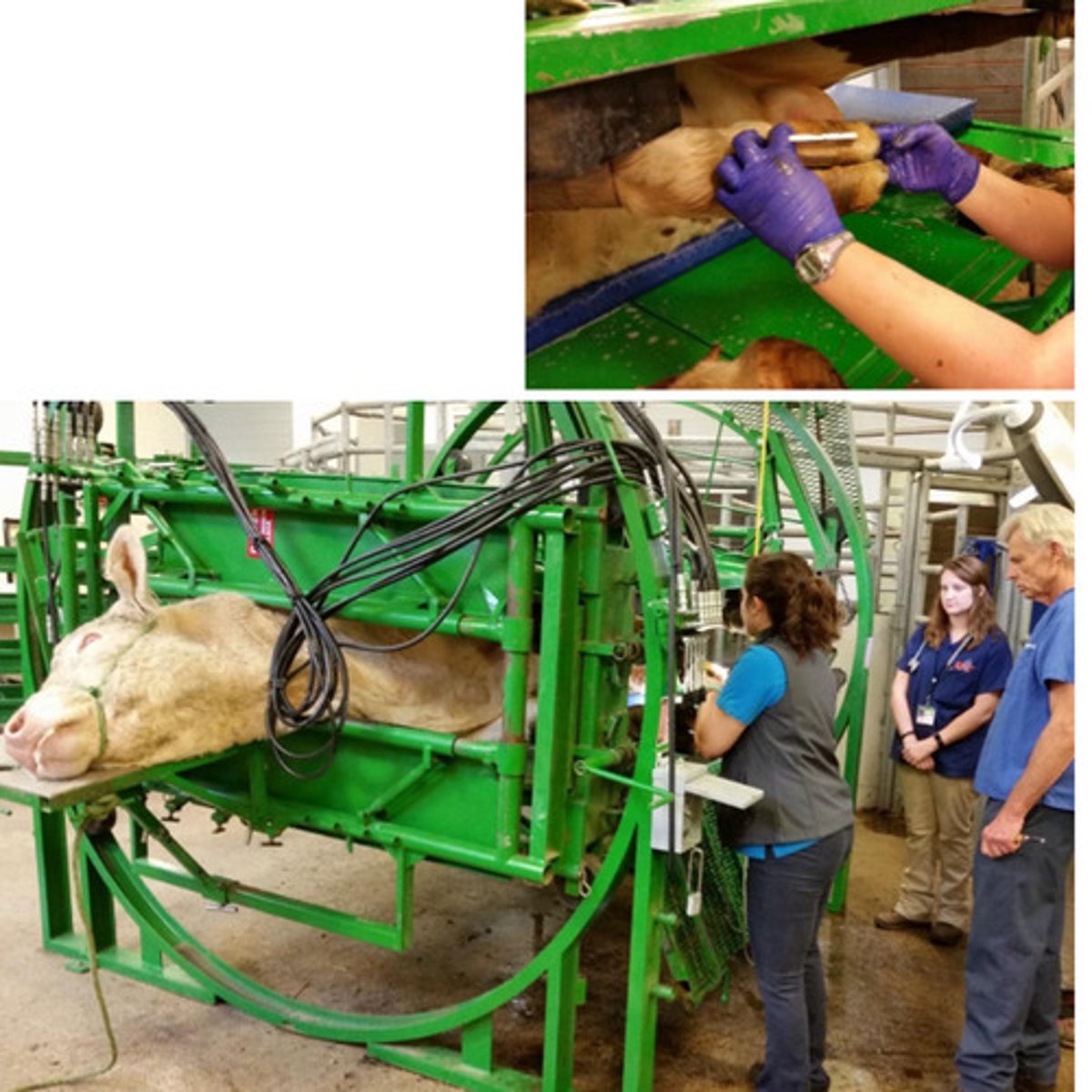
Horizontal hydraulic (360)
GOOD: safe, can squeeze animal
BAD: expensive
What type of chute is this? Name some pros and cons

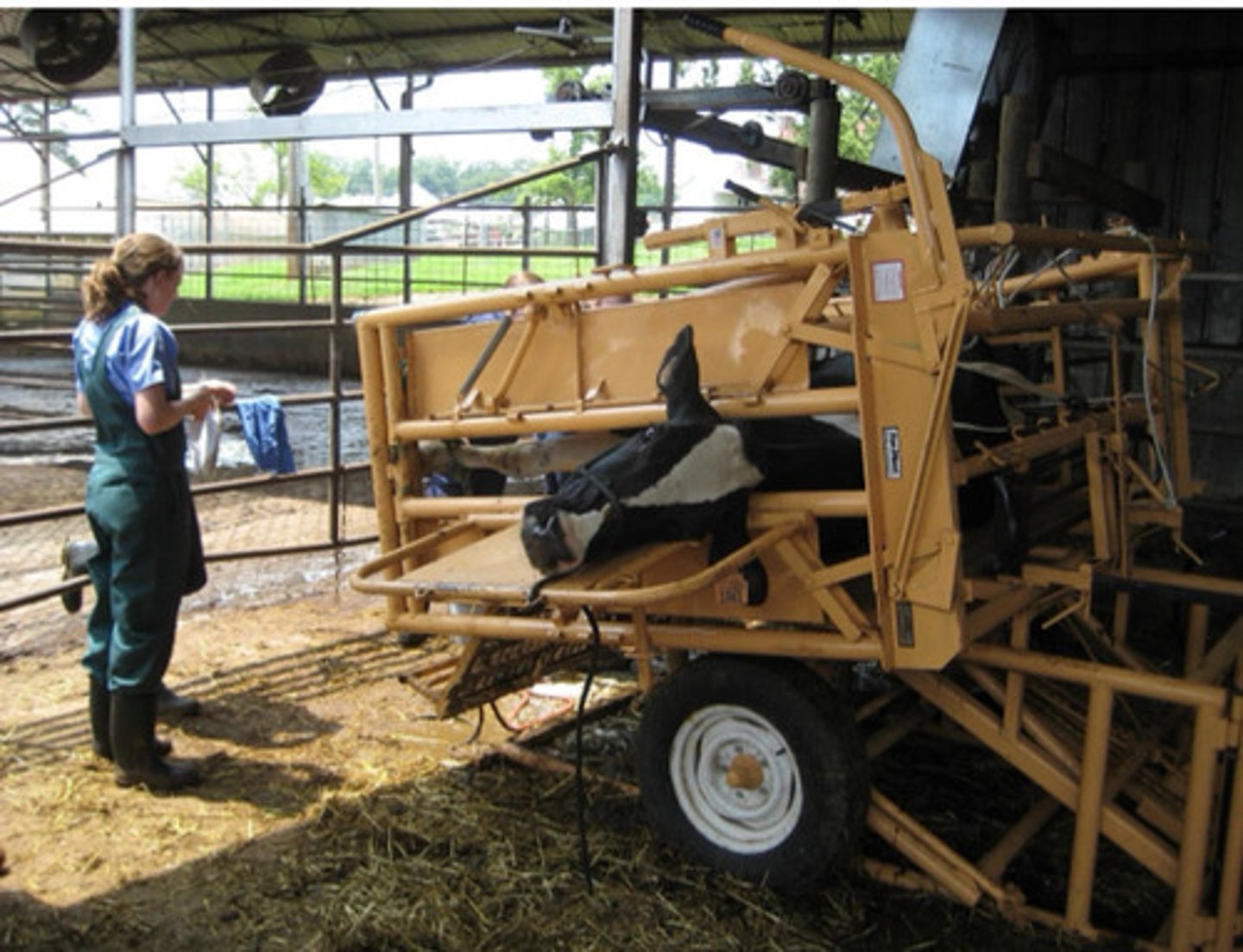
Horizontal manual (tilt table)
GOOD: access to all feet
BAD: can cause muscle ischemia, radial nerve injury, bloat, limited to 30 mins
What type of chute is this? Name some pros and cons

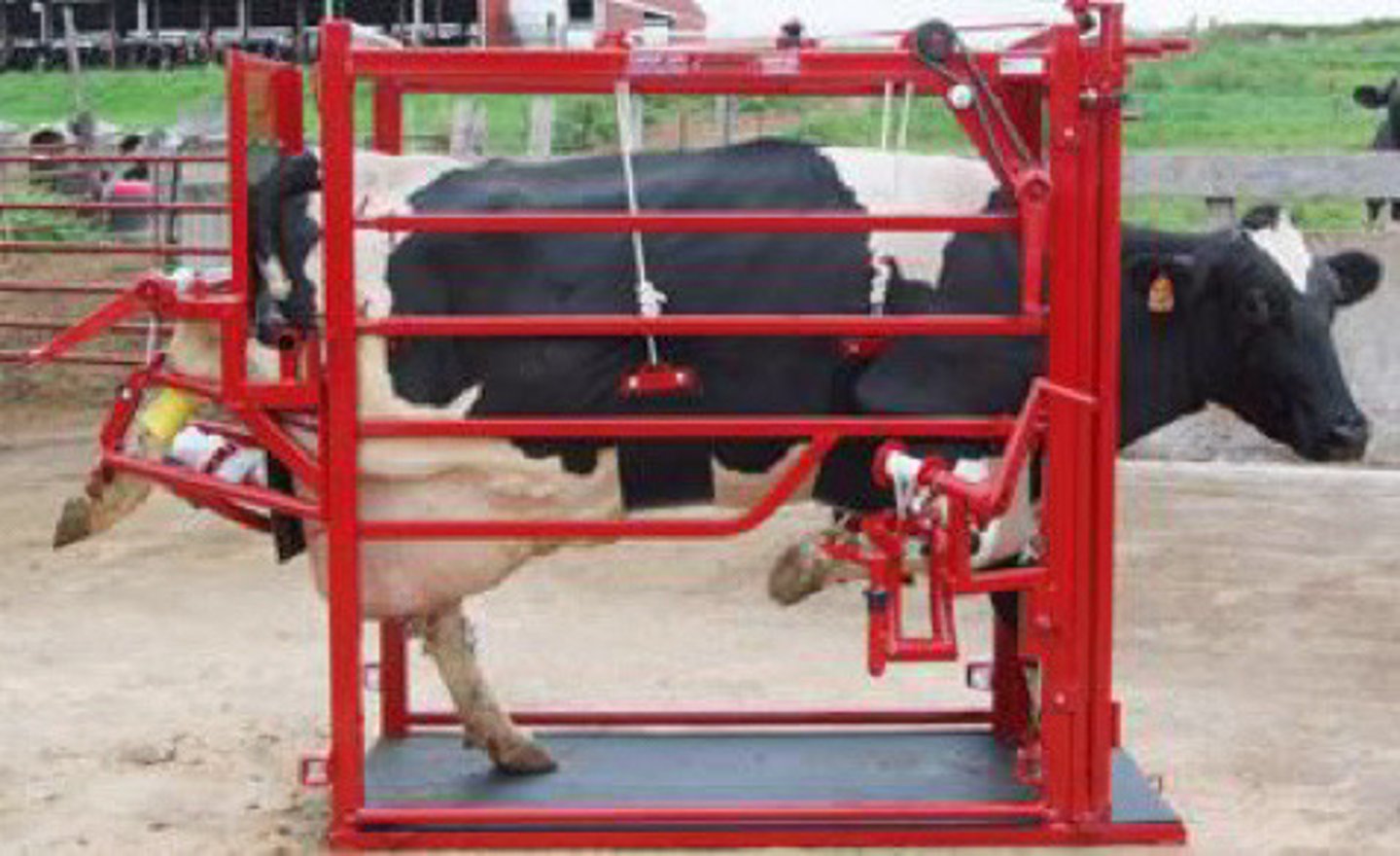
Standing chute
GOOD: better angles for trimming, no risk of bloat
BAD: one leg at a time, difficult for front feet, some animals go down and can get radial/suprascapular nerve injury
What type of chute is this? Name some pros and cons

True
TRUE OR FALSE: You typically need sedation for tilt tables (especially in beef), but not for stand up chutes
Xylazine = 5 days
Acepromazine = 7 days
What are the withdrawal times you need to consider for Xylazine and Ace in cattle?